Cervical dysplasia - CIN - cervical intraepithelial neoplasia - SIL (squamous intraepithelial lesion) - a precancerous condition. This diagnosis is made to approximately 10 thousand women a year, while 6,000 patients ultimately die from cervical cancer. The reason is a late visit to a gynecologist, when the well-treatable stages of CIN1 and CIN2 turned into difficult-to-treat CIN3.
Consultation with a gynecologist, urologist - 1000 rubles, consultation on the results of ultrasound, tests - 500 rubles. (optional).
What is cervical dysplasia, causes
The content of the article
Cervical cancer does not begin suddenly; it is preceded by 3 precancerous stages of dysplasia, when several layers of cells of the squamous epithelium (lining skin) of the cervix undergo changes. Gradually, normal epithelial cells replace atypical - modified ones. They have a different structure, size and change their location. As a result, the epithelium is transformed from multilayered, easily renewed, into single-layered.
It has been established that the main cause of dysplasia is the human papillomavirus, or rather its oncogenic types - sexually transmitted serotypes 16 and 18. At the same time, dysplasia does not start out of nowhere - it is preceded by cervical erosion, which women often ignore, not wanting to treat. In other words, dysplasia is a complication of erosion. Untreated erosion turns into dysplasia in 90% of cases.
This is due to the fact that the virus freely infects immature germ squamous epithelial cells located in the erosion zone. Such zones are called transformation zones, therefore the most important stage in the treatment of erosion is the treatment (closure) of these zones using various methods. Modern clinics use laser and radio techniques. After treatment with a radioknife or laser, all affected cells are removed, closing the path for dysplasia
Signs of epithelial dysplasia are visible only after staining with vinegar
Every country should erect a monument to Hans Ginzelmann, the man who once invented the vinegar test.
Vinegar gives a lens effect : all abnormal lesions of the cervix become more distinct. When processed, it causes short-term swelling of the epithelium - the cells swell and bulge, and healthy vessels, on the contrary, contract and disappear.
Abnormal cells, consisting of cells with large nuclei, turn pale. This reaction allows the doctor to suspect inflammation, metaplasia or dysplasia. The faster the area turns white, the denser it is, the longer it remains on the neck after the test, the more serious the situation.
Stages and symptoms of cervical dysplasia: CIN 1, CIN 2, CIN 3 - what is it?
Dysplasia is more common in women over 25 years of age, when the immune system is weakened due to changes in sexual partners, which forces the vaginal flora to constantly change, childbirth and other reasons. The peak incidence occurs at 35 years of age. At the same time, the risk of developing cancer still exists after age 65. English scientists from Keele University have proven that HPV, which enters the body at a young age, may not manifest itself for years or decades, becoming more active after menopause.
The disease is asymptomatic for a long time, being discovered by chance during a gynecological examination.
In rare cases, the following symptoms may appear in the precancer stage:
- vaginal discharge (spotting);
- discharge after sexual intercourse;
- intermenstrual bleeding;
- pain in the lower abdomen.
The absence of clear typical signs makes the pathology especially dangerous. Women who neglect preventive examinations by a gynecologist are at great risk.
The stages of dysplasia are abbreviated as CIN. To understand the essence of the process by stages, consider the table.
| Stage of cervical dysplasia CIN (Cervical Intraepithelial neoplasia) | Ongoing process | Cure prognosis |
| CIN 1 (CIN 1) - first stage of pathology, mild, initial degree | The changes are mild, covering less than a third of the thickness of the epithelium, measured from the basement membrane | Grade 1 dysplasia rarely leads to malignancy (malignancy). The disease goes away after treatment for HPV. Completely curable. |
| CIN 2 (CIN 2) - second stage of pathology, moderate severity | The structure of epithelial cells changes significantly and is well expressed. Changes affect half the layer thickness | Completely curable |
| CIN 3 (CIN 3) - third stage of pathology, severe | More than ⅔ of the squamous epithelial cells lining the cervix changes | Grade 3 dysplasia transforms into cancer in almost 100% of cases throughout the year. Difficult to treat, often not completely curable |
Dysplasia requires immediate treatment; without it, it easily changes stages, reaching stage CIN 3, which can already be considered cancer. A more accurate name is local cancer, “cancer in place,” i.e. still has metastasized, which leaves hope for a cure. The first stages of precancer SIN 1 and SIN 2 are completely curable with proper therapy.
What do the terms CIN and SIL mean?
In medicine, the diagnosis of cervical dysplasia is called differently. To make the diagnosis clear throughout the world, a unified classification of the stages of the process was introduced. Dysplasia was originally designated as CIN, which stood for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. More accessible is the development of a tumor within the epithelial layer.
When SIN develops into cervical cancer, the process takes a different turn - atypical cells grow inside the tissue, extending beyond the epithelium. The tumor also gives metastases, this CIN is different from cancer. In 2012, WHO introduced a different terminology - CIN was replaced by SIL - squamous intraepithelial lesion. The concept of neoplasia has changed to the more objective term “lesion.” There were only 2 degrees left - a mild degree of damage - LSIL (Low grade SIL) and a severe degree of damage - HSIL (High grade SIL). LSIL is equated to dysplasia 1 (CIN 1), and HSIL to dysplasia 2-3 (CIN 2 and 3). Many specialists still use the first classification, as it more accurately characterizes the scope of the process and allows you to choose the most gentle treatment.
Examination for cervical dysplasia: how to identify CIN 1, CIN 2, CIN 3
Diagnosis of cervical dysplasia throughout the world is carried out according to the standards recommended by the World Health Organization. In Russia, good clinics use the following screening scheme for dysplasia:
- Examination by a gynecologist using a colposcope
(examination of the cervix under a gynecological microscope with high magnification). - Cytological smear - Pap test (taken by a gynecologist during an examination). The smear includes epithelial cells, which are then examined in the laboratory under a microscope. Atypical cells are identified: quantity, quality.
- Cervical biopsy
. This is an additional clarifying examination, carried out in case of poor smear results for cytology and colposcopy. - Blood for tumor markers
. If cancer is already present, this will be visible from the results of blood tests for oncology.
The first two examinations for syn1, syn2 and syn3 are included in the mandatory cancer prevention program in gynecology. Colposcopy and cytological smear should be performed at least once every three years, starting from the age of 25. This program is called cancer screening.
Surgical intervention
How can a doctor eliminate such a dangerous disease as grade 3 cervical dysplasia? Treatment (surgery) can be carried out using the following methods:
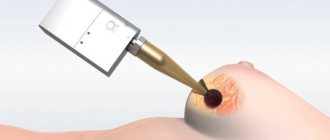
- Laser vaporization. With its help, you can easily and painlessly remove a disease such as grade 3 cervical dysplasia. Laser treatment has many advantages: the doctor controls the depth of exposure, scar formation is virtually eliminated, blood loss during surgery is minimal, and healing is rapid. But not every medical institution has such modern equipment. And such a rather expensive surgical intervention must be carried out by a highly qualified doctor. All this makes treatment inaccessible to many potential patients from the province.
- Cryodestruction - freezing dysplasia with liquid nitrogen. This operation is popular all over the world: it can be done without any problems even in a district clinic. In addition, the duration of the procedure is short - about 10 minutes. The downside is the inability to accurately control the degree of tissue freezing. As a result, the same scars are formed, which can rupture during pregnancy and childbirth.
- Radio wave destruction - exposure to radio wave frequency current. A comfortable and effective method, which provides for the complete restoration of sexual activity, prevents the development of relapse. The disadvantages are similar to those inherent in laser therapy.
- Diathermocoagulation - cauterization of affected areas with electric current. The method is quite cheap and popular. Its disadvantage is pain and scar formation, which during a subsequent pregnancy will prevent the full opening of the uterus.
It should be remembered that the effectiveness of any operation depends on competently conducted examinations, comprehensive laboratory tests, and antiviral and antibacterial therapy.
Evaluation of biopsy results for SIN 1, 2 and 3
The diagnosis of dysplasia is made by the presence of atypical cells in a cytology smear and the identified loss of the possibility of normal maturation of stratified squamous epithelial cells due to increased proliferation (accelerated division) of cells.
Dysplasia first degree (LSIL, CIN 1)
In grade 1 dysplasia, HPV invades cells, gradually changing the structure of cells, causing acceleration of their growth. Moreover, this applies not only to erosion; a similar process leads to the formation of genital and flat condylomas. With strong cellular immunity, after removal of condylomas, the process is inhibited. Since the papillomavirus penetrates into the genome of cells, it is impossible to cure it, which is why erosion and papillomas are removed using different methods, trying not to leave affected cells.
Dysplasia second - third degree (HSIL, CIN 2-3)
The development of the dysplastic process directly depends on the patient’s immunity. And even with treatment started in these stages, the infection remains and progresses in 10% of women, which guarantees the development of cancer. At the same time, the speed of development of the process can be different and reach up to 15 years. For this reason, if a woman has been diagnosed with CIN 1 at least once, she will have to monitor the condition of her cervix throughout her life.
Cell changes in stages CIN 2-3 are only neoplastic in nature - i.e. they are completely transformed, and the boundaries of the process are expanded. The number of atypical cells prevails; they multiply rapidly, replacing the normal epithelial layer of the cervical glands and even the canal.
How to treat cervical dysplasia in different stages
How treatment will be carried out depends on the degree of dysplasia.
| Stage of cervical dysplasia | Diagnostics to confirm and monitor dynamics | Treatment Options | Forecast |
| Analysis result: CIN 1 | Cytology smear every 3 months. Colposcopy. HPV analysis - oncogenic types. Additional examinations for inflammation, hormonal disorders and genital infections. | Waiting tactics. Antiviral therapy. Stimulation of immunity. Treatment of all concomitant diseases. Removal of condylomas. If the CIN 1 test is poor for more than one and a half years, removal of the affected tissue is required. | Complete cure |
| Analysis result: CIN 2 | In-depth examination: biopsy, Schiller test, endocervical curettage | The following are prescribed: cryotherapy, PDT, cauterization with electric current, or more modern gentle but very effective techniques - laser therapy or radiotherapy; in case of significant damage, excision with a loop or conization of the cervix. For CIN 2 and 3, the above methods should be used; the uterus is removed only if it is ineffective. | Complete cure |
| Analysis result: CIN 3 | In-depth examination every 3 months: cervical biopsy, extended colposcopy, endocervical curettage | Laser therapy, radiotherapy, excision, conization of the cervix. If cervical cancer begins and treatment does not help, the uterus will have to be removed. | Depends on many factors: the state of the body, the degree of damage, previously and currently used treatment tactics, etc. |
For pregnant or nulliparous women, expectant management is possible for CIN 2 and 3, provided the coverage area is small. But throughout the entire period of pregnancy, you need to regularly take cytology tests and undergo colposcopic examination.
Rehabilitation
After surgical therapy, a woman should adhere to some medical recommendations:
- refusal of sexual activity for 1-1.5 months;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- do not douche;
- do not use tampons;
- do not go to the sauna or bathhouse.
After 3 months, the woman must undergo a repeat colposcopy and take a smear from the cervix for cytology. If everything is normal, she is removed from the medical examination. Rarely, after surgery to remove dysplasia, the following complications can develop:
- relapse;
- infertility;
- transition to the stage of exacerbation of chronic inflammation in the pelvis;
- scars on the neck;
- dysmenorrhea (menstrual dysfunction).
Where to get tested and treated for CIN 1, CIN 2, CIN 3 in St. Petersburg, prices
Treatment of all stages of precancer requires high-quality diagnosis and treatment using professional modern equipment. The Diana Clinic in St. Petersburg invites all women residents and guests of the city to undergo examination and treatment of dysplasia at any stage. The clinic’s gynecologists use new devices - a colposcope and a Fotek radio knife - this is the best equipment recommended by the Ministry of Health.
In our medical center you can take tests, undergo colposcopy, remove condylomas without pain and complications, cure erosion and dysplasia (laser, radio knife). We perform any gynecological low-traumatic operations, for example, conization of the cervix, excision with electric loops.
An appointment with a gynecologist costs only 1,000 rubles, an appointment based on test results costs 500 rubles. Appointment with an oncologist - 1000 rubles. Today this is practically the lowest and most reasonable price in St. Petersburg.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Review of treatment from Elizaveta, Yaroslavl
Dear Maxim Stanislavovich, leaving this review, first I want to tell you how my story began. So, I came for a preventative appointment with a gynecologist, the doctor noticed changes in the uterus, after learning the test results, it became clear that I have HPV and first-degree dysplasia... The doctor recommended that I be examined again six months later, BUT I, not understanding the seriousness Given this situation, a year later I came to see a paid gynecologist. I took tests and the diagnosis was cr in situ. The doctor offered two options, either coanization or the innovative PDT method, but in order not to injure the young body (I’m 23 years old), she insisted on PDT. After that, I started scouring the Internet in search of the best doctor, and then I found you, with vast experience, and most importantly, with a large number of positive reviews from cured patients. Without a doubt, I chose you, after that I contacted the administrator Oksana, and literally within two days I was given a date for PDT, which is very convenient, because I live in Yaroslavl. Arriving in Moscow at the clinic, I felt the highest level of service.
That's why I wrote this story. To express words of gratitude and so that girls with the same problem, without hesitation, come to you, because you are a qualified and competent doctor who is focused on results.