Content:
- Determination of intermenstrual bleeding in the middle of the cycle
- Types of intermenstrual bleeding
- Causes of bleeding and menstruation in the middle of the cycle
- Diagnosis of bleeding in the middle of the cycle
- Treatment and prevention of bleeding in the middle of the cycle
- Poor blood flow during pregnancy
Many women experience menstruation in the middle of their cycle at least once in their lives.
Naturally, an irregular menstrual cycle causes anxiety in women. Such disorders can occur in teenage girls and women of reproductive age. Often, spotting in the middle of the cycle is not a symptom of any disease and is considered normal. But sometimes the appearance of bleeding between periods can be a sign of serious gynecological diseases.
Determination of intermenstrual bleeding in the middle of the cycle
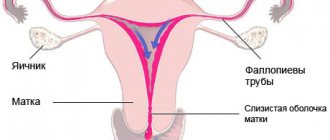
Menstruation is one of the phases of the menstrual cycle of the female body, characterized by the release of blood from the vagina. The beginning of the menstrual cycle is counted from the first day of menstruation.
Sometimes it can be difficult to distinguish dysfunctional uterine bleeding from normal menstruation. Many girls do not remember when their menstrual cycle began and do not know how to calculate their menstrual cycle, so they may mistakenly think that menstruation came earlier or later than expected. For each woman and girl, the duration of the monthly cycle is individual
How to calculate the monthly cycle? It is not difficult. The easiest way is to keep a monthly calendar. It needs to mark 1 day of the onset of menstruation and 1 day of the next menstruation. The number of days between them will be the duration of the menstrual cycle. You need to know that normal menstruation lasts 2-7 days, and the normal menstrual cycle is 21-35 days. The most optimal duration of the monthly cycle is 28 days. Women who experience an irregular menstrual cycle should consult a gynecologist.
Ovulation is the process of the release of a mature egg from the follicle. In women with a normal monthly cycle, ovulation occurs approximately on the 14th day from the start of menstruation. With an irregular menstrual cycle, it may occur earlier or later than this time. After ovulation, the level of estrogen in the female body decreases, and bleeding does not occur because the corpus luteum maintains hormonal balance. A sharp increase or decrease in the level of the hormone estrogen during ovulation can provoke uterine bleeding between, before and after menstruation, and this is not a deviation from the norm. This phenomenon is observed in 30% of women.
Menstrual irregularities
Iron deficiency
Menopause
Climax
Uterine cancer
Cervical cancer
13431 02 February
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Menstrual irregularities: causes of occurrence, what diseases cause them, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Menstrual cycle disorders (MCI) are not a pathology, but only a symptom of problems in the female body. A physiologically normal manifestation of the ongoing ovarian-menstrual cycle is the occurrence of menstruation with an individual frequency and duration for each woman. Menstruation is the name given to repeated uterine bleeding, during which an unfertilized egg, endometrial particles and mucous secretions from the cervix are released from the body along with menstrual blood. Normally, they are not accompanied by significant blood loss due to rapid contraction of blood vessels, and their volume is about 150 ml.
The menstrual cycle is not only menstruation, but also the maturation of the egg in the ovary, ovulation and the growth of the endometrium for the potential introduction of a fertilized egg into it.
A healthy woman of reproductive age may experience anovulatory menstrual cycles, during which fertilization does not occur due to the lack of release of the egg. With age, the number of such cycles increases.
Menarche (first menstruation) usually develops by the age of 11-15 and indicates the readiness of the woman’s reproductive system for fertilization. The time at which menarche appears varies from person to person and depends on many factors, such as weight, diet with sufficient fat, heredity, etc.
Types of menstrual irregularities
The menstrual cycle depends on the coordinated functioning of the endocrine system, so the most common cause of its disorders is hormonal imbalance.
- Disorders associated with pathology of the brain (hypothalamic-pituitary structures), which entail a failure of the neuroendocrine regulation of sexual function.
- Pathology of the uterus and/or ovaries.
- Congenital pathologies, including chromosomal ones.
- Diseases of other endocrine organs, for example, hypo- and hyperthyroidism.
Menstrual irregularities after 40 years of age may be associated with the decline of the reproductive function of the female body, while the amount of estrogen naturally decreases, the number of anovulatory cycles increases, and dysfunctional uterine bleeding may occur.
The unevenness of the menstrual cycle in girls of puberty is explained both by the incomplete formation of the reproductive system and by the widespread obsession with diets at this age, in which the body does not receive enough fats necessary for the synthesis of sex hormones.
Symptoms of menstrual irregularities
:
- Changing the duration of the cycle towards decreasing (less than 21 days) or increasing (more than 35 days).
- Delayed menstruation with normal frequency of previous ones.
- Amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation in a woman of reproductive age for more than 6 months (can be primary and secondary; secondary is typical for girls of puberty).
- Change in the volume of menstrual blood loss towards increase or decrease.
- Change in the duration of menstruation towards a decrease or increase.
- The appearance of intermenstrual discharge of varying degrees of severity.
- Clinically pronounced pain syndrome (algomenorrhea, algomenorrhea).
With an increase in the volume and duration of menstrual bleeding and the appearance of acyclic bleeding, there is a risk of developing iron deficiency anemia.
For many women, infertility is associated with menstrual irregularities - the absence of pregnancy within 1 year of regular sexual activity without the use of contraception. At the same time, the presence of anovulatory cycles often does not manifest itself in anything other than the absence of conception, so the woman considers herself reproductively healthy.
Menstrual cycle disorders at different age periods of a woman’s life
Juvenile period (up to 21 years). Characterized by delayed menstruation, pubertal bleeding, hair loss, insufficiency or excess body weight. Stress and changes in the sleep-wake cycle can be a provoking factor.
Reproductive period (up to 45–50 years). It is necessary to distinguish between pathological causes of menstrual irregularities and physiological ones.
Physiological reasons include changes in the menstrual cycle due to pregnancy, breastfeeding, and the use of intrauterine contraceptives.
One of the common pathological causes is the formation of a follicular cyst: the egg is not fertilized, excessive growth of the follicle is noted, which leads to the growth of the endometrium. This process can last up to 6–8 weeks, resembling the development of pregnancy, but then heavy menstruation follows, which is dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Pathological bleeding can develop during the ovulatory period, which is associated with insufficiency of the luteal phase (that is, hormonal imbalance). Increased changes in the menstrual cycle should be expected after an abortion (spontaneous (miscarriage) or medical, including medicinal). Restoring the menstrual cycle usually takes about three months; if there are complications, the process becomes protracted.
Menopause and premenopause. During premenopause, changes in hormonal levels in conditions of declining reproductive function lead to disruption of cyclicity and heavy menstruation. In addition, women complain of unexplained mood swings and autonomic disorders (the so-called menopausal syndrome).
Uterine bleeding during menopause is an alarming symptom and requires immediate medical attention.
Pregnancy with an irregular menstrual cycle is possible, but its occurrence depends on the severity of the disorder. Often, menstrual irregularities lead to spontaneous abortion in the early stages.
Which doctors should I contact if I have menstrual irregularities?
Any irregularity in the menstrual cycle requires contacting a gynecologist. In most cases, these disorders have a favorable outcome, but about 10% are gynecological cancers. If necessary, the gynecologist can prescribe a consultation with an endocrinologist.
Diagnosis of menstrual cycle disorders
The leading role in the diagnostic search is played by collecting anamnesis with the obligatory clarification of many factors: the presence of pregnancies and the characteristics of their course, methods of contraception, previous diseases, surgical interventions, determination of body mass index.
To exclude inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, most often caused by infections such as gonococcus, genital herpes, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, chlamydia, gardnerella, spirochete pallidum, trichomonas, cytomegalovirus, a smear is taken on the microflora to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to antimicrobial drugs.
Types of intermenstrual bleeding
Intermenstrual bleeding often occurs 10-16 days after the end of the last menstrual period. They are not very abundant and last from 12 to 72 hours. But if the bleeding lasts longer or gets worse, consult your gynecologist.
Spotting in the middle of the cycle is more common than intermenstrual bleeding. A woman's vagina comes out with a little blood that can barely be seen on the toilet paper. This is usually mucus that has a pinkish color. Such discharge appears approximately 14 days before the onset of menstruation and is not a pathology. Intermenstrual bleeding indicates that the egg is ready for fertilization.
Frequent periods can also occur with proyomenorrhea (short monthly cycle). Periodically appearing and usually not intense bleeding lasts 2-3 days. Such spotting is caused by premature rejection of the uterine mucosa due to a decrease in estrogen production in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
During ovulation
To learn to distinguish normal secretion from pathological one, it is necessary to find out the causes of cervical mucus during ovulation. In the middle of the menstrual cycle, vaginal secretions cause the following changes in the body:
- Release of a mature egg with concomitant rupture of the follicular sac.
- A significant increase in estrogen levels, and this hormone makes the cervical mucus from the cervix thinner. The reproductive system creates optimal conditions for the movement of sperm in the uterus and fallopian tubes.
It is these factors that determine what color the secretion will be, its quantity and consistency, provided there are no pathological processes in the body.
You need to know what discharge should be during ovulation. They are characterized by the following signs:
- Color. Transparent, slightly white, pink.
- Consistency. Mucus, egg white state, snot-like, sometimes watery (see photo).
- Volume. About one teaspoon per day (individual indicator).
- Aroma. Completely absent, but a sour smell of discharge without itching is allowed due to the vaginal microflora.
If such discharge is present and the stomach hurts in the middle of the cycle, ovulation has begun.
Remember that every body is individual, so the amount and shade of cervical fluid may vary from woman to woman. The main rule for everyone is the absence of itching, burning, redness of the genitals, as well as severe, especially cutting pain.
When does discharge begin during ovulation?
The approximate date can be calculated using your calendar:
- Determine the duration of the menstrual cycle.
- Divide this number by two.
- We count this number of days from the beginning of the last menstruation.
The resulting date will serve as the beginning of the fertile period.
Rarely does the ovulatory phase occur, which occurs precisely in the middle of the cycle. This is due to hormonal levels, physiological and psychological factors. For more accurate forecasting, it is necessary to measure basal temperature for several months and record the results. According to doctors, for most of their patients, favorable days occur from the 11th to the 21st day of the cycle.
How many days does the discharge last?
To answer this question, it is necessary to find out the duration of ovulation. For everyone it is almost the same - approximately 48 hours. The mature egg remains viable for another day, so the characteristic discharge may still continue.
Cervical mucus, caused by a favorable time for conception, can last only a couple of days, and then gradually thickens due to an increase in progesterone content.
On a note! When vaginal fluid does not tell you anything about the beginning of the fertile phase, it is worth buying a special test that will show two stripes at the moment the egg leaves the ovary.
Additional symptoms
Vaginal discharge is not the only sign of the best time for fertilization. You also need to take into account the following signals:
- may pull in the lower abdomen;
- basal temperature increases (37.1–37.3°);
- strong sexual attraction to partner;
- minor pain and breast engorgement.
Signals of conception
The signs of pregnancy and egg release are very similar, so it is difficult to determine successful fertilization right away. Implantation bleeding causes pink and brown discharge to appear during ovulation, but it occurs after about a week and a half, when the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus.
Remember that liquid and watery secretions are practically excluded, because the reproductive system prepares safe conditions for the development of the fetus, and therefore the vaginal mucus becomes thicker.
No secretion
If you have no discharge, this does not at all indicate pathology or lack of ovulation . A large number of girls do not feel anything at the moment the egg leaves the ovary; they even experience vaginal dryness. Under such conditions, it is unlikely that conception will occur, but fertilization cannot be ruled out. After all, the lack of secretion may be due to low estrogen levels.
It is possible that instead of mucus, uncharacteristic creamy, smearing marks are observed on the panty liner. The reason most often lies in hormonal background, dietary habits and other external factors (strong experiences, stress).
There is no need to sound the alarm when you notice:
- copious (wet) secretion for only a few days;
- slightly yellowish or creamy marks on panty liners;
- bloody smear;
- watery, homogeneous discharge without lumps.
Women often describe white discharge during ovulation. However, it is worth considering that it is colorless mucus that indicates a favorable period for conception. When it comes to cloudy or white secretions, then most likely ovulation is behind you or the vaginal microflora is disturbed.
Remember that normal cervical fluid cannot be released against the background of unpleasant sensations, which most often indicate negative processes in the body.
What does pathological secretion look like when an egg is released?
Failure of the reproductive system cannot be ruled out if the discharge is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Yellow with a green, gray tint (sexually transmitted infection).
- White curds with a sour smell, itching, burning (thrush).
- Heavy bleeding during ovulation - the pad gets wet in less than an hour (bleeding).
- Very liquid, have a foamy consistency (inflammation, infection).
- Dark brown, almost black (endometriosis).
They speak with confidence about a violation when the secretion is supplemented:
- unpleasant smell of fish, rot;
- clotted blood;
- pus and lumps;
- lasting more than two or three days;
- high body temperature;
- severe pain;
- systematic burning, redness and itching of the genitals.
Such symptoms should not be ignored, and visiting the hospital and getting tested is the key to the fastest possible recovery, and will also help to identify pathologies in time in the early stages of development.
Causes of bleeding and menstruation in the middle of the cycle
Often, an irregular menstrual cycle is observed in teenage girls, since at their age the hormonal background has not yet become stable. If, after 2 years after the first menstruation, girls still have periods in the middle of the cycle, then you need to consult a gynecologist who will prescribe treatment to normalize the menstrual cycle.
Constant strong stressful situations, smoking, and alcohol have a bad effect on the body. As a result, women experience irregular menstrual cycles and may experience periods mid-cycle. Such phenomena often occur in women with frequent dysfunction of the genitourinary system; bleeding in such cases is more profuse.
If you move to another city, country or go on vacation to the sea, be prepared for the fact that the start of your menstrual cycle may occur earlier than usual and your period may begin in the middle of the cycle. After all, climate change is also stressful for the body, and it needs time to get used to it.
There can be many factors that provoke bleeding between periods. The main ones:
- pathologies of the endocrine system (diseases of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands, etc.);
- uterine fibroids;
- hormonal disbalance;
- miscarriage;
- the presence of an intrauterine device;
- gynecological procedures (cauterization or cervical biopsy);
- taking certain medications and contraceptives;
- vaginal trauma and vaginal infections.
- depression and stress.
- infectious diseases;
- poor blood clotting;
- deficiency of vitamins K and C;
- inflammation of the urogenital system;
- pathologies of the development of the internal genital organs of a woman (uterine inflection);
- ovarian tumors and cysts;
- chronic diseases (heart, kidney, liver and metabolic disorders);
- physical injuries.
Also, intermenstrual discharge may indicate such serious problems of the female genital area as uterine cancer, polyps and fibroids of the uterus, and the presence of adhesions.
Possible pathological causes of brown discharge: what could it be?
Hormonal disbalance
Estrogen helps regulate the thickness of the uterine epithelium. If there is too little estrogen, the uterine lining may shed during the cycle, resulting in brown or other unusual discharge.
Low estrogen levels can also cause:
- Hot flashes
- Insomnia
- Mood swings, depression
- Difficulty trying to concentrate
- Infections of the genitourinary system
- Weight gain
Ovarian cyst
An ovarian cyst is a small sac-shaped formation filled with fluid that appears on the ovary. A follicular cyst can form if the egg fails to successfully leave the ovary during ovulation. Such a cyst can form asymptomatically and often goes away on its own after a few months. Sometimes the cyst does not go away on its own and begins to increase in size. If this happens, it can cause a number of symptoms, including brown discharge. Cysts that continue to grow in size can be very dangerous and can twist or crush the ovary. If you suspect that you may have a cyst, you should consult your doctor for advice.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
STIs can cause bleeding and brown discharge. Many diseases in this group are asymptomatic in the early stages (for example, gonorrhea and chlamydia). Over time, the following symptoms may appear: pain when urinating, a feeling of pressure in the pubic area, vaginal discharge and bleeding between periods.
Bacterial vaginosis is also a type of infection, but is not necessarily transmitted only through sexual contact. It appears when there is an overgrowth of certain types of bacteria that are present in the healthy microflora of the vagina. This condition may cause changes in the texture, color, or odor of vaginal discharge.
If you suspect that you may have contracted an STI or other infection, be sure to visit your doctor. Without treatment, such infections can lead to chronic pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility and chronic pain.
Endometriosis
With endometriosis, the tissue that lines the walls of the uterus grows outside the uterus. This condition often causes severe pain, heavy periods, and bleeding between periods. If endometrial tissue is unable to leave the body when your period arrives, it can cause very severe pain, brown discharge and problems with fertilization.
Other possible symptoms:
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Diarrhea
- Pain during penetrative sex and urination
- Constipation
- Bloating
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
With PCOS, the menstrual cycle is often unstable. Many women with this condition have only 9 periods per year. With polycystic disease, it is common to experience bloody brown discharge between periods due to lack of ovulation.
Other possible symptoms:
- Darkening of the skin
- Weight gain
- Depression, anxiety, mood swings
- Thinning hair and hair growth in areas of the body that are not typical for women
- Headache
- Acne
Ectopic pregnancy
Sometimes the fertilized egg is implanted not in the uterus, but in the fallopian tubes, ovaries or on the cervix. This condition is called an ectopic pregnancy.
In addition to brown discharge, it can cause:
- Acute pain in the abdomen, pubic area, neck and shoulders
- Fainting
- Dizziness
- Feeling pressure
- Unilateral pain in the lower abdomen
If you experience at least one of these symptoms in addition to the brown spot, then you need to call an ambulance. Without treatment, an ectopic pregnancy can cause a ruptured fallopian tube and severe bleeding. This is deadly.
Miscarriage
About 10-20% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage, usually this happens before the 10th week of fetal development. Symptoms often appear very quickly and include brown discharge and heavy bleeding.
Other possible symptoms:
- Fainting
- Dizziness
- Vaginal discharge contains tissue and blood clots
- Pain and cramping in the lower abdomen
In the early stages of pregnancy, spotting is often completely normal, but you should report it to your gynecologist.
Lochia (bloody discharge after childbirth)
Lochia is the name for bloody discharge that occurs in women for 4-6 weeks after childbirth. Usually at first they are very abundant, scarlet in color, with small clots. After a few days, the bleeding subsides and turns pinkish or brownish. After 10 days, the discharge changes again and becomes yellow or creamy and then goes away. Contact your doctor if the discharge has a foul odor, fever, or large clots. These could all be signs of a bacterial infection.
Diagnosis of bleeding in the middle of the cycle
First of all, to diagnose the causes of intermenstrual bleeding, a gynecological examination is necessary. In addition, you must undergo the following examinations:
- cytological studies of aspirate from the uterine cavity;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- study of the hormonal background of the body;
- thyroid examination;
- hysteroscopy and curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal;
- histological examination of scrapings obtained from the uterine cavity and cervical canal.
Also, if necessary, the gynecologist can prescribe a study of the pituitary gland using magnetic resonance imaging, radiography, computed tomography. Sometimes the brain is also examined using these methods.
Treatment and prevention of bleeding in the middle of the cycle
Treatment methods for bleeding in the middle of the cycle depend on the causes of this deviation, as well as on the woman’s age. Treatment can be conservative or surgical. In case of ovulatory bleeding, conservative treatment is carried out. For anovulatory bleeding (not associated with ovulation), both surgical and conservative treatment may be necessary. The exception is anovulatory bleeding in adolescents, when surgical treatment is used only as a last resort.
Conservative treatment is based on the use of hormonal drugs to normalize the irregular menstrual cycle and stop bleeding. Your doctor may also prescribe sedative medications to treat untimely periods caused by stress.
For severe bleeding, women are prescribed iron supplements. It should be remembered that a balanced diet (including foods such as beef, legumes, liver, vegetables and fruits), proper rest and sleep will help restore health faster.
To prevent bleeding in the middle of the cycle, you need to: regularly see a gynecologist, refuse abortions, have a regular sex life, control your weight, play sports, give up bad habits.
If you notice that your period starts earlier or later each time, please consult a qualified healthcare professional. Untimely treatment of pathologies that cause disruption of the monthly cycle and bleeding can lead to anemia, infertility, and cervical cancer.
Poor blood flow during pregnancy
During pregnancy, it is extremely important to continuously monitor the state of the maternal body of the mother and the baby, it is important that they perform all vital functions. One of the most significant studies is the analysis of blood flow in the arteries of the uterus, the woman’s umbilical cord, as well as cerebral vessels and the fetal aorta. The main causes of perinatal morbidity and mortality include disorders of the uteroplacental blood flow of 1A, 1B, second and third degrees.
Blood flow in the placenta
The placenta, in which the fetus is located, supplies the embryo with nutrients, as well as oxygen from the mother’s blood; it also removes waste products from the child’s body. It is this organ that unites two rather complex vascular systems - the female, which connects the vessels of the uterus and placenta, and the fetal, which passes into the umbilical arteries and leads to the child.
The circulatory systems mentioned above are separated by a membrane, which does not allow maternal and child blood to mix. The placenta is a kind of barrier that is resistant to numerous harmful substances, as well as viruses.
Often, for completely different reasons, placental insufficiency may appear, which inevitably affects the performance of transport, metabolic, trophic, endocrine and other vital functions of the placenta. In this condition, the metabolism between the maternal and child organisms deteriorates significantly, which is fraught with various consequences.
What are the causes of impaired placental blood flow?
Poor circulation in the uterine cavity can be caused by pneumonia, increased blood pressure, various intrauterine infections, as well as insufficient oxygen supply to the child’s body (hypoxia).
To diagnose the blood flow system in modern obstetric practice, three-dimensional ultrasound (so-called Doppler ultrasound) is used, with which the vessels are visible in a 3D (three-dimensional) image. With the help of this diagnostic technique, there is a prospect of diagnosing retroplacental bleeding and assessing cardiac malformations by monitoring blood flow. This technique is irreplaceable, since with its help it is possible to examine defects even in the most microscopic vessels that form the microvasculature, to observe the peculiarities of the formation and development of intraplacental hemodynamics, and in addition to control the amount of nutrients, as well as oxygen, that should enter the fetal body . New prospects have opened up for the early detection of obstetric complications, and if treatment or correction is started without wasting time, then circulatory disorders and subsequent pathologies associated with it can be almost completely avoided.
Hemodynamic disorders during pregnancy
Hemodynamic disorders are divided into 3 degrees of severity:
1. 1st degree includes two subtypes:
- disturbance of patello-placental blood flow 1Is the mildest. Fetal-placental blood circulation is preserved with it. Intrauterine infections often lead to this problem;
- in degree 1B, uteroplacental blood flow is preserved, but fetal-placental pathologies appear.
2. Grade 2 is characterized by the presence of disturbances in both blood flow systems, however, these disturbances do not carry any fundamental changes. 3. In grade 3, uterine circulation disturbance causes defects in normal blood circulation at the level of the fetus.
In the case of the first degree of violations, timely detection and adequate treatment can avoid fetal death. In the case of the second degree, perinatal mortality is about 13.3 percent, in the case of the third - 46.7 percent. During Doppler diagnostics, it was revealed that treatment aimed at correcting placental insufficiency in women with third-degree uterine blood flow disorders was ineffective. In this situation, with conservative childbirth, perinatal mortality was 50 percent, then, thanks to a cesarean section, losses can be avoided. 35.5 percent of newborns are admitted to the intensive care unit with grade 1 blood flow disorders, 45.5 percent with grade 2, and 88.2 percent with grade 3.
After ovulation
To understand what discharge should be after ovulation, it is necessary to determine the current state of the body. The nature of vaginal secretion always changes after ovulation, but supplemented by other signs, indicates the beginning of the gestation period or a health problem.
Conception did not occur
If conception is not accomplished, then spotting after favorable days cannot be considered normal. The second half of the menstrual cycle in this case has its own characteristics:
- predominance of progesterone in the body;
- first a sticky or sticky state of the cervical fluid;
- increased thickness of mucous secretion;
- transparency is replaced by a white, beige shade of discharge;
- gradual decrease in secretion volume.
The characteristics of the discharge can be compared with the photo:
Sometimes cervical mucus disappears completely after ovulation, appearing in copious amounts shortly before menstruation or during sexual intercourse. Therefore, a woman may not have any discharge, and this is not a cause for concern. But excessive vaginal dryness should be discussed with your doctor.
White
A huge number of women experience white discharge after ovulation, which is normal if it does not cause any particular discomfort in the perineal area. You can mark:
- thick, white, odorless, creamy discharge (the influence of progesterone);
- homogeneous light beige, yellowish (epithelial cells are present);
- transparent with white streaks, discharge like snot (transition from estrogen to the predominance of progesterone).
White secretion during this period most often indicates the normal maturation of the next egg.
You should pay attention to copious white discharge after ovulation and completely liquid secretion.
The following diseases are possible:
- candidiasis (curd);
- infection (discharge like water);
- bacterial vaginosis (very strong, even watery discharge);
- violation of the vaginal microflora (discharge with the smell of onions).
Pink
Bloody discharge after ovulation should not be a cause for concern if it is caused by the following reasons:
- examination by a gynecologist;
- sexual contact;
- installation of an intrauterine device;
- taking hormonal medications;
- after childbirth.
But even in this situation, it doesn’t hurt to consult with your doctor to rule out pathology.
Probability of pregnancy
The characteristics of discharge, if conception has occurred, may differ for each individual woman, but some patterns still exist. One of the first symptoms of conception can be considered bloody vaginal secretion, which occurs after about 6–12 days.
The appearance of blood clots in the mucous or slightly creamy secretion is associated with the introduction of the fertilized egg into the uterine cavity, which causes blood streaks approximately a week after ovulation. But this situation lasts only a few hours or at most a couple of days. Usually there is little cervical mucus, and its consistency resembles thick snot or jelly-like discharge. There should not be very liquid discharge, especially like water.
Important! Brown spotting vaginal secretions may indicate an ectopic pregnancy or a threatened spontaneous abortion. If you notice this symptom, you should consult a doctor to clarify its cause.
In the second half of the cycle, white discharge is not always a sign of pregnancy, even if, against the background of such vaginal secretion, the stomach hurts, as before menstruation. Yes, implantation of a fertilized egg is accompanied by some pain, but again, not every girl. Therefore, take into account all the early signs of pregnancy after ovulation in combination:
- cramps in the lower abdomen and pain in the side;
- bust enlargement;
- soreness of the mammary glands;
- the appearance of brown or white discharge after a week;
- bloating and high gas production;
- increased basal temperature;
- nausea (rare);
- change in taste for food;
- low productivity, loss of strength.
Obvious pathologies
Disorders of the reproductive system are indicated by the uncharacteristic color, smell and consistency of the cervical fluid:
- The appearance of yellow, greenish discharge is a signal of the onset of an inflammatory process, infection, or problems with the vaginal microflora.
- Pinkish secretion – polyps, erosion, hyperplasia, sexually transmitted infections. The main symptom is severe pain during sex.
- Scarlet or profusely bloody. Bleeding may occur due to a rupture of the suture, and may also indicate neoplasms in the reproductive system.
- Liquid, watery discharge, foamy with the presence of pus and a foul odor - trichomoniasis.