Obsessive itching in the anal canal is a symptom that is rarely addressed to a doctor. It is considered inconvenient, sometimes indecent, and is often ignored. Meanwhile, itching near the anus or inside it does not occur for no reason. It may hide a serious intestinal or rectal disease, endocrine disorders and parasites.
To say goodbye to unbearable itching in an “inconvenient place” once and for all, you need to find out the reasons for its occurrence, and then select effective treatment methods.
What is anal itching?
Anal itching is a condition characterized by irritation in the anal area. For women, the area where pathology spreads can involve the external genitalia. According to statistics, the disease manifests itself in women and men of mature age, and it is most popular among the stronger sex. This condition in itself is not dangerous. But it causes discomfort and can also be a sign of some serious diseases.
Classification
Proctologists divide itching in the anal area into two types: primary and secondary. This division is necessary to choose the correct treatment tactics.
| Primary (idiopathic) itching | In this case, it is not possible to identify the specific cause of the pathological condition, and it is difficult to cope with this type of illness. Primary itching most often affects men, the main peak of the disease occurs in the age group from 30 to 60 years. |
| Secondary itching | Occurs as a symptom of a disease. To eliminate it, a thorough diagnosis, identification and elimination of the causes of the pathology are necessary. |
Infection with worms
Causes of anal itching and risk groups
There can be many prerequisites for the appearance of this disease. Below are the main reasons that can lead to irritation in the anus:
- Diabetes.
- Eczema.
- Seborrheic and contact dermatitis.
- Cracks in the anus.
- Liver diseases.
- Tumors (malignant and benign).
- Manifestation of allergies to certain medications, soap, anesthetics.
- Fistulas in the anus and rectum.
- Psoriasis.
- Infectious diseases (pediculosis, scabies, dermatomycosis).
- Enzyme deficiency.
- Pancreatitis that has become chronic.
- Skin diseases.
- Lack of compliance with basic rules of personal hygiene.
- Synthetic underwear, which causes irritation, dryness, and impedes air flow (especially for women).
- Using personal hygiene products that are not suitable for you (foam and gel for intimate areas that irritate the skin of the perianal area).
As you can see, the reasons for the occurrence of pathology are mainly divided into 2 groups: those associated with excessive moisture in the anus and proctological problems. We cannot exclude the possible presence of parasites (pinworms, roundworms, etc.), due to which night itching is especially common. In women, the development of pathology can be caused by gynecological diseases in which vaginal secretion is disrupted. In cases where it is not possible to determine the cause of the disease, many experts are inclined to believe that the patient has a special form of mental disorder that causes a desire to scratch the perianal area.
What could be the reasons for the disease in you? It is better to discuss this with your doctor. Remember, you should not self-medicate, especially for women who are embarrassed to come to an appointment with a proctologist. It is much more difficult to combat the advanced stage of the disease, and there is also a risk of triggering the development of new diseases. If you find discomfort in your anus, consult a doctor immediately!
The group of people most susceptible to the disease share some of the following common characteristics:
- Obesity.
- Neglect of personal hygiene rules.
- Excessive sweating.
- Close contact with pets.
- Anal sex.
- Using rough toilet paper after defecation.
- Genetic predisposition to constipation, diarrhea, diabetes and fungal diseases.
- Interaction with harmful substances (work in chemical plants, in high temperature conditions, in dust, radiation).
On methods of diagnosis and conservative treatment of anorectal diseases
Despite the fact that anorectal pathology has long attracted the attention of researchers, until now it has received insufficient attention. Basically, surgical methods of treatment are described, to the development of which A. V. Vishnevsky, A. N. Ryzhikh, M. Kh. Levitan, Zh. M. Yukhvidova, V. D. Fedorov, G. I. Vorobyov made a significant contribution.
The purpose of our article is to present traditional and modern methods of diagnosis and conservative treatment of anorectal diseases.
Diagnostics
Since ancient times, methods such as examination of the anus and digital examination of the rectum have been used to diagnose anorectal pathology. Later, rectoscopy began to be used. These techniques have not lost their importance to this day.
Examination of the anus is the first stage of examination if anorectal pathology is suspected. The method makes it possible to identify external hemorrhoids and hemorrhoidal fimbriae, external openings of fistulas, and anal fissures. With idiopathic anal itching and proctitis, weeping and excoriation of the skin around the anus can be observed; with paraproctitis localized in the subcutaneous tissue, hyperemia and swelling of the perianal skin can be observed. When examining the anus, you can see an anal polyp, prolapse of internal hemorrhoids, the mucous membrane of the anal canal, or all layers of the rectum.
Digital examination has always been and remains a mandatory part of a proctological examination. The importance of this method was repeatedly emphasized in his speeches by Academician V. Kh. Vasilenko. He was supported in this by Professor V.M. Mysh, who wrote: “The scope of diagnostic capabilities of sigmoidoscopy is limited to diseases of the intestine itself, while digital examination through the rectum is an extremely valuable and widely available method for studying both the intestine itself and a number of adjacent organs.” In the diagnosis of rectal cancer, digital examination is of particular importance and makes it possible in 88% of cases to detect a tumor, determine the degree of its displacement, the distance from the anus (which is important for choosing the method of surgical intervention), and the narrowing of the intestinal lumen. In addition to examining the rectum, this method determines the condition of neighboring organs (prostate gland in men, cervix and posterior surface of the uterine body in women).
Anoscopy - examination of the anal canal and lower ampullary part of the rectum using rectal mirrors is also included in the group of methods for mandatory examination of patients with anorectal pathology. During this examination, hemorrhoids can be identified, true polyps can be differentiated from hypertrophied anal papillae, which are hyperplasia of the mucous membrane in the area of Morganian crypts, resulting from chronic inflammation in anal fissures, hemorrhoids or proctitis.
Sigmoidoscopy has long been considered the main method for visual examination of the rectum and distal sigmoid. In subsequent years, the rigid sigmoidoscope was replaced by flexible fiberglass sigmoidoscopes, which make it possible to examine the entire left part of the colon, the most common location of tumors.
Total colonoscopy is performed in cases where sigmoidoscopy reveals polyps or malignant tumors in the rectum or sigmoid colon, when an inflammatory process is detected that is not limited to the distal colon, or there is a pathological discharge (mucus, blood, pus) in the intestinal lumen coming from proximal sections.
Ultrasonography. Currently, to recognize complicated rectal pathology, ultrasound devices equipped with rectal sensors have begun to be used, which makes it possible to obtain information about the transmural spread of the inflammatory process in the distal colon, the presence of infiltrates, fistulas and abscesses.
Thus, today colonoscopy and ultrasound using rectal sensors have joined the arsenal of the above-described and well-known diagnostic methods.
Characteristics of anorectal diseases
Hemorrhoids are one of the most common diseases; it affects 10% of the population. Among proctological diseases, hemorrhoids account for 40%.
The views of researchers on the etiology of hemorrhoids are contradictory. Congenital insufficiency of the venous system, venous stagnation, constipation, and disruption of the rectal sphincter mechanism were cited as causative factors. At the same time, none of the hypotheses based on the pathology of the venous system for a long time could explain the origin of the main symptom of hemorrhoids - the release of scarlet blood. In 1975, W. Thomson experimentally proved the existence of arterial and venous components of the hemorrhoid [9]. He formulated the cause of hemorrhoids as a primary weakness of the epithelium of the anal canal, leading to slipping and displacement of the anal “cushions,” which can occur with chronic constipation or prolonged straining during bowel movements [10].
Summarizing the research conducted to study the pathogenesis of hemorrhoids, G. I. Vorobyov and co-authors came to the conclusion that “the leading factors in the pathogenesis of hemorrhoids are dysfunction of the vessels that provide blood flow through the cochlear arteries and outflow through the efferent veins” [1].
There are several classifications of hemorrhoids [1, 4–6].
According to one of the latest classifications, hemorrhoids are divided according to their clinical course into acute and chronic, and according to their form into internal, external and combined. The chronic course of hemorrhoids, in turn, is divided into four stages: Stage I - discharge of blood from the anus without prolapse of hemorrhoids; II - loss of nodes with spontaneous reduction into the anal canal (with or without bleeding); III - periodic prolapse of nodes with the need for their manual reduction into the anal canal, stage IV - constant prolapse of hemorrhoids along with the rectal mucosa [1].
Harbingers of hemorrhoids over a long period of time (from several months to several years) may be discomfort in the anus or anal itching. The first and main symptom of the disease is anorectal bleeding of varying severity - from scanty bloody traces on toilet paper or stool to massive bleeding, leading to anemia in 1% of cases. The blood is usually bright red, but may be dark if it accumulates in the rectal ampulla. At the very beginning of the act of defecation, blood accumulated in the rectum can be released in the form of clots. More often, patients note the release of blood in the form of drops or a splashing stream. Occasionally, bleeding is observed outside the act of defecation. Hemorrhoids are also characterized by pain in the anus, which occurs during bowel movements, walking, and poor diet (eating spicy foods, alcoholic drinks). The cause of pain may be changes in the perianal area with external hemorrhoids or associated complications (anal fissure, thrombosis of the external hemorrhoidal plexuses). Anal itching occurs quite often with hemorrhoids and is a consequence of excessive mucus secretion, contamination of the anal area with blood and fecal particles. This constantly causes a feeling of wetness around the anus and soiling of the underwear. As a result, scratching appears and excoriation of the skin of the perianal area occurs (Fig. 1).
At the initial stages of the disease, conservative therapy is carried out. Attention is paid to nutrition. Alcoholic drinks and irritating foods contribute to increased hemorrhoidal bleeding, so alcohol, seasonings, spicy and salty foods are excluded from food. After defecation and toileting the anus, soft suppositories are inserted into the anus. For a long period of time, in proctological practice, suppositories of the following composition have been deservedly used for these purposes: Extr. Belladonnae 0.015; Novocaini 012; Xeroformi 0.1; But. Cacao 1.7. In case of bleeding, add S. Adrenalini 1:1000 gtt to the above composition. IY. Other candles listed below are currently in use.
In acute hemorrhoids and hemorrhoids complicated by thrombosis of the hemorrhoid, conservative therapy is first carried out, aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process and regulating stool. On the first day, cold is prescribed to the perineal area, in subsequent days - warm sitz baths with a weak solution of manganese after stool and rectal suppositories of the above composition, as well as suppositories or ointment Ultraproct, Posterizan, Proctoglivenol, Relief, Relief Ultra or Advance. These drugs are prescribed rectally in the form of cream or suppositories 2 times a day after stool and at night. In addition to local therapy, drugs that have a venotonic and angioprotective effect are prescribed orally. One of these drugs, Detralex, belongs to the group of flavonoids and is a combination of diosmin and hesperidin. The drug helps reduce the distensibility of veins, increase their tone, reduce stagnation and improve microcirculation. Detralex is prescribed 6 tablets per day for the first 4 days, then 4 tablets per day for the next 3 days.
The second drug in the same direction, Phlebodia 600, is non-micronized diosmin. The drug is prescribed according to the following regimen: 2–3 tablets per day with meals for 7 days, then, if necessary, treatment can be continued at 1 tablet 1 time per day for 1–2 months. For the same purpose, Diovenor 600, an analogue of Phlebodia 600, is used.
In case of prolapse of nodes, frequent exacerbations that do not respond to conservative therapy, and heavy recurrent bleeding, surgical treatment is indicated (Fig. 2). According to the Mayo Clinic, the most satisfactory results were obtained by alloying the nodes with a latex washer and hemorrhoidectomy.
Anal fissure ranks second among anorectal diseases and is a linear or triangular mucosal defect 1.0–1.5 cm long, located near the transitional fold, above the Hilton line. The origin of the fissure is associated with many reasons, but the most important factor is trauma to the mucous membrane of the anal canal by feces, foreign bodies, and damage to it during childbirth. A predisposing factor may be hemorrhoids.
A sharp crack has a slit-like shape, smooth, even edges. Its bottom is made up of sphincter muscle tissue. With a long course of the pathological process, connective tissue grows along the edges of the crack. Its bottom is covered with granulations. In the area of the outer edge of the crack, excess tissue forms the anal (sentinel) tubercle. Thus, an acute fissure turns into a chronic one, which is an ulcer with scarred edges and a scarred bottom (Fig. 3).
Sometimes an acute crack heals on its own, but more often it becomes chronic. As a rule, there is only one crack and most often it is located on the back wall of the anal canal. Occasionally you can observe two cracks that are located one above the other. It is necessary to distinguish true cracks from various superficial damage to the perianal skin. The most common localization of cracks (at 12 o'clock on the posterior wall and at 6 o'clock on the anterior wall) is explained by the structural features of the anal sphincter. It is at 6 and 12 o'clock that the blood supply conditions are worse, and there is a great danger of injury to the mucous membrane during the passage of feces during defecation due to pressure on the posterior and anterior commissures. Trauma to the mucous membrane leads to acute pain due to irritation of numerous nerve endings and sphincter spasm. A vicious circle is formed - an anal fissure leads to a sharp pain syndrome, pain syndrome leads to sphincter spasm, sphincter spasm prevents the healing of the fissure.
A triad of symptoms characteristic of the clinical picture of an anal fissure is pain during and especially after defecation, sphincter spasm and scanty blood discharge. There are differences in the clinical picture of acute and chronic fissures. With an acute fissure, the clinical manifestations are pronounced. The main symptom is acute pain after defecation, lasting several hours. Sphincter spasm increases pain. The pain becomes throbbing. Blood is detected as droplets on the surface of the stool. Due to sphincter spasm and a feeling of fear before defecation, stool is delayed. Taking laxatives increases pain.
With a chronic fissure, the pain is less acute, its duration after stool is 5–10 minutes. Sphincter spasm is mild. When a chronic anal fissure is complicated by marginal fistulas, purulent discharge, itching, and irritation of the perianal skin appear. A chronic crack is characterized by a cyclic course. It can heal, but at the slightest strain or physical stress it opens again.
Detecting an anal fissure is not difficult. Anamnesis and characteristic complaints suggest its existence. The diagnosis becomes clear already upon examination of the anus. When spreading the buttocks, a crack or guard tubercle is discovered at its outer edge. If the crack is not visible upon examination, then a digital examination of the rectum should be carefully performed. In this case, a compaction will be detected on the affected wall of the anal canal. Sigmoidoscopy in the acute period should not be performed due to severe pain and sphincter spasm. In cases where it is necessary to differentiate an anal fissure from other diseases, the study can be carried out after a preliminary injection of 4-5 ml of 1% novocaine solution under the fissure. Differential diagnosis is carried out with coccydynia and the anal form of Crohn's disease.
Conservative treatment of an acute fissure involves, first of all, eliminating pain, sphincter spasm and normalizing stool. To normalize stool, Mucofalk can be used, containing hydrophilic fibers from the outer shell of plantain seeds that retain water. As a result, the volume of stool increases and its consistency becomes softer. The drug is well tolerated by patients and does not increase pain in the abdomen and anus, which is characteristic of many laxatives. A diet limiting spicy and irritating foods is recommended. Once a day, cleansing enemas of boiled water at room temperature are given. In this case, the enema tip is thickly lubricated with petroleum jelly and inserted along the edge of the anus opposite to the one along which the crack is located.
After cleansing the intestines, take warm (38 °C) sitz baths with a weak solution of manganese for 10 minutes. Self-stool should be avoided during this period due to the risk of increased pain and spasm. Laxatives, as mentioned above, are contraindicated, as they can increase pain. Then soft-based suppositories (Relief, Relief Advance, Ultraproct, Posterisan) are inserted into the rectum. Treatment with suppositories is carried out until the crack is completely epithelized. Cleansing enemas, as a rule, are given during the first 10 days from the onset of the disease, after which the stool is independent.
When conservative therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment is resorted to, which consists of excision of the fissure and sphincterotomy. In recent years, closed lateral subcutaneous sphincterotomy has been proposed for the treatment of uncomplicated anal fissure [3, 7], after which pain disappears faster and there are fewer relapses.
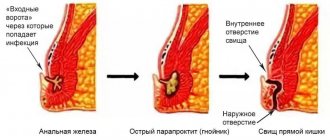
Paraproctitis is inflammation of the tissue surrounding the rectum. Among proctological diseases, paraproctitis accounts for 15%. There are three fascial-cellular spaces: subcutaneous, ischiorectal and pelvic rectal. Accordingly, paraproctitis is divided into subcutaneous, submucosal, ischiorectal and pelvic-rectal. The disease is caused by various microorganisms that penetrate into the cellular spaces from the rectum through the anal glands, damaged mucous membrane, as well as hematogenously or lymphogenously from neighboring organs affected by the inflammatory process.
Of particular importance in the pathogenesis of paraproctitis is direct damage to the mucous membrane of the rectum in the area of the posterior wall of the anal canal, where wide and deep crypts are located, which are the entrance gates of infection. From 6 to 8 ducts of the anal glands open into each crypt. Through them, the infection spreads to the perirectal tissue spaces. According to the clinical course, paraproctitis is divided into acute and chronic. Acute paraproctitis is a purulent inflammation (abscess) of the peri-rectal tissue. Chronic paraproctitis is a consequence of acute inflammation. This is a pararectal fistula, formed after spontaneous opening of an abscess or opening it surgically. The internal opening of a pararectal fistula is a defect in the rectum. The external opening is located on the skin of the perineum (Fig. 4).
In some cases, several fistula tracts and several external openings of the fistula can be observed. The disease begins with a prodromal period (up to three days), during which weakness, headache, and general malaise may be observed. Then chills, fever, and pain in the perineal area appear. When the cellular spaces of the small pelvis are affected by the type of phlegmon, the clinical picture is dominated by general symptoms caused by intoxication. As the process is limited and an abscess is formed, the intensity of the pain increases. It takes on a pulsating character.
The greatest importance in the diagnosis of acute paraproctitis is examination of the anal area and digital examination of the rectum. Upon examination, attention is drawn to hyperemia of the skin in the perineal area on the affected side. Palpation of the perineum is painful, fluctuation can be detected. Digital examination is also painful in many cases and should be performed with caution. This technique should not be neglected, since the information obtained through digital examination can be very valuable for recognizing almost all forms of acute paraproctitis.
Treatment of acute paraproctitis, carried out immediately after diagnosis, is surgical. Basic principles of treatment: 1) opening the abscess; 2) elimination of the internal opening through which the abscess cavity communicates with the rectum.
Chronic paraproctitis, as mentioned above, is a consequence of acute paraproctitis. If, when opening the abscess, the internal opening in the rectum is not eliminated, a rectal fistula may subsequently form. A rectal fistula is characterized by the presence of one or more external openings in the skin of the perineum. Pus, feces and gases may be released from the external openings of the fistula tract. The general condition of patients with chronic paraproctitis suffers little. Pain appears only when the process worsens. Depending on the location of the fistula tract in relation to the sphincter muscle, four types of fistulas are distinguished: subcutaneous-submucosal (intrasphincteric), transsphincteric, complex (extrasphincteric) and incomplete. The latter have only an internal opening in the rectum and do not have an external opening in the perineum. The source of their formation is often an anal fissure.
In the diagnosis of chronic paraproctitis, the same methods are used as for acute paraproctitis. Digital examination of the rectum makes it possible to judge the tone of the sphincter and, in some cases, detect the internal opening of the fistula. Be sure to perform probing with a button probe, which is inserted into the fistula tract through its external opening (Fig. 5).
Using a probe, the direction of the fistula tract and its relationship to the sphincter muscle are determined. Fistulography is a mandatory x-ray examination of rectal fistulas. A test with a dye is used to determine the patency of the fistula tract, the location of the internal opening and purulent cavities in the tissue. Sigmoidoscopy is performed to detect concomitant diseases and high-lying internal fistula openings.
Treatment of all types of fistulas is surgical. The operation can be considered radical only if the opening in the rectum is eliminated by excision of the fistula tract.
Proctitis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum or rectum and sigmoid colon (proctosigmoiditis). Acute proctitis most often has a specific cause. It can be caused by trauma, foreign bodies, mechanical irritation during prostate massage, chemical and thermal burns, and frequent cleansing enemas. The disease may be a consequence of radiation therapy for malignant tumors of the pelvic organs (radiation proctitis) or infections (gonorrheal, dysenteric proctitis). The development of proctitis can be facilitated by diseases of neighboring organs (hemorrhoids, anal fissure, paraproctitis, Douglas pouch abscess, prostatitis, cystitis, vulvovaginitis, etc.). Long-term proctitis and proctosigmoiditis that cannot be treated conservatively should, first of all, be differentiated from distal forms of ulcerative colitis [2].
Acute proctitis has a sudden onset, may be accompanied by fever, chills, is characterized by inflammatory changes in the rectal mucosa, clinically manifested by a frequent urge to defecate, tenesmus due to constipation, a burning sensation and a sensation of a “foreign body” in the anus. Examination of the rectum with a finger and sigmoidoscopy are poorly tolerated by patients due to severe pain. The rectal mucosa is sharply hyperemic, swollen, and bulges into the lumen. The vascular pattern is blurred or absent.
Chronic proctitis, as a rule, is a consequence of an untreated acute disease or has a specific nature. Clinically, the disease is manifested by a periodic feeling of discomfort in the rectum, a feeling of incomplete emptying, periodic exacerbations, accompanied by frequent stools mixed with mucus (sometimes blood), and tenesmus. Endoscopy reveals hyperemia of varying severity and swelling. The diagnosis requires the exclusion of infectious, parasitic and other diseases.
Treatment of acute proctitis is conservative. First of all, you need a diet that excludes all irritating foods and alcohol. After complete cleansing of the intestines, 100.0 ml of warm chamomile infusion (temperature 37–38 °C) is injected into the intestine for therapeutic purposes. An oil enema is given at night (50–75 ml of warm -37–38 °C vegetable oil). Starting from the second week of the disease, morning medicinal chamomile enemas are replaced with enemas of 0.3–0.5% collargol solution. The concentration of the solution is determined by the intensity of the inflammatory process in the intestine. Oil evening microenemas are continued for 14 days. The general course of treatment is 2–3 weeks. After a 10-day break, the course of treatment should be repeated to avoid relapse.
When treating chronic proctitis, the same remedies are recommended as for acute proctitis, but the course of conservative therapy is longer. The best effect is achieved by therapeutic microenemas from a collargol solution.
Anal itching is a pathological condition characterized by persistent scratching in the anus. It is necessary to clearly distinguish idiopathic (primary) anal itching and secondary, often accompanying diseases such as hemorrhoids, anal fissure, helminthic infestations, proctitis and proctosigmoiditis. While the causes of secondary anal itching are known, the etiology of primary (idiopathic) itching is not fully understood.
Often itching in the anus is the patient's main and only complaint. According to the clinical course, acute and chronic anal itching are distinguished. The acute form is characterized by a sudden onset, a constant course, significant intensity and local changes in the skin such as wet eczema with maceration, traces of scratching, hypertrophy of the perianal folds. With chronic itching, on the contrary, the onset is slow, the skin is often dry, thinned, sometimes depigmented, there are no traces of scratching at all or they look like thin linear abrasions.
Diagnosis of the causes of anal itching always begins with determining the type of itching (idiopathic or secondary). First of all, it should be determined whether itching is a symptom of the above diseases (secondary), whether its occurrence is associated with the intake of spicy or salty foods, alcohol, contact with harmful chemicals and radioactive substances, the presence of allergies, etc. From laboratory tests, a blood test is performed for sugar content and three-time stool analysis for worm eggs. In men, urethritis and prostatitis should be excluded; in women, vaginal itching should be excluded.
Treatment of secondary anal itching consists of treating the underlying disease. For idiopathic anal itching, treatment is purely symptomatic.
A diet excluding spicy foods and alcohol is recommended. Thorough toileting of the anus after each act of defecation. After this, ointments (Posterizan, Proctosedyl, Aurobin, Emalan) are injected into the rectum. At night, warm sitz baths with a solution of manganese and microenemas from a 0.33% solution of collargol -50.0 ml are prescribed. The course of treatment is 10 days. For the next 10 days, microenemas (50 ml) of warm vegetable oil are prescribed.
Methods of conservative treatment of anal pathology are being improved as new drugs are developed. From this point of view, one should pay attention to medical collagens, which have become used in the complex therapy of many diseases.
The problem of studying collagen as a new plastic material has long attracted the attention of researchers. At the origins of the development of this direction was Academician of the USSR Academy of Medical Sciences V.V. Kovanov. As a result, a new class of medicinal dosage forms was created - plastic materials with targeted action based on the natural biopolymer of collagen. Currently, medical collagen Emalan, which is a collagen hydrogel for problematic skin and wounds, has become widely used in practical healthcare. It successfully passed clinical trials at the Burn Center of the Research Institute of Emergency Medicine named after. N.V. Sklifosovsky (1995), at the Military Hospital named after. N. N. Burdenko (1999) and in the 72nd Central Clinic of the Ministry of Emergency Situations (2009). It has been established that Emalan reduces signs of inflammation. Under its influence, hyperemia, swelling, pain disappear, itching and peeling of the skin decreases or disappears. All of the above served as the basis for the use of this drug in the treatment of anal pathology.
Of the 112 we observed during 2009–2010. 54 patients had acute and chronic anal fissures, 50 had grade I and II hemorrhoids, and 8 had idiopathic anal itching.
When treating anal fissures, Emalan was included in complex therapy. It was introduced into the rectum on a suppository and in the form of applications to the anus for 3 weeks. In 70.3% of cases, positive dynamics were noted already on days 4–5 from the start of treatment. By the end of the third week, 31 patients had complete healing of the fissures. In patients suffering from hemorrhoids complicated by anal fissure and itching (50), by the end of the third week, against the background of complex therapy, a decrease in symptoms of the disease, such as itching, pain, burning, was observed. The drug turned out to be especially effective in the treatment of patients with idiopathic (8) and secondary (6) anal itching. While taking the drug (gel applications to the anal area 3-4 times a day), a decrease in scratching, maceration and skin hyperemia was noted. By the end of the two-week course, these changes completely disappeared.
Our first experience has shown that the domestic collagen gel Emalan can be successfully used in the complex treatment of acute and chronic anal fissures, proctitis, anal itching and complicated forms of hemorrhoids. The drug makes it possible to increase the effectiveness of therapy and helps reduce treatment time.
Literature
- Vorobyov G.I., Shelygin Yu.A., Blagodarny L.A. Hemorrhoids. M. // "Mitra-Press". 2002. 192 p.
- Grigorieva G. A. Anorectal pathology. Guide to gastroenterology // M.: Medicine. 1996. T3. 606–635 pp.
- Henry M. M., Swash M. Coloproctology and the pelvic floor // M.: Medicine. 1988 (translation from English). 451 p.
- Rivkin V.L., Kapuller L.L. Hemorrhoids // M.: Medicine. 1984. 751 p.
- Rivkin V.L., Dultsev Yu.V., Kapuller L.L. Hemorrhoids and other diseases of the anal canal // M.: Medicine. 1994. 239 p.
- Rivkin V. L., Kapuller L. L. Hemorrhoids. Constipation // M.: Medpraktika. 2000. 158 p.
- Fedorov V.D., Dultsev Yu.V. Proctology. M.: Medicine. 1984. 380 p.
- Haas PF, Fox TA, Haas GP The pathogenesis of haemorrhoids. Disease of the colon and rectum. 1984. T. 27. p. 442–450.
- Thomson WHF The nature of haemorrhoids // British J. of Surgery. 1975. T. 62. p. 542–552.
- Thomson WHF The nature and cause of haemorrhoids. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine. 1975. T. 68. p. 574–575.
G. A. Grigorieva , Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S. V. Golysheva First Moscow State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenova , Moscow
Contact information for authors for correspondence
Classification of anal itching and characteristic symptoms
The disease is divided into 2 types:
1. Primary manifestation.
2. Secondary manifestation.
The primary manifestation of a disorder in the anus is a consequence of dysfunction of the anal sphincter, in which some of the intestinal contents leak out and irritate the skin. A secondary manifestation is a sign of diseases such as hemorrhoids or diabetes. It may also indicate the presence of skin diseases, inflammation of the genital organs, disturbances in the functioning of the sphincter, constipation and diarrhea.
The main symptom of the pathology is itching and burning in the anus, especially worse at night or after eating salty and spicy foods, as well as alcohol. The skin around the anus becomes red and scratchy. Acute itching of the anus is characterized by a rapid onset of the disease, in which eczema and swelling may occur, and for chronic itching it is sluggish, with dry skin.
Manifestations
Itching during hemorrhoids manifests itself in different ways. This can be a debilitating and persistent feeling that makes you want to scratch the entire area around your anus. In this situation, a person is ready for any way to get rid of a negative feeling, especially if he leads an active lifestyle - works or studies, attends various cultural events, plays sports, etc.
Sometimes itching can come in waves, after defecation or after lifting heavy objects, as well as with abuse of alcoholic beverages or chronic constipation.
There are periods, usually associated with remission of the disease, when the itching is not felt at all. Treatment and hygiene can also relieve the discomfort.
Diagnosis of anal itching
Whether there could be other reasons for the appearance of irritation in the anus than those listed above is up to the attending physician to decide. In any case, at your appointment with the proctologist, you must report all the signs of discomfort and pain you experience. To make a complete diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out the following studies:
1. External examination by a specialist.
2. Sigmoidoscopy or anoscopy (diagnosis of the condition of the patient’s rectum) and biopsy.
3. Palpation of the sphincter (to determine a violation in its performance).
4. Rectal smear to check for infection.
5. Analysis of stool for worm eggs and dysbacteriosis.
6. Tests for syphilis and diabetes.
7. Blood test for glucose levels.
8. Skin test using actinolysate, examination of purulent compartments under a microscope.
9. Consultation with other specialists (venereologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist, dermatologist, urologist).
Based on all of the above studies, a final diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed.
How does infection occur?
Infection occurs with the help of one person who infects himself, and in some cases, those around him. In turn, during examination, eggs can actually be found on the surface of bed or underwear, dust that flies in the room. There are especially many worms under the nails, if they are not cut short, when the child scratches the anus, especially in his sleep. Getting into the child's mouth from the surface of toys, but most often unwashed hands or everyday items, food, water, worm eggs begin a new life cycle of their development.
Prevention of anal itching
If you have irritation in the anus that causes severe discomfort, you should see a proctologist as soon as possible. But before meeting with a doctor, you can try to reduce the level of discomfort and alleviate your condition. Here are some tips:
- After defecation, you should wash yourself with water at room temperature instead of using toilet paper.
- For women, it is recommended to wear comfortable cotton underwear.
- It is necessary to follow a diet that limits the consumption of alcohol, hot and spicy foods, as well as foods that lead to constipation or diarrhea. It is better to go to the toilet at approximately the same time, without making excessive efforts.
- Try to touch the irritated area as little as possible.
After completing these steps, signs of improvement and a decrease in discomfort may be observed. It is strongly recommended not to delay going to the doctor, otherwise this will be fraught with the development of complications.
To the tips listed above, you can add a few more useful preventive procedures:
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene. Dry the skin in the anus with gentle movements.
- Use shower products without added dyes.
- For women, periodic consultation with a gynecologist is recommended.
- A little daily exercise is required.
- Stop smoking and alcohol.
- Boost your immunity: walk more, sleep 7-8 hours, eat right and exercise.
Mandatory
It is necessary to constantly ensure that the child has clean hands and cut his nails short, this will help eliminate the causes. In the morning and evening, you must constantly wash yourself using warm water and soap. Before going to bed, it is recommended that the child wear panties that fit tightly to his body, and change them for new ones in the morning. Afterwards, the panties are washed and must be ironed with a hot iron. The bed linen itself is also treated with a hot iron, immediately after the child sleeps.
The apartment is constantly wet cleaned, and toys and pots must be doused with boiling water after use.
There are many reasons why itching occurs and they are all varied. Some are trivial and easy to deal with on your own, but there are others that will require a doctor’s intervention and special diagnostics. In any case, it is better to visit a doctor and determine the true cause of the discomfort.
Diagnosis
Simply complaints of itching, as a rule, are the main reason for the patient to see a doctor. Its main task is to determine the type of disease, form, and causes of secondary itching, which is not so easy to do.
At Es Clinic, a consultation and examination will be carried out, which will help the doctor accurately determine the cause of the itching; if this turns out to be not so simple, a visit to a dermatologist will follow. A rectal examination procedure is also performed.
An indispensable condition is research in laboratories, which involves drawing blood and checking sugar levels, feces are checked for the presence of worm eggs. If the test is positive, an x-ray examination of the colon is performed. One of the goals is to rule out a number of urological diseases or vaginal itching. If intestinal function is poor, an analysis is performed for dysbiosis, and if it is confirmed, special medications are prescribed.
Diagnosis of the causes of burning in the anus
With a similar problem, people most often turn to a proctologist. During the initial consultation, the specialist examines the medical history, analyzes the patient’s complaints, and conducts a digital rectal examination. The doctor can feel hemorrhoids and tumors.
To establish a probable cause or identify a specific disease, laboratory and instrumental research methods are used:
- Coprogram. Advanced laboratory analysis of stool, which helps to detect inflammation, helminthiases, gastrointestinal diseases, dysbacteriosis, and neoplasms.
- Microscopic examination of scrapings from the skin around the anus to detect pinworms (worms).
- Sigmoidoscopy. During an endoscopic examination of the rectum and sigmoid colon, the condition of hemorrhoids is assessed, infectious and inflammatory processes, and cicatricial changes are diagnosed.
- Anorectal manometry. A study of the tone of the anorectal muscle ring is necessary if pathological spasm of the anal muscles or fecal incontinence is suspected.
- Ultrasound of the prostate gland. Makes it possible to exclude urological diseases.
- Determination of glucose in capillary blood. Indicated in case of high probability of metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus.
- Testing for HIV infection.
- Biopsy. If suspicious neoplasms are detected, a biopsy specimen is taken for histology.
Consultation with a urologist, venereologist, dermatologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist and additional research methods - as indicated.
Treatment of burning in the anus
Treatment tactics depend on the causes of the symptom and are aimed at eliminating the underlying disease or provoking factors. To reduce the intensity of the burning sensation, it is recommended to wash the external genitalia and anus with warm water after each act of defecation. It is equally important to choose comfortable, loose-fitting underwear made from natural fabrics.
For proctological diseases, a gentle diet is prescribed to normalize stools and painless bowel movements. The diet limits or completely eliminates fatty foods, spicy foods, and salt. You can take any medications only as prescribed by a specialist.
Conservative therapy
Drugs are selected based on the causes and stage of the disease:
- Hormones. Help stop inflammation and relieve swelling. The use of hormonal ointments topically helps reduce anal burning and discomfort.
- Antibiotics. Infectious diseases are treated with antibacterial drugs, fungal infections with fungicidal agents. When diagnosing parasitic diseases, patients need anthelmintic drugs.
- Rectal suppositories. They reduce the severity of symptoms, facilitate the act of defecation, and protect the rectal mucosa from damage. They use suppositories with an analgesic, healing and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Phlebotropic drugs. Prescribed in the complex treatment of hemorrhoids. They increase the tone of the venous walls, improve microcirculation, which prevents the growth and bleeding from hemorrhoids.
As a general therapy, microenemas with herbal decoctions, oils, and local anesthetics are prescribed. During the acute period, a perineal shower brings relief. The procedure activates blood circulation in the pelvic organs and promotes the resorption of inflammatory foci. To improve the results of therapy, physiotherapy is used: ultrasound, laser radiation.
Surgical intervention
If there are complications, treatment failure, or if indicated, surgical intervention is performed.
In the early stages of hemorrhoids, low-traumatic techniques are used - electrocoagulation (excision with electric current) of the hemorrhoid and sclerotherapy (introduction of special drugs to glue the nodes together).
At the second stage, laser removal of hemorrhoids or latex ligation is effective. A latex ring is placed on the node's stem, which stops its blood circulation and causes death. At the third and fourth stages of the disease, radical surgical excision of the nodes is indicated.
Malignant neoplasms are surgically removed along with the lymph nodes.
The prognosis directly depends on the causes of anal burning, early detection and therapeutic actions. The delicacy of the problem and the feeling of shame leads to the fact that patients do not seek medical help in a timely manner.