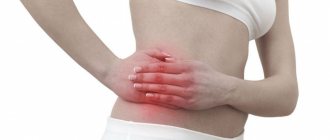
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, a finger-shaped extension of the cecum that is located in the lower right side of the abdomen. With appendicitis, pain occurs in the lower right corner of the abdomen. However, for most people, the pain starts around the belly button and then moves. As the inflammation progresses, the pain tends to get worse and eventually become intense. The localization of pain with appendicitis may be different depending on the age and gender of the patient. This is especially common in children and pregnant women.
The standard treatment for appendicitis is surgical removal of the inflamed appendix - appendectomy
.
What is an appendectomy?
Appendectomy is a surgical operation to remove the appendix.
The appendix is a vermiform appendage that is an appendage of the cecum. It is believed that the appendix stimulates the immune system and improves the body's defense resources. The appendix is a cylindrical organ, hollow inside and without a through passage. The average length of the appendix is 8–10 cm. Appendicitis is a disease associated with inflammation of the appendix. It can occur in acute or chronic form. In chronic appendicitis, appendectomy is performed routinely. An acute form of inflammation of the appendix requires timely surgical intervention.
Early recovery period
After the operation is completed, the patient is observed for several days by the operating surgeon. Sutures are removed 7-10 days after surgery.
Early postoperative rehabilitation includes the following points:
- Detoxification of the body (in this case, activities are carried out both on the first day after surgery and in the following days);
- Following a strict diet;
- Restoring the functional potential of the intestines and bladder.
In the postoperative period, the patient may be prescribed medications (antibiotics, analgesics). Particular attention is paid to the prevention of constipation (for this purpose, a special diet and laxatives are prescribed).
Causes of appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix is caused by opportunistic microorganisms. When examining the affected tissue of the inflamed appendix, Escherichia coli, enterococcus, streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus and anaerobic microorganisms are most often found. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the wall of the appendix from its lumen.
Doctors identify factors that provoke inflammation of the appendix:
- inflammatory process in the intestines;
- deformation of the appendix, in which there is a violation of blood circulation in the walls of the organ, which leads to necrosis of the appendix tissue;
- blockage of the appendix - fecal stones, neoplasms, foreign bodies and accumulation of parasites can close the lumen of the appendix. At the site of the blockage, microbes begin to actively multiply, causing inflammation.
Symptoms of appendicitis inflammation
Chronic appendicitis is a sluggish inflammation of the appendix of the cecum, as a result of which the walls of the organ are replaced by scar tissue and infiltrated by immunocompetent cells. Doctors distinguish three forms of chronic appendicitis:
- Recurrent form - characterized by alternating periods of exacerbation and remission with minor clinical manifestations (moderate pain in the right iliac region).
- Residual form (residual) - develops when, after an acute attack, inflammatory phenomena in the appendix are only partially relieved.
- Primary chronic form - develops without a primary acute attack, development occurs gradually.
As a rule, chronic inflammation of the appendix is accompanied by a dull aching, stabbing or pressing pain in the right iliac region. Pain, as a rule, intensifies with physical activity and poor diet.
Acute inflammation of the appendix begins with swelling of the organ, then it begins to fill with pus.
Minimally invasive techniques for removing the appendix
Despite the fact that classic appedectomy and laparoscopic removal of the appendix of the cecum are used quite often, the popularity of minimally invasive techniques is increasing every day. We are talking about the following forms of surgical intervention:
- transgastric appendectomy. It is performed without external incisions. To gain access to the tissues of the cecum and enter the abdominal cavity, a system of flexible instruments is used. The devices are inserted through the digestive tract, passing through the desired area of the intestine;
- transvaginal appendectomy. Access to the source of inflammation is carried out along an ascending route through a micro-incision in the vaginal wall. When choosing this method for removing the appendix, the location of the lesion plays a significant role.
Operations of this type make it possible to prevent complications associated with direct tissue trauma. They cannot be carried out if peritonitis is suspected, in the presence of multiple large foci with inflammation, or when the patient has manifestations of sepsis.
Symptoms of acute appendicitis:
- severe abdominal pain, which may intensify with palpation;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- nausea, vomiting;
- loss of appetite;
- flatulence (bloating);
- temperature increase.
If such symptoms occur, it is important to seek medical help promptly. If the appendix is not removed in a timely manner, perforation (rupture) of the organ may occur, causing pus to enter the abdominal cavity and cause peritonitis, a complication that can be fatal.
If you are concerned about one or more of the above symptoms, contact your surgeon immediately for advice. You can make an appointment at a convenient time with a surgeon at Euromed Clinic by phone + or online.
Indications
Symptoms of inflammation of the appendix are in many ways similar to those of other diseases of the abdominal organs. But any of the symptoms listed below is a reason to consult a surgeon:
- pain in the lower abdomen on the right side;
- nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite, aversion to food;
- diarrhea or, conversely, lack of stool;
- low-grade fever (37 - 37.5 degrees);
- increased pain when pressing on the abdomen, coughing and other types of muscle tension;
- weakness.
In practice, the symptoms of this disease often differ from the standard. A person may have half of the listed symptoms, or the picture may be complemented by other symptoms. Because of this, patients often self-medicate.
Even if the symptoms are mild, do not delay visiting the doctor. Inflammation can lead to rapid development of complications. GMS Hospital specialists will do everything to ensure that treatment is as fast and effective as possible.
Indications for appendectomy
Surgery to remove the appendix is used for chronic or acute forms of appendicitis. In addition, appendectomy is performed if there is an appendiceal infiltrate, as well as if neoplasms are detected in the appendix.
Emergency appendectomy is usually performed no later than one hour after diagnosis. In case of chronic appendicitis or appendicular infiltrate, surgery to remove appendicitis is performed as planned.
Complications
After surgery to remove the appendix, some complications may develop, so the patient needs constant monitoring. The operation itself usually proceeds well, but some technical difficulties may be caused by the unusual location of the appendix in the abdominal cavity.
The most common complication in the postoperative period is suppuration in the incision area, which can be diagnosed in every fifth patient with purulent types of appendicitis. Other options for unfavorable developments are peritonitis, bleeding into the abdominal cavity due to insufficient hemostasis or sutures slipping off the vessels, suture dehiscence, thromboembolism, adhesive disease in the late postoperative period.
Sepsis is considered a very dangerous consequence, when purulent inflammation becomes systemic, as well as the formation of ulcers (abscesses) in the abdomen. These conditions are facilitated by rupture of the appendix with the development of diffuse peritonitis.
The main methods for removing appendicitis:
- Open appendectomy - performed through an 8-10 cm incision in the right iliac region. Through the resulting incision, the surgeon separates the appendix from the surrounding tissues and then removes the organ. Removal of appendicitis using this method is indicated when the infectious process has spread into the abdominal cavity or when the appendix is located incorrectly.
- Laparoscopic appendectomy is an endoscopic method that allows you to cut out the appendix through three small punctures in the abdominal wall. This type of operation to remove appendicitis is performed routinely for chronic and acute uncomplicated appendicitis. Laparoscopy for appendicitis is a minimally invasive procedure, since the operation causes minimal trauma to the anterior abdominal wall.
Treatment methods
The traditional scenario for the operation to remove the appendix is carried out by creating a small incision not exceeding 12 centimeters. The entire procedure can be divided into several stages:
- Introducing the patient into a state of anesthesia. Today, removal of the appendix is most often performed under general anesthesia. If there are contraindications to general anesthesia, anesthesia is performed using the tight infiltration method or through conduction blockade;
- After this, the surgeon dissects the abdominal wall layer by layer, this allows you to avoid postoperative complications associated with damage to nerve endings, as well as respond in a timely manner to the sudden occurrence of bleeding;
- The muscles, like the edges of the surgical wound, are separated by blunt surgical instruments;
- After opening the internal space of the abdominal cavity, the doctor carefully examines the abdominal wall itself, assesses the condition of neighboring organs and begins to remove the intestinal loops, behind which the appendix itself is located;
- Next, the surgeon removes the appendix and sutures the surgical wound. First, the inflamed process is isolated from other tissues using a clamp and ligature;
- The surgeon places a purse-string suture on the stump (the edges of the sutures are inside the stump);
- After completing all surgical procedures inside the abdominal cavity, the surgeon forms external sutures. The peritoneal walls are usually held together using self-absorbable suture material. The surgeon places from 8 to 12 stitches, using synthetic or silk threads;
- The external postoperative suture must be removed 1 - 2 weeks after surgery.
Contraindications for laparoscopic appendectomy:
- late stages of pregnancy;
- severe blood clotting disorders;/li>
- undergone operations on the abdominal organs;/li>
- severe cardiovascular and respiratory failure;/li>
- abnormal location of the appendix;/li>
- old age;/li>
- pronounced adhesive process;/li>
- widespread peritonitis requiring sanitation and drainage of the abdominal cavity;/li>
- dense appendicular infiltrate;/li>
- gangrenous appendicitis./li>
Preparing for an appendectomy:
In acute appendicitis, preparation for appendectomy is carried out promptly; as a rule, the condition of the patient's cardiac and respiratory systems is assessed.
For a planned operation , the results of blood tests, urine tests, fluorography, and an electrocardiogram are required. Women need to be examined by a gynecologist to rule out inflammatory processes that can lead to complications.
You should not take food or water for at least six hours before surgery. In case of laparoscopic surgery, it is necessary to first perform an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Indications and preparation for surgery
Appendectomy is one of the interventions that in most cases is performed as an emergency. Indication: acute appendicitis. A planned operation to remove the appendix is performed with appendiceal infiltrate after the inflammatory process has subsided, approximately 2-3 months from the onset of the disease. In case of increasing symptoms of intoxication, rupture of an abscess with peritonitis, the patient needs emergency surgical treatment.
There are no contraindications to appendectomy, except in cases of the patient's agonal state, when the operation is no longer advisable. If doctors have adopted a wait-and-see approach due to appendiceal infiltration, then severe decompensated diseases of the internal organs may be contraindications to surgery, but during conservative treatment the patient’s condition can be stabilized to such an extent that he can undergo the intervention.
The operation usually lasts about an hour, both general anesthesia and local anesthesia are possible. The choice of pain relief is determined by the patient’s condition, his age, and concomitant pathology. Thus, in children, people with excess body weight, which involves greater trauma when entering the abdominal cavity, with nervous overexcitation and mental illness, general anesthesia is preferable, and in thin young people, in some cases, it is possible to remove the appendix with local anesthesia. Pregnant women, due to the negative impact of general anesthesia on the fetus, are also operated on under local anesthesia.
The urgency of the intervention does not require sufficient time to prepare the patient, so the necessary minimum examinations are usually performed (general blood test, urine test, coagulogram, consultations with specialists, ultrasound, x-rays). To exclude acute pathology of the uterine appendages, women need to be examined by a gynecologist, possibly with an ultrasound examination. If there is a high risk of thrombosis of the veins of the extremities, the latter are bandaged before surgery with elastic bandages.
Before the operation, the bladder is catheterized, the contents are removed from the stomach if the patient ate later than 6 hours before the operation, and an enema is indicated for constipation. The preparatory stage should last no more than two hours.
When the diagnosis is beyond doubt, the patient is taken to the operating room, anesthesia is administered, and the surgical field is prepared (hair shaving, iodine treatment).
How to remove appendicitis during laparoscopy
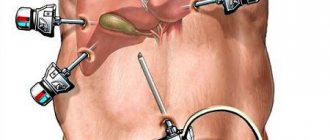
Patients are often interested in what anesthesia is used to remove appendicitis. Surgery is performed under general anesthesia. At the beginning of the operation, the patient is given anesthesia. After antiseptic treatment of the skin in the area of the operation, in the anterior abdominal wall (in the pubic area and right hypochondrium), the surgeon makes three small incisions. The laparoscope is inserted through the first incision, which is located just above the navel. Through other holes, special instruments are inserted to hold the appendix. Next, the surgeon removes the inflamed appendage and removes it from the abdominal cavity.
This is followed by suturing. Typically, absorbable suture material is used and does not require subsequent removal.
Appendectomy
Appendectomy can be performed in two ways:
- traditional open surgery through an incision in the abdominal wall;
— laparoscopic appendectomy.
Both operations are performed under general anesthesia and take from 30 minutes to an hour and a half, depending on the presence of complications and the method used.
Traditional open appendectomy
Classic open surgery to remove the appendix is performed for complicated appendicitis, for example, if the appendix has ruptured and the infection has spread beyond the appendix in the abdominal cavity (peritonitis), retroperitoneal space in the form of phlegmon, or an abscess has formed. In such cases, traditional surgery allows the surgeon to thoroughly cleanse the abdominal cavity of infection (sanitise and drain).
In addition, open appendectomy may be required for patients: with severe obesity; with a pronounced adhesive process that makes access to the appendix difficult; with an atypical location of the process; with a long-term inflammatory process in the appendix, when there is a high probability of complications in the form of spread of inflammation to the cecum or rupture of the appendix.
Another reason for traditional open surgery may be concomitant diseases that prevent the application of pneumoperitoneum (injection of carbon dioxide into the abdominal cavity), which is required for laparoscopic surgery.
Laparoscopic appendectomy
Laparoscopic appendectomy is performed most often and is a fairly simple operation that rarely entails complications. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, the average duration of the operation is about 40 minutes. In most cases, the patient can go home 1-2 days after the operation.
Main stages of laparoscopic appendectomy
Preparatory stage. After the onset of anesthesia, the surgeon will pump carbon dioxide into the abdominal cavity through a special thin needle. The purpose of pumping carbon dioxide is to lift the abdominal wall and at the same time tighten the internal organs, figuratively speaking, “inflate the stomach.” Carbon dioxide is absolutely harmless to the body and its injection allows you to create space in the abdominal cavity for the surgeon to work. After this, two punctures are made in the abdominal wall (one in the navel area and one in the bikini area), through which a laparoscope equipped with a video camera is inserted to examine the abdominal and pelvic organs, as well as to visually monitor the further progress of the operation. The image from the laparoscope video camera is transmitted to the monitor in the operating room and allows surgeons to control their actions.
Diagnostic laparoscopy. At this stage, the surgeon, examining the abdominal cavity and appendix using a laparoscope, confirms or removes the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Evaluates the anatomical location of the appendix and the possibility of accessing it using surgical instruments for laparoscopy. Reveals, if any, the presence of contraindications for continuing laparoscopic appendectomy: spread of inflammation to the dome of the cecum; ruptured appendix (peritonitis); phlegmon of the retroperitoneum; formed abscess; inaccessibility of removing the appendix using the laparoscopic method. In such cases, a transition to a traditional open appendectomy is required.
Removal of the appendix. If the diagnosis is confirmed and no contraindications are identified, the surgeon makes one additional incision (1 cm) to insert the instruments - manipulators necessary to remove the appendix. Then they begin to isolate the appendix, intersect its mesentery, remove the appendix and remove it from the abdominal cavity (through one of the punctures).
The final stage. At the end of the operation, carbon dioxide is removed from the abdominal cavity, stitches and a sterile dressing are applied. After full awakening, the patient is transferred to the postoperative department.
Benefits of laparoscopic appendectomy
1. No incisions in the anterior abdominal wall and, as a result, less pain, less chance of infection, short recovery period;
2. Already 2-3 hours after laparoscopy, the patient can get up. Usually, by the evening or morning of the next day, the condition already allows you to return to normal physical activity, and after a few days to return to work. Marks on the skin from punctures heal quite quickly; after a few months they can hardly be detected;
3. Great information content. The technology of laparoscopy, in which an image from the abdominal cavity is displayed on a monitor screen, makes it possible to detect the smallest pathology that is not visible during classical surgery. This is possible due to the fact that the monitor can magnify the image of organs up to 10 times.
4. Gentle surgical effect. Muscles and vessels are not cut, minimal trauma to the intestines, as a result - rapid restoration of peristalsis and intestinal function.
Recovery after laparoscopic appendectomy
After appendectomy using the laparoscopic method, restoration of work capacity and return to a normal lifestyle occurs faster. As a rule, after 1–2 days the patient is discharged from the hospital. After the operation, the surgeon will prescribe antibacterial therapy and give recommendations on diet and physical therapy to quickly restore the body.
At Euromed Clinic, surgeons perform both open and laparoscopic appendectomies.
Advantages of laparoscopic surgery
At the GMS Hospital surgical center, appendix removal is performed mainly by laparoscopic method.
Advantages of laparoscopic appendectomy:
- minimal surgical intervention;
- insignificant blood loss - due to the low invasiveness of the operation;
- minimal pain after surgery. As a result, there is no need for long-term use of analgesics;
- rapid postoperative rehabilitation;
- cosmetic effect - scars after laparoscopic appendectomy are almost invisible.
Advantages of performing an appendectomy at Euromed Clinic:
- Euromed Clinic is a full-service clinic. Before the operation, if necessary, we will arrange for you consultations with a therapist, cardiologist and any other specialist;
- Our own laboratory allows you to take the necessary tests at once and quickly get results;
- all surgeons at Euromed Clinic are experienced and qualified specialists;
- the operating room is equipped with modern medical equipment;
- use of the latest generation of anesthesia;
- own hospital with modern comfortable rooms;
- experienced surgeons at the clinic use the most modern dressing and suture materials and disposable instruments;
- All reusable metal instruments undergo a three-stage sterilization system and are then placed in vacuum packaging to ensure the sterility of the instrument.
You can make an appointment at a convenient time with a surgeon at Euromed Clinic by calling + 7 812 327 03 01 or online.
Advantages of performing surgery at GMS Hospital
Our surgical center has an abdominal surgery department equipped with the latest technology. This allows doctors to perform surgical treatment with a minimal degree of intervention.
The advantages of treatment at GMS Hospital do not end there:
- Our doctors practice comprehensive treatment of abdominal diseases, including appendicitis. If necessary, patients are observed not only by the surgeon, but also by related specialists.
- Subspecialty surgeons have a high degree of qualification. By contacting GMS Hospital, you entrust your health to competent, responsible specialists.
- We use as low-invasive techniques as possible.
- Modern and safe anesthesia is used for operations.
- During hospitalization, patients are accommodated in cozy, comfortable single hospital rooms.
- Polite and qualified medical staff provide comprehensive support during the period of postoperative rehabilitation.