Approximately 75% of boys born with this anomaly experience spontaneous migration of the testicles within 6 months, and only 1–2% of newborns still have cryptorchidism by the end of the first year of life.
A congenital defect of the left testicle is observed in 20% of cases, the right - in 50%. Bilateral cryptorchidism is diagnosed in 30% of children. Pathology is divided into two groups: ectopia and testicular retention. In the first case, the testicle is fixed in the groin, penis or thigh area, in the second, the testicle stops in the abdominal cavity or inguinal canal on its way to the scrotum. In both cases, it is not possible to manually lower the testicle into the scrotum.
If the testicle has not migrated into the scrotum due to tension in the levator muscle, this anomaly is classified as false cryptorchidism.
, which does not require surgical intervention, disappearing on its own during puberty. There is also a type of disease called an ascended testicle, in which it moves upward, which is caused by too slow growth of the spermatic cord. In any case, before prescribing treatment, a thorough diagnosis of cryptorchidism is carried out to determine the type of pathology.
What is cryptorchidism (undescended testicle)
Undescended testicle or cryptorchidism is a testicular pathology that occurs in newborn boys.
According to statistics, the problem most often manifests itself as undescended testicle, but in 10% of cases both testicles become undescended. Quite often this diagnosis is given to children who were born prematurely. In most cases, the testicle descends into the scrotum during the first months of life. However, if this does not happen, the pathology can be corrected with surgery, thanks to which the testicle will take its correct position.
The exact causes of the pathology are unknown. Genetic predisposition, the general health of the mother, the environment and a number of other factors can affect hormonal levels, which in turn can affect the proper formation of the testicles.
How is surgery performed for cryptorchidism?
Modern medicine has two methods of surgical intervention for cryptorchidism:
| Methodology | Peculiarities |
| Open | Indicated if the testicle can be palpated. It requires a sufficient length of the spermatic cord, so this parameter is first checked, and if necessary, the patient is prescribed a course of hormones. The operation involves making an incision in the groin area more than 20 mm long and searching for the testicle. If it is functional, the surgeon makes an incision in the scrotum and integrates it there, fixing it and suturing it. If not, delete it. |
| Laparoscopic | It is advisable if the testicle cannot be felt. In the process, a laparoscope is inserted through the navel to find the testicle and its descent. If a deficiency in the length of the spermatic cord is detected, reduction is postponed for six months, during which hormonal treatment is carried out. |
On average, the operation lasts from half an hour to one and a half hours. It is performed under general or combined anesthesia.
Cryptorchidism requires timely detection, correct diagnosis and competent treatment, thanks to which the development of serious complications, including testicular cancer and infertility, can be avoided in the future. Surgery is the most effective way to eliminate the problem and achieve the desired result. Trust the pediatric surgeons working at CELT to carry it out!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Risk factors
Experts identify the following reasons that may increase the risk of developing an undescended testicle:
- underweight newborn;
- premature birth;
- hereditary factor associated with an undescended testicle or a number of other pathologies of genital development;
- Down syndrome, abdominal wall defect, and other conditions associated with normal fetal development;
- drinking alcohol, drugs, smoking and second-hand smoke during pregnancy;
- overweight or obesity in a woman in labor;
- the presence of diabetes mellitus in the woman in labor: diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2, as well as gestational diabetes;
- exposure to certain pesticides.
Possible complications
Normally, the temperature in the scrotal area is slightly lower than normal body temperature. These conditions are necessary for the full development and functioning of the testicles. While a boy is 3-4 years old, the testicles continue to undergo changes that affect how well they will function in adulthood.
Testicular cancer. Cryptorchidism carries a risk of developing testicular cancer in adulthood. Surgical treatment for an undescended testicle at an early age reduces, but does not completely eliminate, the risk of future cancer.
Reproductive dysfunction. A general decrease in fertility, low sperm count and poor sperm quality are more common in men who experience an undescended testicle in infancy.
Other complications may include:
Testicular torsion is a pathology of the spermatic cord, which carries sperm from the testicles to the penis. It occurs 10 times more often in men suffering from this problem.
Injury. If the testicle is not positioned correctly, injury may occur. If it is located in the groin area, it can be easily damaged by pressing on the pubic area.
Inguinal hernia. Due to an undescended testicle, the passage between the abdominal cavity and the inguinal canal may become too loose, and part of the intestine may move into the free area.
Price and cost of cryptorchidism surgery in children:
| Service | Price |
| Cryptorchidism inguinal form (ectopic testicle) - 1 degree of complexity (testicle in the lower third of the inguinal canal) | 55000 |
| Cryptorchidism (groin form) 2nd degree of complexity | 63000 |
| Cryptorchidism abdominal (abdominal) form - laparoscopy, first stage | 45000 |
| Cryptorchidism abdominal (abdominal) form - laparoscopy, second stage | 75000 |
The price list published on the website is not a public offer agreement. The provision of services is carried out on the basis of an agreement for the provision of medical services. We ask you to check the cost of services with your attending physician in advance. The cost of the operation includes (no additional payment for services is necessary!):
- inpatient accommodation 1 day double room with all amenities
- preoperative tests
- disposable suture material Vicryl, PDS
- application of intradermal cosmetic suture
- disposable surgical consumables
- surgical instruments Ceatec GmbH Germany
- microsurgical instruments and equipment
- constant telephone communication with the attending physician
- examination any day in the clinic within 14 days after surgery
The cost of the operation does not include: anesthesia, additional diagnostics and treatment of concomitant diseases and their complications.
Anesthesiological support: anesthesiological apparatus Drager Fabius Plus (Germany), combined general anesthesia (inhalation anesthesia, caudal/local anesthesia).
** This is not a public offer agreement. Check the cost of services on the day of your request.
Don't waste your precious time - call!
Our specialists will be happy to answer all your questions
+7
Reviews
With ALL my SOUL and ALL my HEART I express my gratitude to you!!! At birth, my son was diagnosed with bilateral cryptorchidism.
- Julia Bilateral cryptorchidism
Our advantages
Experienced surgeons
Individual approach
Without pain and fear
Comfortable conditions
Scheduling a doctor's visit
Typically, the problem is discovered soon after birth, and your doctor or pediatrician should monitor the scrotum regularly. Before you meet with your doctor, write down a list of questions to discuss. If you have additional questions for a specialist, do not hesitate to ask them. — How often should you schedule visits to the doctor? — How to examine a child’s scrotum at home? — What diagnostics does the child need? — What treatment options are recommended to eliminate the pathology?
Examination and diagnosis
The doctor examines the child, determining the position of the testicle by lightly palpating the scrotum. If it is felt in the inguinal canal, the doctor may try to gently move the testicle into the scrotum. If it moves only partially, immediately retreats to its original place, movement is difficult, manipulation causes pain or discomfort, this condition can be diagnosed.
Having determined that the testicle has not descended into the scrotum, the doctor may order additional tests. They will help determine the position of the testicle, since in some cases an undescended testicle cannot be palpated, for example, if it is located outside the inguinal canal. The doctor may recommend the following types of diagnostics:
- Ultrasonography.
- MRI with contrast agent.
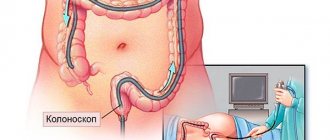
- Laparoscopy.
- In certain cases, examination of the abdominal or groin area is performed through an open incision.
Using ultrasound, the doctor can see a non-palpable testicle, for example, if it is in the groin area.
The technique uses a magnetic field and radio waves, as well as a special coloring element that is injected into the blood and improves image quality. This diagnosis allows you to see the testicle in the inguinal canal or abdominal cavity.
Laparoscopy is a modern minimally invasive surgical method that allows you to detect an intra-abdominal testicle. A small tube with a camera is inserted through a small incision into the abdomen. The surgeon can correct the problem with this intervention, but in some cases additional surgery may be required.
Causes
To penetrate the scrotum during the intrauterine stage of fetal development, the testicle makes its way through the abdominal cavity and passes through the abdominal wall along the inguinal canal. In the embryonic period, the testicle is located first retroperitoneally, and then intraperitoneally. During the first three months of intrauterine life, the gonad is located in the lumbar region, on the side of the spine, adjacent to the kidney. By the end of the 3rd month of intrauterine life, the gonad is located near the internal opening of the inguinal canal. Only at the 8th month does the testicle penetrate the inguinal canal and from here descend into the scrotum. The gonad descends into the scrotum following the guide ligament - gubernaculum testit. The canal through which the testicle enters the scrotum is represented by the vaginal process of the peritoneum, which is obliterated (closed) by the time the baby is born.
The process of lowering the testicle into the scrotum occurs under the influence of several main factors:
- downward traction due to the gonad conductor - Gunter's cord;
- difference in the growth rate of the body and the growth of the spermatic cord;
- increased intra-abdominal pressure;
- bowel movements, the lower section of which, during the final descent of the testicles, is filled with meconium;
- appendage development.
The passage of the testicle through the inguinal canal largely depends on the concentration of androgens (male sex hormones) produced by the embryonic gonad. The greatest role is given to luteinizing hormone, which is actively produced by the pituitary gland of the fetus in the last trimester of pregnancy. Thus, a decrease in the concentration of male sex hormones that are produced in the fetus or a deficiency of gonadotropic hormones in the mother (it has been established that gonadotropic hormones affect the descent of the testicles by regulating the production of androgens) can significantly affect the process of testicular descent. Any mechanical obstacles along the route can also lead to its deviation.
Treatment of cryptorchidism
The main goal of treatment is to move the testicle to the scrotum area and fix the correct position. Elimination of pathology at an early stage of life (before 1 year) reduces the risk of complications that were described above. Our clinic located in St. Petersburg will help you eliminate this disease.
Operation
The disease is successfully treated surgically and, as a rule, doctors recommend a surgical method to solve the problem. During the operation, the surgeon will carefully move the testicle to the scrotum area and then connect it to the tissues with sutures (orchiopexy surgery). The surgery is performed either laparoscopically or by open surgery.
Indications for surgery depend on a number of factors. The patient’s health is taken into account, as well as the complexity of the operation itself. Your doctor will likely recommend surgery three to six months before the boy reaches twelve months of age.
If the surgeon finds pathological or dead tissue, it must be removed. If the patient has an inguinal hernia associated with cryptorchidism, the pathology can also be resolved during surgery.
Postoperative monitoring is necessary to ensure that the testicle is developing correctly and remains in place. It may include the following types of examination:
- Physical examination
- Ultrasound examination of the scrotum
- Hormone test
Hormone therapy
With the help of an injection of the hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), the testicle can take its correct location. During hormone therapy, the patient receives a certain number of hCG injections. Typically, this type of treatment is considered less effective than surgical treatment, so it is rarely recommended.
Other treatments
If a boy is missing one/both testicles, prosthetics may be considered. Implantation can be done during late childhood or upon reaching adolescence. Thanks to prosthetics, the scrotum will look natural.
If your child is missing at least one healthy testicle, your doctor recommends contacting an endocrinologist to discuss possible hormone therapy options that may be needed to achieve sexual and physical maturity.
Clinical guidelines (European Association of Urology)
- Children with an increased cremasteric reflex (retractile testicles) do not require medical or surgical treatment, but they require regular monitoring until puberty;
- the optimal timing of treatment if cryptorchidism has developed is from 6 to 18 months of the child’s life;
- for non-palpable testicles, laparoscopy is the “gold standard”, since it has almost 100% sensitivity and specificity for identifying intra-abdominal testicles, allowing simultaneous surgical correction;
- adjuvant and non-adjuvant hormonal therapy is not standard treatment. Its use must be individualized for each patient;
- in the presence of an intra-abdominal testicle on one side and a normal contralateral testicle in children over 10 years of age, it is advisable to remove the intra-abdominal testicle due to the high risk of malignancy.
- Federal clinical guidelines “Cryptorchidism”
- Pediatric urology-andrology: Textbook. allowance. — Razin M.P., Galkin V.N., Sukhikh N.K.
- Algorithm for the treatment of children with cryptorchidism Al-Mashat N.A., Kovarsky S.L., Petrukhina Yu.V.
- Surgical treatment of cryptorchidism in children Zholumbaev A.O., Raselbaev K.U.
Lifestyle and recommendations
Even after surgery, it is important to regularly carry out diagnostics - this can be done at home. This way you will be sure that the testicles are developing correctly. Check their position during hygiene procedures - changing diapers and baths. When the boy reaches an older age, be sure to talk to him about his testicles. Explain how he can check them himself. Self-diagnosis is an important skill that can help detect a possible tumor.
Due to the absence of one/both testicles, the boy may worry. These concerns are justified, since the appearance of his genitals differs from the genitals of friends and peers in general. He can see such differences, for example, while changing clothes in a sports locker room. The following tips will help him in this situation:
- the boy must understand the meaning of words such as testicles and scrotum;
- convey information to the child in simple words, explain to him that no matter what, he is still a healthy boy;
- talk to your son about possible testicular replacement;
- teach him the right words if someone around the child teases him or asks about his condition;
- buy loose underwear, it will help hide the condition of the scrotum and make it less noticeable when changing clothes or playing sports.
Symptoms
As a rule, a qualified doctor can already discern signs of cryptorchidism in a patient by the appearance of the genital organs. Symptoms of the disease in men 1. External changes in the scrotum. Asymmetry and underdevelopment of the scrotum is revealed by palpation; 2. Nagging pain in the lower abdomen. Causes particular discomfort in the patient during coughing, sexual arousal, and defecation; 3. Deterioration in the quality and quantitative parameters of sperm. The number of active sperm decreases, sperm motility decreases; 4. Testicular torsion. The consequence of twisting of the spermatic cord is the infringement of its constituent arteries, nerves, and lymphatic vessels. The final stage may be testicular necrosis.