Features of herpetic infections
Herpes is a viral infection that is characterized by a variety of clinical manifestations and can affect various systems, organs, and tissues:
- nervous system;
- genitourinary system;
- skin and mucous membranes;
- eyes.
Herpetic infections are characterized by lifelong persistence—preservation in the host’s body. With any weakening of the immune system, the virus reactivates and the disease worsens. Exacerbation of infection can be caused by a variety of factors:
- overwork;
- hypothermia;
- stress;
- inadequate sleep;
- change in the climatic zone of residence;
- solar insolation;
- colds.
The severity of symptoms depends on the type and form of the virus. When the nervous system is damaged, the disease can lead to inflammation of the membranes of the spinal cord and brain and other dangerous complications. Therefore, it is very important to diagnose the infection in time and begin adequate therapy.
Treatment of herpes virus by a specialist
The symptoms of herpes can be similar to those of other diseases. For example, genital herpes can be confused with other sexually transmitted diseases. The cause of inflammation in the mouth is not only herpetic stomatitis, but also aphthous stomatitis. In this regard, when the first signs appear, you should consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment of all forms of herpetic infection in our clinic “Polyclinic +1” is carried out by highly qualified dermatologists, venereologists, and gynecologists. They will conduct a thorough diagnosis and prescribe effective therapy with modern antiviral drugs. An integrated approach helps not only to suppress the activity of the herpes virus, but also to increase the body's defenses and achieve stable remission. When treating herpes during pregnancy, our doctors always take into account the possible risks to the fetus.
Attention! Self-administration of medications can be harmful if the diagnosis is made incorrectly. If you self-medicate incorrectly, you can harm your health by starting the course of the disease. To avoid relapses and complications, you should take medications under the supervision of a doctor.
Cost of treatment at Polyclinic +1
| Medical service | Cost, rub.) |
| Initial appointment with a dermatologist | 900 |
| Repeated appointment with a dermatologist | 600 |
| Initial appointment and examination with a venereologist | 900 |
| Repeated appointment with a venereologist | 600 |
| Drawing up an individual treatment plan | 1 200 |
| Drawing up a detailed treatment plan | 2 500 |
| Taking a smear for analysis | 500 |
| Blood collection for analysis | 500 |
| DNA diagnosis of latent herpes | 300 |
Methods of infection with viruses
Infection with viruses can occur through airborne droplets, household contact, sexual contact and blood contact. Infection is possible both from patients and from carriers of the virus. The infection persists for a long time in a dried state and can be easily transmitted through household items: cups, towels, toys. The virus also spreads through saliva, blood, vesicle contents, semen, vaginal secretions and other body media.
Infection often occurs in the form of autoinoculation, which involves mechanical transfer of viral particles from one site to another. For example, the virus can spread through the skin and mucous membranes when scratching.
Susceptibility upon contact is quite high. It is believed that about 90% of the adult population are carriers of one type or another of herpes and up to 25% suffer from recurrent forms. As a rule, when examining frequently ill children and adults, several herpes viruses are detected at the same time.
Prohibited for shingles
Not used to treat rashes:
- clotrimazole and other antifungal drugs;
- oxolinic ointment;
- ointments with hormonal components - Triderm, Hydrocortisone, Akriderm, etc.
If you have shingles, you should not:
- warm the affected areas of the skin;
- open bubbles;
- treat rashes with alcohol;
- use various folk remedies.
Also:
- you cannot go to the bathhouse or sauna;
- do not take a hot bath;
- Do not rub the skin with a rough brush.
Types of herpes virus infections
More than 100 representatives of the herpetic family of viruses are known. However, most often a person is affected by 8 of them. Let us consider in detail the features and symptoms of the most common infections.
Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2
The herpes virus type 1 causes blistering rashes on the mucous membranes of the lips and nose. As a rule, infection occurs in childhood. By the age of 5-7 years, more than 50% of children are carriers of the infection. Infection often occurs from sick parents: through kisses, household items.
The incubation period lasts from 2 days to 2 weeks. In addition to the characteristic rashes, the infection may be accompanied by elevated body temperature and enlarged local lymph nodes. After damaging the mucous membranes, the virus reaches the trigeminal nerve, where it can remain latent for a long time.
Herpes simplex virus type 2, or genital herpes, is primarily transmitted through sexual contact. In Russia, the average is 20% among the adult population. In European countries, the incidence rate is even higher. The risk group includes people who have promiscuous sex. Most infections occur during puberty, at the beginning of active sexual life.
Symptoms of the virus include:
- blistering rashes on the genitals;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- painful urination;
- itching in the groin area;
- elevated body temperature.
The disease can occur with frequent relapses (6-12 times a year or more).
Herpes virus type 3
This virus can cause two diseases: chickenpox and herpes zoster. As a rule, chickenpox occurs in childhood and is accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- vesicular rash that lasts about 10 days;
- high body temperature, fever;
- headache;
- itching of the skin;
- symptoms of body intoxication.
Chickenpox in adults occurs rarely and can occur in a more severe form: with damage to the eyes and nervous system. In such a situation, a person requires urgent hospitalization. After the disease, the virus remains in the body for life, remaining latent in the nerve ganglia.
Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent the disease in children and adults who did not have chickenpox in childhood and were not vaccinated against it. Vaccination is given to children from one year of age. The immunobiological drug is administered twice with an interval of 6 weeks. Vaccination is also carried out as an emergency measure in the first three days after a person comes into contact with a patient with chickenpox.
Typically, herpes zoster occurs in people over 65 years of age. The disease is severe and is accompanied by severe symptoms:
- severe pain;
- sleep disturbance;
- high temperature;
- vesicular rashes that appear along the nerve endings.
The disease has a rather difficult rehabilitation period. Even after the rash disappears, a person may remain sore for a long time in those areas that were affected by the infection. In all civilized countries of the world, elderly people are vaccinated to prevent herpes zoster.
Epstein–Barr virus
Herpes virus type 4 or Epstein-Barr virus affects the human body in a complex manner, provoking various and sometimes unrelated pathologies. The virus can cause infectious mononucleosis, lymphoma, hepatitis, affect the nervous and immune systems, and the hematopoietic apparatus.
In the human population, infection with the Epstein-Barr virus reaches 75% or higher. Children over two years of age and adults under 30 years of age are at risk. Children under one year of age rarely get sick due to passive immunity received from the mother.
The symptoms of the disease are many-sided and can have various manifestations: from mild discomfort to severe health problems. The most common symptoms of the disease are:
- high temperature, fever;
- sore throat, muscles;
- enlarged lymph nodes, liver, spleen;
- the appearance of rashes, peeling, inflammation, bruising on the skin;
- photophobia;
- nausea.
It is characteristic that the use of antibiotics does not affect the duration of fever.
Herpes virus type 5
Cytomegalovirus infection, caused by herpes virus type 5, occurs in both children and adults. It can occur as a mononucleosis, with high fever, intoxication, purulent sore throat, and damage to the salivary glands. In addition, the infection may be asymptomatic.
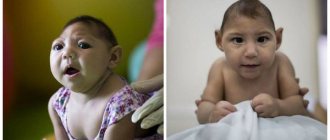
There are also congenital forms of the disease, which often lead to the development of hearing loss, microcephaly in the child, cause enlargement of the liver and spleen, and hematological disorders.
Herpes viruses type 6 and 7
The range of diseases caused by these viruses is diverse. Often infections occur in the form of a sudden exanthema. Hepatitis virus type 6 can provoke chronic fatigue syndrome and infectious mononucleosis. It is believed that a consequence of viruses can be a lymphoproliferative process (the formation of tumors of the lymphatic system).
As a rule, sudden exanthema affects children under two years of age. The disease occurs with high fever and intoxication of the body. Febrile convulsions may occur and a rash appears, which goes away on its own after a few days.
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) is accompanied by rapid fatigue and decreased performance. Patients are concerned about low-grade fever, enlarged lymph nodes, and the appearance of catarrhal manifestations in the pharynx.
Herpes virus type 8
Herpes virus type 8 can cause Kaposi's sarcoma and Castleman's disease. Kaposi's sarcoma is a serious pathology that is accompanied by the appearance of malignant skin tumors. It is quite difficult, especially with immune deficiency. May be complicated by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the palate and lymph nodes.
Castleman's disease is a rare disease in which fever, enlargement of the liver and spleen, anemia, and a sharp decrease in body weight are observed.
Diagnosis of herpes virus infections
The most informative laboratory tests for diagnosing herpesvirus infections are the PCR method and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Depending on the location of the infectious process, blood, saliva, scrapings from the urethra, cervical canal, and vesicles can be examined.
During the diagnosis, the qualitative and quantitative content of immunoglobulins M and G is determined, as well as avidity, an indicator that can be used to assess how efficiently the immune system copes with the virus.
For more successful treatment, a general examination of the body is additionally performed to identify chronic infections. Sluggish chronic pathologies of the genitourinary, respiratory, digestive and other systems can support and cause exacerbation of herpesvirus infections.
How to get rid of constantly appearing herpes on the lips
Herpes is the competence of a dermatovenerologist. Only a qualified doctor can tell you how to treat different types of herpes, taking into account:
- characteristics of the immune system of a particular person;
- the degree of weakening of the body at the time of the disease;
- tendency to relapse.
Medicines that are used for herpes on the lips:
- antiviral drugs in the form of ointments and gels (acyclovir, herperax);
- immunomodulators that increase the body's resistance (cycloferon, arbidol);
- at the stage of herpetic ulcers - softening balms with Vaseline and allantoin.
Many people wonder how to quickly cure colds on the lips in adults in 1 day (based on analogies with the influenza virus, colds on the lips mean a herpetic rash). Answer: if the process has developed beyond the infiltration stage, no way. The vesicle must go the entire way from its appearance to self-opening, the formation of a wound surface and its healing, and this will take an average of 2-3-4 days. An ointment for colds on the lips that would speed up this process has not yet been invented.
But if you just feel characteristic pain and notice swelling, physiotherapy methods (UHF, microwave) can contribute to the reverse development of the infiltrate, and it does not transform into an ugly bubble that spoils the anatomical aesthetics.
Medicine for herpes on the lips of a child should be used strictly according to the doctor’s instructions - regardless of whether this concerns immunomodulators or antiviral drugs.
You can read more about what treatment methods are used for herpes on our clinic’s website