- Home /
- Branches /
- Cardiology /
- Edema
11/01/2021 The article was checked by a cardiologist, member of the European Society of Cardiology, the Eurasian Association of Cardiologists, the Russian Society of Holter Monitoring O.A. Lozbineva. , is for general informational purposes only and does not replace specialist advice. For recommendations on diagnosis and treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
When swelling is detected, specialists at the Yauza Clinical Hospital will conduct the most thorough diagnostics to determine its cause and, accordingly, prescribe treatment using pharmacotherapy, lifestyle correction, and water regimen.
- The volume of fluid inside cells may increase by 20–30% during edema caused by heart failure
- Edema becomes visible when more than 2–4 liters of fluid are retained in the body
- Timely treatment of edema not only improves well-being and appearance, but also prolongs the life of patients
sign up for a consultation
Edema is a symptom of various pathological conditions, which are characterized by excessive accumulation of fluid in the tissues and cavities of the body. To recognize swelling, you need to press for a few seconds on the front surface of the shin. In case of edema, a hole remains in this place, which does not disappear immediately.
What is heart failure?
Heart failure is a pathological condition caused by the inability of the heart to provide adequate blood supply to organs and tissues during exercise, and in more severe cases, at rest.
In heart failure, the heart is not able to effectively pump blood, and therefore the circulation of oxygen and nutrients in the body is disrupted, which leads to stagnation of blood in the tissues, swelling in the legs, in severe cases in the abdominal cavity (ascites), in the lungs . Heart failure is not an independent disease; it is considered a complication of other diseases and conditions. In the United States, heart failure affects about 1% of the population (2.5 million people). Heart failure accounts for one in 20 hospitalizations and is more fatal than many types of cancer. The incidence of heart failure increases with age—10% of the population over 75 years of age in the United States.
Acute form
Along with chronic, there is an acute form of heart failure. The reasons for its occurrence are:
- myocardial infarction;
- major stroke;
- structural defects of the heart, congenital and acquired;
- hypertension.
A distinctive feature of acute cardiovascular failure is the suddenness of the attack and the absence of the listed stages of development. The person's condition quickly deteriorates and death is possible within a few minutes. The occurrence of pathology is indicated by a sharp deterioration in condition, suffocation, severe cough with foam or red sputum, blue discoloration of the skin, and cold sweat.
In such cases, first aid is to call an ambulance. Then the victim should be taken out into the open air, the collar and other tight clothing should be unbuttoned. The best pose is considered to be sitting, with legs down. A nitroglycerin tablet should be given under the tongue. Repeat the dose every 10 minutes until the ambulance arrives.
Important! In acute heart failure, you should not take a supine position.
Symptoms of heart failure
When the heart does not work efficiently, people notice that they expend more energy than before when doing the same work, they get tired faster, and experience rapid breathing (shortness of breath). This is due to the fact that the tissues do not receive enough oxygen. Arrhythmias, dizziness, darkening of the eyes, fainting, swelling of the neck veins, pale skin, swelling in the ankle area - which is called edema and is associated with the accumulation of excess fluid in the tissues - may occur. The skin becomes “loose” and if you press on it with your finger, the resulting “dent” or hole remains for quite a long time. As heart failure progresses, the level of edema observed becomes higher; tissue pastiness can be noticed even in the abdomen and lower back.
These symptoms tend to develop gradually and usually go unnoticed for a long time. Symptoms of heart failure increase, the general condition slowly deteriorates and increasingly affects the person's ability to perform normal work. There are often periods when a person's condition remains fairly stable, interspersed at times with episodes of acute worsening of symptoms. In the later stages, complaints arise not only during exercise, but also at rest, and the ability to work is completely lost. Due to insufficient blood supply, all organs and systems of the body suffer to one degree or another. Abnormal heart rhythms are a bad sign of heart failure—about half of people with heart failure die suddenly as a result of fatal arrhythmias.
The main complaints of patients with the development of heart failure:
- Swelling of the soft tissues of the feet and legs are the initial symptoms of right ventricular heart failure, uniformly affecting both legs, occurring in the late afternoon and disappearing by the morning. With the development of insufficiency, the swelling becomes dense and does not go away completely, ordinary shoes become tight, patients feel comfortable only in house slippers.
- Ascites is an accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
- Enlargement of the liver - discomfort (unpleasant sensations, heaviness) and pain in the right hypochondrium.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Dyspnea is the main, often the first symptom of chronic left ventricular failure. As heart failure progresses, shortness of breath may occur during normal conversation, and sometimes even at complete rest.
- Paroxysmal cough after performing intense exercise.
- Rapid heartbeat (sinus tachycardia) is a feeling of “fluttering” in the chest that occurs during any physical activity.
Treatment in the elderly
In older people, cardiac edema in some cases is considered normal: with age, the main organ begins to age and work somewhat slowly. Even minor interruptions in the rhythm and heart rate, and increased blood pressure provoke a characteristic syndrome.
If during diagnostic measures any serious disease of the cardiovascular system is revealed, the patient will be placed in an inpatient department. He is prescribed medication, and in some cases surgical intervention may be necessary. But doctors, before making a decision on therapy, always take into account the patient’s age and general health. Elderly people can stabilize their condition and reduce the severity of edema without drug intervention.
First of all, a diet is prescribed:
- completely eliminate or radically reduce the amount of salt consumed - no more than 1.5 g per day;
- Do not add salt while cooking; this can be done immediately before eating;
- introduce fresh vegetables and fruits to the menu, including in the form of juices with pulp;
- exclude dairy and fermented milk products with high fat content from the diet.
Diet for the day
Elderly people must control the functioning of their urinary system - they need to consume as much liquid per day as is excreted from the body, but in no case more. The following products should be excluded from the menu:
- fresh bread, pastries and pancakes;
- smoked, salted fish, canned food, too fatty fish;
- raw or fried eggs (omelet is allowed);
- goose and pork meat, sausages, sausages and deli meats;
- feta cheese, cream, sour cream, fatty cheeses;
- meat and fish broths;
- animal fats, including margarine;
- any hot seasonings and spices - mustard, adjika, horseradish;
- pickled, salted and pickled vegetables;
- spinach, radishes, mushrooms, nuts of all varieties;
- representatives of legumes;
- milk and white chocolate, desserts with rich butter cream;
- sweet carbonated drinks, coffee and strong tea.
Meals should be fractional, calorie intake should be controlled, because excess weight aggravates the situation and increases cardiac edema.
You should completely stop drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking. Older people should give their body light or moderate physical activity - exercise regularly, take active walks, swim or do yoga.
Diagnosis of heart failure
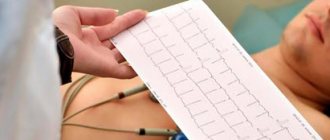
Electrocardiography (ECG) helps doctors identify signs of hypertrophy and insufficient blood supply (ischemia) of the myocardium, as well as various arrhythmias.
An ECG with a load - a special modification of a bicycle (bicycle ergometry) or a “treadmill” (treadmill) - provides information about the reserve capabilities of the pumping function of the heart.
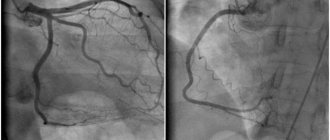
Echocardiography (EchoCG). Using this method, you can not only determine the cause of heart failure, but also evaluate the contractile function of the ventricles of the heart.
X-ray examination of the chest organs in heart failure reveals stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation and an increase in the size of the heart cavities (cardiomegaly).
Radioisotope methods for studying the heart, in particular radioisotope ventriculography, make it possible to assess with high accuracy the contractile function of the ventricles of the heart and the volume of blood they contain in patients with heart failure. These methods are based on the administration and subsequent distribution of radioisotope drugs in the body.
Positron emission tomography – PET – allows using a special radioactive “tag” to identify areas of viable myocardium in patients with heart failure.
Diagnosis of cardiac edema
Cardiac edema is very easily diagnosed, because patients seek medical help with an already clearly formed pathological focus and can characterize it. The specialist’s task is to find out the cause that led to heart failure and edema. For this purpose, as part of diagnostic measures, the following is prescribed:
- Physical examination - performed at the initial appointment with a doctor, does not require laboratory or clinical equipment. The doctor collects anamnesis, visually evaluates the swollen area and characterizes it, palpates the lesion and measures the patient’s blood pressure and pulse rate.
- Measuring central venous pressure is carried out only if there are difficulties in diagnosis. It involves inserting a catheter from sensors into the right ventricle of the heart through a vein. The patient is admitted to the hospital for this procedure.
- Electrocardiography and ultrasound examination of the heart are the most informative diagnostic measures; they allow you to see structural changes in the tissues of the heart, determine the speed of blood flow and detect congestion in the veins. The duration of the procedure is a maximum of 15 minutes, but it allows the doctor to quickly understand where the problem is located.
Blood and urine tests are required, which helps to identify background, concomitant pathologies. But cardiac edema and heart failure themselves do not affect urine and blood formulas in any way; they are not used to diagnose the particular syndrome in question.
Treatment of heart failure
If acute heart failure develops, hospitalization is necessary. The main emphasis in treatment is both on eliminating the causes of heart failure (stress, excessive consumption of table salt, alcohol abuse, smoking, high blood pressure, as well as taking medications that promote fluid retention in the body, etc.), and on correcting it manifestations. Limiting physical activity. Physical activity is acceptable and desirable, but it should not cause significant fatigue or discomfort. The diet should be low in salt, with plenty of fruits and vegetables. It is very important to achieve a reduction in excess weight, as it creates a significant additional burden on a diseased heart.
Currently, the following medications are used to treat heart failure:
- increased myocardial contractility;
- decreased vascular tone;
- reducing fluid retention in the body;
- elimination of sinus tachycardia;
- prevention of thrombus formation in the cavities of the heart.
If medications used to treat chronic heart failure are ineffective, surgical treatment may be recommended - cardiomyoplasty, cardiac pacing. Typically, medical monitoring of patients with heart failure is necessary throughout their lives.
Causes of the disease
The causes of congestive heart failure are pathologies of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems. They can be congenital or acquired:
- genetic predisposition;
- ischemic disease.
- myocarditis
- diseases resulting in thickening of the walls of the myocardium and pericardium;
- thyroid diseases;
- diabetes.
Factors that provoke the occurrence of pathological processes include:
- bad habits, smoking and alcoholism;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- excessive body weight;
- severe infections (usually viral);
- heavy physical activity;
- frequent stress, improper daily routine, lack of sleep.
Congestive heart failure is more common in old age, occurring in 10% of people after sixty years of age. However, the disease also affects young people. In adolescence, it is necessary to carefully monitor the state of the cardiovascular system. The rapid growth of bone and muscle tissue, hormonal changes increase the load on the heart, which does not have time to grow with such rapid growth of the body as a whole.
Young athletes are at risk. Typically, training for teenagers is more gentle; children undergo annual examinations. If signs of congestive heart failure are detected, not only urgent treatment is necessary, but also a temporary refusal to exercise. Doctors recommend taking a break for about a year.