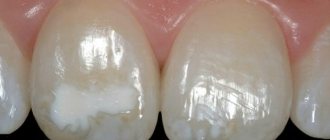
Hyperesthesia is the increased sensitivity of tooth enamel to chemical, mechanical and temperature influences. An unpleasant reaction can occur to acidic foods - fruits, berries, as well as hot and cold foods and drinks. Pain may occur during chewing and touching the enamel with a toothbrush.
In ICD-10, this condition is assigned code K 03.8. It is important to understand that often dental hyperesthesia is not an independent disease, but occurs as a result of the development of certain pathologies.
Varieties
Sensitivity disorders are divided into two groups - increased or decreased.
Reduced ones include analgesia, hypoesthesia, and termanesthesia. With analgesia, a person does not feel pain; it can occur in many diseases and injuries of the nervous system. Hypoesthesia is manifested by a decrease in tactile sensitivity; the patient does not respond to skin punctures or insects crawling on the body. Thermaneesthesia is characterized by a violation of the perception of temperature conditions (warm and cold influences).
Increased sensitivity distinguishes terms such as hyperalgesia, hyperesthesia and hyperpathia. Hyperalgesia is a pathologically increased perception of pain; sharp or increased perception of stimuli is called hyperpathy. In this condition, the unpleasant sensations continue for quite a long time, the patient cannot determine the exact location and the sensations of irritation continue longer than contact with the irritant occurs. Hyperesthesia is an increased perception of stimuli, but at the same time the patient is able to sense the correct location of the stimulus and what type of impact.
Disorders in which the patient perceives a single effect as multiple are called polyesthesia. Allocheiria is a condition in which the patient feels irritation not at the site of its impact, but in the same areas on the opposite side of the body. With dysesthesia, there is a perverted perception of stimuli, that is, their confusion. When exposed to pain, the patient may feel warmth; when exposed to low temperatures, a tingling sensation. Paresthesia is a spontaneously occurring and short-term sensation of numbness, burning and a feeling of “crawling sensations”.
Hyperesthesia (increased tooth sensitivity) - symptoms and treatment
Treatment of hyperesthesia is aimed at reducing the speed of fluid flow in the dentinal tubules. This can be achieved in the following ways:
- blockage of enamel micropores with the help of desensitizers - drugs that reduce tooth sensitivity;
- reducing the size of micropores using mineralizing agents, for example, gels with a high content of fluoride and calcium. These include gels ROCS Medical Minerals, GC Tooth Mousse;
- closing or narrowing of dentinal tubules using a laser [14];
- preparation and filling of teeth for carious lesions;
- surgery on the gum when it recedes as a result of periodontal disease;
- correction of the bite.
In 1935, dentist L. Grossman identified the main properties of an ideal remedy for combating hyperesthesia [12]. In his opinion, it should act quickly and be effective for a long time, not irritate the pulp, not provoke pain and not change the color of the teeth. There are quite a lot of such drugs now. Desensitizing agents (reducing tooth sensitivity) are produced in the form of gel, toothpaste, rinse, varnish, etc. Toothpastes are most often used.
For mild hyperesthesia , as a rule, applications of various solutions are sufficient.
The drug Remodent in the form of a 3% aqueous solution for applications is applied to areas of hyperesthesia for 15-20 minutes. For the course of treatment to be effective, it is necessary to make 8-28 such applications (one 2 times a week) until a positive result is achieved. Sometimes a 3% solution of remodent is used as a rinse (4 times a week). The full course includes about 40 procedures.
Strontium chloride is used in the form of a 25% aqueous solution and 75% paste. When rubbing the paste, stable compounds of strontium appear with the hard tissue of the tooth. This remedy is a good prevention of hyperesthesia after tooth preparation and removal of dental plaque.
To eliminate hyperesthesia, a 30% aqueous solution of zinc chloride is also used. After this, an application is carried out with a 10% solution of potassium ferrocyanide. It seals the tubules with the resulting sediment. The duration of the applications is one minute. The use of a paste containing alkalis is also indicated: sodium bicarbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium, magnesium. It attracts dentinal fluid, which is contained in the micropores of the enamel, and reduces tooth sensitivity.
A modern treatment for hyperesthesia is bifluoride-12, a special colorless varnish containing fluoride, and fluocal, a dental gel containing sodium fluoride. They are carefully applied to the teeth with a brush or foam swab. Both products create a coating that saturates the enamel and dentin with fluoride ions, which leads to a decrease in sensitivity. Fluocal can also be used in the form of an application solution. Typically, a course of treatment with such applications includes only 2-3 procedures. Varnish is usually used as an auxiliary method that enhances the effect of the main drug [15].
Treatment of hyperesthesia with laser has been shown to be the preferred treatment method. It is aimed at narrowing the dentin tubules by combining the proteins of the dentin fluid, partially melting the hard tissues and relaxing the internal nerve receptors. Laser therapy has no side effects [15].
Treatment of generalized hyperesthesia is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease, so it not only relieves symptoms, but also affects the course of the disease. Treatment must be comprehensive. In addition to treating the main cause of hyperesthesia, it is necessary to restore the mineral composition of enamel and dentin, and normalize the content of phosphorus and calcium in the body. For this purpose, calcium glycerophosphate, clamine or phytolon, as well as multivitamin preparations are prescribed. Taking phosphorus-calcium drugs throughout the course of treatment provides a good prognosis. Otherwise, restoration of normal sensitivity will take a long time.
To eliminate pain at the beginning of treatment, in addition to using toothpaste with phosphate, electrophoresis with a 2.5% solution of calcium glycerophosphate is required. The course of such physiotherapy is 10 sessions. In case of hyperesthesia against the background of impaired neurological status, the use of a galvanic collar according to Shcherbak is indicated (also at least 10 sessions).
Studies have shown that the effect of complex treatment of hyperesthesia occurs quickly and lasts for quite a long time. The content of phosphate and calcium in the dental tissues increases, the level of calcium and phosphate in the blood normalizes.
During the treatment of hyperesthesia of any degree it is necessary:
- select personal hygiene products;
- control bad habits (do not bite nails, pencils);
- adjust your diet (exclude soda, sticky sweets, consume vegetables, fruits and dairy products more often);
- wear a mouth guard at night (for bruxism) [14].
Mechanisms of pain
Dental hyperesthesia is a problem of global importance, because it is observed in more than half of the entire adult population of the planet. Statistics also point to the fact that the disease is more common in women than in men. However, despite the widespread prevalence of the disease, it is still not entirely clear how the pain reaction to direct external stimuli occurs. There are three theories about this:
- Nervous reflex. Its essence lies in the fact that the basis of the problem is disturbances in ion exchange processes in dental tissues, as a result of which the dentin receptor apparatus exhibits increased sensitivity.
- Receptor. It is assumed that pain occurs as a result of a direct reaction of the nerve endings of dentin to irritation and subsequent transmission of a signal to the pulp of a particular tooth.
- Hydrodynamic. Accepted by domestic doctors as the most likely. According to the opinion, pain occurs as a result of activation of mechanical receptors of nerve fibers. This occurs due to disturbances in the circulation of dentinal fluid in the tubules, which in turn is caused by various external factors.
In addition, enamel hyperesthesia specifically in women may be a consequence of a lack of hormones in the blood, namely estrogens.
Diagnostics
Hyperesthesia is differentiated from other conditions that have similar symptoms:
- with inflammation of the pulp;
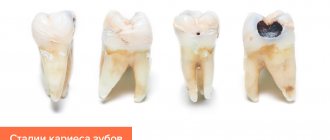
- with caries;
- with a cracked tooth or restoration;
- with a violation of the sealing layer.
A characteristic symptom of hypersensitivity is quickly subsiding, acute pain. To determine it, the doctor checks the condition of the nerve bundle using x-rays or electrodontometry. If the preliminary diagnosis is hypersensitivity, the dentist conducts tests to determine the degree of reaction of dental tissues to temperature, chemical, and tactile stimuli. When the degree is determined, the doctor draws up an individual treatment and prevention plan.
Causes of hyperesthesia
A generally accepted classification of pathology has been developed, based on which the dentist makes a conclusion about the causes of increased tooth sensitivity. The classification systematizes predisposing factors. By comparing them with a specific case and making instrumental diagnostics, the doctor makes a conclusion about the origin of the pathology and classifies it as one of the varieties.
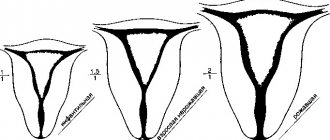
By localization:
- limited
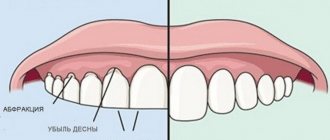
- it affects one or more teeth. Usually these are ground teeth, teeth with a wedge-shaped defect; - generalized
- affects most of the dentition, sometimes the entire row. Progressive erosion of the enamel, exposure of the neck of the tooth during periodontitis, and increased tooth abrasion lead to generalized erosion.
By origin:
- caused by loss of hard dental tissues
. Its appearance is provoked by carious cavities, enamel erosion, increased abrasion, orthopedic preparation (grinding) for prosthetics; - not associated with the loss of hard dental tissues
. It occurs if the neck or root of the tooth is exposed, which can be caused by periodontal diseases, general diseases - endocrine pathologies, neuroses, gastrointestinal pathologies and others. Visually, in such cases, the enamel appears intact.
Medical errors can also be the cause. Hypersensitivity occurs if, during the finishing treatment of the filling, healthy tissue was sanded, the filling technique was violated, the enamel was over-etched, or ultrasonic teeth cleaning or whitening was performed incorrectly.
A lot of calls to clinics occur precisely because of incorrect bleaching. Hyperesthesia can occur after the procedure when it is performed without taking into account contraindications and the characteristics of the patient’s teeth.
The high incidence in women is due to hormonal and metabolic disorders, especially a decrease in estradiol. They show decreased levels of magnesium and calcium, and bone tissue shows lower density. Therefore, women undergoing dental treatment should undergo additional studies as prescribed by a dentist-therapist.
Stages of treatment
After examination and diagnosis, the dentist determines the cause of this disease. It is from this that the treatment plan for hyperesthesia of tooth enamel will be built.
- If the disease is caused by caries, then caries treatment is carried out.
- If sensitivity occurs due to incorrectly selected home hygiene products, then the doctor individually selects a brush and paste for the patient. The enamel is also treated with a special solution - remineralizing gel.
- When a patient experiences recessions, surgical operations are performed to eliminate them.
Treatment of enamel hyperesthesia is a comprehensive approach to the problem, including examination, diagnosis, elimination of the cause and symptoms.
Do not self-medicate, consult a doctor!
Don't wait for your condition to worsen!
Sign up
Possible complications
Dental hyperesthesia can cause a deterioration in a person’s psycho-emotional state. It is fraught with the appearance or worsening of neuropsychic diseases and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Pain often interferes with proper nutrition and forces you to give up your usual meals.
One of the most obvious complications of hypersensitivity is pulpitis - inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of the tooth. Constant irritation of nerve fibers can lead to disruption of the body's compensatory capabilities. Typically, it takes six months to a year for pulpitis to develop. This is a rare complication, but its occurrence requires more complex intervention - pulp removal, endodontic treatment.
Sometimes hyperesthesia can be a harbinger or the only symptom of the development of certain dental diseases. Thus, the development of a wedge-shaped defect can begin with an increase in sensitivity. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor with this problem to find out the exact causes and prevent the development of complications.
Symptoms of the disease
Acute pain in hyperesthesia of hard dental tissues is caused by specific irritants. This could be food, chemical hygiene products, and even changes in air temperature. The most common irritants:
- sour foods - citrus fruits, natural juices;
- mechanical impact - pressure on the tooth with a brush, chewing solid food;
- temperature - hot and cold drinks and foods.
Bursts of pain occur suddenly after exposure to a stimulus and last from a few seconds to several minutes. Both one tooth and several adjacent units can hurt. There are also periods of remission, when pain ceases to bother you for several weeks or months, but this does not mean getting rid of the problem.
Often, sensitive teeth have no external differences - stains, chips or other signs. In this case, hyperesthesia may be associated with a wedge-shaped tooth defect or erosion.