For many people, mushrooms are an incredibly appetizing dish that we sometimes eat in large quantities.
Everything would be fine, but few people know that mushrooms can not only cause poisoning, but also lead to death. Of course, when everything is good, you don’t even need to think about it, but what if the “scenario” has changed? What if you ate a poisonous mushroom along with edible mushrooms? What are the symptoms of mushroom poisoning? What to do if you are poisoned by mushrooms? Who should I contact? Let's look at everything in order.
Fungi are living organisms that, by their origin, are at the junction between plants and animals.
Experts note that mushrooms are a difficult-to-digest product for the intestines, therefore, they are not recommended for use by children, the elderly, as well as pregnant and lactating women, especially in large quantities.
Symptoms of mushroom poisoning
The first signs of mushroom poisoning appear after 1.5-2 hours, but sometimes a day or two after eating them.
Symptoms include:
- Severe abdominal pain;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Diarrhea (diarrhea);
- Increased body temperature – up to 38°C;
- Cold extremities - arms and legs;
- Dizziness;
- Headache;
- Weak pulse;
- General weakness;
- Inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract.
In case of severe poisoning, as well as poisoning with poisonous mushrooms (pale toadstool, red fly agaric, false foam, satanic mushroom), the following symptoms are possible:
- The appearance of delusions, hallucinations;
- Mental disorder;
- Severe diarrhea;
- Increased sweating and drooling;
- Anuria;
- Slight constriction of the pupils;
- Increased drowsiness;
- Jaundice (Gospel disease);
- Heart failure;
- Breathing disorders;
- Pulmonary edema;
- Coma.
If timely and qualified assistance is not provided, a person may fall into a coma, and then death may occur.
Features of champignons
It should be remembered that mushrooms are a kind of sponge that absorbs all the substances in the soil, both useful and deadly. Therefore, it is necessary to beware of landfills, areas of former and existing enterprises, treatment facilities, as well as areas located close to highways. Mushrooms have the ability to absorb radionuclides, heavy metals, various acids, and eating them is fraught with dire consequences, including death.
The champignon mushroom belongs to the Agaricaceae family of the Champignon genus, of which there are about 200 species.
Champignon, which is eaten, has the following characteristic features:
- The flesh is white and turns red when broken.
- The cap is ovoid-bell-shaped, when ripe it acquires a flat-spread shape, brownish-brown in color with dark scales.
- The plates are first white, then dark brown, tapering towards the ends.
- The leg has a cylindrical shape, often slightly swollen towards the base.
- The white membranous ring at the top of the stalk often disappears at maturity.
- The diameter of the cap is usually 7−10 cm, the height of the stem is 4−6 cm, and the width is 1−1.5 cm.
- It grows in coniferous (spruce) and mixed (with spruce) forests, often near anthills or directly on them.
- It grows in groups and begins to grow vigorously after rains.
- The growing season for champignons is late July - mid-October.
In order to find out whether it is possible to be poisoned by champignons, it is necessary to take into account some specific features of these mushrooms.
When going for mushrooms, you need to know that in nature there are many varieties of champignons. However, some of the species can be quite toxic. They are easy to confuse with each other. The varieties of these mushrooms are represented by the following names:
- ordinary (meadow);
- bisporous;
- garden;
- field;
- forest champignon (balagusha);
- coppice;
- sidewalk;
- red-haired;
- yellow-skinned;
- flat-headed (carbolic, scaly).
There are some signs by which an edible champignon can be distinguished from an inedible one. False species include flat-capped, yellow-skinned and rufous. They have an unpleasant "chemical" odor, similar to carbolic acid. Yellow-skinned and red-skinned champignons got their name due to the fact that their flesh begins to turn yellow when cut.
It is noteworthy that when inedible mushrooms are cooked, their chemical smell intensifies, and their color becomes bright yellow. Edible species have a pleasant aroma and turn pinkish-brown when cut. The exception is the field champignon: it is edible, although its flesh also turns yellow when cut.
Champignon or toadstool
Very often, inexperienced mushroom pickers can confuse champignon with toadstool. Distinctive features of these two types of mushrooms:
Read also Greenfinch mushroom: description, benefits and harms, processing methods
| Death cap | Forest champignon |
| White records | Pink records |
| When broken, the flesh remains white | When broken, the flesh will change color |
| No smell | Anise and almond aroma |
These types of mushrooms are very difficult to distinguish from each other at a young age. In this regard, young champignons need to be collected very carefully, and it is better to abandon them altogether. After some time, the color of the plates of these mushrooms begins to differ: the pale toadstool has white plates, the champignon has pinkish or brown-black.
Store-bought champignons
Mushrooms bought in a supermarket are also dangerous, not to mention those bought at a spontaneous market.
For the supermarket, they are grown on special mushroom farms, where the fertilizers may contain substances such as phosphorus and chitin, as well as all kinds of acids. These substances have a detrimental effect on the human body, especially if he has a weakened immune system. For children, such food is generally contraindicated, since their fragile bodies are not able to cope with such a load.
These substances are used to ensure that mushrooms last longer and have an attractive appearance. They are difficult to absorb by the body and are almost not excreted, and when they accumulate in significant quantities, the functioning of internal organs deteriorates. It is recommended to consume no more than 150 g of this product per day. You should not eat mushrooms if you have a stomach or intestinal ulcer. This product has high acidity, which provokes the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. If you feel discomfort when using it, it is better to refuse it.
Canned mushrooms
Despite the fact that many people consider this type of mushroom preparation to be safe, in fact this is not entirely true. The fact is that during heat treatment, toxins remain in the mushrooms, thereby increasing the risk of poisoning. Some harmful substances and microorganisms die during heat treatment. However, it is impossible to achieve the required temperatures at home, unlike factory preservation.
If you find any defects on the jar (poorly closed or damaged lid, presence of cloudy brine, non-compliance with storage rules, etc.), you should refuse to purchase such a product. You should also not try to remove toxins by frying or boiling, as this will not bring the desired result, and such mushrooms can cause significant harm to health.
Another danger is that after preservation, poisonous mushrooms will be almost impossible to distinguish from edible ones, which greatly increases the risk of poisoning.
What other dangers may lie in wait when pickling mushrooms? Mushrooms preserved at home (and not only) can cause poisoning with botulinum bacillus, which gets into the preserve along with the soil, and in the absence of air access it develops rapidly and can lead to disastrous consequences.
Botulinum bacillus produces poison, which leads to muscle spasm, so in parallel with the main symptoms, visual impairment may occur. The consequences of its impact can be extremely unpredictable.
In this case, factory-made products have an advantage over home-made products due to the use of higher temperatures and compliance with the cooking process technology.
Read also: Fly agarics: use, beneficial and poisonous types of mushrooms
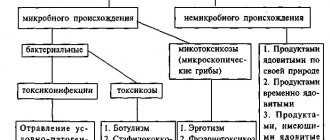
Botulism
Improperly prepared or stored mushrooms, such as canned mushrooms, can cause botulism.
Botulism is a serious and serious disease that develops as a result of an infection entering the body, located mainly in the ground, next to the spores of the mycelium. If the mushroom is poorly washed, peeled, or not sufficiently boiled, an infection can enter the body.
The first signs of botulism appear 12-72 hours after eating mushrooms.
The main symptoms of botulism are:
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Visual impairment (everything floats, doubles);
- Convulsions;
- Diarrhea;
- Headache;
- Labored breathing;
- Dry mouth.
Important! At the first signs of botulism, i.e. After eating canned mushrooms, consult a doctor immediately!
Further treatment
Doctors who arrive on call must assess the patient’s condition. Stabilizing measures are being carried out. Doctors need to return the cardiovascular system to proper functioning and normalize the patient’s breathing. Then you need to:
- administer medications to relieve nausea and vomiting;
- eliminate pain syndrome with antispasmodics;
- replenish the water balance with a dropper.
Once the patient is stabilized, hospitalization may be required. Further treatment takes place in a hospital setting, in the intensive care unit under the supervision of doctors. Botulism requires urgent administration of serum.
First aid for mushroom poisoning
What to do if you are poisoned by mushrooms? The main thing is to remain calm!
Experts recommend following the following help instructions:
- At the first symptoms, call a doctor immediately! If it is not possible to call a doctor, then try to take the patient to the nearest medical facility as soon as possible.
- Maintain bed rest.
- Drink plenty of liquid , this will help quickly remove toxins (poisonous substances) from the body and flush the stomach. This point is especially relevant for vomiting and diarrhea, since with these clinical manifestations the body also loses the fluid necessary for its normal functioning (dehydration). Cold water, chilled strong tea, mineral water, and a light pink solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) are good to drink.
- Take enterosorbents - drugs that bind toxic substances and promote their rapid elimination from the body: “Activated carbon”, “White coal”, “Smecta”, “Enterosgel”.
- If the patient is not vomiting and has no desire to go to the toilet, a laxative is given and an enema is given to remove toxins from the body. This will speed up the introduction of poisons from the intestines.
- Symptomatic treatment:
- In case of breathing problems: Atropine is administered subcutaneously.
- At elevated temperatures: Ibuprofen, Paracetamol.
- For dehydration: “Regidron”, “Litrozol”, “Oralit”.
- In case of severe poisoning with poisonous mushrooms, blood transfusions and hemodialysis may be used, and glucose and insulin may be administered intravenously.
Important! For an accurate diagnosis, potentially poisonous mushrooms that have poisoned the patient cannot be thrown away - they must be given to a doctor for examination.
- A gentle diet is prescribed , which is aimed at quickly restoring the functionality of the digestive system. The diet includes avoiding fatty, spicy, smoked and other heavy foods, alcoholic beverages, and smoking. The menu should include steamed or boiled, chopped vegetables, fruits, and light soups.
If proper assistance is provided, recovery occurs within 1-2 days. In case of severe poisoning, treatment of poisoning and restoration of health can take up to a month.
Possible complications
Intoxication, accompanied by poisoning, contributes to the development of various disorders in the functioning of the whole organism.
Diarrhea and vomiting cause severe loss of electrolytes and fluids. All this is accompanied by skin atony and changes in blood pressure. The amount of urine produced decreases, and the kidneys do not remove the resulting toxins. Due to the effects of harmful substances on the pancreas, chronic or acute pancreatitis worsens. When the stomach is irritated by toxins, gastritis may occur. In most cases, the victim needs the help of qualified specialists to minimize possible harm.