Home | About us | Delivery | Advertisers | Login | Registration
- Medicines
- dietary supplementsVitamins
- Categories from A to Z
- Brands from A to Z
- Products from A to Z
- Medical equipment
- beauty
- Child
- Care
- Honey products appointments
- Herbs and herbal teas
- Medical nutrition
- Journey
- Making medicinesStock
Pharmacy online is the best pharmacy in Almaty, delivering medicines to Almaty. An online pharmacy or online pharmacy provides the following types of services: delivery of medicines, medicines to your home. Online pharmacy Almaty or online pharmacy Almaty delivers medicines to your home, as well as home delivery of medicines in Almaty.
my basket
Apteka84.kz is an online pharmacy that offers its customers medicines, medicinal and decorative cosmetics, dietary supplements, vitamins, baby food, intimate products for adults, medical equipment and thousands of other medical and cosmetic products at low prices. All data presented on the Apteka84.kz website is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical care. Apteka84.kz strongly recommends that you carefully read the instructions for use contained in each package of medicines and other products. If you currently have any symptoms of the disease, you should seek help from a doctor. You should always tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the medicines you take. If you feel you need further help, please consult your local pharmacist or contact our GP online or by telephone.
© 2021 Pharmacy 84.
Progesterone (Progesteronum)
The dosage regimen is individual.
The dose, frequency and duration of treatment are determined according to the regimen depending on the indications and clinical situation.
The progestogenic effect of 20-25 mg of progesterone when administered intramuscularly is equivalent to intravaginal administration (in the form of a suppository) of 100 mg of progesterone.
Secondary amenorrhea
(caused by hormonal imbalance, in the absence of organic pathology).
Orally at a dose of 400 mg 1 time per day (in the evening) for 10 days.
Intramuscularly 5-10 mg/day for 6-10 consecutive days.
Intramuscularly in a single dose of 100-150 mg.
Intramuscularly for adults, the highest single dose is 0.025 g (2.5 ml of 1% or 1 ml of 2.5% solution).
Intravaginally (in the form of a vaginal gel) at a dose of 45 mg (one applicator of 4% gel) every other day in 6 doses. You can increase the dose to 90 mg (one applicator of 8% gel) every other day up to 6 injections (8% vaginal gel is used only if 4% gel is ineffective).
With full ovarian activity or previous treatment with estrogen within 2 weeks before the administration of progesterone, withdrawal bleeding develops within 48-72 hours after the last injection. If menstrual bleeding occurs during treatment, stop using progesterone. Spontaneous normal menstruation may then develop.
Increasing the dose to 90 mg through the use of 4% vaginal gel does not provide the necessary absorption of the substance: the use of 8% gel is necessary.
With secondary amenorrhea of 4 and 8%, vaginal progesterone gel more often causes progestogenic changes in 92 and 100% of patients, respectively, and withdrawal bleeding in 81 and 82% of patients, respectively, in the absence of serious side effects and the associated need to discontinue treatment (2%).
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
(for parenteral use).
Intramuscularly 5-10 mg/day (15 mg/day) for 6-8 consecutive days.
Orally 400 mg/day for 10 days.
The bleeding should stop within 6 days. When combined with estrogens, treatment with progesterone begins 2 weeks after taking them. If menstruation develops during treatment, the use of progesterone is discontinued.
Induction of menstruation
(for parenteral use): before prescribing a progestin, adequate stimulation of the secretory phase of the endometrium with estrogens is necessary. Withdrawal bleeding in women with an intact uterus usually develops within 3-7 days after stopping the progestin.
Intramuscularly 5-10 mg/day for 5-10 consecutive days, stopping 2 days before the expected menstruation.
Orally at a dose of 400 mg/day for 10 days.
Intravaginally (in the form of a gel) at a dose of 45 mg every other day, on the 15-25th day of the menstrual cycle.
Reproductive technologies:
maintaining the luteal phase in women.
Intravaginally (in the form of a gel) at a dose of 90 mg (one applicator of 8% gel) 1 time per day. For in vitro fertilization, treatment begins within 24 hours after embryo transfer and continues for 30 days. When pregnancy occurs, therapy is continued until the placenta becomes independent (10-12 weeks of pregnancy).
Partial or complete ovarian failure: intravaginally (in the form of a gel) at a dose of 90 mg (one applicator of 8% gel) 2 times a day before the transfer of a donor oocyte; when pregnancy occurs, treatment is continued until the placenta becomes independent (10-12 weeks of pregnancy).
When donating eggs
(against the background of estrogen therapy): intravaginally (in the form of capsules) at a dose of 100 mg/day on the 13th and 14th days of the cycle, then 100 mg 2 times a day from the 15th to the 25th day of the cycle. From the 26th day and if pregnancy is detected, the dose is increased by 100 mg/day every week, reaching a maximum (600 mg in 3 doses for 60 days).
To maintain the luteal phase during the in vitro fertilization cycle: intravaginally (in capsule form) 400-600 mg/day, starting from the day of human chorionic gonadotropin injection and until the 12th week of pregnancy.
Intravaginally (in the form of suppositories) 25-100 mg 1-2 times a day, starting a few days before ovulation. If pregnancy occurs, treatment is continued until the 11th week.
Corpus luteum deficiency
(maintaining the luteal phase in women).
Intramuscularly at least 12.5 mg/day, starting a few days before ovulation. The duration of treatment is about 2 weeks, but if necessary, therapy is continued until the 11th week of gestation.
Intravaginally (in the form of a gel) at a dose of 90 mg (one applicator of 8% gel) 1 time per day. When pregnancy occurs, treatment is continued until placental autonomy is achieved (10-12th week of gestation).
Intravaginally (in capsule form) 200-300 mg/day, starting from the 17th day of the menstrual cycle for 10 days. If menstruation is delayed and pregnancy occurs, treatment must be continued.
Intravaginally (in the form of suppositories) at a dose of 25-100 mg 1-2 times a day, starting a few days before ovulation. If pregnancy occurs, treatment is continued until the 11th week of gestation.
In case of corpus luteum insufficiency, intravaginal use of micronized progesterone in the first trimester of pregnancy is superior to its intramuscular administration in terms of the likelihood of continuing pregnancy (30.5 versus 19.1%; p <0.05).
Assessment of endogenous estrogen production
: for parenteral use - diagnosis of menopause by measuring the concentration of estrogen in the absence of menstruation after discontinuation of progestin. The standard method for verifying menopause is measuring the levels of gonadotropins in the blood.
Intramuscularly in a single dose of 100 mg.
Prevention of endometrial hyperplasia
in postmenopausal patients who receive estrogens in the form of hormone replacement therapy.
Orally at a dose of 200 mg 1 time per day before bedtime for 14 days (from the 8th to the 21st day of a 28-day cycle or from the 12th to the 25th day of a 30-day cycle).
Intravaginally (in the form of a gel) at a dose of 45 mg every other day for 12 days of a 28-day cycle.
The dose is adjusted based on the desired uterine response (regular withdrawal bleeding or amenorrhea). In many treatment regimens, hormones are not taken at all during the last 5-7 days of each month.
Premature menopause.
Prevention of habitual and threatened miscarriage
, caused by gestagenic insufficiency of the corpus luteum.
Intravaginally (in capsule form) 100-200 mg 2 times a day daily (until the 12th week of pregnancy).
Intramuscularly at a dose of 10-25 mg daily or every other day until the symptoms of a possible miscarriage completely disappear. With a routine abortion, treatment is continued until the 4th month of pregnancy.
Intramuscularly at a dose of 25-100 mg daily, starting from the 15th day and continuing until the 8-16th week of pregnancy.
Intravaginally (in the form of a gel) 90 mg/day, continuing for 30 days after laboratory confirmation of pregnancy.
Threat of miscarriage:
there is no evidence of the effectiveness of the use of progestins for threatened abortion, with the exception of the administration of progesterone to patients with its deficiency.
Intravaginally (in capsule form) 100-200 mg 2 times a day daily until the 12th week of pregnancy.
Intramuscularly at a dose of 10-25 mg daily or every other day until the symptoms of a possible miscarriage completely disappear. With a routine abortion, treatment is continued until the 4th month of pregnancy.
If there is a threat of miscarriage
caused by insufficiency of the corpus luteum, the use of progesterone (in the form of 8% vaginal gel) for 5 days significantly reduces the severity of pain, the frequency of uterine contractions (p <0.005) and the likelihood of miscarriage within 60 days (p <0.05) compared with placebo ).
Prevention of uterine fibroids.
Endometriosis.
Oligomenorrhea and algomenorrhea
caused by hypogenitalism.
Orally at a dose of 200-300 mg for 10 days (from the 17th to the 26th day of the cycle).
Hypogenitalism and amenorrhea:
after using estrogens - IM at a dose of 5 mg daily or 10 mg every other day for 6-8 days.
Algodismenorrhea:
treatment begins 6-8 days before menstruation. The drug is administered intramuscularly at a dose of 5-10 mg daily for 6-8 days. For algodismenorrhea caused by underdevelopment of the uterus, it is combined with estrogens at a rate of 10 thousand units every other day for 2-3 weeks, then progesterone is administered for 6 days.
Fibrocystic breast disease, mastodynia.
Orally at a dose of 200-300 mg for 10 days (from the 17th to the 26th day of the cycle).
Externally (in the form of a gel). One dose of gel (2.5 g) 2 times a day is applied to the skin of the mammary gland until completely absorbed (including on menstruation days).
Use in children
Efficacy and safety have not been studied. There are descriptions of severe side effects in children who accidentally took high doses of oral contraceptives.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Progesterone
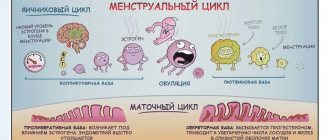
Hormone of the corpus luteum has a progestogenic effect. By binding to receptors on the surface of cells of target organs, it penetrates into the nucleus, where, activating DNA, it stimulates RNA synthesis. Promotes the transition of the uterine mucosa from the proliferation phase caused by follicular hormone to the secretory phase, and after fertilization, it creates the necessary conditions for implantation and development of a fertilized egg. Reduces the excitability and contractility of the muscles of the uterus and fallopian tubes, stimulates the growth of the secretory section of the acini of the mammary glands and induces lactation. By stimulating protein lipase, it increases fat reserves, increases glucose utilization, increasing the levels of basal and stimulated insulin, promotes the accumulation of glycogen in the liver, increases the production of aldosterone; in low doses it accelerates, and in high doses it suppresses the production of gonadotropic hormones of the pituitary gland; reduces azotemia, increases nitrogen excretion in urine. It is quickly and almost completely absorbed after subcutaneous and intramuscular administration. Metabolized in the liver to form conjugates with glucuronic and sulfuric acid. The half-life is several minutes. Approximately 50–60% is excreted in the urine, more than 10% in bile. The amount of metabolites excreted in the urine varies depending on the phase of the corpus luteum.
Progesterone
Before starting to use the drug Progesterone, it is necessary to conduct a medical examination, including examination of the mammary glands and pelvic organs and a Pap smear examination.
Due to the risk of developing thromboembolic complications, use of the drug should be discontinued if: visual disturbances such as loss of vision, double vision, vascular lesions of the retina occur; migraine; arterial or venous thromboembolism, thrombophlebitis, thrombosis, regardless of location.
If there is a history of thrombophlebitis, the patient should be closely monitored.
The drug Progesterone is used with caution in patients with diseases and conditions that may be aggravated by fluid retention (arterial hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, chronic renal failure, epilepsy, migraine, bronchial asthma); in patients with diabetes mellitus; liver dysfunction of mild to moderate severity; photosensitivity.
Patients with a history of depression should be monitored, and if severe depression develops, the drug should be discontinued.
During long-term treatment with progesterone, regular medical examinations (including liver function tests) are necessary; Treatment should be discontinued if abnormal liver function tests or cholestatic jaundice occur.
When using progesterone, it is possible to reduce glucose tolerance and increase the need for insulin and other hypoglycemic drugs in patients with diabetes mellitus.
If amenorrhea occurs during treatment, pregnancy must be excluded.
In case of acyclic bleeding, the drug should not be used until the cause is determined, including a histological examination of the endometrium.
When using the drug Progesterone with estrogen-containing drugs, you must refer to the instructions for their use regarding the risks of venous thromboembolism.
The use of progesterone may affect the results of some laboratory tests, including liver and thyroid function tests; coagulation parameters; pregnanediol concentration.
Crystals may fall out. If crystals fall out, the ampoule should be heated in a boiling water bath while shaking until the crystals are completely dissolved. If the solution becomes transparent and the crystals do not fall out again when cooled to 36-38 °C, the drug is ready for use.