Breast cancer: every woman should know this
Among oncological diseases in women, breast cancer (BC) is the most common. The tumor can occur on one breast or on both. It differs from other cancers in the aggressiveness of its development. Every 8th woman is diagnosed with a malignant breast tumor. It usually occurs in the cells of glandular tissue.
Breast cancer affects not only women, but also men.
Men are also susceptible to this disease (more than 400 men die from breast cancer every year in the world).
The disease develops quickly. The reasons are rapid cell division, disruption of the rhythm of hormone secretion, mutation at the gene level, active spread of metastases throughout the body.
Causes of breast cancer
This is a question many people ask themselves when they hear a diagnosis of breast cancer. The disease can occur for several reasons:
- Genetic abnormalities. If there have been cases of cancer in the family (especially ovarian or breast cancer), the risk of developing it in a woman increases by 2 times. It is also increased by inherited types - Cowdens or Li-Fraumeni syndrome. The closer in blood a relative who has had cancer is, the higher the risk of getting sick.
- Any neoplasm that is benign in nature, for example, fibroadenoma, lipoma, mastopathy, adenoma, cyst, leaf-shaped tumor, papillomas inside the ducts, etc., can eventually degenerate into a malignant tumor.
- If a woman does not have children or had them after 35. Nulliparous women are more likely to develop breast cancer.
- Women have more glandular tissue cells than men, so any deviation in the production of hormones affects the development of tumors. The older a woman is, the more likely she is to develop this type of cancer. In men, this form of the disease is 100 times less common.
- The use of hormone replacement drugs can cause an acceleration of cell division. Long-term replacement immunotherapy disrupts hormonal levels, which results in a risk of disease, especially in the pre- and postmenopausal period.
- If the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, and liver disease can develop. A pathological decrease in hormonal levels adversely affects the health of women's breasts.
- Pregnancy with a diagnosis of breast cancer, however, just like breastfeeding, is considered an aggravating circumstance.
- The presence of extra pounds can provoke the degeneration of cells into malignant ones. Certain types of hormones are converted into estrogen under the influence of fat, and its excess can cause the development of gland cancer.
- Prolonged exposure to the sun is also one of the causes of oncology, including breast cancer.
- Injury to the mammary gland, consumption of large doses of alcohol, violation of the regime and working conditions (night shifts, hazardous conditions), smoking, early onset (before 12 years) of puberty, late onset of sexual activity and lack of regularity, stress and depression, any types of artificial abortion, tight underwear - this is not a complete list of factors leading to the abnormal process of cell degeneration.
Among scientists' assumptions about the cause of breast cancer, there are several theories that have not been confirmed by practice. One of them blames a virus for the tumor, but no one has ever isolated its cells. Also, no confirmation of the development of the disease due to chlamydia or helminths of a certain type was found. Some scientists believe that heredity is to blame. But the predisposition gene was never found. Previously, they fed children up to a year and even later and considered this to prevent breast cancer, but there is no scientific evidence for this.
Basal cell skin cancer
Basalioma is the most common, but at the same time the safest type of skin cancer. Death from basal cell carcinoma is possible only in very advanced cases or with aggressive forms (basosquamous) tumor. The favorable course of basal cell carcinoma is due to the fact that it almost never metastasizes (only 0.5% of cases).
Symptoms and signs
Most often, basal cell carcinoma occurs on the skin of the nose, a little less often on the face and much less often on other parts of the body.
The peak incidence occurs over the age of 40 years. The youngest patient diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma by histology was 39 years old.
What basal cell skin cancer looks like depends on the form:
- Nodular form (synonymous with nodular). The tumor is presented in the form of a nodule. It can be distinguished from other skin formations by an increased number of vessels on the surface, a waxy sheen and small gray-blue inclusions. All these signs are visible in the photo.
Nodular form of basalioma
In addition, on the surface of nodular basalioma there may be another characteristic sign - ulceration.
Nodular basal cell carcinoma with ulceration
- The superficial form of basal cell carcinoma in most cases is presented as an area of redness on the skin. Elements of peeling and the waxy sheen already mentioned above are also possible.
Superficial form of basalioma
- Scleroderma-like form of basalioma is very rare and often presents difficulties in diagnosis. It is characterized by a lighter and harder seal compared to the surrounding skin.
Scleroderma-like form of basalioma
- The pigmented form of basal cell carcinoma makes up a very small part of the total number of these tumors. It is distinguished by a large amount of pigment. In this regard, basal cell carcinoma is often mistaken for melanoma when examined without a dermatoscope.
Pigmented form of basalioma
- The ulcerative form of basalioma can reach very large sizes and in advanced cases is practically untreatable.
Ulcerative form of basalioma
Photos in the initial stage
Unfortunately, basal cell skin cancer is extremely difficult to diagnose in the early stages, i.e. when it is minimal in size. Here are some photos:
Basalioma of the skin of the nose, nodular form, size 5 mm
Basalioma, nodular form, 3 mm in diameter
Nodular basalioma of the temporal region, diameter 2 mm
Diagnosing basal cell carcinoma in the early stages, when the tumor is small, can present significant difficulties. Only a combination of a comprehensive examination of the entire skin, a thorough determination of the history of the existence of the formation and dermatoscopy will help in establishing the diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma at an early stage.
Basaliomas with high and low risk of recurrence (NCCN, 2018)
Area H: Facial mask (including eyelids, eyebrows, skin around eyes, nose, lips [skin and red border of lips], chin, lower jaw, skin/grooves in front and behind the auricle, temples, ears), genitals, palms and feet .
Area M: cheeks, forehead, scalp, neck and legs
Region L: trunk and limbs (excluding shins, palms, feet, nails and ankles)
Notes
- Localization, regardless of size, may be a sign of high risk
- Histological forms of low risk: nodular (nodular), superficial, keratotic, piloid, with differentiation towards skin appendages, Pincus fibroepithelioma
- Area H means high risk regardless of size
- Morphea-like, basosquamous (metatypical), sclerosing, mixed infiltrative, micronodular in any part of the tumor
To assign a tumor the status of “high risk of recurrence”, only one of the factors from the right or left column is sufficient.
Treatment of basal cell carcinoma
The main goal of treatment for basal cell carcinoma is complete removal of the tumor while maximally preserving the cosmetic properties and functions of those parts of the body where this tumor has developed.
As a rule, the best results are achieved by surgical methods. However, the desire to maintain functionality and cosmetic properties may lead to the choice of radiation therapy as the primary treatment modality.
Depending on the degree of risk of relapse (see above), the approach to treating basal cell carcinoma may vary.
In patients with superficial basal cell carcinoma and a low risk of recurrence, when surgery or radiation therapy is contraindicated or inappropriate, the following treatments may be used:
- 5-fluorouracil ointment;
- Imiquimod ointment (Aldara, Keravort);
- photodynamic therapy;
- cryodestruction.
Mohs micrographic surgery may be recommended for patients at high risk of recurrence.
Chemotherapy for basal cell carcinoma includes drugs that are inhibitors of the hedgehog signaling pathway – vismodegib (Erivedge) and sonidegib (Odomzo). These drugs can help in cases where surgical methods, like radiation therapy, are not applicable or contraindicated.
What you need to know about basal cell carcinoma?
- In the vast majority of cases, basal cell carcinoma does not pose a threat to life.
- If a histological examination of a distant formation results in basal cell carcinoma, there is nothing to worry about. It is important to make sure that the formation is completely - be sure to consult with an oncologist.
- If, after removal of a basal cell carcinoma, the histological examination contains the phrase “tumor cells in the resection margin” or something similar, further treatment in order to completely remove the tumor.
- strongly do not recommend removing basal cell carcinoma without histological examination, since even a very typical-looking formation may not be what it seems at first glance.
- Basalioma needs to be treated . Observation is a bad option for a diagnosis like this. Treatment of advanced forms (see photo of ulcerative form) is extremely difficult and expensive.
- If you have already had a basal cell carcinoma removed, you should regularly have your entire skin examined by an oncologist in order to possibly identify another such tumor.
- The likelihood of metastasis in the metatypical (basosquamous) histological type is higher than in other types.
Symptoms and signs of breast cancer
Among the main symptoms of oncology:
- swelling and hardening not only in the mammary gland, but also in the nipple;
- change in the shape, shape, structure, size of the breast;
- the appearance of pain and discomfort;
- modification of the lymph nodes, armpits, shoulder - swelling, lumps, increase in size, nodules, pain;
- any deformation of the skin - wrinkling, redness, retraction, peeling, marbling, swelling, folds, discoloration;
- transformation of the nipple (its retraction), yellow or bloody discharge from it;
- the appearance of a dimple on the skin when raising the arm.
If a woman notices any of the above signs, she should consult a doctor without delay.
What are the types of diagnosis for adenocarcinoma?
The patient needs to undergo a complete examination:
- Blood test to detect tumor markers. Determines the presence of substances that are characteristic of a particular type of glandular cancer.
- Blood testing in the laboratory (biochemical and general analysis). Helps identify disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
- X-ray. With its help, specialists can detect metastases.
- Analysis of urine. Detects inflammation processes.
- Biopsy. Collecting tumor tissue for laboratory research.
- Ultrasound. With its help, doctors study the tissues of the infected organ and the lymph nodes closest to it. Then the tumor is identified and its size is determined.
- Scintigraphy. Doctors use this imaging technique, which involves injecting radioactive isotopes into the body and then producing a two-dimensional image. This helps to find inflammatory processes.
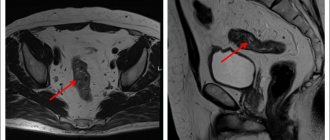
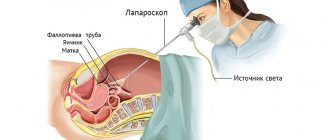
Diagnosis of breast cancer
Self-diagnosis On the 7th – 10th days of the cycle, you need to palpate each lobe of the breast and write down your sensations and observations. If unusual formations are detected, you should definitely visit a gynecologist and preferably a mammologist.
Self-diagnosis helps to detect the first symptoms in time, which means timely initiation of examination and treatment. To confirm the diagnosis or deny it, MRI and mammography are performed.
By controlling the condition of her glands, a woman takes care of her health and prolongs her life. In countries where much attention is paid to the development of medicine, more than 90% of women overcome breast cancer. And in total, almost three million women in the world continue to enjoy life, in whose lives there was once a terrible diagnosis of breast cancer.
Types of rectal cancer
The type of tumor is determined by its location:
- Anorectal location is typical for 5-8% of cases.
- Ampullary occurs more often than others, up to 80%. This is a pathology in the widest part of the intestine.
- Supraampullary localization in up to 12% of patients.
The nature of tumor growth can be:
- exophytic – grows into the intestinal lumen;
- endophytic - grows through the thickness of the wall, infiltrates it, and can cover it circularly;
- mixed growth.
According to the histological picture, the neoplasm can be:
- glandular cancer (adenocarcinoma);
- solid;
- signet ring cell;
- skirr;
- squamous.
Stages of breast cancer
The stage of the disease also depends on the size of the tumor. If the nodule is no more than 2 cm in diameter and no cells are affected in the lymph nodes, doctors diagnose stages 0 and 1 of cancer. Three out of 4 women survive if treated in a timely manner.
At the next stage, the disease can develop in two ways.
1st way The tumor does not grow, but cancer cells appear in the 4–5 lymph nodes closest to the tumor, and the lymph nodes themselves change in size.
2nd way The tumor does not affect the lymph nodes, but increases to 20–50 mm.
Every 2nd woman has a chance of recovery in stage 2.
The 3rd stage is distinguished by: • damage to the lymph nodes next to the tumor; • tumor size over 5 cm; • penetration into the chest and bone tissue of metastases.
The survival threshold is 10–15%.
At stage 4, the prognosis for cure is unfavorable, since metastases penetrate into distant organs and affect the entire body.
Identification example
Hidden primary cancer is uncommon. Moreover, during further examinations the primary lesion may be discovered. If this happens, the tumor is no longer considered a primary cancer of unknown origin. It is given a name in accordance with the organ of origin and, based on new data, the treatment regimen for cancer is modified.
In practice this happens as follows:
- For example, a person is found to have an enlarged lymph node in the neck.
- A biopsy reveals that there is a malignant tumor in the lymph node.
- However, upon cytohistological examination, it turns out that the cells of this tumor are not similar to cancer cells of the lymphatic system.
- The patient is tentatively diagnosed with a primary cancer of unknown origin.
- The tumor cells found are similar to cancer cells of the oral cavity, soft tissues of the throat or larynx.
- The patient is prescribed a series of in-depth examinations.
- During these examinations, a small asymptomatic tumor lesion is found in the larynx.
- The patient's diagnosis is changed to laryngeal cancer and treatment appropriate for this type of oncopathology is prescribed.
However, in some cases, even the most thorough examination does not detect the primary focus. Moreover, it is not always possible to find it even during a pathological examination.
How long do patients with breast cancer live?
The possibility of healing depends on the type of cancer. After all, oncology comes with different levels of aggressiveness. The possibility of recovery from the disease depends on early detection of the disease, correct determination of its type, and well-chosen treatment.
The survival rate with timely detection of breast cancer and complete completion of prescribed treatment in 40% of women is up to 5 years. In the first two stages of the disease, the threshold for cure is 75% of patients , in the 2nd and 3rd stages – up to 40% . At the 4th stage, only ? .
Cost of consultation for ovarian cancer?
| Name of service | Price, rub.) |
| Initial appointment with an oncologist | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with the oncologist | 1500 rub. |
| Primary appointment with a general practitioner | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a general practitioner | 1500 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment (drawing up an individual treatment regimen) | 1500 - 3000 rub. |
All our services and prices
Breast cancer treatment methods
After carrying out the necessary examinations (X-ray, galactography, ultrasound, mammography, biopsy, etc.) and confirming the diagnosis, the woman is usually offered a radical solution - breast surgery. This is the main method of treatment. There are two types of surgical intervention - sectoral or complete breast removal.
After the operation, auxiliary treatment is prescribed: radiation, chemotherapy, hormonal, molecular targeting (targeted). Sometimes it is carried out both before and during surgery. Immunotherapy prevents a woman's own hormones from stimulating the growth of cancer cells. During such therapy, the patient must take one tablet daily for several years (from 5 to 10).
To make a woman feel comfortable after surgery, she is offered reconstructive operations. Breast reconstruction is performed using the patient’s own muscles or using an implant.
Do you know that
It became possible to use a special vaccine to destroy malignant tumors.
Learn about virotherapy - a unique method of treating cancer. Go >>
Find out that aspirin is a supportive treatment for breast cancer patients. Go >>
Why do you need to look for the primary focus?
The main reason for searching for the initial tumor is to choose the right treatment tactics. Secondary metastatic foci consist of the same cells as the initial tumor, even if they develop in completely different organs. This means that for their treatment, the same drugs will be effective as for the treatment of primary cancer, and not those used in the treatment of oncopathologies of the organ where metastasis has developed.
This is especially important in some forms of cancer that respond well to certain chemotherapy or hormonal drugs. For example, many breast tumors are characterized by such features. They can be effectively treated with hormonal drugs. This means that the same drugs are suitable for treating their metastases in the bones, brain, and liver.
Unfortunately, it is still almost impossible to predict the development of a malignant disease. Therefore, the most effective way to fight tumors is to detect cancer at the 1st stage of development. In this case, more than 90% of all malignant neoplasms can be successfully treated. A tumor can be detected in the initial stages of its occurrence only through periodic screenings. Such screening programs also operate in the medical field. At the initial consultation, an oncologist will assess your risk of developing cancer and draw up an individual plan for undergoing preventive examinations for early diagnosis of cancer.
The material was prepared in agreement with Anadolu doctor, therapist and medical oncologist Şeref Komurcu.