Author:
- Elena Vitalievna Naumova, otolaryngologist, leading doctor of the clinic
2.89 (Votes: 9)
If the temperature exceeds 38°C, the lymph nodes are inflamed, white plaque has spread to the tonsils, the back wall of the pharynx, then antimicrobial therapy cannot be avoided. To prevent purulent tonsillitis from developing into a chronic process, taking antibacterial drugs is mandatory. Medicines suppress the growth of bacteria, prevent infection of family members, and reduce the likelihood of complications.
Only an ENT doctor can figure out which antibiotic is effective and safe for purulent sore throat.
Main groups of drugs
Sore throat is provoked by different types of opportunistic microorganisms and treatment depends on the specific causative agent of the disease. First of all, the ENT doctor will give a referral for a blood test and bacterial culture from the tonsils to detect antibiotic resistance.
Most often, purulent tonsillitis is treated with systemic antibiotics:
- Penicillin series. They have fewer contraindications, so they are often prescribed to children and adults with intolerance to other groups of antibiotics. Penicillins are effective only at the initial stage, when ulcers have not formed. It is worth noting that they are not prescribed if the patient has a history of bronchial asthma or urticaria. During pregnancy, they are prescribed only when absolutely necessary in the early stages.
- Cephalosporins. They are beneficial in severe cases of the disease. They are low toxic and effective from the first day of use. Can be prescribed to pregnant women.
- Macrolides. Prescribed if there is no effect from taking medications of the first two groups. Macrolides have an extended list of contraindications and are taken in a short course. It is worth noting that they are prohibited during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Lincosamides. Used for frequent exacerbations of purulent tonsillitis.
General therapy should be comprehensive, i.e. It is possible to speed up recovery and remove the pathogen with oral antibiotics and local treatment. Local antibiotics for purulent sore throat are prescribed to young children and pregnant women.
Forms of sore throat and symptoms of the disease in adults
Each form of sore throat manifests itself differently. It is important to find out which pathogenic microorganism caused the disease. But it is impossible to determine this at home. Only a qualified doctor can accurately identify the nature of the pathogen and prescribe adequate treatment for sore throat, promoting a speedy and complete recovery.
Catarrhal sore throat
Acquired through contact with an infected person, it begins acutely, with a slight increase in body temperature and a feeling of weakness. The tonsils and submandibular lymph nodes are slightly enlarged. Dryness in the mouth and throat is accompanied by a sore sensation; swallowing is painful and difficult. If not stopped in time, the disease can develop into a severe form with subsequent complications.
Lacunar tonsillitis
The purulent form of tonsillitis is characterized by a very rapid onset of symptoms. The lymph nodes become enlarged and swollen, the tonsils are markedly swollen and covered with a white-yellow purulent coating. The throat with lacunar sore throat hurts especially badly.
An increase in temperature to 40 degrees is accompanied by headache, muscle and joint pain, sometimes radiating to the heart. Fever may cause seizures, vomiting, and confusion.
In the absence of proper treatment, lacunar tonsillitis can develop into fibrinous tonsillitis, when severe purulent intoxication of the body begins, in some cases causing brain damage.
Follicular tonsillitis
The purulent form has symptoms similar to lacunar angina. The tonsils are covered with many purulent follicles. Sometimes the patient complains of pain in the lower back, joints ache, like with the flu. Unbearable pain in the throat radiates to the ear.
This form of purulent tonsillitis is dangerous due to a wide range of complications, as well as rupture of the follicles inward, followed by a purulent abscess.
Herpangina
A dangerous viral form acquired by using a shared toilet, shaking hands and any type of tactile contact with a carrier of the disease - a person or animal. Small serous blisters appear on the tonsils, throat and palate. The throat hurts unbearably, the cervical lymph nodes are swollen and painful to the touch.
At the same time, all the symptoms characteristic of influenza appear: fever, chills, headache, nausea, diarrhea.
Confirming the diagnosis of “herpetic sore throat” is only possible by consulting a doctor. A qualified specialist will first of all direct the patient to undergo tests for serological testing and virology, after which he will prescribe a course of necessary antibiotics.
Otherwise, improper treatment can have serious consequences: encephalitis, meningitis, and myocarditis.
Phlegmonous sore throat in adults
This is a purulent form of the disease, typical for the age group of 20-40 years. The causative agent is streptococci, and the cause is not long-standing catarrhal or follicular tonsillitis. With this form of sore throat, redness is observed not only of the palate and tonsils, but also of the peri-almond space.
The throat hurts on one side, the focus of suppuration does not have clear boundaries and requires surgical intervention.
The patient has chills and fever, the voice is hoarse or disappears completely. As a result of purulent melting of the tonsil, a characteristic, unpleasant odor comes from the mouth.
Treatment of phlegmonous sore throat cannot be delayed. In the absence of timely assistance from specialists, in most cases, cervical or brain abscesses, purulent meningitis, and general blood poisoning occur.
Treatment of angina should occur under the strict supervision of a doctor, who will be able to notice in time and prevent the development of complications that are of the most unexpected nature.
Reception features
Each antibacterial drug is taken differently. The dosage, regimen, and duration of therapy are selected by the ENT doctor individually for each patient. Penicillins are usually eliminated from the body quickly, so treatment with drugs of this group involves frequent taking of tablets. Cephalosporins in tablet form are taken every 6-12 hours.
Uncontrolled use of antibiotics entails a decrease in the sensitivity of bacteria to the drug and a lack of treatment effect, and subsequently to the development of persistent resistance of the patient's microflora to antibacterial drugs.
Antimicrobial agents are taken one hour before meals or two hours after meals. Thus, the absorption of the active substance is higher.
Hexoral against purulent sore throat
For acute tonsillitis, all drugs from the HEXORAL® line can be used.
You can treat the throat with a sore throat (acute tonsillitis) using HEXORAL® spray based on hexethidine. It allows you to evenly cover the surface of the mucous membrane of the tonsils and pharynx, which contributes to a more effective fight against infection8. A solution of HEXORAL® with hexethidine and a combination of essential oils7 may be suitable for gargling.
The use of hexetidine preparations is prescribed in clinical guidelines for the treatment of acute tonsillopharyngitis2. Hexetidine is an antiseptic that is active against most bacteria, herpes simplex viruses type 1, influenza A, PC virus that affects the respiratory tract, and fungi. In addition, it has a mild analgesic effect7.
Both HEXORAL® spray and solution are approved for use for local treatment of tonsillitis in adults and children over three years of age7,8.
Lozenges with a neutral mint flavor HEXORAL® TABS based on chlorhexidine and benzocaine have antiseptic properties and analgesic properties. They are approved for use in adults and children aged 4 years and older9.
For adults and children over 6 years old, HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC is available with the flavors of orange, black currant, lemon and honey. It is based on a combination of the antiseptics amylmetacresol and dichlorobenzyl alcohol, which help in the fight against tonsillitis pathogens10.
HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA may be suitable for children over 12 years of age and adults. In addition to the antiseptic component, it contains lidocaine, which can relieve even severe sore throat11.
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.
Up to contents
Literature
- Dergachev V. S. Angina. Clinic, diagnosis and treatment algorithm. Choice of local antibacterial therapy // Regular issues of “RMZh” / No. 18. – 2007. – P. 1350.
- Clinical recommendations Acute tonsillopharyngitis // National Medical Association of Otorhinolaryngologists / 2016.
- Kunelskaya N.L., Turovsky A.B., Kudryavtseva Yu.S. Sore throats: diagnosis and treatment // General Medicine / No. 3. – 2010. – P. 4-9.
- Krasnova E.I., Khokhlova N.I. Differential diagnosis and treatment tactics for acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) at the present stage // Attending physician / No. 11. – 2021. – P. 58-63.
- Shcherbakova M. Yu., Belov B. S. A-streptococcal tonsillitis: modern aspects // Pediatrics / Volume 88. - No. 5. – 2009. – P. 127-135.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® solution // Reg. number P N014010/02 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® aerosol // Reg. number P N014010/01 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS // Reg. number LSR-002626/07 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC // Reg. number P N015976/01 //
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA // Reg. number LSR-004122/09 //
Up to contents
Release form
Depending on the stage of development of the disease, the ENT doctor prescribes different types of antibiotics:
- Tablets and syrups. Used as the disease progresses. Usually the drug effect is noticeable 2-4 days after the start of administration.
- Local medications (sprays, lozenges). They are used as an addition to the main therapy, since they only relieve acute pain when swallowing saliva, and do not kill completely pathogenic bacteria.
- Injections for intramuscular and intravenous administration are prescribed for advanced stages of angina, when the patient cannot swallow a tablet. Basically, antibiotics of the bicillin group are used as active substances once. The effectiveness of injections is much higher, since the active substance is evenly distributed throughout the tissues. A high concentration of the drug lasts longer, so the result is visible faster.
Important to remember! The earlier the diagnosis is made and rational therapy for acute purulent tonsillitis is prescribed, the greater the chances of curing the disease without developing serious complications. At the first manifestations of purulent tonsillitis, do not waste precious time self-medicating, consult a doctor! This will save you and your loved ones from serious consequences!
Consequences of purulent sore throat
Acute tonsillitis can occur with complications. They are usually divided into local and general.
Local complications:
- paratonsillar abscess - an abscess that forms outside the tonsil when infection penetrates into the surrounding tissue;
- acute otitis media – inflammation of the middle ear;
- acute laryngitis - inflammation of the larynx;
- cervical lymphadenitis – inflammation of the lymph nodes1.
General complications occur more often with streptococcal sore throat4, these include:
- rheumatism;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- myocarditis;
- polyarthritis;
- glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis;
- pneumonia and others1.
Up to contents
Causes of follicular tonsillitis in children
The palatine tonsils are the first barrier to various microorganisms that enter the patient’s respiratory tract.
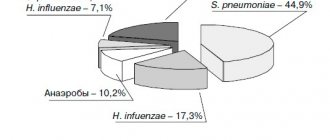
They are accumulations of lymphoid tissue rich in immune cells that protect a person from bacteria and viruses. Follicular tonsillitis is the result of a “breakdown” in the function of the palatine tonsils. This can occur either against the background of massive infection with microorganisms, or with an existing immunodeficiency. In both cases, bacteria and viruses (most often group A streptococci) penetrate the lymphoid tissue and begin to multiply. The tonsils turn from a protective organ into a source of infection, which can penetrate various organs through the bloodstream.
The disease is based on a local inflammatory process. Against the background of vasodilation, the tonsils become red and increase in size. Gray-white films are the result of the vital activity of microorganisms. An increase in their number is an unfavorable sign indicating the progression of the disease.
Factors that create conditions for easier penetration of bacteria and viruses into the palatine tonsils are:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Hypothermia – local and systemic.
- Congenital or acquired immunodeficiency.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases of other internal organs (cholecystitis, pancreatitis, pyelonephritis).
- Metabolic disorders (diabetes, obesity).
- Chronic processes in the paranasal sinuses of a child (sinusitis, sinusitis, ethmoiditis), otitis media, multiple carious teeth.
Follicular tonsillitis in children is rarely primary. The disease often occurs against the background of an already suffered catarrhal form of the disease.