Human bone marrow promotes the production of lymphocytes. After entering the bloodstream, they become immature. The first place where their maturation occurs is the thymus, the second is the lymph node. The localization of the thymus is the upper part of the chest, and the lymph nodes are the neck, groin, and armpit. T-lymphocytes are called cells after the maturation process in the thymus, and B-lymphocytes mature in the lymph node. These two types of lymphocytes produce antibodies that fight foreign tissue and infections. The antibody response is directed only at the antigen that matches it. For example, a child who has had mumps will not develop immunity against measles.
The essence of vaccination is to familiarize the immune system with a certain type of disease. Administration of a vaccine means that a small dose of the pathogen penetrates the body, which is needed for the further destructive effect of antibodies on antigens. However, there are situations when lymphocytes begin to attack the tissues of their own body. This is how autoimmune diseases begin to develop. They occur in approximately 10 percent of the world's population. Medical practice shows that rare autoimmune diseases affect men less often than women. There are ten main causes of death. These causes include autoimmune and immunodeficiency diseases.
Every person’s body has immunity, which begins its development from the moment of birth. It consists of special organs and cells that protect against negative microbial and viral effects. The immune system is based on a mechanism that can distinguish between self and foreign tissue. Various damage provokes dysfunction of the immune system, as a result of which it ceases to distinguish its own cells from foreign ones. This phenomenon activates the production of autoantibodies that mistakenly attack healthy cells. As a result, the regulatory work of t-lymphocytes disappears, and severe autoimmune diseases appear that affect the internal organs and systems of the body.
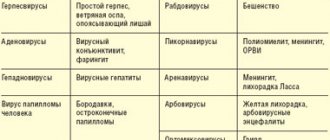
A list of autoimmune diseases should be considered. The first type is a disorder that appears when the histohematological barrier is disrupted. The second type of disease appears after the body’s tissue is transformed from physical, chemical, or viral effects. Deep metamorphotic processes occur in healthy cells, and as a result, they are perceived by others. There are cases where antigenic or exoantigenic concentration occurs. The body will react by damaging the cell on the membrane of which the antigenic complex is preserved. Sometimes contact with a virus provokes the formation of an antigen that has a hybrid property. It can affect the central nervous system.
The third group includes diseases of the autoimmune system, in which coalescence of tissue with an exoantigen occurs. As a result, a natural reaction is activated, aimed at the affected areas. The fourth group includes ailments caused by a genetic deviation or the influence of an unfavorable external factor. This entails a rapid mutation of immune cells, which manifests itself as lupus erythematosus.
The development of an autoimmune disease can develop at any age. Despite this, there is a group of people who are more susceptible to autoimmune diseases. Namely:
- A person who is exposed to negative influences from external factors. Specialists in autoimmune diseases in Moscow highlight the influence of sunlight, chemicals, viral or bacterial infections, which cause pathological processes in the immune system.
- A woman of childbearing age. Autoimmune diseases occur more often in women than in men.
- Certain races and ethnic groups. Signs of an autoimmune disease are more likely to occur in people with white skin. For example, African Americans and Hispanics have a hard time with systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Hereditary factor. It should be remembered that autoimmune diseases are inherited from close relatives. Medical practice shows that a family history can reveal different types of immune disorders.
Why do they appear?
Medical research identifies internal and external reasons why autoimmune diseases occur. One of the internal reasons when aggression and uncontrolled proliferation of lymphocytes occurs is a gene mutation of the first type. At the same time, recognition of healthy cells by lymphocytes disappears. A person inherits such an immune disorder from a close relative. Considering the mutation process in a specific organ or system, thyroiditis and goiter may develop.
Another internal cause is a type 2 gene mutation, in which uncontrolled proliferation of nurse lymphocytes occurs. As a result, immune and autoimmune diseases appear, which are mainly inherited. Among the external causes of autoimmune disease are a severe, protracted infectious disease, after which inadequate behavior of immune cells occurs, as well as the negative impact of environmental factors (radiation, ultraviolet rays). The occurrence of a malfunction of the immune system occurs due to the cunning of the cell that causes the disease. They are able to pretend to be similar to their own, but pathogenic cells. As a result, lymphocytes lose the ability to recognize foreign organisms and begin to fight both.
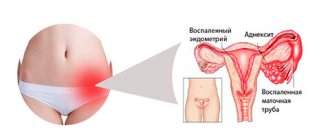
Systemic autoimmune diseases appear when the integrity of the blood barrier that separates a certain organ or tissue from the blood is disrupted. The norm is the absence of penetration of cellular antigens into the bloodstream. This means that T-lymphocytes do not develop tolerance to them. The barrier cells include brain cells, thyroid cells, and cells that produce insulin. In the presence of such a mechanism, chronic autoimmune prostatitis develops. This means that sperm-producing cells are separated from the blood by the blood-testis barrier. Infection, inflammation, trauma can cause a violation of its integrity, as a result of which auto-aggression begins, directed at the prostate tissue.
Searching for causes in cells
Modern research into AIs is carried out at the level of genes, cells, and molecules. And there are many successes in this obscure area for the average person. For example, in 2021, Canadian and American scientists discovered that the ALCAM molecule (activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule) delays the development of multiple sclerosis.
A month ago, Japanese researchers compiled a first-of-its-kind genetic database on AIDS. A research team from the University of Tokyo sequenced the whole genomes of 79 healthy volunteers and 337 patients diagnosed with any of ten different AIDS, including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and multiple sclerosis. Based on a comparison of genomes, Japanese scientists calculated all DNA sequence variants that are in one way or another associated with the disease. Ultimately, the researchers identified 28 different types of immune cells responsible for the disease and measured gene expression in these cells. Now this Immune Genome Data Atlas will allow experts to better understand how immune disorders develop in order to determine which targets to target for treatment.
For example, for Addison's disease, the AIRE gene may be targeted. This year, scientists from Sweden and Norway analyzed 1,223 samples from sick patients and 4,097 samples from healthy people and found certain mutations in this gene. This study of the genetic causes of a rare disease associated with adrenal insufficiency is the largest in the world to date. And, probably, such “genetic investigations” will be carried out for each AIZ.
It has been known for about 50 years that a gene variant called HLA-DR15 is associated with multiple sclerosis. But only last year, scientists discovered an additional risk factor: the likelihood of the disease in a carrier of this gene increases significantly if he is infected with the Epstein-Barr virus.
Scientists from Trinity College Dublin have discovered that immune failure begins with the secretion of IL-17 by immune cells. “The role of IL-17 is indirect - it triggers the production of other immune cells in the lymph nodes, which then infect nerve cells in the spinal cord and brain,” explained one of the authors, Kingston Mills. There are already drugs that can block IL-17. They have enormous potential and, according to Mills, should be considered a “breakthrough” direction in the development of a whole class of new drugs. A similar remedy that can effectively treat psoriasis has already passed the licensing stage.
What causes the immune system to attack its own tissues? Scientists are looking for the answer to this question inside human cells themselves. This year, a German research group in Munich identified a possible target: the hyperactive RANK protein on the surface of B cells.
“B cells, a subset of white blood cells (leukocytes) produced in the bone marrow, play a central role in regulating immune responses. During a normal immune response, activated B cells produce antibodies that attack foreign substances. Defective activation can lead to the formation of autoantibodies that attack the body itself, causing AIDS. The activity of B cells is controlled by various signals, some of which we have yet to understand,” said study author, immunologist and physician Jürgen Ruhland, laureate of the German Science Prize. Leibniz 2021. Ruhland and his team were able to identify one crucial signal that influences B cell activity.
In their experiments, they targeted the B-cell receptors of mice. A few weeks later, most of the rodents with genetically modified receptors fell ill with systemic lupus erythematosus, and then scientists were able to cure the mice using therapeutic antibodies that block the interaction of RANK receptors. This healing mechanism, in their opinion, should work in humans.
What types of autoimmune diseases exist?
Speaking about the classification of disorders, there are three groups of autoimmune diseases. The first group includes organ-specific pathologies, characterized by the direction of antibodies and lymphocytes to the autoantigen of one or more organs. This includes a barrier antigen, to which there is no innate tolerance. The second group includes organ-nonspecific diseases, when autoantibodies and lymphocytes interact with autoantigens of a tissue or organ. The pathological process develops when tolerance already exists. The third group consists of the above mechanisms.
If a person is faced with an immune disorder, he will be interested in which doctor deals with autoimmune diseases. In case of organ-specific autoimmune disease, you must consult a specialized doctor. With a mixed or systemic illness, qualified assistance from many doctors is required. This is a neurologist, hematologist, rheumatologist, endocrinologist, cardiologist, pulmonologist, dermatologist, nephrologist.
New drugs - minimum adverse reactions with maximum effectiveness
The use of biological drugs has proven to be the most effective treatment for rheumatoid arthritis, but serious side effects associated with the systemic nature of their action force scientists to develop new drugs. The next step in the evolution of rheumatoid arthritis therapy may be selective blockers of inflammation that do not have this drawback.
The laboratory of Sergei Arturovich Nedospasov, located at the Institute of Molecular Biology of the Russian Academy of Sciences (Moscow), has been working on this problem for more than 10 years. Scientists believe that one of the possible ways to solve this problem is to create a drug that blocks the key pro-inflammatory cytokine, TNF, produced only by a certain type of cells, for example, macrophages. This selective neutralization will reduce inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis, but will not affect the body's ability to fight infection.
To solve this problem, a bispecific molecule was obtained, which consists of an antibody that blocks TNF and a second antibody that binds to the F4/80 molecule on the surface of mouse macrophages [22]. When creating such a design, scientists used single-domain antibodies obtained from llamas and camels, the bioengineering of which is described in the article by Oksana Goryaynova “Cancer... a camel will cure!” [23]. Experiments on mice have shown that such antibodies actually do their job. Of course, the use of such drugs in the treatment of real patients is still very far away, but the first steps towards this have already been taken.
What are systemic autoimmune diseases?
The appearance of lupus erythematosus is associated with a violation of the autoimmune process, when all internal organs are involved. The disease affects two to three people out of a thousand. Lupus erythematosus occurs when abnormal antibodies are formed in the body due to the influence of a genetic factor. Confirmation is the presence of a relationship between pathology and a lack of hereditary components of immunity. In addition, a toxic substance, a virus, or uncontrolled use of medications can provoke the appearance of an immune disorder.
The systemic disorder occurs without symptoms for a long time, manifests itself as a skin rash, and the musculoskeletal system is disrupted. However, at this time, the intensity of immune imbalance in the body increases, which can cause an inflammatory process in any internal organ. Lupus erythematosus is characterized by damage to the connective tissue present in organs and systems. As a result, skin rashes appear on the face and chest, and the skin becomes sensitive to ultraviolet radiation (redness, rash, spots). A distinctive feature is the appearance on the body of a disc-shaped element, which has a red edge and a pale middle.
With this autoimmune disease, the symptoms are as follows:
- The appearance of lupus arthritis is characterized by sharp or aching pain, swelling, and redness of the joints that are involved in the pathological process. After limited movement of the affected limb, complete immobilization of the bone joint occurs.
- Damaged outer serous membranes of internal organs cause coughing attacks and pain when inhaling and exhaling. The doctor will hear a moist wheeze in the lower lobe of the lung.
- Damage to the heart and blood vessels occurs, aching pain appears, and the rhythm of heart contractions is disrupted.
- Due to pathological vascular changes, the feet and hands turn blue, and the extremities become cold.
- The appearance of visual and auditory hallucinations, a state of delirium.
- With abdominal syndrome, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and anorexia appear.
If the question arises of how to identify an autoimmune disease, a comprehensive examination should be used, which includes clinical, laboratory, immunological, and histological methods. The doctor will prescribe a blood test, an electrocardiogram, an x-ray, an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, and kidneys. With timely treatment of an autoimmune disease, the patient's chances of avoiding pathological changes in an internal organ or system increase. Therapeutic measures consist of taking anti-inflammatory and immune suppressing drugs, as well as corticosteroids.
Inflammatory myopathy
This includes a group of diseases that are caused by muscle inflammation and weakness. The presence of polymyositis and dermatomyositis is often diagnosed in women. Inflammatory myopathy causes slowly progressive weakness of the muscles that control movement on both sides of the body. Dermatomyositis is characterized by a skin rash accompanied by muscle weakness. A person gets tired after a long walk or standing. Frequent stumbling, falling, difficulty swallowing food or water, or inhaling or exhaling air are noted.
Presence of myasthenia gravis
This is an autoimmune disease, how to diagnose and treat it, they will tell you at the Moscow clinic. Characterized by an immune attack on the nerves and muscles that are present throughout the body. A person with myasthenia gravis has double vision, difficulty focusing their eyes and lowering their eyelids. Difficulty swallowing, frequent belching, and choking occur. In addition, there are:
- The onset of paralysis, weakness.
- It's hard to hold your head up.
- It’s hard to go down or up stairs or lift things.
- Intelligible speech disappears.
Psoriasis lesion
With this disease, there is an excessive and rapid appearance of new skin cells, the accumulation of which is found on the skin. A sick person notices the appearance of dense red spots that are covered with scales. The areas where such spots are present include the head, elbows, and knees. Itching and pain also appear, which negatively affect performance and impair sleep.
Psoriasis can be accompanied by a form of arthritis that affects the joints and phalanges of the fingers of the upper and lower extremities. When the spine is affected, pain appears in the back area. A person can seek treatment for an autoimmune disease in Moscow.
For Sjögren's syndrome
The list of autoimmune diseases in humans is supplemented by Sjögren's syndrome, which is characterized by an attack of the lacrimal and salivary glands. With this syndrome, the patient has the following symptoms:
- Dry eyes.
- The appearance of severe dental caries.
- Presence of dry mouth.
- Blurred vision.
- Difficulty swallowing food and drinks.
- Joints become swollen and painful.
- Swelling of the tonsils is detected.
- Fever due to autoimmune disease.
- A person loses his sense of taste.
- The voice becomes hoarse.
- The appearance of excessive fatigue.
Presence of scleroderma
An immune disorder in which abnormal development of connective tissue appears in the skin and blood vessels. The signs of scleroderma are as follows:
- The appearance of shortness of breath.
- The skin thickens.
- Whitening, redness or blue discoloration of the fingers of the upper and lower extremities is visible.
- Body weight decreases sharply.
- Frequent diarrhea or constipation appears.
- The skin of the hands and forearms becomes shiny.
- Painful sensations, swelling of the fingers.
- The skin on the face becomes stretched, looking like a mask.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Wounds appear on the fingers.
Detection of rheumatoid arthritis
When listing what belongs to autoimmune diseases, rheumatoid arthritis should be highlighted, in which the joints and surrounding tissue become inflamed. It can appear at any age. Research to cure this type of autoimmune disease involves taking a blood test for the presence of rheumatoid factor and magnetic resonance imaging of the affected joint.
Presence of diabetes mellitus
When determining what autoimmune diseases are, type 1 diabetes mellitus, in which the metabolism of carbohydrates and water is disrupted, should be included. As a result, the functioning of the pancreas, which produces insulin, is disrupted. It helps process sugar. The disease can be acquired or inherited. Lack of insulin provokes the occurrence of pustular lesions of the skin. Teeth begin to crumble, a feeling of angina pectoris appears, blood pressure jumps, the functioning of the kidneys and nervous system is disrupted, and there is a sharp deterioration in visual function.
Symptoms are gradual. The onset of diabetes mellitus is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Wounds heal slowly.
- The presence of constant dryness in the oral cavity.
- There is an increased tendency to form a purulent process on the skin and tissues.
- Profuse sweating.
- Weakness in all muscles.
- A thirst appears that is difficult to quench. As a result, the patient has to drink several liters per day.
- The skin begins to itch due to excessive dryness.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
The presence of one of the above symptoms is a reason to donate blood to determine the glucose level. If the autoimmune disease is not treated, other signs appear:
- The smell of acetone is heard from the mouth.
- Dysfunction of the visual organ.
- Consciousness is lost.
- Constant headache.
- The face and legs swell.
- Painful sensations in the heart.
- The liver is enlarged.
- My legs become numb and sore, which prevents me from walking fully.
- The skin on the feet loses sensitivity.
- Blood pressure rises sharply.
A person who is faced with diabetes mellitus is interested in whether it is possible to get rid of this type of autoimmune disease, which doctor to see, how long the treatment will last. After the examination, the doctor prescribes a drug that stimulates the pancreas to produce more insulin. As well as medications that can increase cellular sensitivity to insulin, inhibitors and agonists. To get rid of diabetes, you should follow a diet that is low in carbohydrates, do not self-medicate, and go to the gym to increase physical activity. There are times when it is necessary to inject insulin to normalize glucose levels.
Detection of sarcoidosis
Refers to a rare chronic inflammatory disease that affects four out of one hundred thousand people. Lung damage occurs. Rarely occurs in children and the elderly. Sarcoidosis is characterized by difficulty breathing during physical activity, a sharp decrease in body weight, loss of appetite, and excessive fatigue. Apathy, muscle weakness, and coughing attacks may occur. Signs of sarcoidosis include coughing up blood, shortness of breath, and chest pain. In advanced forms, respiratory function decreases due to the inflammatory process in the lungs. There may be a disturbance in the eyeball, joints, and skin. If autoimmune diseases are not treated with immunoglobulins, the risk of complete loss of vision increases.
Sarcoidosis can appear due to contact with beryllium or zirconium, a strong reaction of the body to fungal exposure, pine pollen, atypical microbacteria, as well as genetic predisposition. To determine the pathology, X-rays and Kveim Silzbach skin testing are done. If you have a question about how to treat this type of autoimmune disease, you should visit a qualified doctor. He determines the causative agent of the disease, how long the illness lasts, and prescribes medications, the use of which will help avoid damage to vital organs. Without timely initiation of therapy, the prognosis for an autoimmune disease of this type is not comforting. The person may go blind and have respiratory failure.
Literature
- Immunity: fight against strangers and... one's own;
- Systemic lupus erythematosus: a disease with a thousand faces;
- Rheumatoid arthritis: change the composition of the joints;
- Nasonov E.L., Alexandrova E.N., Novikov A.A. (2015). Autoimmune rheumatic diseases - problems of immunopathology and personalized therapy. Bulletin of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. 2, 169–182;
- Babaeva A.R., Kalinina E.V., Zvonorenko M.S. (2016). New opportunities to improve the effectiveness and safety of treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Medical alphabet. 22, 5–12;
- Josef S Smolen, Robert Landewé, Ferdinand C Breedveld, Maya Buch, Gerd Burmester, et. al.. (2014). EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Ann Rheum Dis
.
73 , 492-509; - Nasonov E.L. (2015). Methotrexate for rheumatoid arthritis - 2015: new facts and ideas. Scientific and practical rheumatology. 4, 421–433;
- Kanevskaya M.Z. and Gurskaya S.V. (2013). Methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatic diseases. Modern rheumatology. 4, 47–53;
- D. T. Felson, J. S. Smolen, G. Wells, B. Zhang, L. H. D. van Tuyl, et. al.. (2011). American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Provisional Definition of Remission in Rheumatoid Arthritis for Clinical Trials. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases
.
70 , 404-413; - Patrick Durez, Jacques Malghem, Adrien Nzeusseu Toukap, Geneviève Depresseux, Bernard R. Lauwerys, et. al.. (2007). Treatment of early rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized magnetic resonance imaging study comparing the effects of methotrexate alone, methotrexate in combination with infliximab, and methotrexate in combination with intravenous pulse methylprednisolone. Arthritis Rheum
.
56 , 3919-3927; - Monoclonal antibodies;
- 12 methods in pictures: immunological technologies;
- Autophagy, protophagy and others;
- Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology 2021: for self-criticism;
- Zaichik A.M., Poletaev A.B., Churilov L.P. (2013). Recognition of “One’s own” and interaction with “One’s own” as the main form of activity of the adaptive immune system. Bulletin of St. Petersburg State University. Episode 11. Medicine. 1;
- Autoimmunity. Modern views on the physiological and pathological aspects of autoimmunity. NSU Electronic Archive;
- For the first time in half a century, there is a new drug for lupus;
- Nasonov E.L. and Karateev D.E. (2013). The use of genetically engineered biological drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: general characteristics (lecture). Scientific and practical rheumatology. 2, 163–169;
- Logvinenko S.I., Shcherban E.A., Pridachina L.S., Pridachina A.N., Maslova Yu.Yu., Kashichkina A.A. (2016). Genetic engineering in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew's disease). Scientific bulletins of BelSU. Series: Medicine. Pharmacy. 19, 179–182;
- Masahiko Mihara, Misato Hashizume, Hiroto Yoshida, Miho Suzuki, Masashi Shiina. (2012). IL-6/IL-6 receptor system and its role in physiological and pathological conditions. Clin.
Sci. .
122 , 143-159; - Nasonov E.L., Alexandrova E.N., Avdeeva A.S., Panasyuk E.Yu. (2013). Inhibition of interleukin 6 - new possibilities for pharmacotherapy of immunoinflammatory rheumatic diseases. Scientific and practical rheumatology. 4, 416–427;
- Suponitskaya E.V., Alexandrova E.N., Aleksankin A.P., Nasonov E.L. (2015). The effect of therapy with genetically engineered biological drugs on B-lymphocyte subpopulations in rheumatic diseases: new data. Scientific and practical rheumatology. 1, 78–83;
- Babaeva A.R., Cherevkova E.V., Galchenko O.E., Solodenkova K.S. (2012). Biological agents in the basic therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Medicinal Bulletin. 7, 3–9;
- Muravyov Yu.V. and Muravyova L.A. (2016). Untimely thoughts on the use of genetically engineered biological drugs for rheumatic diseases. Scientific and practical rheumatology. 3, 361–366;
- Psoriasis: at war with your own skin.
What is the prevention of autoimmune diseases?
To reduce the risk of immune pathology, viral infections and acute respiratory diseases should be completely treated. A person’s diet should include foods that contain vitamins and microelements. As well as fresh vegetables, fruits, whole grains, low-fat dairy products, a lean source of protein. Eliminate saturated fats, cholesterol, salt, refined sugar. The number of meals is two to four times.
Minimize stressful situations and nervous tension, since disturbances in the central nervous system increase the sensitivity of the immune system to the negative effects of external and internal factors. Start meditating, reading books, choosing a hobby. Also, a person should get proper rest. Poor sleep provokes a disruption in hormonal production. Do moderate physical activity and yoga. It is necessary to increase the load only after consulting a doctor. By following preventive rules, a person will reduce the likelihood of an immune disorder.
Carrying out analyzes
In medicine, there are a number of indicators that can be used to characterize the stage of the disease or confirm its absence. A comprehensive analysis is carried out:
I. General blood test. The increase in ESR determines the state of the disease.
II. Blood chemistry. Rheumatoid factor is detected, and in case of inflammation - C-reactive protein.
III. Immunological tests are performed to confirm the analysis, as well as to determine the titer of autoantibodies. When assessing, the doctor must take into account their severity and persistence. Only autoimmune diseases show persistent overproduction.
The quality of the research conducted is directly affected by preparation for the exam. Before this, you should avoid drinking alcohol, limit physical activity and exposure to emotional factors, and stop taking medications. Tests are taken on an empty stomach, after 8 or 12 hours of fasting (strictly on an empty stomach). During the day, blood counts can vary greatly, so all tests are taken only in the morning.
Determination of the reaction of settling red blood cells
Measuring the erythrocyte sedimentation reaction is required to record and control the inflammatory process. The patient takes a blood test, the result of which is to determine the rate at which red blood cells settle to the bottom of the laboratory vessel. With an exacerbation of the inflammatory process, which is associated with an autoimmune disorder, an increased amount of fibrinogen is found in the blood. As a result, red blood cells stick together.
Clumped red blood cells form into columns, which tend to settle at high speed. At normal rates, red blood cells settle at 15 millimeters per 60 minutes, typical for a man under 50, 20 millimeters for a woman under fifty, and for men over 50, less than 30 millimeters for a woman over 50. If a higher value is recorded, this indicates the presence of an autoimmune disease. A blood test for autoimmune diseases cannot determine the specific type of immune disorder. But such a test is necessary to identify and monitor tissue necrosis, rheumatological disease and other pathological conditions in which symptoms are mild.
Determination of the yeast component
Testing in the process of diagnosing autoimmune diseases is prescribed when there is discomfort in the epigastric region, pain in the abdomen. A person's level of antibodies to Saccharomyces present in baker's yeast is checked if there is a suspicion of developing ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease. To ensure the accuracy of the examination, a biopsy is performed. In vitro tests for autoimmune diseases help the doctor determine the type of disease, the degree of damage to internal organs, and also monitor the effectiveness of treatment measures.