Gastroenterologist
Vinogradov
Dmitry Alekseevich
4 years of experience
Gastroenterologist
Make an appointment
Millions of people of all ages suffer from heartburn. And only a quarter of patients turn to doctors for medical help. Symptoms include a burning sensation in the esophagus, a feeling of fullness in the stomach, pain in the lower chest and is accompanied by a bitter, acidic taste in the throat and mouth. Heartburn is not so harmless in its clinical nature. It is periodic or chronic in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and can vary in frequency and intensity. Pharmacy medications provide only temporary relief, so a visit to a gastroenterologist and the prescription of adequate therapy is the main recommendation.
Causes of heartburn
Unpleasant symptoms of heartburn occur due to irritation of the esophageal mucosa. Normally, the environment in the stomach is acidic; it is regulated by hydrochloric acid. In the esophagus – neutral. These two sections of the digestive tract are separated from each other by the sphincter. If the orbicularis muscle does not fully perform its function, reflux occurs (reverse movement of stomach contents). The esophagus is not protected from the negative effects of acid, which causes a burning sensation. The causes of heartburn may include the following:
- gastrointestinal diseases (GERD, ulcers, gastritis, cholecystitis);
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- cancer of the gastric cardia;
- frequent consumption of fresh baked goods, coffee, chocolate;
- drinking alcohol, smoking;
- diet with fatty foods;
- chronic stress;
- taking medications (NSAIDs, to lower blood pressure).
Ask for help
As you can see, there could be several reasons why you experience heartburn. But don't worry: there are many ways to help you get rid of unpleasant symptoms. You can start by being a little more careful about your diet and changing your daily habits.
However, if you are unsure about the symptoms of heartburn, or if you experience heartburn too often and it becomes increasingly uncomfortable, consult your doctor or pharmacist. They will be able to advise you on a drug that will specifically target your symptoms.
How to get rid of heartburn and its consequences
Chronic or frequent heartburn causes an inflammatory disease with a recurrent nature called esophagitis - this is the most common consequence. The resulting ulcers and their subsequent scarring provoke a narrowing of the esophagus, which interferes with food intake. Heartburn may also be accompanied by bloating. To improve your well-being, the following is recommended:
- exclude late dinner before bedtime;
- the upper body should be elevated 15-25 cm during rest;
- immediately after eating, you should not bend over or lie down;
- conduct an audit of food products;
- quit smoking and drinking alcohol;
- Avoid tight belts and clothing that compress the abdominal area.
When to urgently call an ambulance
If heartburn occurs in the stomach from inappropriate food, the situation is not so dangerous. You should be wary of pain and a burning sensation in the chest that occurs due to an attack of angina or an increasing threat of myocardial infarction. With progressive symptoms such as bloody vomiting and black stools, you should call an ambulance. JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) in the Central Administrative District has emergency teams on staff, its own fleet of vehicles and the latest generation equipment. They work 24/7. Severe heartburn and stomach pain may also be due to an exacerbation of the ulcer, which is also a reason to call an ambulance. If necessary, the team will take care of transporting and accompanying the patient to the hospital for hospitalization, where a final diagnosis will be made and treatment will be prescribed.
When to see a doctor
If heartburn in the throat begins to bother you frequently, regardless of the time of day, body position, or with a balanced diet, you should consult a doctor. Attacks cannot be tolerated or ignored due to the possible transition of the underlying causes into a chronic condition. The formation of ulcers in the esophagus due to the constant influence of hydrochloric acid on the mucous membrane provokes bleeding. They can lead to Barrett's syndrome and the subsequent development of oncology. You need to make an appointment to undergo diagnostics and receive heartburn medication to stabilize your well-being.
What is heartburn and why does it happen?
The medical term “gastric heartburn” is a condition in which, after eating, a burning sensation occurs in the epigastric region, which extends from the stomach to the throat, along with abdominal pain, belching, and a sour or bitter taste. Why do we have such unpleasant symptoms? To understand this condition, you need to know how the digestive system works.
In a healthy person, the activity of the pharynx, esophagus and cardinal sphincter (the valve between the esophagus and stomach) is clearly coordinated. The function of the sphincter is to send food from the esophagus to the stomach without delay and to prevent stomach contents from flowing back into the esophagus, even if the person is on his head.
Proper functioning of the valve is very important because it prevents concentrated stomach acid from damaging the esophagus. If the function of the sphincter is impaired and the valve does not close tightly, aggressive gastric juice enters the esophagus, causing the characteristic symptoms of heartburn (burning).
Root causes and treatment of heartburn
Symptoms may return if the underlying cause is not determined. In severe cases, the doctor may recommend going to the hospital to clarify them. At JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) in the center of Moscow, you can undergo diagnostics and take tests to establish the correct diagnosis. For this purpose they prescribe:
- laboratory blood tests (general, biochemical, for the presence of antibodies to Helicobacter pylori);
- gastroscopy;
- urease breath test (detection of Helicobacter pylori infection);
- esophageal pH monitoring;
- esophagomanometry, etc.
Symptom of heartburn during pregnancy
It is a fact that 80% of women experience heartburn when carrying a child from the first months of pregnancy. Increased progesterone in the body relaxes the muscles, which causes dysfunction of the esophageal sphincter. Another reason is increased abdominal pressure due to fetal growth. Heartburn pills (antacids) without complex chemical compounds help to cope with poor health. They usually have a minty flavor, which helps get rid of the sour and bitter taste in the mouth. They are prescribed by a doctor after consultation.
Treating heartburn at home
A fast-acting remedy for heartburn is baking soda in the amount of 1/2 tsp. per glass of water. You need to drink in small sips. The method is suitable only for emergency cases, but with frequent use of sodium carbonate, the acid-base balance is disturbed. To maintain it, you should also give up citrus fruits and carbonated drinks, raw onions and garlic, hot and spicy foods.
Following a diet is better than soda for heartburn during periods of exacerbation. Small meals 5-6 times a day will also be useful. Chamomile tea and drinking low-alkaline mineral waters can also help. Popular folk remedies or how to get rid of heartburn at home is a set of the following recommendations:
- drink tea from St. John's wort and plantain (1 tbsp per 200 ml of water);
- drink 1 tbsp. 15 minutes before meals, infusion of dried dried fruit (20 g per 200 ml of water);
- eat buckwheat daily;
- chew barley grains during an attack.
Diagnostic measures
It is very easy to diagnose the presence of heartburn; it is much more difficult to establish the cause of this pathology. To do this, use a wide range of instrumental techniques:
- X-ray with contrast – records the main disorders of the structure of the esophagus – narrowings, diverticula, hernias;
- radioisotope examination of the esophagus (scintigraphy) – effectively detects hernias, protrusions, tumors;
- MRI of the esophagus, stomach - well reflects the structure of soft tissues, forming a three-dimensional image of the organ, registers the slightest changes in the structure;
- endoscopy of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, or fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) using a long tube with an optical tip - makes it possible to visually examine the structure of the internal walls and assess the degree of damage, as well as measure the acidity of the contents and take a tissue biopsy;
- esophagomanometry – measurement of the contractile activity of the esophagus, coordination of its peristalsis with the work of higher organs;
- daily pH-metry – 24-hour monitoring of changes in acidity in the upper gastrointestinal tract;
- impedancemetry - study of esophageal peristalsis; carried out using a probe with electrodes that measure the difference in resistance (impedance) as liquids, pieces of food, and gas structures pass through the esophagus;
- Ultrasound of the stomach, duodenum, liver, pancreas - evaluates the structure and functioning of organs in dynamics.
Prevention is the best cure for heartburn
Preventing reflux is part of treatment by following a diet and limiting negative factors. Remember that heartburn from water is reduced by diluting the amount of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. Drink it throughout the day. Avoid eating large portions of food and lead a healthy lifestyle. In this case, heartburn and nausea will not bother you. If attacks are frequent and symptoms last for 2-3 months, you need to undergo an examination, which will prevent the exclusion of severe diagnoses.
Types of heartburn
Doctors define two isolated types:
- “Acid” burns to the stomach;
- Heartburn that is bitter or alkaline.
The first type of heartburn occurs when stomach acid enters the esophagus, in which case a characteristic sour taste appears in the mouth along with a burning sensation. When “bitter” heartburn of the esophagus is caused by bile infiltration enzymes, and pancreatic enzymes, which have an alkaline reaction, cause a bitter, unpleasant taste.
Therefore, before starting treatment for heartburn, it is necessary to determine its type, since drugs in an alkaline or acidic environment have opposite properties. For example, if alkaline heartburn takes medications to reduce acidity, the result will be zero, and the unpleasant symptoms will only worsen.
Heartburn with gastritis: which doctor should I contact?
A gastroenterologist specializes in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases. If additional research is necessary, other specialized specialists may be involved. For consultation, examination and treatment, please call +7 (495) 775-73-60 or leave a request for feedback on the website with your contact details. The clinic is located at: Moscow, 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskoy lane, building 10, Mayakovskaya metro station. The following stations are also within walking distance: Belorusskaya, Tverskaya, Novoslobodskaya and Chekhovskaya.
Give me heartburn medicine. And it would be desirable to also help with bloating - are there any such remedies?
Yes, today there are combination drugs that simultaneously neutralize hydrochloric acid and stop the manifestations of flatulence due to the inclusion of simethicone in the antifoam composition. It reduces the surface tension of gas bubbles in the digestive tract, promoting their rupture. An example of such a drug is a combination of aluminum, magnesium hydroxide and simethicone in the form of a suspension. It simultaneously neutralizes hydrochloric acid, reduces gas formation in the intestines, and also envelops the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, protecting it from the damaging effects of aggressive substances [5].
Classification of heartburn
Since heartburn is not an independent disease, but only a symptom, it has no official classification. However, for ease of diagnosis, gastroenterologists conventionally divide heartburn into three degrees of severity:
- Easy. Discomfort in the esophagus occurs no more than once a month. Heartburn in such cases is physiological in nature or is explained by dietary errors. After eliminating the provoking factor, the problem ceases to bother the patient.
- Moderate. Occurs at least once a week and is accompanied by symptoms such as nausea and sour belching. This type of heartburn is highly likely to indicate problems with the digestive system.
- Heavy. Occurs regularly, accompanied by sour belching, nausea, vomiting, discomfort in the abdominal area and unstable stool. It can occur both after meals and on an empty stomach.
Briefly about heartburn
“Heartburn is a feeling of discomfort and a burning sensation that appears in the upper abdomen (epigma) and in the sternum (along the esophagus). May spread from the stomach to the mouth, sometimes accompanied by a bitter or sour taste in the mouth. Heartburn occurs due to the reflux of gastric contents (hydrochloric acid, activated pepsin, bile acid) into the esophagus. The problem may occur periodically or be permanent. There are several causes of burning in the esophagus, among them: chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, gastroesophageal disease (GERD). Interestingly, in 50% of cases it is GERD that causes heartburn. A trigger can also be overeating, eating at night, addiction to fried, spicy and fatty foods, pregnancy, taking certain medications, bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse).”
Chuikova Olga Sergeevna
expert
Gastroenterologist, Department of Therapy, Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia
How long does heartburn last?
Much depends on the reason. If heartburn is caused by a short-term increase in intra-abdominal pressure (for example, when lifting weights), then it can last 30-40 minutes. The same applies to situations when a person lies down to rest after a heavy meal: due to a change in the inclination of the body, the contents of the stomach partially fall into the lower part of the esophagus. But usually, when the body position is normalized, this feeling goes away within an hour, even without medication1.
Factors that provoke heartburn. Image: MedPortal.
If heartburn is caused by eating spicy food or flour products, then it lasts longer - up to several hours, and much depends on the amount of food eaten and the individual characteristics of secretion.
There are situations when heartburn haunts a person constantly, and there are a number of reasons for this - from frequent consumption of alcohol and inappropriate food to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. It is especially difficult for pregnant women: their heartburn increases every day and continues until childbirth.
Heartburn due to hiatal hernia. What to do?
“A hiatal hernia (HH) can also cause heartburn. To eliminate attacks, you must follow a diet, excluding fried, fatty foods, strong tea and coffee, citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, hot and spicy sauces and ketchup. The last meal should be no later than 2-3 hours before bedtime. If you have heartburn at night, it is best to sleep with the head of the bed elevated. It is important to reduce excess body weight and limit the consumption of gas-forming foods (white cabbage, legumes, etc.). Antacids or alginates can be taken as symptomatic therapy. If heartburn does not go away while following a diet and diet, you should consult your doctor to select the optimal treatment regimen.”
Chuikova Olga Sergeevna
expert
Gastroenterologist, Department of Therapy, Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia
Heartburn and reflux disease. The essence of the problem.
Heartburn and reflux disease. The essence of the problem.
The American Gastroenterological Association has prepared a number of brochures with recommendations for patients regarding problems with the digestive tract. This brochure is about heartburn and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
The main thing about heartburn
- Heartburn is the most common symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Heartburn can occur if acid or other stomach contents enter the esophagus.
- Although heartburn is rarely life-threatening, it can significantly reduce the quality of your life. Heartburn affects the patient's daily activities, sleep and diet.
- Heartburn can often be relieved by making behavioral changes, quitting certain habits, or taking over-the-counter medications, but if symptoms persist or become increasingly bothersome, you may need to see a gastroenterologist for further testing, including to rule out more serious conditions.
GERD?
Between the esophagus and the stomach is the lower esophageal sphincter, formed by muscles.
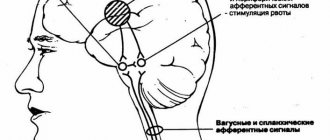
When swallowing occurs, this sphincter opens, allowing food to pass into the stomach. After a swallow, to prevent the return of food lumps and the flow of gastric juice into the esophagus, this sphincter quickly closes. When the lower esophageal sphincter relaxes uncoordinatedly or very weakly, acidic stomach contents can back up into the esophagus. This reflux is called gastroesophageal (gastroesophageal) reflux and often causes heartburn, that is, a burning sensation behind the breastbone, where the ribs meet. In addition to heartburn, symptoms of GERD may include: persistent sore throat, hoarseness, chronic cough, shortness of breath similar to heart-related chest pain, and a feeling of a lump in the throat. If acidic contents from the stomach regularly enter the esophagus, GERD can become chronic. The occurrence and severity of gastroesophageal reflux and heartburn are influenced by various factors, including:
- the ability of the lower esophageal sphincter muscles to open and close correctly
- composition and volume of gastric juice entering the esophagus during reflux
- quality and speed of cleansing of the esophagus from harmful substances that have reached its mucosa
- neutralizing effect of saliva and others.
People experience heartburn and GERD in different ways. Heartburn usually manifests itself as a burning sensation that begins behind the breastbone and travels up to the throat. Often there is a feeling that swallowed food is returning back to the mouth, which is accompanied by a sour or bitter taste. Heartburn usually occurs after eating.
Symptoms
Symptoms of heartburn may include:
- burning in the chest area
- burning behind the sternum and manifestations of reflux, which are aggravated if the patient lies down or bends over.
Sometimes, despite the presence of refluxes that damage the mucous membrane of the esophagus, there are no symptoms of the harmful effects of acid on the esophagus.
How common is heartburn?
Although heartburn is common, it is rarely life-threatening. However, heartburn can seriously limit daily activities and work efficiency. With a proper understanding of the causes of heartburn and targeted treatment, most patients achieve improvement.
Does a hiatal hernia cause heartburn?
| Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and hiatal hernia |
A hiatal hernia allows the stomach to slide into the chest cavity through a hole in the diaphragm.
Although a hiatal hernia does not cause heartburn, it does predispose you to heartburn. A hiatal hernia can cause the esophagus to shorten, which can lead to chronic heartburn. Hiatal hernia can occur in people of any age and often occurs in otherwise healthy people aged 50 years and older. Note: Any chest pain or difficulty swallowing requires immediate medical attention.
All possible causes of such pain should be analyzed .
How to get rid of heartburn?
The recommendations listed below are not universal. Patients should keep a diary so they can be helped to better manage their symptoms. Each of the items listed below contributes to the development of symptoms and should not be avoided until it has been proven that they do not aggravate the symptoms in a given patient. Discuss all of these recommendations with your doctor.
- Avoid foods, drinks and medications that interfere with the action of the lower esophageal sphincter or irritate the lining of the esophagus, such as fried or fatty foods
- chocolate
- mint
- alcohol
- coffee (decaf coffee too)
- carbonated drinks
- ketchup and mustard
- vinegar
- tomato sauce
- citrus fruits and their juices
- aspirin, anti-inflammatory and pain relievers, except acetaminophen.
- Reduce the portion sizes of food you eat. Don't overeat!
- Eat food no later than 2-3 hours before going to bed.
- Raise the head of the bed by 10–15 cm, using, for example, telephone books.
- If you are overweight, lose weight.
- Avoid situations that may increase pressure on the abdominal cavity, as this can provoke reflux from the stomach into the esophagus. Try simple things like avoiding tight clothing or body-hugging outerwear. Less obvious causes of reflux include squats, leg lifts and abdominal exercises.
- Quit smoking, as cigarettes reduce the ability of the lower esophageal sphincter to work properly.
If heartburn does not go away
| Serova O.A. (YarOKB) monitors pH using the Gastroscan-24 device |
| Device and probe for impedance pH-metry “Gastroscan-IAM” |
| Storonova O.A. ( MMA named after I.M. Sechenov) for processing the results of esophageal manometry obtained on the Gastroscan-D |
To relieve infrequent heartburn, over-the-counter medications may be helpful if taken strictly as directed.
If long-term and frequent use of over-the-counter medications becomes necessary, or if they do not completely alleviate the patient's condition, a gastroenterologist should be consulted. Patients with severe heartburn or heartburn that does not improve despite the above measures may need a more complete evaluation. Various tests and diagnostic procedures are currently used to determine the causes of heartburn and decide on further treatment.
Endoscopy
- a procedure during which a thin flexible tube with a video camera and a light at the end is inserted into the patient's esophagus. Through this tube (endoscope), the doctor can see and evaluate the condition of the esophageal mucosa.
Biopsy
- taking a small piece of the esophageal mucosa for examination.
Esophageal manometry
- a procedure for measuring pressure in the esophagus, necessary to determine critically low pressure in the lower esophageal sphincter and detect other disorders in the functioning of the esophageal muscles.
Impedancemetry
- a procedure in which the speed of fluid movement in different parts of the esophagus is measured. When used in conjunction with pH monitoring, impedance monitoring provides the clinician with a more complete picture of reflux in the esophagus, identifying both acidic and non-acidic reflux episodes. A combined test (pH + impedance testing) is also recommended for patients refractory to proton pump inhibitor therapy with persistent typical symptoms of GERD, chronic cough, unexplained excessive belching and regurgitation.
Acidity monitoring ()
— For difficult-to-diagnose patients, doctors can choose one of two methods for measuring acidity (pH) in the esophagus. In the first option, a thin tube - a pH probe - is inserted into the patient's esophagus through the nose, the other end is connected to a small recording device that the patient wears on a belt. With their help, reflux events during normal daily activities and the patient’s normal diet are recorded over a 24-hour period.
In the second method, instead of a tube (pH probe), a small wireless pH sensor is used, which is attached to the esophageal mucosa. It transmits the collected data to a receiver worn on the patient's belt for 24 to 48 hours. This is also where the patient carries out normal daily activities. After some time, the disposable sensor detaches from the esophageal mucosa and exits naturally from the digestive tract.
Surgery.
A small number of patients with heartburn may require surgery due to severe reflux and poor results of medical treatment. To reduce the number of refluxes, a fundoplication operation is performed. Patients who do not want to take medications necessary to relieve heartburn are also candidates for surgery.
Medicines to relieve heartburn
| Various antacids | |
| Foaming agent Gaviscon and H2 blocker Quamatel (famotidine ) | |
| Prescription Ultop in Russia and over-the-counter in the USA Prilosec OTC (both PPI omeprazole) | |
| Prokinetics Ganaton (itopride) and Motilium (domperidone) | |
There are a number of over-the-counter and prescription medications available to help relieve heartburn. These drugs inhibit acid production or help the stomach muscles empty it. Many of these drugs may be effective in combination with each other due to their different mechanisms of functioning. To find out which medicine (or medicines) is best for a particular patient, a consultation with a gastroenterologist is necessary.
| Antacids. Often the first medications recommended to relieve heartburn and other symptoms of GERD are antacids, which neutralize stomach acid. They are sold without a prescription. Patients taking antacids may experience a variety of side effects, including diarrhea and constipation. Some antacids may be an additional source of calcium. |
| Foaming agents . These over-the-counter medications work by creating a foamy barrier at the top of the stomach that prevents reflux. |
| H2 blockers . H2 blockers are available in both over-the-counter and prescription versions, and they reduce stomach acid secretion and provide short-term symptom relief. H2 blockers are effective in about half of patients with GERD symptoms. |
| Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). These medications (formerly all prescription drugs, but now some are available over-the-counter) are more effective than H2 blockers and can relieve symptoms and heal the esophageal lining in almost all patients with GERD. |
| Prokinetics . These prescription medications help strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter and increase the rate at which the stomach emptys. However, their side effects, including fatigue, drowsiness, depression, anxiety and problems with physical activity, may limit their use. |
Treatment for GERD does not improve lower esophageal sphincter function.
If acid suppression treatment is stopped, GERD symptoms are likely to return. Even if this does not happen, the complications listed above may occur asymptomatically, which makes it extremely important to consult a gastroenterologist before stopping any kind of treatment. Translator's Notes. 1. In Russia, the list of prescription or over-the-counter drugs is different than in the United States. However, at the time of translation of this brochure (2012), it was not a problem to buy an official prescription drug from the drugs listed above without a prescription in Russia. 2. In the United States and some other countries, there are a number of drugs sold with a prescription and at the same time without a prescription (Over-the-Counter; OTC). At the same time, the over-the-counter version differs from the prescription version only in the reduced content of the active substance. 3. Illustrations added during translation.
We also recommend the following articles: “British Society of Gastroenterology's advice for heartburn and gastroesophageal reflux”, “Is it just minor heartburn or something more serious?”, “Advice from the American College of Gastroenterology for problems with swallowing and heartburn”, “A conversation with Dr Donald Castell” What is GERD?”, “Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in questions and answers” and “Heartburn”, “Not a joke, but a stomach complaint!” Back to section
Prevention
To avoid heartburn, you should carefully take care of the health of your entire digestive system. Anyone who is predisposed to high stomach acidity should adhere to the following rules:
- Adjust your diet - do not overeat, give up harmful acid-forming foods - refined sweets, fried foods, smoked foods, marinades, hot and spicy dishes. The last meal should be 4 hours before going to bed.
- Adjust the body's water balance - drink 1.5-2.5 liters of pure still water per day.
- Maintain correct posture - in a “crouched” position, the stomach is compressed and the cardiac valve automatically opens slightly.
- Watch your weight - it should not go beyond the norm, otherwise the likelihood of heartburn increases many times over.
- Get rid of bad habits - quit smoking, limit your alcohol consumption.
- Take medications strictly according to indications, following the dosage and rules of administration.
- Avoid sudden physical activity.
- Try not to tighten the epigastric area with tight, tight clothing and belts.