March 21, 2019
Do you know that skin is an organ? And this organ is the largest in humans, which means it is more susceptible to adverse effects than others. The branch of medicine that studies the skin, its structure, functioning, protection, as well as hair and nails, which are appendages of the skin, is called dermatology (from the Greek words “derma” - skin and “logos” - study). A dermatologist specializes in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases and pathologies of the skin, nails and hair.
What does a dermatovenerologist treat?
Modern dermatovenereology is one of the most extensive areas of therapeutic science, and a dermatovenereologist treats diseases belonging to its different areas:
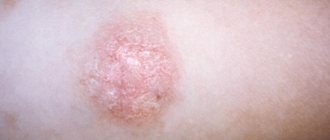
- dermatology – diseases of the skin and its appendages: nails, hair, sebaceous and sweat glands – psoriasis, vitiligo, atopic dermatitis, eczema, alopecia, folliculitis, etc.;
- venereology – sexually transmitted diseases, genital infections and sexually transmitted diseases: syphilis, gonorrhea, molluscum contagiosum, chancroid, herpes, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, etc.;
- mycology – diseases caused by fungi, including candidiasis;
- conservative cosmetology, the goal of which is to improve the appearance of the skin without surgery.
Pediculosis
Pediculosis is caused by human louse, which is divided into three subtypes: head, body, and pubic.
The head louse lives on the scalp, the body louse - in the folds of clothing (it comes to the skin only for feeding), the pubic louse - in intimate areas, sometimes in the armpits. Pediculosis is transmitted through sexual contact. Has recognizable symptoms:
- numerous spots on the surface of the skin of a bluish or bluish-grayish color;
- excoriation - scratching of bites, often a secondary infection occurs with the development of purulent pustules;
- Nits—lice eggs—are found on the hairy areas.
Pediculosis poses an infectious danger, since lice can be carriers of a certain type of pathogenic bacteria - rickettsia, which causes Volyn fever. Lice also carry relapsing fever.
When to contact a dermatovenerologist
Skin is the largest organ of the human body. Currently, there are a huge number of dermatoses and chronic skin diseases, the treatment of which must be carried out in a timely manner. In addition, many skin diseases have a chronic course and are prone to frequent relapses. Contagiousness is another feature common to many skin and venereal diseases.
Unprotected sexual intercourse is a matter of particular concern for one’s own health. Sexually transmitted diseases - sexually transmitted diseases and sexually transmitted infections when neglected can cause irreversible harm to many organs and systems of the body. Modern medicine lists more than 10 sexually transmitted diseases. A dermatovenerologist can successfully cope with all these diseases with the help of timely diagnosis and the prescription of modern medications.
The following symptoms should be the reason for consulting a dermatovenerologist:
- skin rashes on the mucous membranes, genitals, skin of the body;
- itching of the skin;
- changes in skin pigmentation;
- the appearance of various neoplasms on the skin or mucous membranes;
- pustules in the mouth, white plaque on the inside of the cheeks and tongue;
- changes in the color and structure of nails;
- peeling of the skin;
- hair loss has become more intense than usual;
- itching of the scalp, formation of profuse dandruff;
- hair fragility;
- changed color, structure, size of the mole;
- discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse;
- more abundant than usual discharge from the genitals with an uncharacteristic color or odor;
- development of ulcers, rashes, itching in the genital area and mucous membranes of the mouth;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- burning in the genitals;
- pain in the genitals, testicles, abdominal area.
Self-medication or treatment using traditional medicine methods for sexually transmitted diseases is unacceptable and will not lead to results. If the patient has even the slightest reason for concern, it is necessary to see a dermatovenerologist. Timely therapy prescribed by a dermatovenerologist allows you to avoid unpleasant and dangerous consequences and complications and restore health. Modern drug treatment allows you to get rid of sexually transmitted diseases reliably and without dangerous consequences and complications. It is worth remembering that both sexual partners need to be treated by a dermatovenerologist.
A dermatovenerologist performs a preventive examination when a patient registers for work or study.
Skin structure
The skin consists of three main layers: the top layer of the epidermis, the main layer of the dermis with nerves, glands and hair follicles, and the third layer of subcutaneous fat. Each of the three layers can be affected by different diseases. For example, psoriasis is a disease of the epidermis, and cellulite is a pathology of subcutaneous fat.
Sometimes the disease affects all layers, as, for example, in the case of burns or if, due to the abuse of traditional medicine, the foci of the disease have spread deeper. And only a qualified specialist can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. Depending on the results obtained during the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe not only external procedures, but also medications, diet, and consultations with related specialists. Modern high-tech equipment allows you to carry out any operations at a high level, quickly and painlessly. Doctors use ultrasound, laser and radio wave equipment.
How is the appointment going?
What does a dermatovenerologist do during an appointment? The initial consultation with a dermatovenerologist begins with collecting the patient’s medical history and complaints. The dermatovenerologist will definitely clarify whether treatment was previously carried out and what medications were used. In the case of chronic skin diseases (psoriasis, vitiligo, atopic dermatitis), the doctor will clarify whether the patient has a family history of these diseases. The patient’s goal at this stage of admission is to formulate as accurately as possible the complaints about the conditions that bother him.
What does a dermatovenerologist look for:
- healthy skin areas;
- pathological areas of the skin;
- assesses the prevalence of the process.
Very often, already at this stage the doctor can assume the correct diagnosis, based on his own experience. If any doubt arises, the dermatovenerologist will necessarily prescribe additional laboratory and instrumental tests:
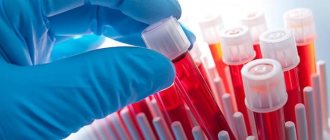
- general blood analysis;
- scraping the skin for mites;
- bacteriological culture;
- microscopic mycological examination;
- smear of the rash element;
- smear for urogenital infections;
- linked immunosorbent assay;
- biopsy of a mole or any other neoplasm;
- PCR diagnostics;
- dermatoscopy.
In some cases, to determine changes in the structure of the tumor or the extent of the pathological process in the deeper layers of the skin, an ultrasound, CT scan, or consultation with a specialist may be required. Cytological examination of neoplasm tissue will help determine the nature of its cells.
After the disease is diagnosed, the dermatovenerologist prescribes treatment.
Skin diseases (psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, vitiligo, neurodermatitis) often have a chronic course and are prone to relapses. Patients with such diseases need constant monitoring by a dermatovenerologist in order to prolong remission and smooth out the severity of the process during an exacerbation.
Children's specialist
An examination by a dermatovenerologist is relevant even for children. After all, diseases can be transmitted to babies at birth from the mother’s body. In this case, diseases can manifest themselves both during the first days of life and “sleep” for a long time, waiting for a decrease in immunity. Therefore, there is a separate specialist - a pediatric dermatovenerologist who treats manifestations of STDs in children. This doctor can also examine and prescribe treatment for a child who suffers from dermatological diseases caused by exposure to the sun, allergens, etc.
Treatment in children must be approached in a special way. Therefore, under no circumstances should you visit an “adult” dermatovenerologist. Children will not be able to tolerate taking therapeutic drugs prescribed to adults without complications . Instead of cytostatics and corticosteroids, younger patients are prescribed immunosuppressive medications, which reduce allergic reactions.
You can contact a child specialist with both infants and middle-aged children. The reason to visit a doctor is the appearance of crusts on the skin, rashes, itching, redness, and blisters.
A pediatric specialist treats:
- trichomoniasis;
- chlamydia;
- psoriasis;
- mastocytosis;
- lichen;
- HPV;
- and much more.
After consulting with a specialist about various skin diseases, the physician may refer the patient for a smear or other diagnostic method
Preparing for an examination by a dermatologist-venereologist
In order for the examination by a dermatovenerologist to be as informative as possible, it is necessary to properly prepare for the appointment. As a rule, preparation does not cause any difficulties for the patient. If you have an appointment, please follow these guidelines:
- do not use cosmetics, as well as medicinal ointments and creams on pathologically changed areas of the skin, so as not to change the clinical picture of the rash;
- You can take a shower before use, but do not use aggressive detergents. Use baby soap instead;
- If the cause of your complaints is problems on the scalp or hair, do not wash your hair before visiting a dermatovenerologist for a couple of days. This is necessary so that, if necessary, the doctor can carry out some dermatological tests.
- If you have nail fungus, it is not recommended to cut your nails before visiting a dermatovenereologist because nail particles may be required for microscopic examination. Before visiting a dermatovenerologist, women are advised to remove polish from the nail plate.
- If you suspect a sexually transmitted disease or venereal disease, women should not douche before visiting a dermatovenerologist, so as not to distort the clinical picture of the disease.
When complaining of skin rashes, the patient should remember what could have preceded them: eating unusual foods, contact with animals, taking medications, unprotected sexual intercourse. This information will be necessary for the dermatovenerologist to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
If you find yourself with symptoms indicating the development of a dermatovenerological disease, be sure to make an appointment with a dermatovenerologist. The examination and tests will not take much time, but will help dispel doubts about your health status and, if necessary, undergo treatment. Most sexually transmitted diseases respond well to treatment by a dermatovenerologist, and the sooner treatment is started, the higher its effectiveness.
How do sexually transmitted diseases differ from sexually transmitted infections (STIs)?
Classic venereal diseases include gonorrhea, syphilis, chancroid and several other diseases that are not common among Russians, but they all require a systematic dispensary approach. STIs are the same venereal diseases, but not classic, but modern, although these pathogens were discovered recently, and infections most likely existed a long time ago.
Formally, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, genital herpes and human papillomavirus are also sexually transmitted diseases, but they can be observed and treated by gynecologists and urologists, since patients come to them with organ manifestations of STIs, and not because of the presence of an infectious agent. The agent is detected during examination, while the clinical manifestations of all STIs are very similar, which cannot be said about classical sexually transmitted diseases - they have their own typical “face” and can be transmitted through everyday contact without sexual contact. HIV infection is so complex that it has been classified as a separate section of infectious diseases.
The main difficulty in identifying sexually transmitted diseases and STDs is their asymptomatic course. In most cases, a person does not feel any symptoms of the disease, but the presence of a hidden infection in the body can seriously affect health in the future.
Chlamydia, ureaplasmosis and mycoplasmosis lead to prostatitis in men, and to inflammatory diseases of the uterus and appendages in women. The human papillomavirus (HPV) can cause cancer of the cervix, vulva, and penis. Hepatitis B virus – liver cancer.
If you are looking for where to get a consultation with a dermatovenerologist in the Presnensky district, call ProfMedLab: +7 (495) 120-08-07.