Among elderly people, in 30% of cases such a fracture leads to death within a year after the injury. The cause of death is inactivity of a person, leading to the development of deadly complications.
X-ray of a fracture
In more than 90% of cases, fractures in the hip joint area occur in people over 70 years of age with grade II-III osteoporosis. Their femur breaks due to a fall. Such fractures heal very poorly due to low bone mineral density and poor blood supply to the hip joint. At a young age, hip bones break less often, which is due to their high strength and resistance to traumatic factors.
From your height
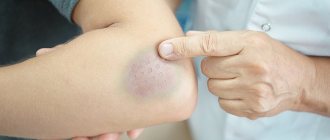
“Reached for a jar on the top shelf,” “bent over for a stick,” “climbed out of the bathroom” - in old age, these simple everyday situations can result in injuries, the worst of which is a hip fracture.
It must be said that a femoral neck fracture occurs at 40 and 50 years of age, in both men and women. However, according to data from open sources, about 90% of those injured with a hip fracture are people over 60 years of age and, most often, women. The injury is particularly problematic due to the fact that in old age bones heal much less well.
The bones of the elderly are fragile, so most femoral neck fractures in the elderly occur as a result of falling from their own height while walking, running, carelessly moving on stairs, ice, etc.
At the same time, experts point out that the fracture itself is not as dangerous as the complications it can cause. As already mentioned, quite often this injury in the elderly is accompanied by an exacerbation of various diseases, which can put them to bed for a long time and even lead to death.
An accident happened to my grandmother’s sister on the eve of the new year 2021, on December 31 - she tripped and fell at home. An X-ray at the emergency room showed a femoral neck fracture. I had to refuse the operation: severe hypertension and age 84 years. Despite the care of a professional doctor (her niece), the injury literally broke the previously strong-willed woman - she became depressed, became very weak, stopped eating, and died just six months later.
Destruction of the acetabulum
According to statistics, pelvic bone fractures occur in people aged 21-40 years. Their main causes are car accidents and serious domestic injuries. Acetabular fractures account for about 15-20% of all traumatic injuries to the pelvis. They are accompanied by fractures and dislocations of the femoral head.
Comminuted fracture.
Uncomplicated acetabular fractures in young people are treated without surgery. Surgery is required for T-shaped fractures, interposition of fragments in the joint, unreduced fracture-dislocations and massive fractures of the posterior edge of the cavity.
Neck or skewer?
The upper end of the long femur has a complex structure. The rounding at the end is the head of the bone, the narrower part connecting the head with the body of the bone is the neck, and on both sides of this neck there are bone protrusions - trochanters (the outer one is especially noticeable), muscles are attached to them. The neck is the most fragile part of the femur.
“A neck fracture is one of the fractures of the upper thigh in the elderly, but not the most common,” says Dmitry Khryapin, an orthopedic traumatologist at the traumatology department of the V.V. City Clinical Hospital. Veresaeva. — The most common fracture in older people is a pertrochanteric hip fracture: there were 250 such patients in our department last year. In 2016, 185 people were admitted to the department with hip fractures. Most people call all these fractures fractures of the femoral neck, although the difference between them is very big: a pertrochanteric fracture heals better - the bone always heals - both with and without surgery, but the neck does not always.”
Trochanteric, intertrochanteric and subtrochanteric views
The second most common place among fractures of the hip joint is occupied by injuries in the trochanteric region of the femur. They come with or without displacement. Violation of bone integrity can have varying severity and severity. Fractures in the trochanteric area are more common in relatively young people. They arise as a result of a fall or the action of a tear-off mechanism.
The most favorable course is for fractures of the greater and lesser trochanter, which are not accompanied by displacement of bone fragments. They do not cause serious damage or complications. Their treatment usually does not require surgery. Surgery and internal fixation of bone fragments are needed only if they are displaced.
AO classification of trochanteric zone fractures:
- Simple pertrochanteric. One fracture line that runs in the area between the greater and lesser trochanter.
- Multicomminuted pertrochanteric. Several bone fragments are formed in the trochanteric zone. Breaking bone into pieces.
- Subtrochanteric. They are located in the proximal femur below the lesser trochanter, but no further than 5 centimeters from it.
Subtrochanteric fracture.
We need to operate!
Geriatricians insist that an elderly person with a hip fracture should be operated on. “In the civilized world, almost 100 percent of older people with a hip fracture undergo surgery,” says Andrei Ilnitsky, head of the department of therapy, geriatrics and anti-aging medicine at the Institute for Advanced Studies of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency. — Risks, of course, exist, as with any other operation. But the risk from not performing the operation and from complications associated with limited mobility is disproportionately higher.”
According to Dmitry Khryapin, about 2/3 of injured patients undergo successful surgery.
“Of the older people admitted to the department with both types of fractures, approximately 70-80 percent were operated on,” says the practicing traumatologist. — The operations were different - this included osteosynthesis, when the bones are connected with screws, and endoprosthetics. Last year we had about two hundred quotas for them and all of them were chosen.” He explained that osteosynthesis operations for the remaining patients were financed from other sources, and for endoprosthetics, according to a planned procedure, patients were sent to other hospitals according to quotas.
Surgical treatment and prosthetics
Surgical intervention is possible only if there are no contraindications associated with age and chronic diseases. During the operation, punctures and fragments are fixed - this leads to faster rehabilitation and restoration of the damaged bone.
Main types of surgical operations:
- Osteosynthesis is the fastening of damaged bone elements with special metal structures. Most often, this operation is performed on patients under 65-70 years of age.
- Installation of a bipolar prosthesis is prescribed for patients in the age category from 70 to 80 years.
- Unipolar hip replacement is considered the best option for elderly patients.
In the process of unipolar endoprosthetics, the femoral head is removed and replaced with an artificial implant. Surgical intervention takes a minimum of time and is considered the safest and most gentle for elderly patients.
For complex, labor-intensive and multi-level surgical procedures, special fixing screws, three-blade nails, and dynamic hip screws can be additionally used.
Grandmother fell: our actions
If the grandmother has fallen and complains of pain, but can walk, albeit with difficulty, complaints about girdling pain around the hip joint, severe pain in the groin, acute or, conversely, dull pain in the joint when walking should alert loved ones. A fracture of the femoral neck may also be indicated by symptoms such as increased pain when moving and tapping on the heel of the injured limb, a slight inversion of the injured leg to the outside, which is noticeable in the foot, the inability to hold the leg in a straightened position (with the ability to bend and straighten the leg) , shortening the leg by several centimeters.
Trouble has happened. An elderly man is in painful shock, then depressed, confused, scared that he will now die forever. What to do?
First of all, he needs to be morally supported and encouraged. In the 21st century, a hip fracture is not a death sentence. Director of the Medical Research Institute Kirill Proshchaev advises: “An elderly person must be told that medicine has changed in almost one generation, and now people with hip fractures undergo surgery and the operation can restore their mobility and their previous way of life.”
Immediately after the injury - before the doctors arrive - you need to provide first aid: place it on a flat surface, fix the leg with a splint so that both the hip and knee joints are captured at the same time. ATTENTION: Doctors prohibit trying to bring the injured leg into a normal position.
It is important to get an injured elderly person to the hospital as quickly as possible, because the faster the necessary medical care is provided, the more effective the treatment will be. For example, during a fracture, hemoglobin drops significantly, blood clots or fatty tissue enter the blood, which can cause complications in the first day or two.
Resolve the issue of surgery with doctors. Typically, they try to perform the operation in the first two weeks after the injury. Unfortunately, in district and regional centers the issue takes longer to resolve - we must try to do everything possible to speed up the day of the operation.
If there is no risk that an elderly person will simply die on the operating table from heart or kidney failure, a sharp drop and surge in pressure, etc., surgical intervention is necessary - fastening the joint or bones with screws (osteosynthesis) or installing a joint prosthesis (endoprosthetics).
“The issue of timing of the operation is decided in each case individually, but we try to operate in the coming days,” explains Dmitry Khryapin. - As I already said. operations are carried out free of charge, for Muscovites according to quotas.”
Treatment of femoral neck fracture
Treatment of injuries of this kind is carried out by orthopedists. Conservative therapy, i.e. non-surgical treatment, is indicated only if there are serious contraindications to surgical intervention. This is due to the fact that most patients tolerate surgery much easier than long-term and ineffective conservative therapy, which requires prolonged bed rest.
In addition, for older patients, who account for more than 90% of all hip fractures, early intervention is extremely important. Otherwise, there is a serious risk of complications, including bedsores and congestive pneumonia. But severe inflammatory processes in the lungs can be fatal for older people. In young patients, prolonged immobility often causes muscle atrophy and post-traumatic contractures of the knee and hip joint. Therefore, whenever possible, preference is given to surgery for a femoral neck fracture.
The only case where effective treatment of a femoral neck fracture is possible is an impacted fracture with a horizontal line. In such situations, for young patients, the entire hip joint is fixed with a plaster splint, which reaches all the way to the knee, for 3-4 months. At this time, patients can walk, relying on crutches and without putting stress on the injured leg. Elderly patients have to be hospitalized and remain in skeletal traction for 1.5-2 months. From the first days of treatment, exercise therapy is carried out.
Today, surgical treatment of injuries of this kind is carried out by internal osteosynthesis or hip replacement. Young patients, as a rule, are offered osteosynthesis, while elderly people are almost always recommended to undergo endoprosthetics, which is due to circulatory disorders in the hip joint, slow regeneration of bone tissue and a low rate of fusion of fragments.
Carrying out osteosynthesis for elderly people sharply increases the incidence of complications, including due to the fact that the implantation of metal implants into the bone sharply increases their tendency to resorption. In addition, osteosynthesis for older people is fraught with the formation of a false joint, which causes disability.
In all cases, surgery should be performed as soon as possible after the injury. If this possibility is not available for one reason or another, then skeletal traction is performed before the operation.
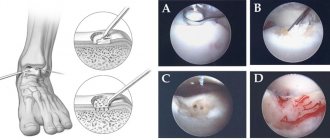
Osteosynthesis
The essence of the internal osteosynthesis technique is the correct placement of fragments formed as a result of a fracture and their reliable fixation using pins, screws, knitting needles, plates and other means made of biocompatible materials. Most manufacturers use titanium, molybdenum-chromium-nickel and other alloys for their manufacture, since they have shown themselves to be the most resistant to oxidation in body tissues.
But for osteosynthesis to be successful, several conditions must be met:
- absence of severe osteoporosis;
- maintaining normal levels of bone mineral density;
- maintaining normal nutrition of the bones of the hip joint;
- the ability to accurately and firmly compare the fragments formed as a result of a femoral neck fracture;
- no need to traumatize periarticular tissues during surgery;
- compatibility of implant and bone.
Thus, osteosynthesis is not always possible even in young victims. If the above conditions are not met, there is a high probability of fracture nonunion. Therefore, in such situations, in order to reduce risks, preference is given to endoprosthetics. But even if the patient’s condition fully complies with the requirements for osteosynthesis, it does not always lead to the expected result. Thus, in 10–30% of cases, nonunion of a femoral neck fracture is observed, and in 10–40% of patients, aseptic necrosis of the femoral head develops. In such cases, it is also necessary to subsequently undergo total hip replacement.
Today there are several different techniques for performing internal osteosynthesis:
- Osteosynthesis using 3-blade Smith-Petersen nails. These nails are very thick and, thanks to the presence of 3 blades, are able to reliably hold fragments of the femur. During the operation, a nail is inserted into the femoral neck from the side of the femoral trochanters using a special hammer.
- Osteosynthesis using 3 screws. This method of surgical treatment of a fracture is more reliable and consists of screwing a number of thin knitting needles into the neck with a drill from the side of the trochanters. Then X-rays are taken and the most successfully installed knitting needles are selected, and the rest are removed. They are used as conductors for further screwing in special screws in the form of a hollow tube with an external thread.
- Osteosynthesis using a dynamic DNS hip screw. The method involves introducing a special metal structure with several screws into the femur. It requires special professionalism from the surgeon, and the design itself is quite bulky, although it provides reliable fixation.
The surgeon chooses a specific technique based on the individual characteristics of the patient’s femur structure, the type of fracture, its direction and some other factors. But always after internal osteosynthesis, patients undergo early activation, since this largely determines the success of the operation.
After internal osteosynthesis, recovery takes at least 12 months; joint replacement is associated with a shorter rehabilitation period - 5-6 months. Regardless of the type of surgical intervention performed, all patients in the early postoperative period are prescribed antibiotic therapy and drugs to prevent the occurrence of thromboembolic complications.
After osteosynthesis, patients can get out of bed and move their legs after 3-5 days. Subsequently, they must be assigned:
- massage;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- exercise therapy;
- swimming in the pool.
Metal plates, pins or other devices installed during surgery are removed only after the femoral neck fracture has completely healed and normal functional activity has been restored. This usually occurs 1-1.5 years after osteosynthesis. But if the operation was performed on older people, metal structures may not be removed.
Endoprosthetics
Hip replacement is the main method of treating femoral neck fractures in elderly patients and young people with severe injuries. Carrying out this operation meets all the requirements for preventing the development of complications in people of the older age group, since it allows for early activation. After its completion, getting out of bed and physical activity are possible within 2-3 days, provided there are no complications, and after the end of the rehabilitation period, the person is able to move independently absolutely normally.
The essence of endoprosthetics is to replace the hip joint or only part of it with an artificial implant that completely repeats the functions and structure of the deformed part. This operation is shown:
- all patients over 70 years of age with a hip fracture;
- in the presence of a false joint;
- all patients with aseptic necrosis of the femoral head;
- for severe fractures, the formation of several bone fragments, bone fragmentation, etc.
In addition, hip replacement is performed in cases of grade 3 deforming coxarthrosis and the presence of tumors in the hip joint.
Depending on the severity of the situation, in case of injury with aseptic necrosis of the femoral head, total (complete) arthroplasty with replacement of the entire hip joint, as well as only partial arthroplasty using monopolar or bipolar femoral heads, can be performed. In the first case, the head and neck of the femur, as well as the acetabulum, will be replaced with an artificial prosthesis. Its elements are firmly fixed on the surface of bones, including those affected by osteoporosis, through the use of special cement, which is especially important for elderly patients.
In young patients, a cementless method of fixing a total endoprosthesis is more often used. In this case, a special spongy layer is located between the surface of the implant and the bone. Over time, bone grows through it, which ensures strong fixation of the prosthesis.
Total arthroplasty for hip fractures has a favorable outcome in more than 90% of cases and leads to a complete recovery. But after 15-25 years they may need to be replaced.
Sometimes patients may be offered the installation of a monopolar femoral head prosthesis, which replaces only the neck and head of the femur, i.e. the socket is not replaced. The disadvantage of such devices is the rapid wear of the articular cartilage due to the constant friction of the synthetic head against the glenoid cavity. Bipolar femoral head prostheses do not have this disadvantage. For devices of this kind, the head is enclosed in a special capsule, which, after installation, is adjacent to the acetabulum. Therefore, the main friction of the endoprosthesis elements occurs within itself, which reduces wear of the joint.
But, despite all the advantages, endoprosthetics cannot always be considered due to the presence of concomitant diseases that increase intraoperative risks. The operation is contraindicated for:
- severe heart failure;
- chronic respiratory failure grade 2-3;
- inflammatory process in the hip joint or other organs;
- previous history of sepsis;
- the patient’s inability to move independently as a result of other injuries or diseases;
- absence of a medullary canal in the femur.
Thus, some contraindications are temporary and after they are eliminated, the operation can be performed. In other situations, patients are shown conservative treatment, which, although it does not lead to fusion of bone fragments, allows saving life. It consists of performing skeletal traction for 5-10 days, after which the patient is allowed to turn on his side, sit up in bed and hang his legs from it. Painkillers are used all this time. After 3 weeks from the start of conservative therapy, the patient is allowed to walk on crutches, without which he will not be able to move independently.
After endoprosthetics, rehabilitation takes much less time and is easier. Already on the second day after surgery, the patient can get out of bed, but only with the help of medical personnel. Soon he is allowed to move independently using a walker or crutches. These aids should be used for 2-3 months, after which, if recovery proceeds properly, they can be abandoned. Patients are also prescribed massage, physiotherapy and exercise therapy, and if all the doctor’s recommendations are strictly followed, they can return to their normal lifestyle within 6 months after the operation.
What happens after the operation
Treatment of a hip fracture is a long process; it makes sense to imagine in advance what and how you will need to plan:
After the operation, the patient is sent to the intensive care unit for some time.
He is given antibiotics and blood thinners for a week.
A pillow is placed between the legs to keep the legs apart.
Almost immediately after the operation, the patient is recommended to move: sit up in bed, do breathing exercises, and perform simple muscle exercises.
3-7 days after the operation, the patient is helped to get to his feet with the help of crutches and begin to move with the assistance of a specialist.
On days 10-12 after surgery, the sutures are removed and the patient is discharged home.
Rehabilitation - it’s important not to be lazy
After discharge, the elderly person and his relatives must continue rehabilitation procedures according to the recommendations of the attending physician. A person must learn to walk again and return his life to normal. You can recover at home under the supervision and care of relatives and caregivers, or in a boarding house for the elderly.
In any case, experts are convinced that an elderly person should become an active participant in rehabilitation.
“In addition to the maximum possible physical activity - breathing exercises, exercises for the arms with and without weights, and others, an elderly person should lead a lifestyle as close as possible to normal: watched the evening news - continue to watch it, used the Internet - continue to use it, studied a foreign language - continue to teach him, crafted, created with his hands - continue these studies. Our task is to create an environment around an elderly person during the period of restrictions on movement that maximally simulates his previous lifestyle,” advises Andrei Ilnitsky.
It happens that older people with similar fractures are lazy to do the exercises prescribed for them to straighten their legs, etc. It is not always possible to motivate and organize them. In this case, specialists will help. “In addition to active movements, you can use passive ones, when a rehabilitation specialist or a person performing his functions takes the limbs of an elderly person in his hands and performs the necessary movements with them,” says Ilnitsky.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy is prescribed to elderly patients after surgery and conservative treatment. Medications help relieve pain spasms, relieve inflammation and reduce hematoma, and speed up the recovery process.
To eliminate sharp pain, a Novacoin blockade is performed.
It is not prescribed during the period of deterioration in the patient’s well-being, when blood pressure decreases, or when the patient develops a state of shock.
3-4 days after the exacerbation period, injections with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Diclofenac or Ibuprofen - are prescribed. After 3-4 days, the injections are replaced with oral medications.
Such medications not only effectively eliminate painful spasms in the area of the injured joint, but also inhibit the further development of the inflammatory process. For complete regeneration of damaged bone elements, drugs from the group of chondroprotectors are prescribed - Dona, Alflutop.
Complivit Calcium D3, Kalcemin, Calcium D3 and other complexes that contain calcium help strengthen bone tissue and stimulate recovery processes. Additionally, diuretics may be prescribed to relieve swelling - Furosemide, Mannitol.
How to reduce complications
At home, for 6-8 months after surgery, an elderly person must adhere to several rules that reduce the risk of various complications:
- do not allow full flexion (or more than a right angle) in the hip joint.
- while sitting, place a pillow on the chair so that your knees are lower than your hips;
- do not cross your legs - neither sitting nor lying down;
- do not lean forward - always stand with a straight, even back;
- sit on a chair with your legs slightly apart,
- hold on to the railing when going up or down stairs;
- Use shoes with non-slip soles and low heels.
When visiting any doctor, you need to inform him about the presence of an endoprosthesis. If you experience pain at the surgical site or fever, you should contact your surgeon immediately.
Do not forget that the endoprosthesis is a mechanism and is subject to wear and tear. It can be made of metal, plastic, ceramics. Depending on the material and load, the prosthesis can last up to 15 years. How to extend its “service life”? It is advisable not to gain weight and try not to lift heavy objects.
In addition, it is better not to engage in active sports (tennis, skiing, etc.), but swimming and walking will not harm an elderly person with an endoprosthesis.
Recovery Features
After treatment in one way or another and consolidation of bone fragments, patients enter a period of rehabilitation, which is carried out at home or in specialized centers. In the first case, older people and their loved ones will need to strictly follow the recommendations received from their attending physician and take prescribed medications. Also shown during this period:
- exercise therapy;
- massotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- diet.
In general, this stage has much in common with conservative treatment for a femoral neck fracture, but does not require immobilization. The duration of recovery largely depends on the chosen method of treatment and the individual characteristics of the patient.
If rehabilitation takes place at home, the injured elderly person will need to purchase a specialized bed with an anti-decubitus mattress and a special frame. If material resources do not allow this, it is necessary to re-equip the existing bed and replace the usual mattress with a harder and higher one. A rope is installed at the foot of the bed, which will act as reins. With its help, the patient will be able to get up and out of bed independently.
Diet is also given a lot of attention. To fully restore the body, you will need to switch to the most balanced diet, which will contain all the necessary minerals, vitamins, amino acids, etc. in proper quantities. Therefore, it is important to provide the elderly person with a varied diet, which will include fresh fruits and vegetables, dairy products, meat and offal, cereals, fish and seafood. At the same time, you will need to avoid spicy, fried, fatty, smoked foods, as well as carbonated drinks, alcohol and coffee.
In order for recovery to proceed as successfully as possible and without complications, patients themselves need to avoid deep bending, sitting on low chairs, sleeping on an injured limb, crossing their legs and some other actions.
Since the rehabilitation period is quite difficult from a psychological point of view even for the most cheerful pensioner, it is important to support him and provide him with interesting leisure time.
The patient’s relatives will need to constantly help him even with basic hygiene procedures, make sure that he does not remain in one position for a long time to avoid the formation of bedsores, regularly change his underwear, etc. It is also important to follow the recommendations received from the doctor and help your elderly loved one perform breathing exercises, Exercise therapy.
To facilitate the patient’s movement, it is worth installing handrails or other supporting structures around the perimeter of the room in which he lives. It is also recommended to carry into it all the things that an elderly person may need and place them so that they are at hand.
A very common problem that many older people face when treating and recovering from a femoral neck fracture is constipation. To avoid its occurrence, it is recommended that the patient drink plenty of fluids and, if necessary, use mild laxatives. At the same time, the toilet should also be converted by installing a special lining on it to increase the height. This will protect the hip joint from excessive stress and re-injury.
It is impossible to operate, to treat
At the V. Veresaev City Clinical Hospital, as Dmitry Khryapin notes, hip replacement is contraindicated for patients who lead an inactive lifestyle and suffer from senile dementia. “We perform osteosynthesis for pertrochanteric fractures for almost everyone,” says the traumatologist. “The contraindications here are acute heart attacks or strokes that occurred simultaneously with the fracture.”
Treatment without surgery consists of caring for the patient - preventing bedsores, pneumonia, etc., as well as activating him - first in bed, and after some time - with the help of a walker.
The main difficulties in treating such fractures are that bone healing takes a very long time (six to eight months), very long bed rest leads to bedsores, varicose veins and other complications, which is why doctors try to reduce it as much as possible.
In the postoperative period and if surgery is not possible, the most effective care can be provided by specialists from boarding houses for the elderly and nurses with medical education.
Contact rehabilitation assistants
Care by relatives almost always loses to professional care, experts say.
At home, after being discharged from the hospital, elderly people often just lie there for a month or two, since relatives cannot care for them. This causes muscle atrophy in the elderly, which provokes a whole chain of problems: the foot may drop, people drag their leg, the load on the knee increases, and since the leg is not fixed, problems with the knee joints begin.
When an elderly person does not get out of bed at all, does not exercise, contracture begins - ossification of the joints, curled legs that cannot be straightened by anything.
If relatives have time to care, then without special knowledge and skills, they often understand their task only in feeding and hygiene procedures. “But an elderly person, first of all, needs not a nurse, but a tireless assistant in activation, who knows at least its simplest methods - physical exercises, intellectual training, methods of auxiliary and substitutive movement, and so on,” says Kirill Proshchaev. – We need to decide whether one of the relatives or a hired specialist will perform the role of such a specialist. And if it is decided that this will be a relative, make the same demands on him as on a hired specialist: he should not show his negative emotions, fatigue, should not be overly compassionate, lament, ooh and ah, and he should always be in front of the elderly person neat, cheerful and energetic. At the same time, the caring relative should have the right to leave and weekends - and the family should provide for these moments - because he has an increased risk of emotional burnout.”
Question answer
Hello. And when can you intensify movements in the upper part of the body?
Hello. Activate movements in the upper part after removing the plaster cast and replacing it with a special bandage. But it is not recommended to overwork the body, since during any exercise the soft tissues seriously “press” on the neck and head of the joint.
Hello. Please advise an exercise for an elderly person after a hip injury and what is better: crutches, a cane or a walker?
Hello. For older people, it is always more convenient to use a walker and even perform exercises while leaning on them, as can be seen in the video.
Going again after surgery is realistic
The speed of rehabilitation, says Sergei Sadovsky, executive director of the “Care and Care” network of boarding houses for the elderly, depends on the condition of the elderly person preceding the injury - whether he was independent.
“Usually, if a person was fully self-sufficient before the injury, then lying down is not normal for him and he will try to get up faster. But even elderly people who are already walking can be greatly “slowed down” by the fear that the same thing will happen to the second leg, and they begin to subconsciously feel sorry for the healthy leg and avoid activity.”
As the expert said, at the beginning of summer, a grandmother was brought from the hospital to one of the network’s boarding houses for rehabilitation after surgery on the femoral neck. “A week later she started walking, but overall she stayed with us for less than a month and went home on her own two feet,” says Sadovsky. “And this is one example of many when patients in private boarding houses and nursing homes show more positive dynamics of recovery,” says Sadovsky.
According to him, this grandmother’s stay, along with all consumables, cost the relatives 55 thousand rubles. This is half the price of staying at any resort. “We start with a set of physical exercises, then we help the elderly person sit up, and after a week we put him on a walker, and at the same time a psychologist works with the elderly person,” explains Sadovsky. — Recovery can take from two weeks to 4 months. Early rehabilitation, in a certain sense, is the guarantee that an elderly person will quickly return to normal life, and its duration will be significantly reduced, which is the advantage of professional care in private boarding houses.”
Recovery time after a fracture
Recovery time cannot be accurately calculated, since everything depends on its severity, nature, age of the patient and other factors. But on average they are at least six months. Only after this time will a person be able to stand on the injured limb, completely transferring his body weight to it.
In most cases, the treatment stage is accompanied by the following terms:
- On the third day after applying the plaster cast, the patient must begin to massage the lumbar region. Then you should move to the uninjured limb. After a week, you can begin to massage the hip that was injured. This should be done carefully, following the doctor's recommendations.
- After two weeks, if the cast is removed, you can begin to move your knee. It is best to do this under the supervision of a doctor and only after his permission. Moreover, in the initial stages the patient will need outside help. After about a month, you can begin to perform flexions and extensions on your own. After 2 months, the patient can attempt to sit down. This must be done according to specialized instructions.
- After 3 months, the patient will be allowed to stand up using crutches and begin to move independently. In this case, the support should be on the healthy limb; you can only step lightly on the sore leg.
- Gradually, the load on the hip should be increased and after six months you can make attempts to return to a full life.
To keep grandma from losing heart, we set small goals.
Sometimes rehabilitation and treatment do not go as quickly as the elderly would like and he loses heart. In this case, Kirill Proshchaev recommends setting the elderly person not the final goal - to walk the same way as before the fracture, but to clearly identify and talk through intermediate goals with him and achieve them.
“Don’t forget to praise for achievement and motivate to move on: for example, this week we managed to walk through a room or ward, let’s go out into the corridor or another room from the windows of which the sunset is visible next week,” explains the expert.
Another equally important question: what to do if for some reason the elderly person did not undergo surgery or he himself refused the operation and he developed apathy and lost the meaning of life and self-confidence.
As Andrey Ilnitsky says, a person who cannot walk on his own can move with the help of substitute means, for example, a stroller. “Many people have moved and are moving this way – from famous politicians, for example, US President Roosevelt, to Paralympians and ordinary people who are in every city,” the expert sums up. “The main thing is to provide an elderly person in a wheelchair with access to go for a walk, to the store, on excursions, to the garden, and so on.”
Reducing the risk of another fall: a safe home, a stick, a familiar route
During the rehabilitation process, it is important to protect the elderly person from another fall. It is believed that a person who has suffered a fracture is already at risk of repeated falls. Experts recommend using a wand and under no circumstances being ashamed of it, remembering the fashion for this accessory in the 19th century.
“The most important thing is to create safe conditions in the house where an elderly person who has undergone trauma and surgery lives, to eliminate risky moments,” Andrei Ilnitsky points out. “These are, for example, carpets with curved corners, poor lighting in the corridor or pantry, furniture on wheels without locks that can move at any time, thresholds between rooms, and so on, and make auxiliary devices - handrails in the bathroom and toilet.”
He also advises relatives to walk with the elderly person several times along the usual routes to the store, to the park, and so on, so that he is convinced that he can go the same way. But next to him, at first, until the person has adapted after the fracture and surgery, is his assistant, who will not let him fall.
Classification
A collum femoris fracture can be extra-articular or intra-articular, depending on its location – medial or subcapital, transcervical, basocervical or lateral. If we consider the position after injury, then they are abductive and abductive.
Doctors agreed that for treatment it is more expedient to classify the pathology according to the types of fractures:
- medial varus and valgus;
- lateral;
- epiphysiolysis (detachment of the epiphysis).
Cervical-diaphyseal angle (on the left – normal, on the right – with a basicervical fracture)
If we take into account Garden’s classification (1961), then the type of displacement of fragments determines 4 groups of such fractures:
- incomplete;
- complete, but without displacement of fragments;
- with partial displacement of fragments;
- with complete displacement of fragments.
Angles of inclination of the fracture line and the horizontal line of the pelvis
The Pauwels classification (1935) introduced three types of medial fractures with corresponding angles of inclination of the fracture plane to the horizontal line of the pelvis:
- Type I – <30°;
- Type II – ≤ 50°;
- III type – > 70°.
A description of such fractures is given in the table:
| Fracture type | Description of injury and method of treatment |
| More common in older people due to osteoporosis and trauma. In case of injury, there is no wedging of bone fragments, and there is no open angle between the axis of the head and neck to the medial side. The fracture line will be oblique or transverse where the neck meets the femoral head. Part of the Adam's arch may break off along with the head, which will lead to shortening of the limb. Surgical treatment and conservative methods are used: traction followed by reduction of bones and application of a Whitman-Thurner plaster bandage before surgery or if it is impossible to perform it. |
| If the valgus position is insignificant, the fragments are wedged in; a normal angle between the head and neck may be maintained, or small and open posteriorly, where the fracture line passes. An impacted femoral fracture is considered stable and surgery is not performed. But at an angle of more than 20°, the bones are set and during the operation a nail is inserted to connect the fragments. |
| This injury is rare and is characterized by a fracture line running along the lateral border crossing the base of the neck, without reaching the trochanter. The patient has a noticeable varus position of the limb and outward rotation. |
| A rare traumatic disease such as slipped femoral head occurs in young men. In this case, the epiphysis at the level of the growth plate is hidden or acutely displaced or completely exfoliated. On clinical examination, the radiograph shows a staff-shaped cervical curve. The neck itself will be widened and arched, and the epiphyseal fissure will be irregular and wider than on the side of the healthy limb. The stroke of the head will be almost vertical rather than horizontal. To evaluate the fracture, you need to take a photo from the back and side. There are five stages of epiphysiolysis:
With the progress of epiphysiolysis, an operation is necessary, during which screw fixation is performed through the growth zones, wires, autograft or allograft are inserted, which overlap the growth zone. At stage III, an intertrochanteric angular or spherical detorsion-rotation valgus osteotomy with metal osteosynthesis is performed. At stage IV, closed reposition of the epiphysis and transcervical fixation with Nowlis wires are performed, tunnelization of the head and neck is performed, and an autograft or allograft is introduced. At stage V, epiphysiodesis and corrective osteotomy are performed at the end of the femur bone to correct the malposition of the leg. The doctor may prescribe skeletal traction of the hip, then immobilization of the pelvis and hip with a plaster bandage, surgical extra-articular fixation of the epiphysis and neck using a bundle of pins, screws, and bone grafts. Patients will be able to transfer body weight to the problematic limb only after the pathology has been excluded or cured. |
CT scan shows a fracture line between the femoral condyles
Chondral damage to the medial femoral condyle exists and is common during dislocation. In this case, a piece of cartilage or bone may break off from the femur or patella when the patella “jumps” over the femoral condyle.
In this case, pain and blockage will be caused by bone or cartilage fragments that remain inside the cavities of the knee. There will be no active movements in the joint, the patient will not be able to lift his straight leg. If the peroneal nerve is damaged, sensation and movement of the foot will be impaired.
Patella chipping due to chondral fracture of the medial condyle