What happens when there is a bruise? What are the symptoms and consequences of bruises? What is the most effective way to treat bruises?
A bruise is a closed injury to tissues and organs without significant disruption of their structure. This is the most common type of injury. Bruises the skin. The integrity of the upper layers of the skin is not damaged during a bruise, but a swelling and hematoma (bruise) quickly appear at the site of the impact, and pain is felt.
There are bruises of soft tissues , periosteum, joints, bruises of the neck, back, spine, chest, head. When a joint (for example, a knee) is bruised, its volume increases several hours after the injury, function is impaired, and pain intensifies (especially when moving). In this case, the leg is slightly bent, its extension is sharply painful. The difference between a joint bruise and a dislocation is the preservation of movement in it.
With bruises , there may be only a slight swelling (“bump”), which does not cause much trouble. However, if the injury was accompanied by loss of consciousness, weakness, nausea, vomiting, etc., then this may be a sign of a more serious injury - a concussion or even a brain contusion .
With bruises , in addition to damage to soft tissues, blood flow in the vessels passing here may be secondarily disrupted, which disrupts the blood supply to the brain.
With bruises of the back (spine), the blood circulation of the spinal cord may be impaired (there is a decrease in sensitivity in the limbs, muscle function, etc.).
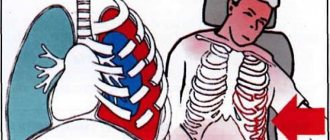
With bruises of the chest, only local changes in the superficial soft tissues may be noted, but with a strong blow, for example, as a result of a fall, breathing may be impaired, and with blows to the heart area it may stop. Abdominal bruise is sometimes accompanied by damage to internal organs (for example, rupture of the liver, spleen, accompanied by internal bleeding).
What is a bruise?
A bruise is damage to the skin, muscle tissue and, in the worst case, nerve endings. According to severity, bruises are divided into four degrees:
1. Minor damage. The result is a small abrasion or scratch. Such a bruise goes away on its own within 2–3 days 2. Rupture of muscle tissue. The result is swelling and hematoma. 3. Damage to the skin, muscles and tendons, bone bruise. 4. This is the most severe degree of injury, as a result of which the organs can no longer function normally. It's better to see a doctor.
What happens when you get hurt
When a bruise occurs, damage to the skin, subcutaneous fat and muscles occurs, and the blood vessels and nerves passing through them can also be damaged. Blood leaks from injured vessels. With soft tissue bruises, hemorrhage increases at the site of injury and a more or less pronounced swelling forms. Blood gradually permeates the tissues and can accumulate (hematoma) or flow into nearby cavities, such as a joint (hemarthrosis).
Bleeding from small vessels stops spontaneously in about 5-10 minutes. Of the large ones, it can last more than a day. The color of the bruise depends on the age of the injury: a fresh one has a purple-bluish color, after 3-4 days it becomes blue-yellow, and on the 5-6th day it turns yellow. At the site of the bruise , a swelling - edema - always appears, pain occurs, which passes over time, but unpleasant sensations when moving or palpating persist for a long time. With severe bruises , disruption of the functioning of nearby organs is possible.
As a result of a bruise of the lower leg in places where the skin and subcutaneous tissue are adjacent to the bone, necrosis of the skin and its subsequent rejection are possible. When hitting bones that are poorly protected by soft tissue, not only very painful bruises of the periosteum with its detachment occur, but also bone damage (cracks and fractures). A blow in an oblique direction relative to the surface of the skin can cause its detachment along with subcutaneous tissue, followed by filling of the resulting cavity with lymph and blood.
Symptoms of bruise
The symptoms of a bruise are difficult to confuse with something else. Almost immediately there is pain in the damaged area, the formation of edema and hematoma. It is typical for bruises that the pain decreases after some time, and then increases again due to increased swelling. This distinguishes a bruise from a fracture. When a fracture occurs, the pain does not subside, movements are difficult and painful. By the way, a hematoma may not appear immediately. The time of its appearance is related to the depth of the hemorrhage. If you bruise the skin or subcutaneous tissue, a hematoma will appear almost immediately, and if the bruise is on muscles or bones, you will see the hematoma after 2-3 days. A fresh hematoma is red in color, then it turns purple, blue, green, yellow. By the color of the hematoma it is easy to determine the age of the bruise.
First aid
The general principles of its provision are universal:
- Ice on the affected area - cooling reduces swelling and relieves pain.
- Immobilization – if serious injuries are suspected, it is advisable to completely immobilize the area and complete rest until diagnosis is carried out.
- Applying a pressure bandage just above the injured area reduces swelling and prevents the spread of the hematoma.
- Treatment with an antiseptic is relevant in the presence of abrasions and wounds on the surface of the skin. In case of severe bruising, it is not advisable to use iodine - it has a warming effect and increases the manifestation of hematomas.
- Taking painkillers is carried out only for prolonged severe pain. If the painful sensations can be tolerated, it is better to stop taking medications, this will enable doctors to better assess the condition during the first examination.
- Going to the emergency room is necessary if you suspect serious injuries, primarily with bruises to the head, chest, abdomen, or spine. Ordinary bruises on the surface of the body can be treated without consequences at home.
Attention!
If you have a severe bruise, you should never massage or warm the damaged area, or wash or rub your injured eyes. It is undesirable to drink alcohol (it dilates blood vessels and accelerates the development of a hematoma), and if the injury occurs in the abdominal area, the patient should not be allowed to eat or drink at all until the ambulance arrives.
Further features of first aid depend on the anatomical location of the injured area.
For leg bruises
In case of severe bruises with suspected fracture, you should not move the limb, bend or straighten it. To establish the nature of the damage, you should pay attention to the characteristic symptoms of a fracture:
- mobility is severely limited, and every attempt causes severe pain;
- when moving in the area of damage, a characteristic crunching sound is heard;
- the amplitude during extension looks unnatural.
On a note!
In the absence of external differences, pain becomes the main criterion. In the case of a fracture, it does not subside, movements are difficult and painful, while bruises are characterized by a gradual decrease after injury and a re-increase as swelling forms.
Basic first aid techniques:
- The victim is provided with complete rest, placed in a horizontal position with the limb elevated and fixed with a splint.
- For bruises in the joint area, apply a pressure bandage to prevent dislocation.
- Apply a cooling compress to the area of greatest damage.
- Superficial injuries (abrasions, scratches) are treated with an antiseptic.
- For severe pain, a painkiller is given.
For hand bruises
For shoulder or forearm injuries, first aid is provided according to the same principle as for leg injuries. Immobilization is carried out by tying the limb to the body or with fixation in a sling.
Similar actions are performed when the hands are damaged. In this case, the forearm and hand are fixed in a horizontal position, which avoids increased blood flow to the damaged area and ensures maximum peace. To do this, splints or a tight bandage with an elastic bandage are applied to the hand and secured to a sling using a scarf.
For spinal bruises
It is strictly prohibited to independently transport a victim with suspected spinal injury. When providing first aid, it should be taken into account that every careless movement can aggravate the condition and provoke the appearance of neurological symptoms. Until the possibility of a fracture or displacement of the vertebrae is excluded, the patient is shown complete immobilization of the entire body - a rigid surface (shield) under the back, the head is fixed with a special head holder.
Attention!
Even in the absence of a fracture, compression of the spinal cord nerve roots may occur, requiring careful handling even with seemingly minor back injuries.
For head injuries
Express diagnostics for concussion is indicated for any head injuries, including minor bruises. If there are corresponding symptoms (nausea, vomiting, headache, loss of coordination, speech, hearing, dizziness), examination is mandatory.
On a note!
Rapid diagnosis of a concussion includes testing the fluidity of eye contact. The victim is asked to follow the movements of the finger: if the eyes move smoothly, there is no concussion, if jerks, twitchings, and inability to concentrate the gaze are observed, there is.
A concussion requires specialized diagnosis and treatment, so the patient should be transported to the emergency room or trauma department of a local hospital as quickly as possible. Until the ambulance arrives, he should not be left alone, as his condition may worsen at any time. The following steps should be followed:
- ensure complete rest - the person is placed in a supine position;
- turn your head to the side - to prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract (if there are symptoms of a concussion);
- treat external wounds with antiseptics;
- constantly talk to the victim, preventing him from falling asleep until the doctors arrive.
For nasal injuries with bleeding, it is necessary to tilt the person's head down and insert cotton swabs soaked in hydrogen peroxide into the nostrils. If there is no bleeding, the head, on the contrary, is tilted back, and ice is applied to the bridge of the nose to reduce swelling. With proper assistance, the condition will stabilize within 15–20 minutes.
The eyes deserve special attention. Checking with an ophthalmologist is advisable even for mild concussions. If the bruise occurs directly on the eye itself, it is necessary to apply a clean (preferably sterile) bandage to it and urgently go to an ophthalmologist. The presence of a disorder in this fine structure, especially with tissue swelling and the presence of hemorrhage, can only be identified by a specialist with the appropriate education. In case of severe injuries, the sooner help is provided, the higher the chances of saving vision.
What to do if you get hurt. First aid
- Don't panic under any circumstances. Try to move less, but rather sit or lie down.
- If the skin is damaged, it must be treated with disinfectants. They will not speed up wound healing, but will destroy microbes that slow down tissue regeneration. For these purposes, hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine digluconate, and an aqueous solution of furatsilin are suitable. All these products are inexpensive, you can buy them at any pharmacy and always keep them in your medicine cabinet. Important: alcohol-containing products - iodine solution, brilliant green, pure alcohol - cannot be applied to an open wound, only along its edges. If you apply it, you will get a burn.
- Then you need to apply a cold compress. Make it from ice or any product from the freezer. We recommend wrapping the ice in thick cloth. It is important to do this to prevent frostbite. You can also apply a cloth soaked in cold water or a bottle of milk from the refrigerator. Thanks to the cold, the damage to the blood vessels will decrease, the bleeding will stop, the pain will become less severe, and the hematoma will not grow. Keep the cold for about 20 minutes, after an hour you can repeat the procedure.
- If the bruise is severe, it is better to consult a doctor. Especially if you hurt your head.
Which parts of the body are most susceptible to injury?
Sprains mainly occur in the knee joints or ankles when running or walking on uneven surfaces or ice. Injuries often occur when playing team sports with sudden braking and acceleration. Poor warm-up, lack of regular physical activity, fatigue, and pregnancy increases the likelihood of sprains.
Treatment for a hamstring strain is common for dancers and people involved in active sports. Injury occurs as a result of overexertion and lack of proper rest.
The following parts of the body are primarily susceptible to bruises:
- Chest - often accompanied by damage to internal tissues, so treatment of a chest contusion should begin immediately.
- Knee – if the damage is severe, hemarthrosis may develop.
- Nose – sometimes accompanied by displacement of the nasal septum.
- Shoulder – leads to temporary limitation of mobility.
- Elbow – depending on the nature of the damage, arthrosis or arthritis may develop.
What types of injuries are there and their differences:
Remedies for bruises
Popular and inexpensive pharmaceutical products that will relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Buy them in all LekOptTorg pharmacies and on the website:
- . Used for pain relief in inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Tablets are contraindicated in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy. Diclofen is used with extreme caution for diseases of the liver, kidneys, asthma, heart failure, and also in old age. The maximum dose of 150 mg should not be used for more than 5–7 days. For detailed instructions for use, please see the product card on our website.
- . Helps relieve pain and reduce fever (temperature). It is used for traumatic inflammation of the musculoskeletal system and soft tissues. Do not take during pregnancy or breastfeeding. For detailed instructions for use, please see the product card on our website.
- . Unlike other drugs, it does not relieve inflammation, but only relieves pain. But most often, paracetamol is in every first aid kit. Tablets are not recommended to be taken on an empty stomach, as well as in case of liver and kidney failure. Detailed instructions for use can be found on our website in the product card.
Common reasons why you might get a sprain or bruise
- Carelessness when handling heavy objects.
- Getting into a traffic accident.
- Falling while going down the stairs.
- Participating in high-risk sports, such as martial arts, volleyball, powerlifting, basketball, etc.
- Fall due to fainting.
- Living conditions - twisting your feet, stumbling, walking on slippery surfaces or wearing high-heeled shoes.
- Excess weight, uncomfortable shoes, clothes, equipment.
- Arthrosis, infectious diseases, flat feet (these ailments can lead to changes in the structure of the joint).
Treatment of sprains and bruises with the “Sun” device
The AMnp-02 “Sun” device is suitable for treating sprains of the knee joint, ankle and other parts of the body. It has universal healing properties. AMnp-02 uses the method of low-frequency magnetic therapy, which is easily tolerated and can be used for the elderly and children aged 3 years and older.
The device is compact and mobile, with virtually no contraindications. The device is indicated not only for bruises and sprains, but also for arthritis, arthrosis of large joints, lymphostasis (formed when bones are broken), and osteochondrosis of the spine. Ultraviolet irradiators have, among other things, a bactericidal effect, which helps in the treatment of skin diseases associated with a bruise.
The device is sold together with a fixation belt, a cable and a power supply, and a magnetic field indicator. Designed to last for 8-10 years, weighs less than 1kg, making it easy to carry.
Ointment for bruises with an analgesic effect: “Diclofenac”
The active substance diclofenac is included in a number of analogue drugs:
- "Voltaren";
- "Diclofenac"
- "Ortofen".
These are common anti-inflammatory drugs belonging to the non-steroidal group. For use by adults and children over 6 years of age. Apply to the skin 1 to 4 times a day. Has a local anesthetic effect.
Side effects are rare. They may be associated with dermatitis, erythema, and attacks of bronchial asthma. Use during pregnancy is permissible only in the first and second trimesters. Moreover, a preliminary consultation with a doctor is required. You can buy all diclofenac-based ointments without a prescription.