December 4, 2017
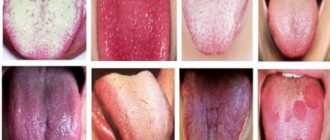
According to modern classification, a folded tongue is a birth defect. This pathology does not occur often and manifests itself in the form of the formation of transverse and longitudinal grooves. Among other names that are found in literature and practice, the term “scrotal tongue” is common.
Tongue with folds
UltraSmile.ru is in a hurry to reassure you - this disease is not dangerous and not contagious. In general, such a pathology should not interfere with living a full life. However, a person with a folded tongue is at risk - in the absence of proper attention to the problem, there is a high risk of developing concomitant diseases, including cancer.
Folded tongue: photos and symptoms
Usually the anomaly is detected in early childhood, but it also occurs in adults, since sometimes this problem does not bother the patient in any way, and the person is not even aware of its presence. The signs of the disease are as follows:
- Macroglossia, or enlargement of the tongue, which can affect a person's speech and chewing function. Usually the patient keeps his teeth in an open position.
- Folds and grooves appear on the surface, which are covered with papillae.
- The tongue is significantly thickened.
- The back and tip of the tongue are smoothed, the filiform papillae have atrophied.
- Increased sensitivity (especially in people who have undergone infectious diseases and surgical operations).
- Regular tingling and pinching sensation.
- Lymph nodes are enlarged.
- Smell from the mouth.
The folds, in turn, are different: transverse, deep longitudinal (and not very deep), fringed. Usually the main longitudinal fold (it is the largest and deepest) runs from the tip along its midline. The remaining folds lead exactly to it.
Sometimes this pathology accompanies desquamative glossitis (geographic tongue) - this is inflammation, as a result of which some areas of the organ become several shades lighter or acquire a gray tint. In general, the picture of the organ resembles a map, which is why it got its name.
Treatment
A folded tongue can be a separate disease, or it can be a symptom of a serious chronic illness. Therefore, the treatment of this pathology may differ in different patients.
As a rule, if the folded tongue does not bother the patient in any way, then he is not given any specific treatment. Typically, such people are only advised to pay more attention to the hygienic care of their tongue, not allowing food debris to accumulate in the tongue folds.
However, if the disease becomes complicated and develops into glossitis, then treatment becomes necessary.
If the signs of scrotal inflammation of the tongue tissue are a manifestation of a general pathology in the body (for example, it is one of the symptoms of a disorder of the cardiovascular, endocrine, respiratory or digestive systems), then the underlying ailment must be treated.
Drug treatment
The following measures are usually used in the treatment of glossitis:
- root cause control and comprehensive examination;
- anti-inflammatory treatment using antibiotics;
- corticosteroids for rapid relief of acute inflammation;
- use of antimycotics (to fight fungal infections);
- immunity-boosting drugs;
- rinsing and irrigating the mouth with herbal decoctions;
- local and general anesthesia using tablets and gels;
- sanitation of the oral cavity.
If glossitis bothers the patient as an aesthetic defect, laser treatment is often effective. At the same time, the folds seem to evaporate and smooth out, and the tongue itself shrinks and becomes more even.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is not often used for scrotal glossitis. It involves surgically suturing the grooves of the tongue. After the surgical stage, restorative treatment using laser and medications is used.
The postoperative period after such suturing usually passes quickly. In this case, it is recommended to maintain “speech rest”, a minimum of chewing movements and gentle diet therapy.
After treatment for a folded tongue, it is important for the patient to reduce all risk factors as much as possible:
- eliminate alcohol and smoking;
- monitor oral hygiene;
- treat dental ailments in a timely manner;
- use high-quality fillings.
Folded tongue is not a serious illness, and the prognosis for patients is quite favorable. For such people, it is enough to be attentive to oral hygiene, paying special attention to cleaning the tongue. Symptoms that indicate an infection or other complications in the mouth should cause concern. Then it is unacceptable to refuse to contact specialists. Otherwise, the quality of life of people with this language anomaly is high enough to live long and joyfully.
Sources used:
- Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. —St. Louis: Mosby, 2007.
- Rationale for the prevention of cancer of the oral mucosa, tongue, lip / Bulyakov R. T., Sh. Kh. Gantsev and O. A. Gulyaeva. — M.: LAP Lambert Academic Publishing
- Guide to practical dentistry: monograph. / L. Baum, R.V. Phillips, M.R. Lund. — M.: Medicine
- National Library of Medicine (USA)
Our team of doctors
Maxillofacial surgeon, Implantologist
Bocharov Maxim Viktorovich
Experience: 11 years
Dental surgeon, Implantologist
Chernov Dmitry Anatolievich
Experience: 29 years
Orthopedist, Neuromuscular dentist
Stepanov Andrey Vasilievich
Experience: 22 years
Endodontist, Therapist
Skalet Yana Alexandrovna
Experience: 22 years
Orthopedic dentist
Tsoi Sergey Konstantinovich
Experience: 19 years
Endodontist, Therapist, Orthopedist
Varvyanskaya Anastasia Andreevna
Experience: 6 years
Dentist-orthodontist
Enikeeva Anna Stanislavovna
Experience: 3 years
Treatment of glossitis
The treatment of glossitis is based on the correction of underlying diseases and the elimination of factors that provoke the occurrence of the inflammatory process. In addition, the therapy program includes:
- adherence to a diet that includes the inclusion of various purees, slimy porridges and pureed soups in the patient’s diet;
- rinsing the mouth with solutions of furatsilin or chlorhexidine;
- applications with solutions of pyromecaine, trimecaine, lidocaine and other anesthetics;
- relieving signs of dry tongue using a mixture of glycerin and anesthesin;
- accelerating the process of regeneration of affected tissues using drugs made on the basis of solcoseryl and vitamin A;
- surgical intervention (in the presence of pronounced hyperkeratic changes).
It is important to know that with timely and competent treatment, inflammatory lesions of the tongue can be easily corrected. An unfavorable outcome of the disease, characterized by the development of abscesses, cellulitis and cancer, is observed only in the absence of adequate therapy.
Possible causes of pathology
The exact causes of the anomaly are unknown. But there are a number of factors that can provoke the appearance of pathology:
- chronic diseases of the liver, stomach, duodenum;
- skin diseases;
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- bone marrow diseases;
- acute infections;
- violation of the mucous membrane of the tongue and its trophic function;
- lack of vitamins and essential microelements in the body;
- collagenosis;
- human reaction to vaccination;
- hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause, lactation).
Causes of glossitis
Inflammatory lesions of the tongue can be an independent disease of bacterial, fungal or viral origin, or a sign of systemic pathologies. At the same time, the factors contributing to its development are:
- bacterial invasion;
- a viral or fungal infection enters the patient’s body;
- oral burn;
- mechanical injury to the tongue and epithelial tissues of the oral cavity;
- smoking;
- eating spicy and spicy foods;
- excessive use of fresheners and mouth rinses;
- alcoholism;
- poisoning with metal salts;
- neglect of hygiene requirements.
Injury to the tissues of the tongue by the sharp edges of fillings, prosthetic devices and damaged teeth, as well as frequent and prolonged exposure to electric current or chemicals leads to chronic glossitis. In addition, the chronicization of the pathological process is facilitated by decreased immunity, dysbiosis and autoimmune reactions in the body.
Treatment of folded (scrotal) tongue
The anomaly usually does not bother its owners, however, sometimes they complain about its appearance: cracks.
A folded (scrotal) tongue requires especially careful care. Because food residues may be trapped in the folds. Because of this, bad breath occurs, as well as accompanying unpleasant symptoms: burning and inflammation.
In addition, the grooves may bother people who have suffered acute infections or surgical interventions. The reasons in this case are also clear: the overall tissue reaction in the body decreases, and the sensitivity of the surface of the folded tongue increases significantly. Therefore, it reacts painfully to chemical irritants and drugs.
If the patient does not properly care for the diseased organ, then the inflammatory processes can drag on, and this is a very favorable place for the development of fungal infections.
The dentist treats this pathology. It is he who will select oral care.
Sometimes a folded tongue requires surgery. This happens in cases where the organ is too enlarged and interferes with the patient. The operation involves excision of part of it.
So, in general, drugs are used to eliminate related problems:
- Fungal and bacterial diseases: anti-inflammatory, antifungal drugs, immunocorrectors, antiseptic treatment.
- Candidiasis: clotrimazole cream, shading with aniline dyes, 10% sodium borate solution in glycerin.
- Painful sensations: antiseptic rinses, mouth baths with citral solution, application of medications with anesthesin.
Diagnostics
This diagnosis is made based on the overall clinical picture. It is important to take into account that this pathology is one of the symptoms of Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome. This means that a folded tongue can be either a congenital or acquired pathology.
It is very important at the diagnostic stage to differentiate the pathology of the folded tongue and sclerosing glossitis, which is similar in manifestations. This change in the structure of the tongue occurs against the background of secondary syphilis. In this case, a similar structure of the tongue, resulting from an increase in the size of the connective tissue, is accompanied by compaction and decreased mobility. The folded tongue, on the contrary, is quite soft, although larger in size. There are no difficulties when chewing or speaking.
Features of care
If you have this pathology, you do not need to self-medicate; careful care and supervision by a specialist are required. In general, you should take care of your oral cavity as follows:
- general oral hygiene;
- rinsing;
- if the patient uses removable dentures, they should also be thoroughly cleaned after eating;
- it is necessary to avoid spicy, salty food, it should not be too hot or cold;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, alcohol);
- You need to brush your teeth with a special paste;
- the toothbrush should be made of synthetic materials: this will help avoid damage;
- regular visits to the dentist.
Such careful care will help neutralize the oral cavity from bacteria, which will prevent their proliferation and the occurrence of associated infections.
Author:
General symptoms of glossitis
The first signs of inflammation of the tongue are discomfort, burning and the sensation of a foreign body in the mouth. Subsequently, the tongue noticeably swells and acquires a burgundy or scarlet hue. The symptomatic picture of the disease may include:
- increased salivation;
- dullness or complete loss of taste;
- perversion of taste;
- pain and difficulty eating;
- slurred speech;
- the patient's desire not to use the tongue when creating sounds.
Symptoms of chronic glossitis
Chronic glossitis is characterized by persistent swelling and changes in the structure of the tissues of the tongue. With bacterial inflammation, hyperemia, soreness, swelling of the affected area and a local increase in temperature can be observed. The development of glossitis, which is of viral origin, is accompanied by the appearance of small blisters on the surface of the tongue, which eventually open and form painful erosions. The disease, which is of a fungal nature, is manifested by the appearance of a dense or loose white coating on the affected surface, as well as hyperplastic changes in tissue.
Symptoms
The course of the disease is asymptomatic. The mouth opens normally, the skin is not changed. The mucous membrane is pale pink. However, the organ has increased dimensions. In a third of patients, atrophy of the filiform papillae is observed, which is why the appearance is also changed. There are depressions on the back and side surfaces.
Folded tongue
There are main factors that can stimulate glossitis of the tongue, namely:
- infectious diseases;
- cancer diseases;
- chemical irradiation;
- radiation exposure.
Also, folded glossitis can serve as a sign of the development of:
- fungal infection;
- atypical amyloidosis;
- acromegaly;
- desquamative glossitis.
Such diseases require timely and serious treatment.
Folded glossitis has some symptoms when it worsens:
- sensation of pain and burning;
- when interacting with hot and spicy things, the burning sensation increases;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- pronounced red color;
- unpleasant sensation while chewing;
- organ hypersensitivity.
In the absence of proper treatment, glossitis can provoke the development of diseases in the digestive organs.
What is dangerous, consequences
With proper care, the grooved tongue does not cause discomfort to the owner. Failure to comply with important points of care for a diseased organ and neglect of the disease can lead to the appearance of various infections, for example:
- Catarrh;
- Candidal glossitis;
- Phlegmon;
- Abscess;
- Hyperkeratosis.
There is also a risk of tongue cancer. Acromegaly may occur when both cheeks and tongue are folded. In case of inflammation, you need to brush your teeth very carefully so as not to touch the painful surface of the organ with the brush.
Geographic fold tongue
There is also a condition called geographic tongue (desquamative glossitis). It is characterized by the presence of reddish or gray spots on the surface. They are separated from each other by yellowish formations of thread-like nipples. Thanks to this, the organ resembles a geographical map. Often, scrotal tongue becomes one of the concomitant diseases.
Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome
The disease presents with significant swelling of the lips and tongue, as well as facial nerve palsy. Folding is a symptom of the disease in half of the cases.
Folded tongue with white spots
White spots may be signs of concomitant pathologies. Among them:
- Desquamative glossitis;
- Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome.
- Candidiasis glossitis.
Classification
The classification of the disease is made depending on the shape of the folds that have formed in the area of this organ.
Folds are:
- fringed;
- deep longitudinal;
- transverse;
- less deep;
- directed towards the deep longitudinal fold.
The localization of the main longitudinal fold is usually marked from the tip to its midline. It is the deepest, both transverse and longitudinal grooves lead to it. Based on the International Classification of Diseases ICD-10, folded tongue is coded K14.5.
Etiology
The causes of a folded tongue are varied.
A folded tongue can be caused by a negative effect on the body of a pregnant woman:
- radiation;
- infectious diseases of various types;
- frequent exposure to stressful situations;
- toxins;
- lack of food.
However, there are cases when the disease does not appear from birth, but develops in adulthood.
Factors in its progression may include:
- chemical or thermal effects;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pathologies of the skin;
- collagenoses;
- deformation of the trophic function of the mucosa;
- disorder of the endocrine system;
- infection;
- organ injuries;
- mental disorders;
- pathologies of the central nervous system.
Excessive intake of vital vitamins, trace elements and minerals, as well as functional metamorphoses in the body, can also cause the acquisition of pathology.