How our body functions and what changes occur in it every month is always interesting. Especially during the period when we are pregnant or hope to become pregnant. We almost certainly never monitor our condition as carefully and closely as during the period when we hope to become pregnant. From feeling tired to feeling slightly nauseous, the smallest symptoms are studied and tested for their significance. In this article, we will look at some of the most common problems associated with implantation bleeding. This problem is frightening and confusing if the desired pregnancy has already occurred.
Thus, let's try to figure out what are the symptoms and signs of implantation bleeding, how to recognize the earliest signs of implantation and pregnancy? This self-control may be much stronger in people undergoing assisted fertility treatment, which is understandable. In this context, we will look at whether and how to expect any different implantation symptoms during pregnancy.
Content:
- Determination of intermenstrual bleeding in the middle of the cycle
- Types of intermenstrual bleeding
- Causes of bleeding and menstruation in the middle of the cycle
- Diagnosis of bleeding in the middle of the cycle
- Treatment and prevention of bleeding in the middle of the cycle
- Poor blood flow during pregnancy
Many women experience menstruation in the middle of their cycle at least once in their lives.
Naturally, an irregular menstrual cycle causes anxiety in women. Such disorders can occur in teenage girls and women of reproductive age. Often, spotting in the middle of the cycle is not a symptom of any disease and is considered normal. But sometimes the appearance of bleeding between periods can be a sign of serious gynecological diseases.
Dysfunctional reasons
Anovulatory cycles are those cycles during which normal ovulation does not occur. The basis may be hormonal changes in FSH and LH, estrogen and progesterone. The imbalance causes excessive growth of the endometrium, which sloughs off irregularly at the end of the cycle, causing bleeding even outside the normal menstrual cycle, often long and heavy.
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a disease that affects young women between the ages of 20 and 40. It is characterized by anovulation (in the absence of a normal menstrual cycle and infertility), hirsutism, acne, insulin resistance with an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
By menorrhagia we mean a pathological increase in the amount and duration of menstrual flow, which, however, in this case usually occurs at the end of the cycle.
Stress and eating disorders (anorexia nervosa, bulimia, etc.) can lead to intermenstrual losses and abnormal cycles, as well as metabolic diseases (metabolic syndrome) and hormonal dysfunctions, such as thyroid disease.
By metrorrhagia we mean heavy vaginal bleeding that occurs outside of the normal menstrual cycle.
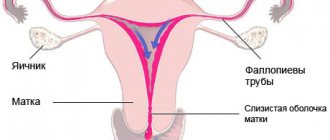
Determination of intermenstrual bleeding in the middle of the cycle
Menstruation is one of the phases of the menstrual cycle of the female body, characterized by the release of blood from the vagina. The beginning of the menstrual cycle is counted from the first day of menstruation.
Sometimes it can be difficult to distinguish dysfunctional uterine bleeding from normal menstruation. Many girls do not remember when their menstrual cycle began and do not know how to calculate their menstrual cycle, so they may mistakenly think that menstruation came earlier or later than expected. For each woman and girl, the duration of the monthly cycle is individual
How to calculate the monthly cycle? It is not difficult. The easiest way is to keep a monthly calendar. It needs to mark 1 day of the onset of menstruation and 1 day of the next menstruation. The number of days between them will be the duration of the menstrual cycle. You need to know that normal menstruation lasts 2-7 days, and the normal menstrual cycle is 21-35 days. The most optimal duration of the monthly cycle is 28 days. Women who experience an irregular menstrual cycle should consult a gynecologist.
Ovulation is the process of the release of a mature egg from the follicle. In women with a normal monthly cycle, ovulation occurs approximately on the 14th day from the start of menstruation. With an irregular menstrual cycle, it may occur earlier or later than this time. After ovulation, the level of estrogen in the female body decreases, and bleeding does not occur because the corpus luteum maintains hormonal balance. A sharp increase or decrease in the level of the hormone estrogen during ovulation can provoke uterine bleeding between, before and after menstruation, and this is not a deviation from the norm. This phenomenon is observed in 30% of women.
What are other symptoms of implantation in early pregnancy?
Since implantation bleeding only occurs in about a third of pregnancies, you'll likely be among the majority who don't experience it. However, your vigilance for the signs and symptoms of successful implantation is probably still massively high! So what are the other early signs that you might be pregnant? These may include:
Morning sickness
This can begin as early as 4 weeks after conception (10-14 days after embryo transfer), although it more often occurs around 6 weeks. Fortunately, for those who go through it, morning sickness is usually temporary and usually improves by 16 to 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Sensitivity to smells and tastes
Sudden sensitivity to smell and taste can be a sign of early pregnancy and undoubtedly contributes to ongoing stories about pregnant women's "cravings" for certain foods. Both increased sensitivity and morning sickness are the result of hormonal changes occurring in your body.
Frequent urination
It may seem strange when your baby is still very young, but the need to urinate more frequently in early pregnancy is one of the most common symptoms. It is also the result of hormonal changes that cause faster blood flow through the liver and kidneys to remove waste as efficiently as possible. In addition, the uterus quickly increases in size even at this early stage of pregnancy and therefore puts more pressure on the bladder, especially at night.
Breast tenderness
The well-known symptom of breast tenderness is another sign of early pregnancy. This is the result of an increase in blood flow and fluid retention in the mammary glands against the background of a sharp increase in the level of female sex hormones in the blood serum.
Stomach cramps
Cramping may occur on its own or be accompanied by slight bleeding, which may be a signal of implantation. You might think that all these possible early signs and symptoms of pregnancy would make it easy to be sure that it is happening. But the fact is that some symptoms are also present in some people as a precursor to their normal monthly cycle with premenstrual syndrome. So, despite all the possible clues, the only way to be sure of pregnancy is to take a pregnancy test and confirm the pregnancy with your doctor.
Types of intermenstrual bleeding
Intermenstrual bleeding often occurs 10-16 days after the end of the last menstrual period. They are not very abundant and last from 12 to 72 hours. But if the bleeding lasts longer or gets worse, consult your gynecologist.
Spotting in the middle of the cycle is more common than intermenstrual bleeding. A woman's vagina comes out with a little blood that can barely be seen on the toilet paper. This is usually mucus that has a pinkish color. Such discharge appears approximately 14 days before the onset of menstruation and is not a pathology. Intermenstrual bleeding indicates that the egg is ready for fertilization.
Frequent periods can also occur with proyomenorrhea (short monthly cycle). Periodically appearing and usually not intense bleeding lasts 2-3 days. Such spotting is caused by premature rejection of the uterine mucosa due to a decrease in estrogen production in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
What is implantation bleeding?
About 30-40% of women experience slight blood loss after the embryo implants in the uterus. This phenomenon is known as implantation bleeding. Since this happens early in your cycle, it may even be the first sign you realize you're pregnant. Bleeding usually occurs in the first weeks of pregnancy, since the uterus is an organ rich in blood vessels that can easily become damaged. When the embryo sticks to the inner wall of the uterus, the small veins and arteries that normally connect to the endometrium rupture and this can cause bleeding. If this occurs, usually 6-10 days after fertilization, it usually coincides with the theoretical date of menstruation and can therefore be confused with the onset of menstruation. There is no set pattern, and implantation bleeding may occur in one or all of a given person's pregnancies.
Causes of bleeding and menstruation in the middle of the cycle
Often, an irregular menstrual cycle is observed in teenage girls, since at their age the hormonal background has not yet become stable. If, after 2 years after the first menstruation, girls still have periods in the middle of the cycle, then you need to consult a gynecologist who will prescribe treatment to normalize the menstrual cycle.
Constant strong stressful situations, smoking, and alcohol have a bad effect on the body. As a result, women experience irregular menstrual cycles and may experience periods mid-cycle. Such phenomena often occur in women with frequent dysfunction of the genitourinary system; bleeding in such cases is more profuse.
If you move to another city, country or go on vacation to the sea, be prepared for the fact that the start of your menstrual cycle may occur earlier than usual and your period may begin in the middle of the cycle. After all, climate change is also stressful for the body, and it needs time to get used to it.
There can be many factors that provoke bleeding between periods. The main ones:
- pathologies of the endocrine system (diseases of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands, etc.);
- uterine fibroids;
- hormonal disbalance;
- miscarriage;
- the presence of an intrauterine device;
- gynecological procedures (cauterization or cervical biopsy);
- taking certain medications and contraceptives;
- vaginal trauma and vaginal infections.
- depression and stress.
- infectious diseases;
- poor blood clotting;
- deficiency of vitamins K and C;
- inflammation of the urogenital system;
- pathologies of the development of the internal genital organs of a woman (uterine inflection);
- ovarian tumors and cysts;
- chronic diseases (heart, kidney, liver and metabolic disorders);
- physical injuries.
Also, intermenstrual discharge may indicate such serious problems of the female genital area as uterine cancer, polyps and fibroids of the uterus, and the presence of adhesions.
Causes of vaginal bleeding
Postpartum period
After separation of the placenta, the uterus is a wound surface, so bleeding is normally observed. In the first days after childbirth, there may be copious brown discharge from the vagina; postpartum women are forced to use special absorbent pads designed for the postpartum period. Gradually, the amount of discharge decreases, it becomes bloody, and by 2-3 weeks it is replaced by leucorrhoea. Prolonged uterine bleeding, discharge with an unpleasant or fetid odor, or streaks of pus should be reported to the treating obstetrician-gynecologist.
Inflammation of the genital organs
A common cause of light brown or “meat slop” colored discharge is inflammatory diseases of various parts of the female reproductive system. Bleeding is associated with erosions and destructive changes in the epithelial layer, damage to small vessels. These diseases are characterized by a combination of brown discharge with other leucorrhoea (cloudy, mucous with a specific odor, purulent). Bloody discharge begins against the background of pain in the lower abdomen and increased body temperature. The symptom is caused by:
- Damage to the uterus
: endometritis, cervical erosion, endocervicitis. - Inflammation of the appendages:
salpingitis, oophoritis, adnexitis. - Vaginal diseases
: colpitis (vaginitis), vulvitis.
Pathologies of pregnancy
Bloody vaginal discharge is one of the reliable signs of spontaneous abortion or late miscarriage. The appearance of sanguineous discharge and blood is preceded by discomfort above the pubis, which is gradually replaced by a nagging, aching pain and radiates to the sacrum. Spotting brownish and then bloody discharge usually first bothers you periodically, then if left untreated it becomes constant and can turn into massive bleeding. In addition to abortion, bleeding from the genitals can be caused by:
- Ectopic pregnancy.
At first, women report spotting brown discharge that occurs due to the cessation of menstruation and aching pain in the lower abdomen. Termination of a tubal or cervical pregnancy is accompanied by massive bleeding with clots. - Chorionic carcinoma.
Bloody discharge in 80% of patients begins shortly after birth. When a tumor node is infected, the discharge is purulent and mixed with blood. Bleeding 3-5 weeks after a miscarriage or abortion is typical for a placental polyp. - Birth injuries.
The discharge of bright red blood is observed when the genital tract ruptures during the passage of the fetal head. The complication is more common during rapid labor or in the case of a clinically narrow pelvis. Massive blood loss is accompanied by shock. - Placental abruption.
Taking into account the age of detachment, the blood may have a scarlet or dark cherry color. In this case, the woman feels severe abdominal pain radiating to the perineum. In severe cases of abruption, the condition may be complicated by the development of Couveler's uterus.
Injuries
The flow of bright scarlet blood from the vagina after falls or bruises of the perineum is caused by damage and ruptures of the genital organs. The symptom is accompanied by sharp pain in the groin, difficulty urinating, and sometimes blood is found in the urine. Bloody discharge occurs with injuries to the genital organs in girls associated with household or sports injuries to the groin area. In teenage girls, heavy bleeding occurs during voluntary or violent sexual activity. Vaginal bleeding can be caused by reasons such as:
- Violent sexual intercourse
. Minor bleeding is observed due to trauma to the vaginal mucosa. Such bleeding is short-lived and is accompanied by nagging pain in the perineum. - Vaginal lacerations.
There is bleeding from the genital fissure, which is combined with swelling and cyanosis of the skin of the labia majora, and sharp pelvic pain. Massive blood loss is typical for damage to the clitoris. - Perforation of the uterus.
Perforating damage to the organ associated with curettage or criminal abortion causes profuse, bloody, bright red vaginal discharge. Bleeding develops against the background of the woman’s severe general condition and severe abdominal pain.
Taking oral contraceptives
In 30-40% of women taking hormonal contraceptives, during the first 3 months after the prescription of contraceptives, scanty bleeding from the vagina is observed, usually without any odor. The reasons for their appearance are associated with the body’s adaptation to the supply of hormones from the outside, a change in the synthesis of its own estrogens. Brownish discharge is also noted when the pill regimen is not followed. Heavy bleeding indicates atrophic processes in the uterus due to hormonal imbalances and requires an immediate visit to the doctor.
Endometriosis
Periodic, odorless, spotting brownish discharge occurs in 50-60% of patients with endometriotic growths. Bleeding from the vagina occurs due to hyperplasia of endometrial tissue and damage to the uterine cervix. Scanty bloody discharge appears a couple of days before menstruation, accompanied by intense pelvic pain and discomfort during sexual relations. With diffuse endometriosis, copious bright red discharge is possible. Retrocervical endometriosis is characterized by a combination of vaginal and rectal bleeding.
Benign neoplasms
Most often, patients with uterine fibroids report brown, odorless discharge. This benign neoplasm is characterized by heavy bleeding in the middle of the cycle, which is combined with general symptoms - pain in the lower abdomen, weakness, dizziness. Bloody discharge that occurs against the background of menstrual irregularities is characteristic of atypical endometrial hyperplasia. Spotting brown discharge, mainly after sexual intercourse, is observed with polyps of the uterus or cervical canal. Scanty bleeding occurs with condylomas of the uterine cervix.
Malignant tumors
Oncological diseases are characterized by copious brown discharge with a foul odor, in which individual clots and tissue fragments are visible. With cancer of the vulva and vagina, a triad of symptoms is observed: spotting, periodic mucous leucorrhoea and pain in the perineum. For cervical cancer, moderate bleeding is typical, observed after sexual intercourse, douching, and vaginal examination. Brown discharge also appears with adenocarcinoma and sarcoma of the uterus, germ cell tumors.
Rare causes
- Complicated course of genital infections
: chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis. - Installation of intrauterine devices
. - Iatrogenic factors
: trauma to the vaginal epithelium or endometrium during diagnostic procedures, consequences of curettage (RDV). - Emergency contraception.
- Sexual crisis in newborns.
- Pathology of the blood system
: thrombocytopenia, coagulopathy, vasopathy.
Diagnosis of bleeding in the middle of the cycle
First of all, to diagnose the causes of intermenstrual bleeding, a gynecological examination is necessary. In addition, you must undergo the following examinations:
- cytological studies of aspirate from the uterine cavity;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- study of the hormonal background of the body;
- thyroid examination;
- hysteroscopy and curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal;
- histological examination of scrapings obtained from the uterine cavity and cervical canal.
Also, if necessary, the gynecologist can prescribe a study of the pituitary gland using magnetic resonance imaging, radiography, computed tomography. Sometimes the brain is also examined using these methods.
General information
Even small spotting that appears in a woman from the vagina between periods indicates that it is necessary to be vigilant and, with the help of a doctor, be sure to understand how dangerous it is and for what reason these symptoms appeared.
Brownish brown discharge and mucous discharge streaked with blood, which appear, for example, on the 15th day of the cycle, should also alert you. If these are acyclic manifestations, the development of diseases can be suspected. According to statistics, small spotting or bleeding in girls and women between menstruation occurs in approximately 80% of cases. 20% of women note that such discharge is not spotting, but abundant, and it can appear unexpectedly, or the woman notices that after sexual intercourse there is bleeding .
It is especially important to pay attention to any discharge during pregnancy . Why women in this position bleed should be found out immediately, regardless of whether there is pain in the lower abdomen or not. You should consult a doctor immediately, as blood or dark discharge in women may indicate a miscarriage.
The causes of intermenstrual bleeding will be discussed below.
Treatment and prevention of bleeding in the middle of the cycle
Treatment methods for bleeding in the middle of the cycle depend on the causes of this deviation, as well as on the woman’s age. Treatment can be conservative or surgical. In case of ovulatory bleeding, conservative treatment is carried out. For anovulatory bleeding (not associated with ovulation), both surgical and conservative treatment may be necessary. The exception is anovulatory bleeding in adolescents, when surgical treatment is used only as a last resort.
Conservative treatment is based on the use of hormonal drugs to normalize the irregular menstrual cycle and stop bleeding. Your doctor may also prescribe sedative medications to treat untimely periods caused by stress.
For severe bleeding, women are prescribed iron supplements. It should be remembered that a balanced diet (including foods such as beef, legumes, liver, vegetables and fruits), proper rest and sleep will help restore health faster.
To prevent bleeding in the middle of the cycle, you need to: regularly see a gynecologist, refuse abortions, have a regular sex life, control your weight, play sports, give up bad habits.
If you notice that your period starts earlier or later each time, please consult a qualified healthcare professional. Untimely treatment of pathologies that cause disruption of the monthly cycle and bleeding can lead to anemia, infertility, and cervical cancer.
Malignant organic pathologies
They most often occur in the perimenopausal period and consist of malignant tumors of the genital organs. Most common:
- cervical cancer (the most important risk factor is human papillomavirus infection);
- endometrial cancer;
- ovarian cancer;
- cancer of the vagina and vulva.
Ovarian cancer
These are pathologies with a very poor prognosis if they are not recognized in time and treated.
Poor blood flow during pregnancy
During pregnancy, it is extremely important to continuously monitor the state of the maternal body of the mother and the baby, it is important that they perform all vital functions. One of the most significant studies is the analysis of blood flow in the arteries of the uterus, the woman’s umbilical cord, as well as cerebral vessels and the fetal aorta. The main causes of perinatal morbidity and mortality include disorders of the uteroplacental blood flow of 1A, 1B, second and third degrees.
Blood flow in the placenta
The placenta, in which the fetus is located, supplies the embryo with nutrients, as well as oxygen from the mother’s blood; it also removes waste products from the child’s body. It is this organ that unites two rather complex vascular systems - the female, which connects the vessels of the uterus and placenta, and the fetal, which passes into the umbilical arteries and leads to the child.
The circulatory systems mentioned above are separated by a membrane, which does not allow maternal and child blood to mix. The placenta is a kind of barrier that is resistant to numerous harmful substances, as well as viruses.
Often, for completely different reasons, placental insufficiency may appear, which inevitably affects the performance of transport, metabolic, trophic, endocrine and other vital functions of the placenta. In this condition, the metabolism between the maternal and child organisms deteriorates significantly, which is fraught with various consequences.
What are the causes of impaired placental blood flow?
Poor circulation in the uterine cavity can be caused by pneumonia, increased blood pressure, various intrauterine infections, as well as insufficient oxygen supply to the child’s body (hypoxia).
To diagnose the blood flow system in modern obstetric practice, three-dimensional ultrasound (so-called Doppler ultrasound) is used, with which the vessels are visible in a 3D (three-dimensional) image. With the help of this diagnostic technique, there is a prospect of diagnosing retroplacental bleeding and assessing cardiac malformations by monitoring blood flow. This technique is irreplaceable, since with its help it is possible to examine defects even in the most microscopic vessels that form the microvasculature, to observe the peculiarities of the formation and development of intraplacental hemodynamics, and in addition to control the amount of nutrients, as well as oxygen, that should enter the fetal body . New prospects have opened up for the early detection of obstetric complications, and if treatment or correction is started without wasting time, then circulatory disorders and subsequent pathologies associated with it can be almost completely avoided.
Hemodynamic disorders during pregnancy
Hemodynamic disorders are divided into 3 degrees of severity:
1. 1st degree includes two subtypes:
- disturbance of patello-placental blood flow 1Is the mildest. Fetal-placental blood circulation is preserved with it. Intrauterine infections often lead to this problem;
- in degree 1B, uteroplacental blood flow is preserved, but fetal-placental pathologies appear.
2. Grade 2 is characterized by the presence of disturbances in both blood flow systems, however, these disturbances do not carry any fundamental changes. 3. In grade 3, uterine circulation disturbance causes defects in normal blood circulation at the level of the fetus.
In the case of the first degree of violations, timely detection and adequate treatment can avoid fetal death. In the case of the second degree, perinatal mortality is about 13.3 percent, in the case of the third - 46.7 percent. During Doppler diagnostics, it was revealed that treatment aimed at correcting placental insufficiency in women with third-degree uterine blood flow disorders was ineffective. In this situation, with conservative childbirth, perinatal mortality was 50 percent, then, thanks to a cesarean section, losses can be avoided. 35.5 percent of newborns are admitted to the intensive care unit with grade 1 blood flow disorders, 45.5 percent with grade 2, and 88.2 percent with grade 3.
Bleeding during menopause
After the completion of the menstrual cycle, any discharge of blood from the vagina indicates the development of pathology. Gynecologists name the following reasons for bleeding during menopause:
- Functional disorders of the genital organs
. Bloody discharge can occur with pathologies of the uterus, cervix, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. - Hormonal changes in the body.
After the onset of menopause, a woman’s body experiences surges in the production of sex hormones. Sometimes this leads to heavy or scanty bleeding from the vagina. - Taking medications.
This symptom is especially often caused by hormone therapy. Doctors prescribe hormones to eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of menopause. - Chronic non-gynecological pathologies.
Sometimes scanty vaginal bleeding in postmenopause has nothing to do with the functioning of the reproductive system.
Bleeding in old age during menopause is a good reason to urgently consult a doctor.
You can undergo a comprehensive diagnosis and receive qualified medical care for vaginal or anal bleeding by contacting a medical specialist. The clinic’s specialists are highly qualified and have extensive experience in the treatment of hemorrhages of various natures.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Bloody and brown discharge - when is this normal?
Brown and sometimes even black discharge is the result of drops of blood mixed into it. “Normal” dark discharge may appear in a healthy person in the following cases:
- if dark-colored drops appear a few days before your period, this indicates that your period will begin soon;
- several days after menstruation ends, and how many days such discharge should normally last is an individual question for each woman;
- in the middle of the monthly cycle this is possible when taking oral contraceptives;
- after violent sexual intercourse, provided that the woman was not sufficiently aroused, and due to insufficient lubrication, the vaginal mucosa was damaged;
- after the first, as well as several subsequent sexual contacts, when the girl is just beginning to have a sexual life.
Brown and bloody discharge as a symptom of disease
Such symptoms may indicate illness in the following cases:
- bloody or brown discharge appears in the middle of the monthly cycle (for example, on the 16th day of the cycle or the 12th day of the cycle, depending on its duration), while the woman does not take hormonal oral contraceptives;
- with discharge, the lower abdomen hurts, there is dryness, burning, itching in the vagina, the temperature rises, pain is felt during sexual intercourse;
- during menopause or if a woman has had no menstruation for a year now;
- in case of constant discharge after sex.
Discharge before and after childbirth
Brown or pink discharge appears a few days before childbirth , when another hormonal change occurs in the body. The cervix gradually prepares to open, and the plug is gradually pushed out. As a rule, it comes out gradually, so the daub can appear a day or two before birth, and earlier - 12-13 days. But if blood appears a few days before the expected birth, you should consult a doctor immediately, as this may be evidence of pathologies.
After childbirth, when the placenta is released, blood continues to be released for several weeks. Such discharge is called lochia . Gradually, they become darker from bloody, and their number decreases. In the second week they are yellowish-brown, orange, then they gradually lighten. But even a month after giving birth, the problems can continue. But if the number of lochia has increased significantly, or they continue 2 months after birth, you need to tell your doctor about it.
Discharge before menstruation
5-6 days before menstruation, due to hormonal changes in the body, a woman may notice that the nature of what is released from the vagina is a little unusual. Leucorrhoea may be cloudy and creamy. They are no longer pale transparent, but white or yellowish, sometimes abundant and watery, but more often viscous and thick.
After taking a smear in the days before menstruation, an increased number of leukocytes , gram-negative rods, and epithelial cells is determined.
A variant of the norm can also be ichorous discharge - ichor appears several days before menstruation, while the woman is not bothered by other unpleasant symptoms.
However, if the white discharge is abundant and prolonged, with an unpleasant odor, sometimes darkish, gray, and the woman is bothered by itching and a burning sensation, we may be talking about thrush .
Many women are interested in how normal dark brown discharge is before menstruation, which for many appears a day, and sometimes even 2-3 days before menstruation. Pinkish or dark discharge before menstruation is absolutely normal, provided that spotting of this color appears on the eve of menstruation. Since menstruation is a consequence of the death of the egg, its release occurs gradually. And if such discharge occurs for no more than one day before menstruation, we are not talking about pathology.
Therefore, you need to know: if you have brown discharge before your period, what it means depends on how long this phenomenon lasts. If it starts about a week before your period, you may suspect that a reproductive system disorder is developing. Therefore, you must definitely visit a doctor.
It should be noted that if instead of menstruation a brown or burgundy smear appears, pregnancy may be suspected. It is known that among the many symptoms that allow one to suspect an interesting situation, there is also a sign of pregnancy - light brown discharge. Sometimes a woman notes that such smears lasted 1 day and ended.
However, to be sure that a woman is expecting a child, an examination with a doctor or a test showing two stripes will help.
Spotting before menstruation begins due to the following reasons:
- hormonal imbalance;
- endometriosis;
- endometrial hyperplasia ;
- climate change;
- stress or severe shock;
- use of hormonal contraception or termination of use;
- uterine polyps.