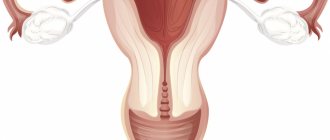
A bicornuate uterus is a uterine malformation in which the uterus is completely or partially divided into two horns, with fusion in the cervix. A normal female uterus is shaped like an inverted pear: the upper part is the bottom, and the lower part is the cervix. If there is an anomaly in the development of this organ, the “pear” turns out to be split into two parts. This pathology refers to developmental anomalies of the uterus and vagina, is quite common and can either not cause problems or cause infertility, miscarriage, cycle disorders, etc.
Reasons for development
The formation of pathology can be influenced by negative factors in the first trimester of pregnancy, when the organs of the fetus develop. Damaging factors include alcohol or drug abuse, smoking, vitamin deficiencies, mental disorders during pregnancy, diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism or maternal heart defects.
Infectious agents such as rubella, influenza, measles, syphilis and other diseases have an adverse effect on the embryo. A bicornuate uterus can form as a result of chronic fetal hypoxia or during pregnancy accompanied by toxicosis. Also, the anomaly can be combined with other pathologies, for example, with defects of the genitourinary system.
In addition, the reasons for the development of a bicornuate uterus include:
- Radioactive exposure.
- Intoxication with heavy metal compounds.
- Taking potent medications that affect the course of pregnancy and the physical development of the fetus.
- Excessive mental overload.
The formation of a bicornuate uterus in the fetus is possible only in the first weeks and months of pregnancy. At later stages, such pathology does not develop.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
Currently, there is insufficient data and established ideas about which symptoms of a bifurcated uterus should be considered typical and which are atypical. Special literature usually mentions painful irregular menstruation, spontaneous abortion, bleeding, infertility (infertility, inability to conceive). Other sources emphasize a relatively large proportion of asymptomatic bifurcation of the uterus (i.e., an option when the structural anomaly is not accompanied by any physiological discomfort) and, at the same time, a significantly higher, compared to the norm, frequency of complicated pregnancy (if pregnancy generally occurs), i.e. malpresentation of the fetus, placental pathology, premature birth, etc.
Diagnosis of a bifurcated uterus, on the one hand, is complicated by the nonspecificity of complaints (see above), which only give reason to suspect this anomaly along with many other, much more probable causes. On the other hand, the use of almost any method of non-contact imaging or minimally invasive endoscopic diagnostics (ultrasound, MRI, X-ray contrast hysterosalpingography, hysteroscopy, diagnostic laparoscopy) leaves no doubt.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Anatomical features of a bicornuate uterus
Depending on the size of the division of the uterine cavity into two parts, 3 types of anomalies are distinguished:
- Full. The pathology is characterized by splitting and separation of horns in the area of the uterosacral ligaments. Pronounced separation leads to the formation of separate niches that resemble two one-horned uteruses located almost next to each other. Pregnancy in this case can proceed normally in the recess of one of the horns.
- Incomplete. The pathology is accompanied by splitting of the cavity in the upper part of the organ and the formation of a shallow opening between the two horns. The sizes and shapes of both horns are often the same.
- Saddle-shaped. A depression is formed in the area of the fundus of the uterus, resembling a saddle in shape. Conception in this case is possible, but if a woman has accompanying anomalies, a miscarriage may occur. Pathology in combination with a narrow pelvis can provoke an abnormal position of the fetus, which precludes natural childbirth.
Septum in the uterus
A septum in the uterus is the most common deviation in the development of female genital organs. This condition is observed in approximately 2% of all women, and accounts for more than half of the cases of all congenital pathologies of the uterus. If there is a septum in the uterus, a woman’s fertility may be impaired - pregnancy does not occur at all, or is interrupted at different stages.
Causes of a septum in the uterus
The reason for the presence of a septum in the uterus is a violation of intrauterine development under the influence of unfavorable environmental factors or diseases of the mother during pregnancy. At 19-20 weeks, the fetus’s septum should collapse to form a single uterine cavity, but sometimes this does not happen due to disruptions in the process of embryogenesis.
Diagnosis of septum in the uterus
There are no specific symptoms. For this pathology of the uterine cavity, hysteroscopy is indicated. This will help confirm the diagnosis. A septum in the uterus can also be detected by ultrasound hysterosalpingoscopy or ultrasound examination.
Treatment of septum in the uterus
Before becoming pregnant with a pathology of the uterus, characterized by the appearance of a septum in it, a surgical operation should be performed to remove it.
Depending on the thickness, the septum is destroyed with endoscopic scissors or a hysteroresectoscope. After treatment, the prognosis for fertility is favorable.
At VitroClinic you can diagnose any type of pathology of the cervix and uterine body. We employ specialists with extensive professional experience and have all the necessary equipment.
Symptoms
A bicornuate uterus often occurs without pronounced clinical signs. Sometimes a woman experiences uterine bleeding and pain during menstruation. Often, with this diagnosis, spontaneous abortion occurs. This is due to improper blood supply to the fetus and lack of space. Miscarriage usually occurs in the first trimester. It is also possible that pregnancy and childbirth will occur without complications.
If there is a closed horn, the patient complains of abnormal stool, urination disorders, purulent vaginal discharge, which occurs against the background of an inflammatory process and infection.
Often, with a bicornuate uterus, patients are diagnosed with abnormalities in the location of the placenta, which threatens bleeding and premature detachment. The presence of an abnormal structure of the uterus increases the risk of breech presentation of the fetus or leads to isthmic-cervical insufficiency. Sometimes a bicornuate uterus provokes disturbances in the contractility of the uterus and bleeding after childbirth. If the fetus is not positioned correctly in the uterus, a woman is advised to have a cesarean section.
baby uterus
“Children's uterus” is a pathology in which there is a decrease in the length of the uterine body to 30-70 mm. The small size of the organ often prevents such women from having children.
The prognosis depends on the length of the uterus. The worst prognosis is characterized by an embryonic (rudimentary) uterus, when the length of its body is less than 3 cm.
Reasons for the appearance of a “baby uterus”
A “baby uterus” can be congenital or acquired. The congenital form occurs due to a violation of embryogenesis. The exact reasons for this phenomenon cannot be established. These could be infections, toxins or other unfavorable factors affecting the mother’s body during pregnancy.
The acquired baby uterus is secondary, i.e. occurs against the background of other diseases in adolescence. These may be infections, dishormonal disorders, severe somatic diseases. As a result, the uterus does not fully develop.
Diagnosis of the “baby uterus”
The woman may not feel any symptoms. Sometimes patients complain of irregular cycles, too scanty or, conversely, too heavy menstrual bleeding, and decreased libido.
Upon examination, a woman may have a narrow pelvis and incompletely formed external genitalia.
Diagnosis is carried out using instrumental research methods.
Treatment of the “baby uterus”
Treatment of uterine pathology is aimed at eliminating the causes that caused its underdevelopment. Physiotherapeutic procedures aimed at normalizing blood circulation in the pelvic organs are indicated. It is important to correct hormonal levels and provide the patient with adequate nutrition.
Sometimes infertility develops due to pathology of the uterus due to its small size, as well as concomitant dysfunction of the genital organs. Often pregnancy occurs, but recurrent miscarriage occurs.
If the length of the uterine body is reduced slightly, the pregnancy may end in childbirth. Such women need constant monitoring - they have an increased risk of premature birth.
Diagnosis of pathology
The presence of a bicornuate uterus may be indicated by the patient's complaints - pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation, excessive bleeding, infertility, miscarriages. During the examination, the gynecologist probes the uterine cavity. With its help, the doctor determines the shape of the uterus and the presence of an anomaly.
A bicornuate uterus is detected during ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvis. The results of magnetic resonance imaging, hysteroscopy, laparoscopy, and x-ray of fallopian tube patency also help confirm the diagnosis. MRI is used in cases where the results of ultrasound methods are not completely clear. It is also advisable to carry out MRI in order to clarify the presence of a malformation of the uterus in a woman with extensive adhesions of the abdominal cavity.
1.General information
A bifurcated uterus, or bicornuate (two-humped) uterus, saddle uterus is a relatively rare variant of malformation, i.e. incorrect, abnormal development of a key organ of the female reproductive system. The uterine “sac,” which is normally solid and symmetrical, in the case of bicornus, takes the form of a double wide anastomosis of the fallopian tubes, which merge into a single cavity only in the lower sections, closer to the cervical canal (cervix). Sometimes the bicornuate uterus is accompanied by doubling of the cervical canal, abnormalities of the vaginal septum, and asymmetry of the “horns.” The limiting case can be considered uterus didelphys - the presence of two anatomically separate uteruses, each with its own canal, and in some cases with a bifurcation of the vagina.
A bifid uterus occurs, according to various estimates, with a frequency of 1 to 5 cases per 1,000 women.
Sign up for a consultation
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Treatment
Surgical intervention for a bicornuate uterus is carried out in case of infertility or after 2-3 miscarriages. During the operation, the surgeon restores the uterine cavity. Surgical practice involves removing the entire uterine horn septum.
The standard intervention in the presence of an anomaly is metroplasty (Strassmann operation). It is performed under anesthesia through an abdominal incision or laparoscopy is performed. As a result of the operation, the defect in the structure of the uterus is eliminated, which several times increases the chances of carrying a normal pregnancy and giving birth to a healthy child.
In 98% of cases, the operation gives a positive result. Complications occur in 2% of cases. The most common include:
- Heavy bleeding.
- Development of infectious diseases.
- Perforation of the uterus.
- Air embolism.
- Pulmonary edema.
After surgery, adhesions may form. To prevent them, after surgery you should take hormonal medications for 3 months. The patient is also given an intrauterine device. If the treatment is successful, then the woman can plan a pregnancy six months later. Surgical correction of the abnormal structure of the uterus reduces the risk of miscarriage from 90 to 30%.
The septum is often incised using a laser. Its main advantages are the accuracy of dissection and the absence of bleeding. The main disadvantage of the operation is the high cost.
If the patient is diagnosed with placental insufficiency, she is prescribed medications that speed up the metabolism. Such drugs improve blood viscosity and accelerate the process of absorption of microelements through the placenta. If a woman has increased uterine tone, which threatens spontaneous abortion, it is recommended to take antispasmodics daily under the supervision of a doctor.
Symptoms of uterine abnormalities
The main signs of uterine development abnormalities are:
- absence of menstruation;
- menstrual irregularities (rare, scanty or, conversely, heavy menstruation, accompanied by bursting pain in the lower abdomen);
- decreased libido, insufficient development of secondary sexual characteristics;
- severe premenstrual syndrome;
- infertility;
- repeated spontaneous abortions;
- miscarriage;
- frequent urination, pain in the lower abdomen.
Forecast
With severe clefting of the uterine cavity, the likelihood of premature birth or spontaneous abortion increases. Management of pregnancy in women with a bicornuate uterus involves the prevention of miscarriage, bleeding and the development of isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
For patients with insufficient volume of the uterine cavity, it is possible to give birth to a child thanks to modern reproductive technologies, namely in vitro fertilization with surrogacy.
Pathology of the cervix
Female pathologies of the uterus can affect different parts of this organ. Cervical pathology is quite common. This is a group of diseases, many of which threaten not only fertility, but also the life of a woman. Among them:
- pathology of the cervical epithelium (true erosion, pseudo-erosion, ectopia, ectropin, leukoplakia, erythroplakia);
- inflammatory diseases (cervicitis, endocervicitis, ectocervicitis);
- post-traumatic conditions (scars on the cervix, isthmic-cervical insufficiency)
- oncological diseases and precancerous conditions (polyps, dysplasia, cancer).
Causes of cervical pathology
Congenital pathology of the cervix develops very rarely; much more often the disease affects a woman during her life. The causes are different for different diseases. These are mainly dishormonal disorders, infections, and lifestyle features.
Pathology may develop after operations, abortions, complicated childbirth, which can cause the formation of scars on the cervix. Isthmic-cervical insufficiency develops, which reduces the chances of bearing a child during pregnancy (the damaged cervix is not able to withstand the pressure exerted by the fetus).
Diagnosis of various types of cervical pathology
Diagnosis of cervical pathology is carried out using colposcopy. The Schiller test (staining the cervix with Lugol's solution) and the acetate test (treating the cervix with 3% acetic acid) are used. If necessary, tissue is taken for biopsy.
Treatment of cervical pathology
Treatment for cervical pathology may vary depending on the type of disease. In some cases, conservative treatment is used (for example, for dishormonal diseases), in others - surgical treatment (isthmic-cervical insufficiency, benign or malignant tumors, precancerous conditions).
At VitroClinic you can diagnose any type of pathology of the cervix and uterine body. For this we have all the necessary equipment.
Make an appointment
Prevention
Since the diagnosis of a bicornuate uterus is due to an intrauterine anomaly, a woman during pregnancy is advised to avoid taking antibacterial drugs, give up alcohol, drugs and cigarettes, and not stay in direct sunlight for too long. It is important to cure existing infectious diseases that can cause a miscarriage.
Regular examination by a gynecologist allows you to detect pathology at an early stage and prevent complications. Before planning a pregnancy, you should undergo a complete examination. If chronic diseases are detected, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment. It is also useful to take folic acid and vitamin complexes.
Symptoms
The following signs may indicate deviations in the anatomical development of a woman’s reproductive organs:
- menstrual dysfunction of various kinds, most often bleeding, dysmenorrhea;
- early miscarriages due to insufficient horn size and poor blood supply;
- inability to get pregnant for a long period.
Often the pathology does not produce pronounced symptoms; the woman learns about the anomaly during a gynecological examination.
Treatment of bicornuate uterus in Israel – prices
Treatment of a bicornuate uterus in Israel is more affordable than in medical centers in the European Union, Canada, and the United States, and is 25-40% cheaper, without being inferior in quality.
Find out how much an operation to correct a uterine anomaly costs in Top Ikhilov. Fill out the application and our medical manager will calculate for you the approximate cost of treatment in your case.
Advantages of bicornuate uterus correction at the Top Ichilov center
The first thing women pay attention to when deciding whether to undergo treatment for a bicornuate uterus in Israel is the reviews of patients who have already undergone corrective surgery in Israeli clinics. Of course, we do not have the right to vouch for all clinics in Israel, but we can confidently say that surgical treatment of a bicornuate uterus at the Top Ichilov center has a number of advantages.
- The center employs world-class gynecologists with extensive experience in treating congenital and acquired diseases. Some of our doctors are the authors of scientific research in the field of surgical correction of congenital anomalies of the uterus and are recognized by the international medical community as the best in their field.
- To diagnose this pathology, our center uses the latest hardware methods to detect abnormalities in the anatomy of the uterus as early as possible.
- Treatment in our clinic is carried out using several modern highly effective surgical techniques, preference is given to minimally invasive methods that reduce the risk of postoperative complications. After such an operation, the vast majority of patients are able to successfully become pregnant and bear a healthy baby.
- As a preventive measure after open metroplasty surgery, our surgeons necessarily use absorbable anti-adhesive barriers to minimize the risk of adhesions and impaired fertility, which eliminates the need for the patient to undergo additional surgery to cut adhesions.
- Each patient of our medical center uses the services of a curator-translator, who fully assumes all responsibilities for organizing treatment and everyday life.
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(6 votes, average: 5 out of 5)
What exactly is a uterus?
The uterus is a muscular organ. It is located in the pelvic area. In a non-pregnant state (normally) it is the size of a matchbox. The uterus is a hollow organ consisting of 3 main layers:
- perimeter (external) – covers the body of the organ, borders the peritoneum and bladder;
- myometrium (muscular) – is the middle layer. Serves to stretch and reduce the size of the organ, participates in labor during contractions of the uterus (contractions);
- endometrium (internal) – grows anew every menstrual cycle. It serves as the attachment site for the embryo and plays a huge role in the development of the baby. If pregnancy does not occur, it dies from the uterus and comes out mixed with blood (menstruation).
During a special period in a woman’s life—pregnancy—the uterus can stretch many, many times. This organ is the only one in the body that has such elasticity. Agree, it’s hard to imagine a soft matchbox into which you could put a newborn baby. What if it's twins or triplets?
Recently, the number of multiple pregnancies has increased sharply. This can be attributed to the fact that many couples in the 21st century began to resort to modern reproductive technologies, for example, in vitro fertilization (IVF). Now the birth of triplets is no longer nonsense. Multiple births have occurred before. A sufficient number of cases described in world medicine indicate the birth of four, five, six and even seven living healthy twins at once. The only case in the world of the birth of eight viable babies at the same time was registered in the USA in 2009. American Nadia Suleiman gave birth to 6 boys and 2 girls at the same time as a result of IVF. But the absolute world record, listed in the Guinness Book, was set by a resident of India. She gave birth to 11 living children. Her uterus reached an unrealistically large size during pregnancy.