Ulcers caused by trauma
The main reason for the appearance of ulcers when the mucous membrane is injured is infection in the wound. Most often, white rashes occur due to the habit of biting nails or the tip of a pencil or pen.
Fans of seeds and hard toothbrushes may also be at risk. Many people believe that hard bristles remove plaque better. Actually this is not true. If you carefully brush your teeth with such a brush, you can damage the enamel, gums and cause inflammation.
Other causes of mucosal injury:
- uncomfortable dentures;
- braces or other orthodontic structures;
- habit of unconsciously biting your cheek or tongue;
- exposure to mucous membranes with drugs or acids.
How to treat?
It is enough to remove the irritating factor and wait 1 - 2 weeks. Usually the ulcers go away on their own. If this does not happen, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
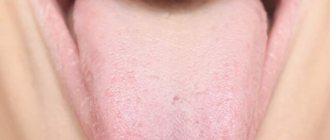
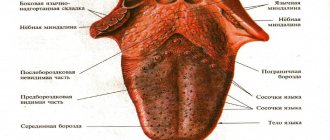
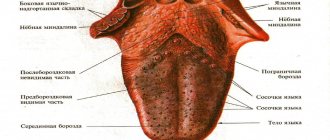
What is plaque on the tongue?
The most numerous - filiform papillae - form a white coating on the tongue due to their structure:
- the lamina of the mucous membrane of the filiform papilla is covered with stratified squamous epithelium;
- this is a keratinizing epithelium that periodically exfoliates, covering the entire tongue with a light white coating;
- In case of any malfunctions in the human body, desquamation slows down and a layer of keratinized cells grows, which acquire different colors depending on what pathology led to the malfunction.
By the color of the plaque and where it is localized, diseases that have led to pathological changes in the tongue are judged.
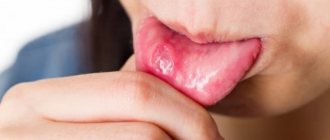
Ulcers caused by oral diseases
White sores in the mouth can appear due to diseases of the oral cavity. The most common cause is stomatitis. It comes in several types:
- aphthous;
- herpetic;
- bacterial;
- fungal.
| White ulcers in adults and children occur with aphthous and herpetic stomatitis. This disease can appear due to stress, untreated caries, lack of vitamin C, or overexertion. It is better not to self-medicate, but to immediately consult a doctor. Recommendations, in addition to medications, may include treatment of caries, a balanced diet, stress reduction, etc. |
| There are two separate forms of stomatitis - Bednar's aphthae and Setton's aphthae. The former develop only in a child due to injury to the mucous membrane or poor oral hygiene. Such rashes are also called erosions. Setton's aphthae is a more complex and painful phenomenon. It begins with the appearance of compactions, which then develop into painful ulcers. They most often form on the inside of the cheeks, in the corners of the lips and on the sides of the tongue. |
| Another cause of white sores is gingivitis. In smokers, such rashes are much more common due to the effects of nicotine on the mucous membranes. Those who have poor oral hygiene, reduced immunity and hormonal imbalances are also at risk of encountering gingivitis. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis: when the tissue that supports the tooth is affected. And this is a direct path to tooth loss. |
Diseases of the oral cavity and plaque on the tongue
Most often, the condition of the tongue depends on the conditions in the oral cavity. The presence of plaque may be due to:
- caries;
- stomatitis with fungal and bacterial etiology;
- periodontal disease – systemic damage to periodontal tissue (gums, bone and tooth ligament);
- glossitis - inflammation of the tongue that occurs as a result of mechanical damage to the organ, or as a condition accompanying other diseases;
- gingivitis - inflammation of the gums without damage to bone tissue.
The mucous membrane of the tongue reacts very sensitively to any problems in the oral cavity caused by inflammation, caused by bacterial or fungal infections.
They are diagnosed quite easily:
- A loose white coating indicates that a yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida has settled in the mouth.
- The presence of periodontal disease and gingivitis is determined by the condition of the gums.
- The presence of caries is accompanied by an unpleasant odor and putrefactive damage to the bone tissue of the tooth.
- Glossitis is accompanied by a burning sensation, salivation, pain and inflammation.
If everything is more or less clear with these signs, then plaque caused by systemic diseases is not so easy to recognize without special knowledge.
Diagnostics
An in-person examination by a dentist is enough to detect the problem. Sometimes a doctor can immediately diagnose and prescribe treatment. But if the disease is not of a dental nature, additional examination will be required.
For diagnostic purposes the following is carried out:
- general blood test to identify an infectious process;
- FGDS for detection of peptic ulcer;
- biochemical blood test for glucose content and determination of hormone levels if endocrine disorders are suspected;
- examination by a neurologist and conducting tests to diagnose damage to the nervous system;
- blood test for HIV and hepatitis B, C to find the cause of immunodeficiency;
- examination by an otolaryngologist to detect acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis).
Carrying out all types of diagnostic procedures is not necessary; often the cause is determined at the initial stage. Based on the results of the examination, a treatment regimen is selected.
What else can cause plaque on the tongue?
There are many other reasons that cause plaque on the tongue:
- Chronic alcoholism leads to the development of fatty hepatosis, and later cirrhosis of the liver. As you know, a dirty yellow or even greenish coating on the tongue is characteristic of people suffering from liver diseases. In addition, alcoholics are rarely concerned about body hygiene, much less oral hygiene. This further enhances the coating and odor on the tongue of a person suffering from alcoholism.
- Plaque can occur as a side effect of taking medications, mainly antibiotics. Taken orally, they kill the beneficial microflora of the small and large intestines, causing dysbiosis, accompanied by poor digestion and absorption of food. And this, in turn, leads to the formation of plaque on the tongue.
- Intoxication of any origin necessarily causes a coating on the tongue. Thus, cancer patients after a course of chemotherapy all suffer from a dirty-brown coating on the tongue, which is caused by toxic chemotherapy, as well as tissue breakdown products destroyed by cancer cells.
- Impaired immunity, especially if failures occur in that part of the immune system that is located in the intestines, also leads to the formation of plaque, because T-lymphocytes die, settling in the form of a yellowish coating on the tongue and intestinal walls.
In these cases, consultation with a specialized specialist is necessary.
Prevention and elimination of plaque
The main “commandment” for the prevention of this unpleasant phenomenon is compliance with hygiene rules and regular sanitation of the oral cavity. This concept includes:
- mandatory brushing of teeth in the morning and evening;
- using floss to clean the space between teeth;
- using a toothbrush with a grooved surface, which cleans the surface of the tongue in the presence of plaque;
- the use of mouth rinses, which help get rid of unfriendly bacterial microflora present in the mouth even in absolutely healthy people.
There are many more ways to sanitize the oral cavity in order to prevent unhealthy plaque on the tongue, which you should familiarize yourself with in more detail.
Plaque on the tongue in children
In children from birth to 5 years of age, the immune system is so imperfect that a slight coating on the tongue is considered normal. Moreover, a rare baby has avoided thrush, which affects the oral cavity and tongue from the first days of life. But you need to know and be able to differentiate plaque on a child’s tongue in order to recognize dangerous infectious and autoimmune diseases in time and seek medical help:
- Thrush is characterized by a loose, cheesy coating on the tongue and oral mucosa. Cleansing causes the baby to cry because the papillae are hypertrophied and react painfully to touch.
- A dirty gray coating on a child's tongue may be an indicator of scarlet fever. This is an infectious disease that must be treated under the supervision of a doctor. With scarlet fever, the tongue gradually turns from dirty gray to scarlet, similar to strawberries, with characteristic dots along the entire surface of the tongue.
- A filmy coating covering the root of a child’s tongue indicates that he has diphtheria. This sign requires urgent hospitalization, because the disease develops rapidly and leads to suffocation.
- Black or dark brown plaque in babies can be caused by a latent form of diabetes, bacterial sore throat, or taking strong antibiotics.
- There is also such a thing as “geographical language”. It is also typical for young children. These are red spots scattered across the entire surface of the tongue against the background of a light white coating, making the picture resemble a map of the world. In this case, benign migratory glossitis is diagnosed. It occurs against the background of helminthic infestation, vitamin deficiency, acute infectious diseases, and exudative diathesis. Only a doctor can identify the cause of the disease, so you should contact him immediately.
All other causes of plaque on the tongue in children are not much different from adults. These are the same dysbacteriosis, gastritis and even stomach ulcers, problems with the liver and gall bladder.
Plaque in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract, or digestive system, includes:
- oral cavity;
- esophagus;
- stomach;
- liver;
- gallbladder;
- pancreas;
- duodenum;
- small and large intestines;
- rectum and anal sphincter.
Any malfunctions in the organs of the digestive system cause plaque on the tongue:
- if it is concentrated in the area of the root of the tongue and has a gray tint, this means that the large intestine and rectum are affected;
- a thin yellow coating in the middle of the tongue indicates the presence of gastritis or gastroduodenitis, and a thick layer localized in the middle indicates its exacerbation;
- with cholecystitis - inflammation of the gallbladder - a yellow-brown coating appears, while the tongue itself is dry, bitterness and dryness in the mouth are felt;
- if there is a problem with the biliary tract, the plaque can take on a color from yellow to green; it is the greenish shade that indicates that not everything is in order with the biliary system;
- a bluish coating indicates an intestinal infection;
- a thick yellow coating in combination with heartburn, belching and a burning sensation indicates that pancreatitis has worsened - inflammation of the pancreas;
- a reddish-brown, and sometimes even black, coating may indicate oncological processes or abscess inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract.
In any case, plaque on the tongue is not the main sign of diseases of the digestive system. Only a doctor, having collected an anamnesis, can make the correct diagnosis.
Plaque for bronchitis and pneumonia
The area of the tongue immediately following its tip is an indicator of the health or disease of the respiratory system (bronchi and lungs). Based on the condition of this area, one can judge the presence of bronchitis or pneumonia:
- Red spots indicate that pneumonia or bronchial asthma is possible.
- A light film on the front of the tongue indicates the presence of a respiratory allergy or congestion in the lungs.
Plaque on the tongue caused by inflammatory processes of the upper and lower respiratory tract is not decisive in the diagnosis of these diseases.
What diseases does plaque on the tongue foreshadow?
It is believed that the nature of the disease and its location can be determined by the color of the plaque:
- White plaque is quite acceptable if it is easily removed after hygiene procedures. If it lies in a thick layer and has a cheesy consistency, then this is a sign of fungal infection, intoxication, the presence of foreign bodies in the oral cavity - implants or dentures - and the allergic reactions they cause.
- A gray coating may indicate that a course of antibiotic treatment has been carried out or there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Most often these are ulcerative lesions of the stomach or duodenum. A decrease in general immunity can also be the cause of plaque of this color.
- A yellow coating indicates stagnation of bile or problems with the liver. It can also be observed with kidney damage, then its localization is at the edges of the tongue. Constipation also causes such plaque, in which case bad breath also appears.
- The green color of plaque occurs from excess bilirubin during hepatitis of various etiologies. This may also be a consequence of a viral infection.
- Brown plaque can be a consequence of gastronomic preferences - among lovers of brewed coffee and strong black tea. Heavy smokers also often have a brown coated tongue. Inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal mucosa can cause such plaque.
- A bluish coating is a consequence of problems with the cardiovascular system. This may be coronary heart disease or chronic hypotension.
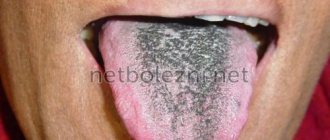
- A dark, almost black coating should alert you. This is a consequence of a serious pathology in the body - oncology, severe dehydration, rare Crohn's disease or cholera infection.
For adults, a constant coating on the tongue may mean that the person is a heavy smoker. It is difficult to find among smokers those whose organs have not been damaged by nicotine tar. This means that they are no longer healthy.