Material reviewer
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors consisting of smooth muscle cells and fibrous connective tissue. The disease is diagnosed in 80% of women who have entered menopause. The main characteristic of the neoplasm: low risk of malignancy. The tumor becomes cancerous only in 3% of cases. That is why doctors recommend that patients adhere to an observation strategy. Even large tumors can be eliminated without surgery. At the Medical Center of Dr. Sergei Anatolyevich Kapranov, they are ready to help even those patients who have prepared for hysterectomy. Sign up for a consultation and find out how to save your reproductive organ.
Types of fibroids
Large benign tumors can grow in any part of the uterus. The choice of the optimal method of therapy and the intensity of developing symptoms depend on the location of the tumor.
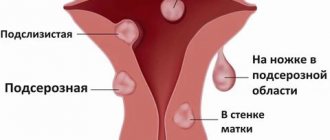
- Features of intramural fibroids.
The tumors are limited to the muscular wall of the uterus, but can grow to the size of a watermelon. A woman may complain of heavy menstruation, pain in the pelvis and lower back, and frequent urination. In the later stages of the disease, the patient develops a large swollen abdomen.
- Differences between submucosal fibroids.
The tumor grows in the uterine cavity, on the surface of the mucous membrane. With timely treatment, pathological tissues can be released along with menstrual blood. Large submucosal tumors do not leave room for the attachment of the fertilized egg and provoke mechanical infertility.
- Features of subserous fibroids.
Neoplasms grow on the uterus, from the outside. Subserous tumors can put pressure on the bladder or intestines, causing bloating and cramping pain.
With timely treatment, neoplasms will not be able to provoke serious consequences, such as infertility or heavy bleeding.
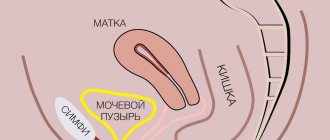
What does subserous fibroid look like?
Externally, subserous myomatous nodes have a shape close to spherical or ovoid. Subserous fibroids can be partially embedded in the wall of the uterus, and then it looks like a “mound” on the surface of the organ (spread-based fibroids). In other cases, the node is on a thin stalk, like a mushroom.
Fibroids may grow in size, but do not grow into adjacent normal muscle tissue. It is clearly demarcated and can be removed during surgery.
The consistency of the nodes is dense, and when cut they are gray in color. Inside, they consist of muscle fibers that run in different directions. The space between them is filled with connective tissue.
Subserous uterine fibroids can grow to large sizes. There is a known case when the weight of the formations reached almost 30 kg.
Myomatous nodes are “echogenic” - they are clearly visible during ultrasound. On the screen of the device, the doctor sees a formation with smooth edges, well demarcated from the surrounding tissues. Because of it, the contours of the uterus are deformed. Pedicled subserous nodes are sometimes difficult to distinguish from ovarian tumors.
If the blood supply to the node deteriorates, an ultrasound scan can reveal its swelling, decreased echogenicity (it becomes darker in the images), and heterogeneity of the structure. If certain areas of subserous fibroids die due to impaired blood flow, they appear as dark, irregular spots.
Symptoms of the disease, possible complications
Fibroids are usually detected during a standard gynecological examination of the uterus. The physician may detect a hard mass during palpation of the abdomen. In most cases, the woman does not complain of any abnormalities in her health. But large fibroids can provoke the development of the following symptoms:
- abnormally heavy menstrual bleeding;
- menstruation that lasts more than a week;
- pressing pain in the pelvic area;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- constipation
If large fibroids are not treated, acute pain may develop and the normal blood supply to the uterus may be disrupted. Problems may also arise during pregnancy and childbirth. Patients with myomatosis are often diagnosed with placental abruption. The complication is fraught with the development of hypoxia in the fetus and premature birth. Also, patients with myomatosis more often require a cesarean section.
Symptoms
From the point of view of clinical course, subserous fibroids are the most problem-free. Heavy, prolonged and painful periods, anemia, problems with the onset and carrying of pregnancy - all these disorders, as a rule, cause submucosal fibroids.
The subserous node is located externally and grows towards the abdominal cavity, so it can exist for a long time and grow greatly without causing any symptoms.
Often the diagnosis is made by chance when a woman undergoes an ultrasound for another reason.
Large subserous uterine fibroids can put pressure on the bladder and rectum, causing chronic constipation and frequent urination, urgency (a strong desire to go to the toilet right now). These manifestations are nonspecific; they can also occur with other diseases, such as hemorrhoids, cystitis, and genitourinary infections.
Due to large subserous nodes, the abdomen enlarges, but many do not attach much importance to this symptom. Often a woman thinks that she has simply gained weight.
+7 (24/7) Expert consultation
Overview of diagnostic methods
To make a final diagnosis, a standard gynecological examination is not enough. To assess the size and nature of the tumor, the patient is given a referral for additional examinations.
- Transvaginal ultrasound.
An ultrasound probe is inserted into the vagina, which allows you to build an image of the uterine cavity. The procedure is inexpensive, but allows you to assess the location and size of the fibroids.
- MRI/CT.
An expensive examination is usually carried out only in cases where it is known for certain that surgical removal of the tumor cannot be avoided. A tomograph allows you to obtain a three-dimensional detailed image of the uterus and determine the exact location of the tumor.
- Contrast sonohysterography.
A vaginal ultrasound is performed simultaneously with the introduction of saline into the uterine cavity. The resulting images allow the most accurate assessment of the volume and location of the tumor.
Depending on the results of the examinations, the patient is referred for surgery or
selecting an alternative treatment option for fibroids.
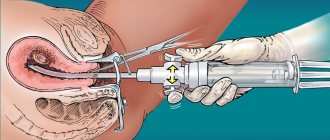
Hysteroscopic myomectomy
An operation to remove internal myomatous nodes located in the submucosa and having a base. Access to the uterus is through the vagina. A hyteroscope device is inserted inside and the tumor is removed using surgical instruments.
The procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis under general anesthesia. Contraindications include infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system, suspicion of cancer of internal organs, and a depth of the uterine cavity of more than 10 cm.
Overview of therapy methods
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to treating uterine fibroids. The therapy program is developed individually for each patient. The doctor will take into account the presence of specific symptoms and contraindications to surgery. If one small uterine fibroid is detected, the specialist will suggest following the watchful waiting method. The patient will have to visit the gynecologist 2-3 times a year, and if characteristic symptoms occur, undergo an unscheduled ultrasound. Most small fibroids do not interfere with normal conception and gestation and tend to disappear spontaneously, especially with a sharp drop in the level of reproductive hormones.
Myths:
1. Myoma will definitely turn into cancer and must be removed as quickly as possible.
In fact, uterine fibroids are not a cancer. At the initial stage of development of the disease, regular observation is simply necessary.
2. A woman will never be able to get pregnant.
This is far from the case, and even if at the moment fibroids are the cause of infertility and miscarriage, then with the help of treatment everything can be corrected.
3. You cannot plan a pregnancy with fibroids.
Most often, nodes located in the muscle layer do not interfere with conception, subsequent pregnancy and birth of a child. But the very presence of fibroids on the uterus indicates that malfunctions are occurring in this organ.
Such a pregnancy needs to be given more attention. But if the nodes cause deformation of the uterine cavity, then sometimes they require removal before planning a pregnancy.
Drug therapy for fibroids
A small hormone-dependent tumor can be cured without surgery. Taking medications containing synthetic hormones helps to quickly eliminate unpleasant symptoms and normalize the length of the menstrual cycle. You need to understand that drug therapy does not guarantee the complete disappearance of fibroids, but will help to significantly reduce their size.
In modern practice, the following types of drugs are used.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists.
This type of medication blocks the production of estrogen and progesterone, which puts a woman into artificial menopause. The ability to conceive is lost, but the size of the fibroids is significantly reduced.
Commonly prescribed GnRH agonists:
- Lucrin Depot, Eligard (active ingredient leuprorelin);
- Zoladex (active ingredient goserelin);
- Diferelin (active ingredient triptorelin).
The disadvantages of using GnRH agonists include the development of hot flashes and the appearance of emotional instability. Drugs in this group should not be used for longer than six months, as bone thinning develops. If after six months of therapy the size of the tumor has not changed, the patient is offered surgical removal of the uterine fibroids.
- Progestin-releasing intrauterine device (IUD).
Installing an intrauterine device will help eliminate heavy, painful menstruation. But it must be borne in mind that progestin only alleviates symptoms, but does not reduce fibroids. The IUD will be the best option for women who have chosen observation tactics and are not planning a pregnancy.
- Tranexamic acid.
A non-hormonal drug is prescribed to relieve severe menstrual pain. With long-term use, a decrease in the volume of fibroids may be noticed.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Medicines in this group are inexpensive and can quickly and effectively relieve pain associated with the growth of fibroids. The disadvantages include the lack of influence on the abundance of menstrual bleeding and tumor size.
- Birth control pills.
A gynecologist may recommend taking birth control temporarily even for women who want to become pregnant. Oral contraceptives will help control menstrual bleeding, but will not reduce the size of fibroids.
During drug therapy, it is additionally recommended to take iron supplements and vitamin complexes.
Treatment
The treatment tactics for uterine leiomyoma are chosen by the doctor in accordance with the size of the myomatous nodes, the severity of its clinical symptoms and the age of the patient. Both conservative and surgical methods can be used for treatment.
All patients with uterine leiomyoma are advised to undergo dynamic observation by a gynecologist, who must be visited at least once every three months.
Asymptomatic small uterine leiomyoma is subject to conservative treatment with hormonal drugs - progesterone derivatives, which help normalize ovarian function and prevent tumor growth.
In addition, to suppress the secretion of gonadotropins and create pseudomenopause, injections of GnRH agonists are prescribed, which have a prolonged effect. It must be taken into account that long-term use of these drugs can lead to the development of osteoporosis.
Conservative treatment helps to restrain further growth of myomatous nodes, but is not able to completely eliminate the disease.
It is possible to radically get rid of uterine leiomyomas with the help of surgical treatment, but certain indications are necessary for its implementation:
- large size of the myomatous node;
- rapid rate of increase in the size of uterine leiomyomas;
- severe pain syndrome;
- concomitant diseases: ovarian tumors or endometriosis;
- torsion of the leg of the node and its necrosis;
- impaired function of adjacent organs (rectum, bladder);
- infertility;
- submucous uterine leiomyoma (surgical treatment is prescribed if conservative therapy is ineffective);
- suspicion of malignancy of uterine leiomyoma.
The nature of the surgical intervention and its volume are determined taking into account the patient’s age, state of reproductive and general health, and the degree of expected risks.
The obtained objective data allows the doctor to make the right choice of the type of surgical intervention:
- conservative – the uterus is preserved;
- radical - the uterus is completely removed.
Conservative surgical treatment is preferable for women planning pregnancy, since this method does not interfere with their reproductive function.
In addition, myomectomy is an organ-preserving method, during which myomatous nodes are removed from the uterus.
The least traumatic method of performing myomectomy is hysteroscopy, which involves excision of the myomatous node using a laser. The manipulation requires the use of local anesthesia and visual supervision by a physician.
During radical surgical interventions, the uterus with myomatous nodes is completely removed, as a result of which the woman loses her reproductive function. Similar methods include hysterectomy, supravaginal amputation, panhysterectomy.
The use of laparoscopic techniques for conservative myomectomy and supravaginal amputation of the uterus provides a significant reduction in surgical trauma to tissues, the severity of adhesions in the future and significantly shortens the rehabilitation period.
Non-invasive treatment options
HIFU ablation
High-intensity focused ultrasound can be used to eliminate benign tumors. The procedure is not considered a full-fledged operation because it is performed without incisions and is performed on an outpatient basis. HIFU ablation is performed in an MRI scanner equipped with an ultrasound transducer. Under the influence of ultrasonic waves, the tumor heats up and begins to collapse.
Advantages of HIFU ablation:
- low risk of developing inflammatory processes;
- disappearance of adverse symptoms within a few days after the procedure;
- fertility preservation;
- the opportunity to return to normal daily life immediately after discharge from the hospital.
HIFU ablation is a safe procedure that will be effective for small fibroids.
Uterine artery embolization
In modern clinics, procedures are carried out to destroy uterine fibroids without surgery. Medical Center of Professor S.A. Kapranov removes tumors by embolization of the uterine arteries. Special blocking drugs interrupt the blood flow to the fibroids and provoke the death of blood vessels. Minimally invasive surgery allows you not only to get rid of the tumor, but also to forget about the accompanying unpleasant symptoms. Embolization does not provoke serious side effects or complications. But for several weeks after the procedure, the patient may complain of lethargy, periodic nausea, and fever. After just 7 days, the woman will be able to return to normal daily life and forget about pain.
Brown or reddish vaginal discharge is considered a normal consequence of embolization. The use of sanitary pads is recommended, but tampons are strictly prohibited. Watery discharge is also considered normal. Thick yellowish leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor should cause concern. If the situation is complicated by a sharp increase in temperature or pain in the pelvic area, you should urgently consult a doctor.
Specialists at the Center for Endovascular Surgery support their patients at all stages. You can seek help even if you had embolization months ago.
Laparoscopic or transcervical cryomyolysis
An alternative method of minimally invasive surgery: cryomyolysis. The procedure is performed transcervically or during laparoscopy. Neoplasm tissues are destroyed under the influence of extremely low temperatures. To gain access to the uterine cavity, the doctor may make 2 small incisions in the patient's lower abdomen. After exposure to a cryoprobe, the neoplasm may become denser. Within 12 months after the procedure, the pathological tissues will gradually soften and come out with the next menstruation. Laparoscopic cryomyolysis is considered one of the most effective methods of treating fibroids without surgery. Unlike a full-fledged surgical intervention, the recovery period after laparoscopy lasts only 4-5 days.
Laser endometrial ablation
The procedure is performed without incisions, transcervically. To remove fibroids, a special instrument that emits microwave energy or electric current is inserted into the uterine cavity. Under the influence of ultra-high temperatures, the endometrium, including fibroids, is completely destroyed. Ablation is effective only when diagnosing submucosal neoplasms. For subserous uterine fibroids, a different treatment method is selected.
The disadvantages of laser ablation include:
- loss of fertility;
- no effect on large tumors;
- the need to regularly take contraceptives (to prevent the implantation of the fertilized egg outside the uterine cavity).
It is necessary to understand that treating large fibroids without surgery does not provide a 100% guarantee of absence of relapses. Only with physical removal of the uterus can the patient count on the fact that the disease will not develop again.
Surgical treatment options for uterine fibroids
| Treatment technique | Features and results |
| Arterial embolization | The uterine arteries are clogged with embolization material to stop arterial blood flow, as a result of which the myomatous nodes are replaced by connective tissue. This is a common minimally invasive treatment method that does not require anesthesia. The hospital stay lasts one day. |
| Laser ablation | The laser beam is used to precisely target the tumor site, leading to its death. |
| FUS ablation (ultrasound ablation) | A high-intensity ultrasound beam is used to target the connective tissue of fibroids through the abdominal wall. Tissues undergo destruction and thermal necrosis occurs. Today, medicine has MRI equipment with a built-in ultrasound emitter, so the entire procedure is carried out under MRI control. Healthy tissues are not damaged, anesthesia and hospitalization are not required. |
| Laparoscopy | Diagnosis and removal of small single lesions during one procedure. |
| Hysteroscopy | Submucosal nodes are removed |
| Laparotomy | An operation with abdominal access (through an incision in the abdominal wall) is rarely performed when there are restrictions on performing gentle procedures. |
| Hysterectomy | The uterus is removed along with the tumor if it is significant in size, there is compression of organs, regular bleeding leading to large blood loss, anemia or hemorrhagic syndrome. |
Physiotherapy
For small fibroids, especially when long-term observation is chosen, a woman can try alternative methods of therapy. Physical therapy exercises, massages, and acupuncture sessions will help eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
For painful menstruation, it is recommended to make compresses with castor oil. It is necessary to soak a clean flannel cloth with warm castor oil, wrap it in bandages and apply it to the lower abdomen. The cramps should go away within 10-15 minutes. You can also perform self-massage on a daily basis.
- Apply warm castor oil all over your belly.
- Make several circular stroking movements clockwise and counterclockwise.
- To relieve spasms, you can do a cycle of rubbing movements.
Aromatherapy enthusiasts can add a few drops of organic lavender essential oil to castor oil. The aroma of lavender activates blood circulation and promotes complete relaxation.
If you have uterine fibroids, you can also do yoga and perform simple physical therapy exercises.
Herbs and natural supplements
Herbal remedies, vitamins, and dietary supplements can also help treat uterine fibroids without surgery. But we must not forget that taking any medications must be agreed with your doctor. Some herbs affect hormones and actively interact with medications used in the treatment of myomatosis.
The following herbs and infusions can be used to reduce the size of fibroids:
- Chinese cinnamon;
- Rhodiola rosea;
- horsetail;
- yarrow.
Official medicine does not approve of traditional methods of treatment. You shouldn’t take risks and test recipes found on the Internet on yourself. It is especially dangerous to self-medicate with large fibroids. However, doctors recommend some natural extracts and dietary supplements for use by women who require vigilant monitoring.
- Epigallocatechin gallate.
The substance can be found in freshly picked tea leaves. Antioxidants reduce the risk of fibroid growth and prevent oxidative stress. You can add 3-4 cups of freshly brewed tea to your daily diet. But dietary supplements with concentrated extracts have proven real effectiveness. Daily intake of capsules with epigallocatechin gallate in an amount of 800 mg can eliminate all unpleasant symptoms and reduce the size of tumors in the uterus.
- Resveratrol.
The beneficial substance can be found in blueberries, mulberries and grapes. There are official studies confirming the positive effects of concentrated resveratol on the uterus. It has been proven that the polyphenolic compound slows down the proliferation of tumor cells. But it must be borne in mind that in order to achieve the required concentration of reservatol, one would have to consume up to 10 kilograms of grapes daily.
- Curcumin.
The main active component of turmeric has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Curcumin may be used in the treatment of fibroids. The substance destroys tumor cells and inhibits the growth of tumors.
Treatment with Mirena coil
The Mirena intrauterine device for uterine leiomyoma is a hormonal IUD of the latest generation and is used for contraception and treatment. Thanks to the main active ingredient - levonorgestrel, the endometrium is thinned, the blood supply to the tumor is reduced, as a result of which many symptoms of uterine leiomyoma disappear.
The use of Mirena for uterine leiomyoma allows you to achieve the following results:
- cessation of intermenstrual bleeding;
- reduction in the volume of menstrual flow;
- elimination of painful sensations in the lower abdomen characteristic of leiomyoma;
- reducing pressure on nearby organs (with subserous leiomyoma);
- improvement of general well-being.
However, the main advantage of the Mirena spiral is that its use helps to reduce the myomatous node itself. Thanks to the normalization of hormonal balance, the tumor loses its stimulus for development. In addition, Mirena helps prevent the development of endometriosis, hyperplastic processes of the endometrium, often accompanying leiomyoma.
What vitamins can you take if you have fibroids?
Taking certain vitamin complexes will be a good addition to the prescribed treatment . Numerous studies have confirmed that the risk of fibroid increases in women suffering from a deficiency of vitamins A and D. Beneficial effects on the uterus and the menstrual cycle:
- thiamine (B1);
- pyridoxine (B6);
- vitamin E;
- retinol (A);
- calciferol (D).
You can also take Omega-3 and Omega-6 acids. You should not buy vitamin complexes without consulting your doctor. When treating fibroids with medication, any supplements are strictly prohibited.
Hormone provocateur
The growth of the rudiment of the myomatous node is triggered by the hormone progesterone. A damaged cell that “believes” itself to be pregnant is very sensitive to this hormone. It is not without reason that the cells of myomatous nodes actively divide during periods when the level of progesterone in a woman’s body increases significantly (this is the second phase of the menstrual cycle and pregnancy).
There is not a single reliable theory explaining the cause of the occurrence of uterine fibroid precursor cells. It is assumed that the damaging factor may be a small number of pregnancies (and, accordingly, many menstrual cycles). According to another theory, a defect in the cells of the uterus occurs in the prenatal period, when they are in an unstable state for a long time.
Permitted and prohibited products
If the doctor has not given permission to take synthetic supplements and use traditional recipes, you need to make changes to your diet. Certain foods can speed up the process of reducing the size of the tumor. The basis of the diet for fibroids should be:
- fatty fish: salmon, mackerel, tuna;
- red berries;
- green vegetables;
- leaf salads;
- citrus fruits (especially lemons and limes).
If you plan to treat myomatosis without surgery, especially with medication, it is necessary to exclude estrogen-containing products from the menu. The hormone stimulates the development of the mucous membrane lining the uterus. Too much estrogen obtained from the daily menu can negate the effect of medications and provoke the growth of fibroids. It is worth excluding from the diet:
- soy products;
- flax seeds, sesame seeds;
- walnuts, peanuts, almonds;
- red meat;
- animal fats;
- dried fruits.
Proper nutrition will contribute to treatment and speed up the healing process.