Williams syndrome ("elf face" syndrome) is a syndrome that occurs as a consequence of hereditary chromosomal rearrangement, sufferers of which have a specific appearance and are characterized by a general mental retardation with the development of certain areas of intelligence.
The syndrome was described in 1961 by a cardiologist from New Zealand, J. Williams, who identified among his patients who had similar defects in the cardiovascular system, people who also had a similar appearance and moderate retardation.
Williams syndrome is a rare congenital disorder that occurs as a result of inherited chromosomal mutations and is characterized by changes in appearance, mental disorders, a number of unique personality characteristics, and abnormalities of internal organs.
This genetic disease received its name in honor of the pediatric cardiologist from New Zealand J. Williams, who in 1961 proved the hereditary nature of the syndrome. He observed sick children with cardiac dysfunction and similar external signs.
The syndrome is the result of a spontaneous mutation or is inherited. Several genes may be missing in the genotype of patients. This is the reason for the variety of clinical symptoms of the pathology.
Patients with this syndrome exhibit severe defects of the face, heart and blood vessels, bones and joints, and central nervous system.
- Children with Williams syndrome have mental disorders and have difficulty learning. The consequence of chromosomal rearrangement in the body is mental retardation. In patients, a general delay in psycho-emotional development is accompanied by success in various fields of culture and art: music, rhetoric, rhythm.
- Anomalies of the heart are represented by congenital defects, and anomalies of the blood vessels are represented by persistent narrowing of the aorta, branches of the pulmonary trunk and other large arteries.
- “Elf face” is one of the main signs of the disease, characterizing the appearance of patients.
- Other less typical symptoms include: muscle hypotonia, umbilical hernias, malocclusions, hypercalcemia.
- Williams syndrome is a rare, sporadic disease. It occurs in 1 newborn out of 10,000 - 20,000. Boys and girls get sick equally often, regardless of social status and nationality.
Like most chromosomal abnormalities, Williams syndrome can be suspected by the presence of specific external features and characteristic behavior. The peculiar anatomical features of the face allow us to assume pathology. The diagnosis is confirmed by molecular genetic, electro- and echocardiographic studies.
Treatment of the syndrome is symptomatic. To eliminate congenital heart defects, a number of surgical interventions are performed. Psychotherapy sessions and sessions with a psychologist help improve the socialization of patients and improve their quality of life.
What is Elf Face Syndrome?
Williams syndrome (Williams syndrome, “elf-face”, Williams-Beuren) is a rare genetic disease that is accompanied by specific damage to internal organs, delayed intellectual development and a typical appearance of the patient.
All children with this genetic syndrome are similar to each other. Their unusual facial features give the baby a resemblance to a folklore character, an elf. Because of this phenomenon, the disease received its second name – “elf face” syndrome. The disease was first described in the sixties of the last century.
Cardiologist from New Zealand J. Williams discovered a pattern in the development of pathology of the heart and blood vessels and the unusual appearance of patients. The doctor suggested the genetic nature of the disease and gave impetus to further research into the syndrome. Subsequently, the disease received its name in honor of the New Zealand doctor.
WHERE TO GO IN THE MOSCOW REGION IF YOU SUSPECTED GENETIC DEVIATIONS?
Residents of the Moscow region can undergo an examination and get an appointment with a specialist at the Center for Orphan Diseases. The institution appeared in the region two years ago. It became part of the Moscow Regional Consultative and Diagnostic Center for Children in Mytishchi. Since then, young patients with rare hereditary diseases have received the most accurate diagnosis, comprehensive treatment and rehabilitation here. Niemann-Pick, Wilson-Konovalov and Gaucher diseases, mucopolysaccharidosis, juvenile arthritis with systemic onset, osteogenesis imperfecta, hereditary angioedema, glycogenosis - only a small part rare genetic diseases with which patients have already applied to the Center. The institution not only treats patients, but also trains new specialists and conducts scientific and practical work. Address: Mytishchi, st. Comintern, 24 a, building 1. Telephone.
By the way
One of the rarest diseases that occurs among the child population of the Moscow region is Gaucher disease. At the moment, only one minor with this disease has been recorded in the region. Gaucher disease is a hereditary disease that affects the hematopoietic organs and skeletal system. It seriously affects physical development.
Why does Williams syndrome develop?
With the help of various modern research methods, it was possible to establish the cause of the development of pathology. Changes in the child’s body occur due to the loss of a section of chromosome 7, located on its long arm. The “lost” gap consists of approximately 25 genes and carries important information necessary for the normal formation and functioning of the child’s body.
It is in this section of the chromosome that the genes responsible for the development of the brain and the ability to fully perform their functions are located. In addition, a defect in the DNA molecule manifests itself in insufficient formation of the protein elastin, the thyroid hormone calcitonin, disruption of the trophic processes of nervous tissue, and carbohydrate metabolism.
Elastin is one of the main proteins of connective tissue, which provides its important properties - firmness, elasticity, and ability to recover. Thanks to this substance, the normal functioning of organs subject to stretching and compression (vessels, skin, tendons and others) is ensured. The main symptom of elastin deficiency in patients with Williams syndrome is problems with the cardiovascular system. These babies develop lesions on the walls of blood vessels and valves, and arterial hypertension occurs.
A defect in the DNA molecule occurs spontaneously in most cases. Absolutely healthy parents give birth to a baby with a genetic pathology. Usually it is not possible to find the prerequisites for the development of the disease (the impact of unfavorable factors on the developing body of the fetus, the appearance of a genetic syndrome in the family).
In the studies conducted, there was no connection between the occurrence of pathology and the gender or nationality of the child. Therefore, it is very difficult to predict the development of the disease in the unborn baby. At the same time, an autosomal dominant mechanism of transmission of the mutation has been proven. Patients with elf-face syndrome pass on the hereditary defect to their children in 50% of cases.
Features of the psyche
The mental state of people with J. Williams syndrome includes a characteristic complex of unique manifestations:
- Sensory motor skills are impaired, accompanied by hypersensitivity to sound and gravitational anxiety.
- Increased activity, emotional outbursts, impulsiveness, obsessive communication skills, attention deficit.
- High degree of anxiety and fear of innovation.
- Reduced level of attention in the process of learning and mastering science (especially mathematics), relatively easy mastery of reading.
- Violation of expressive and impressive speech.
- Well-defined ear for music, sense of rhythm.
These characteristics suggest the formation of a certain neuropsychological type associated with the development of the central nervous system.
Symptoms of the disease
Early manifestations
The first signs of pathology cannot always be noticed immediately after the birth of a child, although the baby is born with facial features characteristic of the syndrome. Over time, the appearance of young patients becomes more and more typical, and the presence of a genetic disease is obvious.
These babies are often born post-term , but their weight does not reach normal values and remains below normal for a long time. Then problems arise with feeding the “special” babies, and the children refuse to eat. Often the innate reflexes of a newborn , swallowing and sucking, are discoordinated , and it is difficult for the child to perform movements usual for this age. And constant regurgitation and vomiting, constipation aggravate the situation, the baby does not gain weight for a long time, and lags behind in physical development.
Parents can contact a neurologist with complaints about late mastery of skills, irritability and tearfulness in their children. Upon examination, the doctor notices decreased muscle tone in the child, although tendon reflexes are usually increased. Connective tissue pathology manifests itself in the occurrence of umbilical and inguinal hernias, which often recur.
In the case of congenital heart defects or hip dislocation, special attention is paid to the treatment of these manifestations of the syndrome. Surgical interventions cannot be ruled out if the resulting pathologies are life-threatening for the baby.
As the child grows up, problems with digestion and weight gain fade into the background. Signs of retardation in physical, mental and mental development become more clearly visible.
Classic symptoms of the disease
A doctor may suspect a diagnosis of Williams syndrome by noticing a combination of characteristic manifestations of the disease:
- features of the child's appearance.
It’s not for nothing that this disease is called “elf face” syndrome; babies with the genetic syndrome really look like fairy-tale characters. Noteworthy are the full cheeks, large mouth with swollen lips, especially the lower ones. The child's forehead is wide, and the brow ridges diverge along the midline.
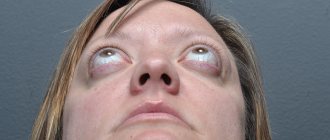
Bright blue eyes are set wide, framed by swollen eyelids. The little patient's nose is upturned, with a blunt end, and the chin is somewhat pointed. In addition, when examining babies, low-lying ears, a protruding back of the head, and squint are often discovered.
All these features give the baby’s face a special expression that can be observed in all children with Williams syndrome, especially when smiling. It is not necessary for one child to have all the external signs of an “elf face”; there are different options for their combination, but the appearance of the babies remains typical. Over time, the baby’s facial features change, and the similarities between patients become more noticeable;
- retardation in physical development.
Babies with Williams syndrome do not gain weight well in the first years of life and may later acquire the necessary skills due to muscle hypotonia. In patients with the genetic syndrome, doctors note impaired coordination and motor skills. Such babies have difficulty learning to take care of themselves and make movements that are simple for other children. Teeth erupt late, are often irregularly shaped, affected by caries, and malocclusion is possible.
By the age of 3, children usually catch up with their peers in physical development. The situation changes in adolescence, when many of the “special” children begin to gain weight, become plump and loose, which is associated with disruption of the endocrine system.
Other patients acquire new features in appearance - a long neck, curvature of the spine, flat feet, and deformation of the chest. These pathologies are associated with muscle hypotonia widespread throughout the body. Weak muscles are not able to create the necessary frame and hold the torso in the correct position.
All patients with Williams syndrome have a peculiar, “creaky” voice of low timbre. This feature appears in early childhood and is associated with a lack of elastin in the vocal cords;
- mental retardation.
Parents notice the first signs of developmental delay when the baby does not begin to pronounce words by the due date, and the children’s speech development suffers. The ability to pronounce short words appears at the age of about 2 years, simple phrases - at 4 - 5 years. This aspect is of great concern to mothers and fathers, because the baby has a friendly character and enjoys “communicating” with other children. Over time, with proper training, the guys will catch up with this skill;
Despite the difficulties in mastering simple skills, these kids are distinguished by excellent abilities in music and playing musical instruments. As the child grows up, there is a gradual development of the child’s intellect, the baby begins to speak, is capable of poetry and music, but the final IQ indicators do not exceed 80, even in an adult. The child has difficulty with motor skills, exact sciences, mathematics, writing, and reading.
Due to the specific gravitational uncertainty, it is very difficult for the baby to maintain balance. Particular difficulties arise when walking on uneven surfaces, climbing stairs, or riding on a swing.
Due to the way the brain functions, children with Williams syndrome have very specific developmental delays. They play musical instruments with pleasure, have excellent hearing and the ability to improvise, but only a few of them master musical notation. And the well-developed, poetic oral speech of these children looks unusual against the background of difficulties in learning to read and write, and a general developmental delay;
- characteristics of temperament.
Babies with elf-face syndrome are usually good-natured and very sociable. They enjoy communicating with peers and adults they know well. Difficulties may arise in contact with strangers due to increased anxiety in children.
The little ones are characterized by emotional incontinence, rapid mood swings, hysteria, and possible manifestations of hyperactivity. All these features, combined with underdevelopment of intellectual functions, form the character traits of an adult patient with Williams syndrome: friendliness, spontaneity, infantility, foolishness and, at the same time, talent;
- pathology of the circulatory system.
Damage to the cardiovascular system is observed in most patients with Williams syndrome. This symptom is explained by a lack of connective tissue protein in the blood vessels, the development of elastin arteriopathy.
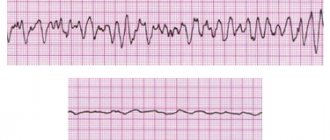
The disease manifests itself as a narrowing of the arteries - supravalvular stenosis of the aorta, pulmonary trunk, stenosis of the renal arteries, cerebral vessels, and heart. The child has arrhythmia and high blood pressure. Such patients are registered with a cardiologist for a long time and undergo regular examinations to identify the dynamics of disorders.
Damage to the cardiovascular system in newborns is especially severe. The birth of a baby with a congenital heart defect requires timely and adequate treatment, often using surgical methods;
- pathology of other organs.
Children with “elf face” syndrome are registered with many specialists for a long time; they require the help of a dentist, since malocclusion, pathologies of dental development and caries make themselves felt already in early childhood. Sick children also experience muscle weakness, pathology of the musculoskeletal system, hernial protrusions, vision problems, and strabismus.
Hypercalcemia, an increased concentration of calcium in the blood, is explained by endocrine disorders and manifests itself in digestive disorders (which are most pronounced in young children), psycho-emotional changes, and impaired neuromuscular conduction.
The most dangerous symptom of hypercalcemia is calcification of blood vessels and heart valves. An increased concentration of calcium in the blood leads to its “settling” in tissues and disruption of the functioning of the circulatory system. The affected walls of blood vessels become thinner and lose their elasticity, which leads to the development of cardiovascular failure.
Symptoms
The first symptoms of pathology can be noticed immediately after the birth of the child. Sick children have an asymmetrical face, small eye sockets, deformed ears, and an underdeveloped lower jaw. These are external signs of pathology, which are often accompanied by pathological changes in internal organs.
Symptoms from the visual analyzer:
- Anophthalmia,
- Microphthalmos,
- Microcornea - small cornea,
- Aniridia - absence of the iris,
- Ptosis of the upper eyelid,
- Strabismus - deviation of the visual axis of the eye from the point of fixation,
- Cataract,
- Dermoids and lipodermoids on the surface of the eyeball are small tumors
- Damage to the extraocular muscles.
Clinical signs of ear damage:
- Abnormal placement of the ears
- Minimum ear sizes
- Deformation of the ears,
- Flat or protruding ears
- Characteristic outgrowths on the ears,
- Eardrum defects,
- The connection of the auricle with the corner of the mouth, giving the face a distorted appearance,
- Narrowing of the ear canal
- Fistulas and parotid fistulas,
- Absence of external auditory canal,
- Hearing loss
- Bilateral asymmetric conductive hearing loss,
- Complete lack of hearing.
The lower jaw in patients is underdeveloped. One half of the face is smaller than the other, facial muscles are poorly developed. The sky has the appearance of a high arch, sometimes splitting. The mouth gap is too wide, the bite is disturbed, additional frenulums and clefts appear on the small tongue. The growth of teeth is impaired. The soft palate, lips and tonsils are deformed. There are tracheoesophageal fistulas. The mouth is large, one corner higher than the other. The cheekbones are underdeveloped, the forehead protrudes, and tongue anomalies are present.
Children with Goldenhar syndrome have problems with the spine: underdevelopment of the cervical spine, scoliosis, clubfoot, wedge-shaped vertebrae, their fusion, the presence of hemivertebrae, fusion of the cervical vertebrae with the back of the head, bone abnormalities, short neck, curvature of the spine.
Manifestations from the cardiovascular system are symptoms of congenital heart defects. Sick children are born with underdeveloped lungs, absence of pelvic organs, facial nerve paresis, and hydrocephalus. They have learning difficulties. Every 10 sick child is born with damage to the central nervous system.
Diagnostics
Typically, identifying the syndrome is not difficult due to the characteristic clinical picture of the disease and consists of several stages:
- determination of external signs.
When examining the patient, attention is drawn to the characteristic appearance, lag in mental and physical development. Often, the doctor notices a hoarse, hoarse voice in the child, muscle weakness, strabismus, umbilical and inguinal hernias;
- laboratory research.
By examining the blood using biochemical methods, one can detect increased concentrations of calcium, cholesterol, and thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Thanks to molecular genetic analysis, a mutation in chromosome 7 is determined, which helps to verify the genetic nature of the disease and determine the severity of the pathology;
- instrumental methods.
With the help of a timely comprehensive examination, it is possible to identify signs of disorders in various organs and prescribe appropriate treatment in a timely manner. Using methods such as EchoCS and ECG, pathologies of the circulatory system and heart rhythm disturbances are determined. Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is necessary to exclude dysfunctions in the functioning of internal organs, primarily the kidneys.
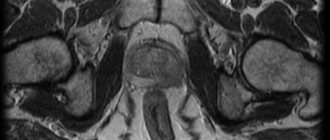
X-ray examination will help determine and select the correct treatment for diseases of the musculoskeletal system (deformities of the spine, sternum, foot). Magnetic resonance imaging can detect signs of cerebral hypoplasia, a decrease in the posterior part of the corpus callosum and the volume of white matter of the brain;
- specialist consultations.
To confirm the baby’s pathologies, a cardiologist, ophthalmologist, traumatologist, orthopedist, dentist, neurologist and other specialists are consulted.
Modern principles of intensive care
Therapy in the post-resuscitation period is carried out according to the following principles: extracranial and intracranial measures.
Extracranial events:
1. Since the level of cerebral blood flow becomes dependent on the level of mean arterial pressure, it is recommended to provide hypertension (MAP) in the first 15–30 minutes after successful resuscitation
2. Maintaining normal levels of PaO2 and PaCO2.
3. Maintaining normothermia of the body. The risk of poor neurological outcome increases for every degree >37°C.
4. Maintaining normoglycemia (4.4–6.1 mmol/l). Hyperglycemia is associated with poor neurological outcome.
5. Maintaining hematocrit level within 30–35%. Carrying out mild hemodilution, which ensures a decrease in blood viscosity, which significantly increases in the microvasculature due to ischemia.
6. Control of seizure activity by administering benzodiazepines.
Fighting hypercalcemia
It is important to maintain proper calcium concentration in the blood to avoid dangerous complications of the disease. During the neonatal period and infancy, the issue of the need to feed the baby with special mixtures with a low content of the element is decided. As the child grows, his diet gradually expands, new products are introduced, but calcium levels must be constantly monitored.
In general, the volume of administered fluid and nutrients should be sufficient to ensure the normal functioning of the body without overloading with calcium-containing products. If there is a significant increase in calcium in the baby’s blood, medication, infusion therapy, and the administration of potassium supplements may be required.
For children with Williams syndrome, the use of vitamin-mineral complexes containing calcium and vitamin D is contraindicated.
Treatment of cardiovascular pathology
Depending on the severity of the manifestations, the treatment tactics for pathology of the heart and blood vessels also change. Minor problems are treated conservatively, blood pressure is reduced with drugs from the group of ACE inhibitors, calcium antagonists, diuretics, beta-blockers. In severe cases, surgery is required.
Symptomatic therapy
Children with “elf face” syndrome are registered with many specialists. They perform correction of visual acuity, elimination of dental defects, treatment of flat feet and spinal pathologies, and removal of hernias.
A neurologist often prescribes in complex treatment drugs that improve cerebral circulation and stimulate the mental development of a child - Piracetam, Vinpocetine, Cerebrolysin. To stimulate physical development, it is good to use physiotherapy methods - massage, exercise therapy, magnetic and ultrasound therapy and others.
Social adaptation of the child
Psychotherapy, work with psychologists, speech therapists are necessary to improve the intellectual development of the child and support the family. Competent specialists will explain to parents what exercises contribute to the development of speech, writing, reading, and non-verbal skills. Families in which an unusual child is born need the help of a psychologist who will help to accept the child’s uniqueness and teach the baby to adapt to the people around him.
A feature of children with an “elf face” is a pronounced difference between verbal and non-verbal IQ levels. Intellectual development occurs due to mastery of speech, while spatial concepts do not develop. These children find it difficult to complete tasks such as assembling a pyramid, drawing a picture, mastering mathematics, or performing a physical exercise.
General information about pathology
Most patients have disturbances in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, which are represented by the aorta and arteries of varying degrees of severity. When the lumen of the renal artery decreases, half of the patients suffer from high blood pressure.
Significant quantitative levels of calcium are observed in the bloodstream, which causes psycho-emotional changes and painful bloating during the first months of life.
Patients suffering from the disease have low body weight. They gain it much more slowly than their healthy peers. The first year of life is very difficult regarding feeding. Children have frequent vomiting and impaired sucking and swallowing processes.
You may also experience:
- pathologies of the stomach and intestinal tract;
- hypofunction of the thyroid gland;
- defects in the structure of the kidneys;
- hernias of various localizations;
- low muscle tone.
Prognosis and prevention
The life expectancy of patients with Williams syndrome is slightly lower than that of other people. Health problems consist mainly of pathology of the heart and blood vessels and metabolic disorders.
Parents of “special” children should be aware of cases of sudden death in children with Williams syndrome, which most often occur before the age of 6 years. The cause of death is acute myocardial ischemia and ventricular arrhythmia. Therefore, regular examination of the cardiovascular system and timely treatment of pathologies is very important to maintain the baby’s health.
Children with a genetic syndrome lag behind their peers in development, but their lively character and easy-going disposition give the child the opportunity to socialize. Communication with other children is very important for the development of an unusual child, and parents should make every effort to help the child adapt to society. Adult patients cannot engage in work activities due to their illness and require supervision and control from relatives throughout their lives.
There are no preventive measures to prevent the syndrome, since in most cases the cause of the pathology is a spontaneous mutation. If a person with a genetic syndrome decides to have a child, the risk of having a baby with the pathology reaches 50%. In this case, medical and genetic counseling of the family is required.
Blood testing
This test is performed by drawing 5 ml of blood from a child suspected of having Williams syndrome. “Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) testing” is a type of specialized chromosomal analysis using specially prepared elastin probes. If a patient has two copies of the elastin gene (one on each of their #7 chromosomes), they probably do not have WS. If a person has only one copy, the diagnosis of WS will be confirmed." according to the Williams Syndrome Association. The results of this test can take several weeks and are only performed in specialized laboratories, so your healthcare provider must ensure that the test can be performed before the blood is drawn and sent.
Psychological characteristics
Mental retardation in Williams syndrome is observed in all cases. This syndrome is characterized by a deficit of visual-figurative thinking; abstract thinking is almost completely absent. The degree of intellectual defect is quite significant, IQ on average ranges from 40 to 50 (moderate mental retardation - imbecility).
One can note the great similarity of the psychopathological picture of the defect in all patients: with a significant decrease in intelligence, patients have a relatively large vocabulary, are very talkative, prone to imitation, children’s speech is quite good, however, it is just a set of cliches. At the same time, spatial representations, organization and planning of activities always suffer. The personality traits of these children are very characteristic and constant: good nature, friendliness, obedience, emotionality, desire to communicate, and gullibility. Almost always there is a good ear for music, even with a pronounced intellectual defect. Neurosis-like disorders are often detected - enuresis, habitual vomiting, obsessive actions, headache. Some children experience hyperactivity, fears and anxiety.
Some children can study in a auxiliary school; they master reading and writing, but they are unable to perform activities related to organizing even the simplest labor operations.
Treatment
- To normalize blood pressure, patients are prescribed antihypertensive drugs from the group of ACE inhibitors, calcium antagonists, diuretics, and beta-blockers.
- Nootropic drugs to improve cerebral circulation and adequate mental development of patients - Piracetam, Vinpocetine, Cerebrolysin.
- If the level of calcium in the blood is high, its correction with medication is required - intravenous administration of saline, diuretics, potassium supplements.
- When severe forms of pathology develop, glucocorticosteroids are prescribed - Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures improve joint mobility - exercise therapy, magnetic therapy, ultrasound, electrotherapy, acupuncture, massage.
- Psychological correction consists of teaching sick children correct speech, reading and writing, reducing anxiety and fear.
- Friendliness and mutual understanding in the family play an important role in the treatment of sick children.
- Psychotherapy and sessions with a psychologist are an integral part of the treatment process.
- Surgical intervention is aimed at eliminating congenital heart defects in children, which often lead to the death of patients.
Appearance Features
Elves from English folklore appear to be children with Williams syndrome.
Patients have a special facial structure, called “elf face” in specialized literature, since it resembles the face of elves in their traditional, folklore version. They are characterized by a wide forehead, scattered eyebrows along the midline, full cheeks drooping down, a large mouth with full lips (especially the lower ones), a flat nose bridge, a peculiarly shaped nose with a flat, blunt end, and a small, somewhat pointed chin.
The eyes are often bright blue, with a star-shaped iris and bluish sclera. The shape of the eyes is peculiar, with swelling around the eyelids. Convergent strabismus.
Older children are characterized by long, sparse teeth. With age, the face of patients changes somewhat: the brow ridges become massive, the pastiness of the face is less pronounced, there is no flat nose bridge or epicanthus
Noteworthy is the increased distance from the base of the nose to the upper lip.
The similarity of faces is enhanced by a smile, which further emphasizes the swelling of the eyelids and the peculiar structure of the mouth.
None of these traits are mandatory, but their overall combination is always present [ what?
].
General information
Williams syndrome (Williams-Beuren syndrome, “elf-face” syndrome) is a genetic disease caused by the absence of several genes, the number of which can range from 25 to 29. This fact is associated with a fairly wide range of clinical manifestations of the condition and differences in their severity.
This syndrome was first described in 1961 by a cardiologist from New Zealand, J. Williams - he identified a number of phenotypically similar children with similar congenital disorders of the cardiovascular system. At the moment, using the methods of modern genetics, it has been possible to prove the hereditary nature of Williams syndrome.
Williams syndrome
Appearance Features
Elves from English folklore appear to be children with Williams syndrome.
Patients have a special facial structure, called “elf face” in specialized literature, since it resembles the face of elves in their traditional, folklore version. They are characterized by a wide forehead, scattered eyebrows along the midline, full cheeks drooping down, a large mouth with full lips (especially the lower ones), a flat nose bridge, a peculiarly shaped nose with a flat, blunt end, and a small, somewhat pointed chin.
The eyes are often bright blue, with a star-shaped iris and bluish sclera. The shape of the eyes is peculiar, with swelling around the eyelids. Convergent strabismus.
Older children are characterized by long, sparse teeth. With age, the face of patients changes somewhat: the brow ridges become massive, the pastiness of the face is less pronounced, there is no flat nose bridge or epicanthus
Noteworthy is the increased distance from the base of the nose to the upper lip.
The similarity of faces is enhanced by a smile, which further emphasizes the swelling of the eyelids and the peculiar structure of the mouth.
None of these traits are mandatory, but their overall combination is always present [ what?
].