Mark Anatolyevich, what could be the reason for liver enlargement?
- In general, liver enlargement itself is just a symptom of the disease. It is necessary to first find out the cause of the disease, and then eliminate it.
Diseases that contribute to liver enlargement are cirrhosis and fatty hepatosis (fatty liver).
These diseases are chronic and are caused by various factors, including malnutrition, alcohol abuse, or infectious viral hepatitis.
General information
Pathological enlargement of the liver in medicine is called hepatomegaly .
This condition develops in many liver diseases, as well as in diseases of other organs and systems, chronic infections, parasite infection, tumor infiltration, etc. In liver diseases, this symptom is most often observed. In some cases, the liver can reach very large sizes and weigh more than 10 kg. However, when talking about what hepatomegaly is, it should be taken into account that an enlarged liver may indicate many pathological processes. Accordingly, the diagnosis of hepatomegaly means that the doctor must determine the underlying causes of this condition and provide adequate treatment. ICD diseases - K76 (other liver diseases). Why a person develops hepatomegaly, how this condition is treated, and what to do to prevent it will be discussed in this article.
Pathogenesis
Speaking about the pathogenesis of this condition, experts consider several possible options for its development. In this case, either a true enlargement of the liver may occur due to damage to the vascular bed, a neoplastic or infectious process, or other changes - intoxication, degenerative, traumatic, endocrine, autoimmune. Changes can also occur at the anatomical level.
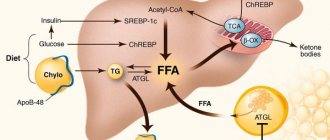
With the development of pathological processes, the liver increases in size and its structure becomes denser. In hepatosis, the process is caused by dystrophic changes in the liver cells, in acute hepatitis - by lymphomacrophage infiltration. If cirrhosis , nodes form in the liver and fibrosis occurs. If the veins of the liver are affected or heart failure , the enlargement of the organ is associated with blood stagnation. With tumors and abscesses focal changes occur.
Benign and malignant tumors
Most often, liver cancer is diagnosed in men over 40 years of age and less often in women over 55 years of age. The most common is secondary liver cancer as a result of metastases in the organ. The risk of developing primary liver cancer increases in people who smoke and drink alcohol, as well as those who work in hazardous industries, suffer from diabetes and obesity.
Hemangioma is a tumor of a plexus of blood vessels that tends to increase in size without developing into a malignant neoplasm. It occurs in women 5 times more often than in men. It is believed that the formation of a tumor occurs during the intrauterine period of development, when the baby’s mother is adversely affected.
The trigger for tumor growth is hormonal changes associated with pregnancy, menopause, and taking contraceptive medications. The tumor develops asymptomatically and makes itself felt only when it reaches 4 cm, when the patient experiences pain in the right side. However, in most cases, hemangioma does not manifest itself in any way and is discovered by chance during a medical examination.
Biochemical and general blood tests do not reveal any abnormalities; only when the tumor is very large, bilirubin increases. Hemangioma itself is not dangerous, but as the tumor grows, the hepatic ducts become blocked, making it difficult to remove bile.
There is also a high probability of blocking the main feeding artery, which provokes a liver infarction and disruption of the functioning of neighboring organs. Complications of hemangioma occur in 15% of patients; if the tumor ruptures, internal bleeding occurs in 85%, leading to the death of the patient.
Classification
When making a diagnosis, the condition is classified from an anatomical and morphological point of view. The following types of damage are distinguished:
- bile ducts;
- parenchyma;
- connective tissue;
- vascular network.
In addition, during the diagnostic process it is noted whether hepatomegaly is combined with jaundice , enlarged spleen or ascites .
Hepatosplenomegaly is an enlargement of the liver and spleen. This condition can occur in a number of diseases and conditions. These are liver diseases, infectious and parasitic diseases, metabolic diseases, etc. Since an enlarged liver and spleen is a typical manifestation of many diseases, it is very important to promptly identify this condition and conduct additional examinations.
Taking into account the degree of liver enlargement, the following types of hepatomegaly are distinguished:
- Moderate – the size and structure are slightly changed. Moderate hepatomegaly is the easiest to treat.
- Pronounced - the organ is enlarged by 10 cm relative to the norm.
- Diffuse – an increase of more than 10 cm.
Partial hepatomegaly is distinguished separately, which is characterized by an uneven increase - the process affects only a part or one lobe.
Depending on the reasons for the development of such a pathological process, the following forms are distinguished:
- Drug injury – develops as a side effect when using certain medications.
- Toxic damage - occurs as a result of the influence of toxins - household (polluted air), natural (consumption of poisonous mushrooms), industrial (work in hazardous enterprises).
- Alcoholism is a very common form. fatty liver , alcoholic hepatitis , fibrosis , and cirrhosis can develop .
- Viral infection - occurs due to infection with hepatitis B and C.
- Infectious lesions - characteristic of mononucleosis , hepatitis A.
- Immune damage is a consequence of malfunctions in the immune system, when antibodies “erroneously” act on the liver.
- Cancerous lesion is a consequence of oncological processes. It can develop with ineffective treatment of hepatitis and cirrhosis .
- Dystrophic damage is a consequence of changes in the volume of liver cells and the accumulation of fat in them. This type of injury is called hepatic coma and can be fatal.
What is the treatment?
— One of the most common causes of liver disease is viral hepatitis. In this case, antiviral therapy is prescribed.
If it is toxic, alcoholic hepatitis, then you need abstinence from alcohol, medication support and diet.
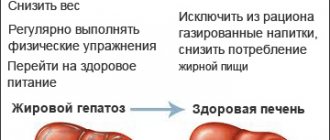
In case of fatty hepatosis associated with excess body weight, measures aimed at reducing excess body weight, diet, drug treatment, and surgical intervention if necessary are prescribed.
In the case of cirrhosis, that is, more severe liver damage, treatment is more difficult, but it is possible. First of all, therapy is aimed at eliminating the causes of cirrhosis.
The next step will be treatment with various medications that allow the liver to function more optimally. Well, the last resort treatment for cirrhosis is liver transplantation.
Causes of liver enlargement
Liver enlargement can be caused by various reasons. In adults and children, this organ may enlarge due to the influence of one or more factors.
Most often, the causes of enlargement of the left lobe of the liver or the right lobe are associated with the following diseases and conditions:
- Neoplastic processes - the development of tumors, mainly metastatic, as well as hemangiomas or adenomas .
- Disturbances in the vascular bed - the hepatic and portal veins can be affected due to the formation of a blood clot. Also, such disorders may be a consequence of pathology of the hepatic artery, Budd-Chiari syndrome .
- Degenerative lesions - non-alcoholic steatohepatitis , steatohepatosis .
- The influence of substances toxic to the liver - alcohol abuse, taking medications.
- Infectious viral processes - infectious mononucleosis , viral hepatitis , nonspecific cholangitis , etc.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Amyloidosis.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Congenital pathologies.
- Injuries.
In addition, experts identify some factors that increase the likelihood of developing hepatomegaly:
- Regular alcohol abuse.
- Long-term use of high doses of medications, vitamins, biological additives.
- Excess weight , unhealthy and irrational nutrition.
Symptoms of liver enlargement
Signs of hepatomegaly are associated primarily with true enlargement of the liver. It is diagnosed if the size of the organ along the right midclavicular line is more than 12 cm, or its left lobe is palpated in the epigastric region. In normal condition, the liver is soft and can be easily felt under the ribs.
It is also important to take into account the fact that there are no nerve endings in the liver, so even with the development of pathological processes, symptoms may not appear. Often, in the initial stages, adults periodically experience only minor discomfort or pain at the location of the organ. Only during an ultrasound examination can characteristic echo signs be determined.
Symptoms of liver enlargement
Consequently, signs of liver enlargement in adults, and sometimes in children, are often diagnosed already in the later stages, when the pathological process is already actively developing. Then a more pronounced clinical picture is observed. If the liver is enlarged by 2 cm or more, the following signs may be observed as the pathological process develops:
- Discomfortable sensations in the area of the right hypochondrium. They may worsen after eating and physical exertion.
- A feeling of heaviness after consuming a small amount of water or food.
- Periodic heartburn .
- Belching with an unpleasant odor.
- Disorders of the digestive system - constipation , diarrhea , nausea, periodic vomiting. Possible vomiting of bile.
- Discolored stool that may contain particles of undigested food.
- Yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes, yellowness of the sclera of the eyes. The skin may also take on a sallow tone.
- Itchy skin.
- Sudden mood swings, irritability.
- Drowsiness or insomnia .
- Tachycardia.
- Heavy sweating.
- High blood pressure .
- Pain in the chest area, feeling of tightness.
- When palpating the liver at a doctor's appointment, a person may feel pain.
Liver hemangioma on ultrasound
Hemangioma is a vascular formation inside the liver, consisting of a plexus of blood vessels. It is benign in nature, but tends to increase in size. The cavernous tumor reaches a diameter of up to 20 cm, and if left untreated it turns into an atypical hemangioma covered with keratinized tissue.
The tumor is easily diagnosed by ultrasound; it has clear tuberous contours and hyperechogenicity. Increased blood flow is confirmed using Doppler scanning. However, ultrasound only confirms the very fact of the presence of a tumor, but MRI provides more reliable information.
Tests and diagnostics
To determine the presence of hepatomegaly and the causes of such manifestations, the examination is carried out according to the following scheme:
- The doctor conducts a detailed survey of the patient about complaints and examines the medical history.
- Next, palpation is performed to determine the size, boundaries and density of the liver.
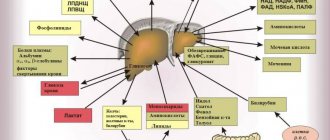
- It is important to determine the results of a general and biochemical blood test. Using the data obtained, it is possible to determine the presence of infectious and inflammatory processes and assess the level of liver enzymes . A general urine test is also performed.
- Markers of viral hepatitis are determined.
- An ultrasound of the liver is performed. This is a fairly informative method that allows you to determine the condition of the liver, portal vein, and hepatic artery.
- Informative studies are CT and MRI.
- If necessary, the doctor prescribes a laparoscopic examination.
- According to indications, a puncture is performed and material is taken for a biopsy .
In the normal state of the organ, its length is 14-20 cm, its cross-sectional size is 20-22.5 cm, in the sagittal plane - 9-12 cm. The length of the right lobe is 11-15 cm, the thickness of the left lobe is approximately 6 cm, and its height is less than 10 cm. Deviations can be no more than 1.5 cm.
Hepatomegaly is diagnosed if the size of the organ exceeds 12 cm or an increase in the left lobe of the liver is noted (in this case it is palpated in the epigastric region). During the diagnostic process, liver prolapse and the location of other tissues in the right upper quadrant (this could be tumors, an enlarged gallbladder) are also excluded.
Liver cirrhosis - symptoms, signs, treatment, causes, nutrition and stages
Table of contents
- Classification
- Causes
- The first signs and degrees of cirrhosis in adults
- Symptoms of liver cirrhosis
- Complications
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of liver cirrhosis
- Nutrition and diet for cirrhosis
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
Liver cirrhosis is a serious chronic disease.
According to statistics, in developed countries it is
one of the six leading causes of death
for people aged 35 to 60 years. It kills about 50,000 people every year in the United States. In Russia, where the population is half as large, mortality from cirrhosis is comparable to American rates.*
This disease is an extensive lesion of the liver, in which the tissues of the organ die and are gradually replaced by fibrous (connective) fibers. During the replacement process, the structure of the organ changes radically. Violation of the normal structure of the liver leads to the fact that it can no longer perform its functions. This is called liver failure.
Classification
Experts distinguish several types of liver cirrhosis.
For the reasons that led to the development of the disease, the following variants can be determined:
- Viral
- it is caused, for example, by hepatitis C and various biliary tract infections - Toxic
– caused by the consumption of alcohol, certain medications, food poisons and other substances that have a toxic effect on the body - Congenital
- represents the consequences of certain diseases that the patient’s parents suffered from, for example, hemochromatosis or tyrosinosis - Stagnant
- its origin is associated with circulatory failure - Metabolic and nutritional
– develops due to obesity, as well as in severe forms of diabetes mellitus
Separately, mention should be made of the group of liver cirrhosis of unknown etiology. We are talking about those cases when it is not possible to clearly determine the cause of the disease.
Causes
From the above it is clear that the occurrence and development of liver cirrhosis is due to many reasons. Most often, people get sick due to alcohol abuse.
According to various estimates, this reason accounts for from 40-50 to 70-80% of cases.*
The next most common factor influencing the occurrence and development of cirrhosis is exposure to viruses. Most cases are hepatitis C, but also hepatitis B.
In addition, cirrhosis is caused by:
- Biliary tract diseases
- Various intoxications - for example, chemical or medicinal
- Poor nutrition – first of all, chronic deficiency of vitamins and proteins in the diet
Cirrhosis caused by hereditary diseases is relatively rare. The same can be said about the disease of unknown etiology mentioned above, when it is not possible to determine the causes of its occurrence.
In about 50% of patients, liver problems are caused by a combination of different factors. For example, doctors often find cirrhosis caused by both binge drinking and hepatitis B.
The main peak incidence occurs in the age group over 40 years. Approximately 70-75% of those suffering from cirrhosis of the liver are men.
The first signs and degrees of cirrhosis in adults
First sign
the fact that a person’s liver is not all right – asthenovegetative syndrome. At the same time, the patient constantly feels tired, although there is no reason for this. He feels weak, becomes irritable and reacts sharply to completely innocent words or actions. He often has headaches.
Next, the so-called dyspeptic complex of syndromes. It includes:
- Nausea, which sometimes develops into vomiting
- Belching
- Alternating diarrhea and constipation
- Abdominal pain, aggravated by eating fried, pickled and fatty foods, as well as by drinking alcohol
- Reluctance to eat, up to complete lack of appetite for a long time
- Heaviness in the stomach
- Bloating
All of the above may indicate other diseases. Therefore, at this stage it is not always possible to clearly diagnose liver cirrhosis. Moreover, in about 20% of people who suffer from it, the true cause of the problem can only be determined after death.
There are three stages of the disease based on severity
- Initial
– symptoms either do not appear at all or are minimal - Clinical
– the symptoms are pronounced, and the doctor, when examining the patient, observes a typical picture of the disease - Terminal
– irreversible changes are detected, leading to death
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis
In approximately 60% of patients
The symptoms of liver cirrhosis are quite noticeable. The specific picture largely depends on what stage the disease is at. But there are signs that are especially common.
The initial stage in most cases is not accompanied by biochemical disorders. But the disease progresses, and at the second stage the so-called hemorrhagic syndrome.
Main signs of hemorrhagic syndrome
- This:
- Bleeding from the gums and nose
- In women - uterine bleeding
- Hematomas (bruises) on the body that appear for unknown reasons
- Stomach and intestinal bleeding
- Ecchymoses are pinpoint subcutaneous hemorrhages that look like a rash.
At the same time, the patient increasingly feels weak. Irritability gradually gives way to apathy and indifference, memory and attention impairments appear. Possible problems with sleep: the patient suffers from insomnia at night, and feels drowsy during the day. Over time, coordination of movements is impaired, the patient experiences problems with writing, and his speech becomes less and less intelligible.
When examining a patient
The doctor may visually detect the following symptoms:
- The liver and spleen have increased in size
- On the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity there are dilated veins and spider veins
- The skin, mucous membranes and whites of the eyes have turned yellow
Complications
Liver cirrhosis can lead to various complications.
This could be, for example, bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus or pneumonia, peritonitis and other complications caused by infections. The following negative consequences often occur:
- Hepatic coma
is a disorder of the functions of the central nervous system, which manifests itself in a sharp decrease in the size of the liver, increasing drowsiness, disorientation, slowing down of thought processes and, ultimately, in the fact that the patient falls into a stupor, and then into a comatose state - Thrombosis in the portal vein system
- blood clots (blood clots) prevent free blood flow in the liver, which leads to cell death - Hepatorenal syndrome
- leads to impaired renal function, especially common in those who suffer from acute liver failure or alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver - Liver cancer or hepatocellular carcinoma
is a rapidly developing malignant tumor that is often associated with hepatitis C and hepatitis D
Liver cirrhosis is a dangerous disease in itself. But if complications occur, the risk of death increases significantly. So, with hepatorenal syndrome, if you do not start treating it on time, death occurs 10-14 days after the development of this complication.
Diagnostics
Experts recommend
Contact your general practitioner as soon as you think you have signs of liver cirrhosis. The doctor will refer the patient for laboratory tests. When he has the test results in hand, he will send the patient to a gastroenterologist or directly to a doctor specializing in liver diseases - a hepatologist. In some cases, for example, if signs of hepatic encephalopathy are detected, you will need to visit a neurologist. Also, when making a diagnosis, the following data are taken into account:
- History
- Visual inspection
- Instrumental diagnostics
Basic laboratory tests
which are carried out in case of suspected liver cirrhosis are:
- Liver complex biochemical tests
- it shows how well the liver performs its functions and helps to determine whether its activity is impaired - Complete blood count
- it is done because signs of cirrhosis may be a decrease in the number of leukocytes and red blood cells, as well as a noticeable decrease in hemoglobin levels - Coagulogram
- it needs to be done to find out if there are problems with blood clotting - A fecal occult blood test
helps identify hidden bleeding in the stomach and/or intestines. - Serological markers of viral hepatitis
are used to clarify the factors that could lead to the development of the disease - A blood test for alpha-fetoprotein
should be performed if liver cancer is suspected. - The level of creatinine and electrolytes
must be established to determine renal failure
Treatment of liver cirrhosis
If the patient is diagnosed with liver cirrhosis
, treatment can be carried out using different methods. The choice of a specific tactic is largely determined by the stage at which the disease is located and the reasons for which it arose. Specialists also take into account the individual characteristics of the patient. However, it is impossible to cure already formed cirrhosis. Modern medicine can only cope with the reasons due to which it arose.
Radical method of treating cirrhosis
- transplantation of the affected organ. They resort to it if there is an immediate threat to the patient’s life. In all other cases, medicinal methods are used. As a rule, the patient should adhere to a strict diet, and in case of alcoholic cirrhosis, it is necessary to eliminate the intake of alcohol in the body. The choice of medications depends on what type of cirrhosis doctors have to deal with. For example:
- For viral hepatitis, antiviral agents are used, in particular pegylated interferons
- For biliary cirrhosis associated with insufficiency of bile acids in the intestines, medications are used to narrow the bile ducts
- Autoimmune hepatitis can be treated with drugs that suppress the immune system (immunosuppressants)
Nutrition and diet for cirrhosis
Diet for the treatment of cirrhosis
is extremely important. Proper nutrition is both an excellent option for preventing the disease and a way to eliminate the causes that led to its occurrence. If there are no complications, the patient is prescribed a complete high-calorie diet. It necessarily contains proteins, fats and carbohydrates. However, it is necessary to exclude from the diet everything that irritates the digestive organs. First of all, this is:
- Alcohol
- Chemical additives
- Preservatives
If you have cirrhosis, you should refuse
from consuming foods that are:
- Spicy
- Sour
- Spicy
- Too salty
The diet must be prescribed by a specialist
which takes into account:
- Patient's eating habits
- Individual tolerance of products
- He already has diseases of the digestive system
The diet is modified if there are any complications of cirrhosis or other diseases.
To normalize metabolic processes in liver cells, the doctor may prescribe a vitamin complex. As for any medications, they must be used carefully. You should take only those pills that are prescribed by specialists and for which there are clear and unambiguous indications.
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
Treatment of liver cirrhosis
- an important area of activity of the MEDSI clinic. We use effective modern techniques to eliminate the causes that influenced the occurrence of this disease and make the patient’s daily life more comfortable. Our clinic employs a team of international doctors. She takes a comprehensive approach to solving each specific problem. Any patient is guaranteed an individual approach: the doctor selects an examination plan, which is based on genetic factors, risk factors, concomitant pathologies, and medications taken.
Communication with doctors
starts with diagnosis. Experienced specialists who have the necessary laboratory equipment at their disposal will perform tests and study their results. Fast and accurate diagnosis is ensured thanks to the availability of the latest generation diagnostic equipment: magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, video colonoscope, etc.
Our clinic specialists
They use cutting-edge techniques – fast track surgery and minimally invasive treatment. We have operating rooms equipped with the necessary modern equipment. Also we have:
- Reanimation and Intensive Care Unit
- Comfortable hospital with 3 meals a day, round-the-clock medical monitoring, single and double luxury rooms, toilets and showers
Don't forget: cirrhosis
is an extremely dangerous disease, and the sooner we begin treatment, the greater the likelihood that the threat to the body can be significantly reduced. MEDSI clinic staff are ready to answer your questions and provide the necessary advice.
You can make an appointment with a specialist 24 hours a day. Call us at +7 (495) 7-800-500.
* Sadovnikova I.I. Cirrhosis of the liver. Questions of etiology, pathogenesis, clinical picture, diagnosis, treatment / Breast Cancer Appendix “Diseases of the Digestive Organs” No. 2 dated November 4, 2003
Treatment with folk remedies
For hepatomegaly, any folk remedies should be used very carefully and in no case should they replace the main treatment. Before using any traditional method, you should consult your doctor about the advisability of its use. In addition, traditional methods also have certain contraindications.
- Milk thistle tea . This medicinal plant protects liver cells and promotes the regeneration of new ones. Also acts as an anti-inflammatory agent. The main active component of the plant is silymarin, which is part of a number of hepatoprotective drugs. To prepare milk thistle tea, you need 1 tsp. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over the seeds of the plant. After half an hour, strain and drink warm in two doses.
- Infusion of immortelle . The inflorescences of this plant contain a lot of flavonoids that have hepatoprotective activity. The use of products with immortelle helps restore the detoxification function of the liver. To prepare an infusion of immortelle, add 10 g of flowers to 250 ml of water and heat the container in a water bath for half an hour. After 10 minutes, strain and squeeze. Add water so that the total amount of product is 250 ml. Drink in 4 doses throughout the day.
- Rose hip decoction . Rose hips also contain many flavonoids. Rosehip helps eliminate spasms of the bile ducts, has a beneficial effect on the digestion process, and produces an anti-inflammatory effect. To prepare a decoction, add 200 g of berries to 1 liter of water, bring to a boil and cook for 15 minutes. Strain, drink 150 ml 4 times a day.
- Collection of herbs . This collection may include oregano, nettle, chamomile, calendula, centaury. Herbs should be mixed in equal proportions and an infusion should be prepared by pouring 2 tsp. mixture 250 ml water.
- Beetroot, pumpkin . These vegetables should be included in the menu more often, preparing a variety of dishes from them. Raw pumpkin is beneficial, as is freshly squeezed beet juice.
Drugs used for recovery
Liver recovery after chemotherapy sometimes baffles specialists and is the subject of debate. When choosing a hepatoprotector, you must adhere to the principles of evidence-based medicine. All medications used are divided into five types:
- Natural or synthetic products with milk thistle flavonoids. The active ingredient is silymarin, which includes the component silibinin. Stabilizes cell membranes and prevents their death, stimulates the production and outflow of bile. In pharmacies you can buy Karsil, which normalizes metabolic processes, Gepabene, supplemented with antispasmodic effects, Legalon, which prevents liver fibrosis and enhances its antitoxic function.
- Medicines based on essential phospholipids are endowed with protective mechanisms that protect the liver from the influence of dangerous toxic factors. Phospholipids, being embedded in cell walls, activate their regeneration. This group includes Essentiale, Phosphogliv, Essliver.
- Medicines from animal liver parenchyma cells that improve the condition of the organ due to their similarity to human hepatocytes. Among them is Hepatosan.
- Herbal preparations, which include extracts and seeds of wormwood, yarrow, nightshade, etc. They lower cholesterol, stabilize the synthesis of bile and enzymes. The most famous of them are Liv 52, Tykveol and Khofitol.
- We recommend taking VIALIFE capsules or VIALIFE solution, because they contain the highest possible concentration of chlorophyll, which:
- strengthens the immune system;
- enhances cell regeneration;
- saturates tissues with oxygen;
- has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, detoxifying effects.
- Physiological metabolites are most in demand. Their appointment makes it possible to simultaneously carry out full-fledged chemotherapy without changing the regimen or reducing doses. For example: Heptral with antidepressant action. It regulates absorption and natural metabolism in liver cells. 95% of the drug, involved in metabolism, reduces inflammation, neutralizes damaging sources, suppresses the formation of connective tissue, and stimulates regeneration. It is prescribed parenterally (intravenously), orally (by mouth), or both methods are combined to enhance and accelerate the effect. Intended for critically ill patients with multiple organ failure.
Prevention
The essence of prevention is to prevent diseases that lead to liver enlargement. To do this, it is important to follow the following recommendations:
- Eat right and do not abuse unhealthy foods, control your intake of carbohydrates and fats.
- Get rid of bad habits.
- Avoid uncontrolled use of medications, carrying out drug treatment only as prescribed by a doctor.
- Follow all hygiene rules to avoid parasitic or viral infection.
- Those who have suffered from liver disease should undergo regular preventive examinations with a doctor.
- Practice regular physical activity, but it should not be excessive.
What cases from practice related to liver disease do you remember?
— Severe liver damage occurs with viral hepatitis, when a person for a long time did not know that he had a virus, for example, hepatitis C. This hepatitis can be asymptomatic for many years, ultimately leading to cirrhosis of the liver.
That is, a person lived a normal life and suddenly he began to develop symptoms of cirrhosis. Upon further examination, it turned out that the patient’s liver functions were impaired, the disease was already at a serious stage, and the person was on his way to the operating table for a transplant. We have to fight such cirrhosis, and we are talking about survival, not about cure.
In children
Hepatomegaly in a child may be associated with neonatal jaundice. In a small child, it develops due to birth injuries, as well as dysfunction of the mother’s endocrine system. As a rule, liver enlargement in newborns does not require treatment and goes away within a month.
Minor hepatomegaly, which is determined by palpation or ultrasound in a child under 7 years of age, is also considered a physiological phenomenon. It is normal if the liver protrudes beyond the edges of the ribs by 1-2 cm. The condition, as a rule, normalizes as the child grows. However, if an increase in the right lobe of the liver or its left lobe is detected, it is better to undergo additional studies to exclude the development of diseases.
An enlargement of the left or right lobe of the liver in children may be associated with the following diseases and conditions:
- inflammatory processes;
- toxic damage;
- congenital TORCH infections;
- dysfunction of the biliary tract;
- metabolic disorders;
- tumors, metastases.
A particular cause for concern is the situation when hepatomegaly in children is combined with other alarming symptoms: fever, vomiting, rashes, weight loss, poor appetite, yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes. In this case, you should immediately consult your doctor.
Diet
Diet for an enlarged liver (hepatomegaly)
- Efficacy: no data
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 1400-1500 rubles. in Week
Diet is one of the important components of complex treatment of this condition. If the increase is insignificant, sometimes only nutritional correction can normalize the condition of the organ.
First of all, it is important to limit the amount of salt to 6-7 g per day and the amount of sugar to 50 g per day. You should drink up to 2 liters of water daily. You need to eat fractionally - up to 6 times a day in small portions.
For hepatomegaly, it is recommended to include the following foods and dishes in the diet:
- Low-fat dairy products.
- Vegetables – fresh, as well as stewed, baked and boiled.
- Lean meat, fish.
- Vegetable soups.
- Vegetable oils.
- Fruits.
- Marmalade, dried fruits, honey, biscuits.
- Cereals.
- Egg white.
The following foods should be excluded from your diet:
- Spicy, fried, salty dishes.
- Smoked meats and canned goods.
- Fatty meat and fish.
- Mushrooms.
- Egg yolk.
- Legumes.
- Sorrel, spinach, radish, onion.
- Fatty dairy products.
- Muffins, baked goods, cocoa, nuts.
- Alcohol.
- Soda, coffee, sour juices.
General lifestyle recommendations
Liver recovery after chemotherapy includes a whole range of measures. In addition to medications, care from medical personnel and relatives, regimen and diet play an important role in this. The following will help tidy up your liver:
- lean meats - turkey, chicken, veal, rabbit;
- fermented milk products - kefir, cottage cheese, yogurt without fillers and additives;
- seasonal vegetables and fruits;
- vegetable oils;
- boiled and stewed dishes;
- for sweets – honey and dried fruits;
- cereal products.
You should reduce your consumption of legumes. Completely exclude the intake of spicy, smoked and fried foods. Remove sausages, marinades, and pickles from your diet. Alcoholic and carbonated drinks are prohibited.
Dietary supplements help replenish vitamins and microelements. Some of them contain bacteria necessary to recreate the intestinal microflora. Decoctions and infusions of corn silk, oats, and milk thistle are useful. Our experts also recommend taking VIALIFE chlorophyll capsules, which will help minimize the side effects of toxic chemotherapy drugs in the shortest possible time, thanks to the properties of the maximum possible dosage of chlorophyll in the composition. Regular walking, a daily routine and good sleep are necessary, as the liver is subject to circadian rhythms.