Forecast
Possible consequences of the disease
Hemangiomas can cause necrosis (death) of tissue, so the lesion becomes an entry point for infection. The addition of a purulent process can cause sepsis. With hemangioma of bones, their destruction is possible. In addition, the process can contribute to blood clotting disorders and the formation of blood clots. Malignancy is possible - degeneration of hemangioma into cancer.
With timely consultation with a doctor, the neoplasm is successfully treated in 100% of cases. Source: What a pediatrician needs to know about infant hemangiomas. Zakharova I.N., Kotlukova N.P., Roginsky V.V., Sokolov Yu.Yu., Zaitseva O.V., Maykova I.D., Idrisova G.R., Pshenichnikov I.I.: Medical Council , 2021.
Hardware methods
CO2 laser was previously used to remove hemangiomas , which has a good hemostatic effect. The disadvantage of the CO2 laser is long-term rehabilitation due to damage to the integrity of the skin, as well as the formation of a scar at the site of the removed hemangioma. Pulsed dye laser ( PDL) is effective only for superficial tumors. Its effect develops quite slowly, which does not allow the use of the PDL laser for complications. Currently, intensive pulsed light - IPL and long-pulse Nd:YAG laser 1064 nm, as well as their combination, are used to treat hemangiomas for aesthetic purposes. These techniques are non-ablative and are based on selective heating of pathological vessels due to the absorption of light energy by hemoglobin.
Questions from our users:
- hemangiomas on the skin of the abdomen causes
- hemangiomas on the skin of the neck
- hemangiomas on the skin during pregnancy
- hemangioma on the skin treatment
Types of hemangiomas
There are 2 types of hemangiomas - congenital - formed during intrauterine development - and acquired; acquired in early childhood are often called infantile. By structure, single and multiple hemangiomas (hemangiomatosis) are distinguished; by structure - capillary, arterial and venous.
By education they are local and segmental. Local hemangiomas grow from one point, are distinguished by smooth edges and relatively small sizes. Segmental - large, with a “ragged” edge, often develop as part of combined pathologies of the chest, aorta, pelvis and sacrum, heart defects, etc.
Hemangiomas are classified according to their location:
- simple – formed on the surface of the skin;
- cavernous – grows under the skin;
- combined – the process involves the superficial and deep layers of the dermis;
- mixed - not only dermal, but also nervous and muscle tissues are involved in the process.
Diagnosis and treatment
If a baby is diagnosed with a vascular tumor, he must be examined by a pediatrician and a surgeon. Additionally, consultation with an ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, or gynecologist (depending on the location of the formation) may be required. To assess the depth of skin lesions, an ultrasound examination is performed. The speed of blood flow in the tumor must be measured. Additionally, radiography may be performed in the area of localization of the formation.
Hemangiomas located in the neck and head must be treated immediately after detection. Education in this area can grow rapidly. The risk of dangerous complications increases. If the hemangioma is located on the body and is not a major cosmetic defect, doctors choose a wait-and-see approach.
Small tumors are easily removed by electrocoagulation. If the vascular pathology is located deep and it is impossible to eliminate it with minimal trauma, classical surgical excision is used.
If the pathological formation is located in the orbital area or occupies a large area, radiation therapy (using X-rays) is used. Additionally, hormones may be prescribed.
In most cases, the prognosis of therapy is favorable. In 5% of babies, vascular formation develops rapidly in the first year of life, then gradually disappears without any treatment. If the tumor is located on the face, it can be easily removed using radical techniques.
Why do hemangiomas appear?
The exact causes of hemangiomas have not yet been identified; It is generally accepted that their appearance can provoke disruption of intrauterine development of the fetus due to a viral illness of the mother or oxygen starvation. Additional risk factors for the formation of congenital hemangioma:
- multiple and/or late pregnancy;
- increased amount of estrogen in the mother;
- her sedentary lifestyle;
- unbalanced diet;
- alcohol or nicotine intoxication of the fetus;
- his low birth weight.
In adults, the cause of neoplasm can be a hereditary predisposition, diseases of the cardiovascular system, excessive ultraviolet radiation, and increased levels of the female hormones estrogen.
Table of contents
- Etiology and pathogenesis
- Clinical manifestations
- Treatment methods
- Medicinal methods
- Surgical methods
- Hardware methods
Hemangioma (capillary hemangioma, capillary hemangioma) is a benign tumor that develops from hyperplastic vascular endothelium. It is often absent at birth, but appears in childhood and is characterized by progressive growth.
In our company you can purchase the following equipment for removing hemangiomas:
- M22 (Lumenis)
- AcuPulse (Lumenis)
- Fraxel (Solta Medical)
- UltraPulse (Lumenis)
A feature of hemangiomas is the possibility of spontaneous involution, therefore the treatment tactics for these neoplasms are selected individually for each patient, based on the current state of the tumor and its dynamics. Spontaneous regression distinguishes hemangiomas from other vascular malformations, such as port-wine stains.
According to statistics, capillary hemangiomas occur in 1–2% of newborns, with about 50% of neoplasms forming on the head (often in the eye area) and neck. 30% of patients say that their parents or doctors recorded signs of hemangioma immediately after birth, but the majority note the onset of manifestation of this neoplasm at the age of 6 months. The ratio of men to women in the incidence of hemangioma is 1:3.
Signs of hemangioma and pathogenesis
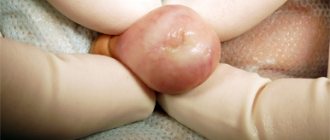
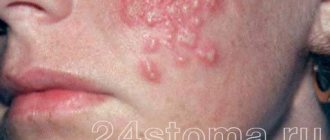
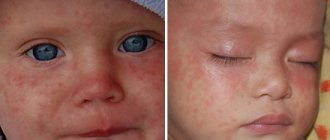
Hemangioma is a red spot, in the center of which there is a point, and from it comes a network of small vessels. Usually the neoplasm is smooth and can protrude 1-2 cm above the skin. When pressed, it turns pale, but quickly returns to its normal appearance. A characteristic symptom is temperature unevenness: upon palpation, the hemangioma is noticeably warmer than the surrounding areas of the body. It may not manifest itself clinically and may be discovered by chance during examination.
The disease occurs in phases: growth, stabilization, and optionally spontaneous regression. Complications are possible during the growth and stabilization phases of hemangioma. If a neoplasm grows near a functional organ, its function may deteriorate - for example, in the periorbital zone it can contribute to decreased vision, and on the laryngeal mucosa - obstruction of breathing.
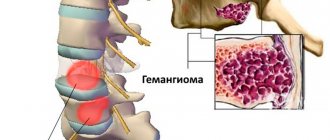
If the hemangioma is localized near the nerve ending, as it grows, weakness and numbness of the limbs, disruption of the bladder and gastrointestinal tract are possible. Large spinal hemangiomas can cause pain and increase the risk of compression fractures. New growths are easily injured, so they can cause bleeding.
Symptoms
Unlike Movsesyan's hemangioma, a normal vascular formation in most cases can be detected immediately after birth. In the first years of life, intensive tumor growth occurs. Hemangioma can increase several times in size. Most often, such neoplasms are localized in the area of the scalp, face, and genitals. Less commonly, red spots can be found on the stomach, legs and arms. The external tumor resembles a lumpy burgundy-colored lump. The size of the spot can range from a few mm to 10-15 cm.
When hemangioma is detected in children, temperature asymmetry is most often diagnosed. Education can be hot.
A simple formation, unlike Movsesyan's hemangioma, can undergo spontaneous regression without special therapy. In rare cases, the red spot disappears on its own.
How are hemangiomas treated?
The main method of treatment is surgical. In addition to cosmetic reasons, there are medical indications for this:
- rapid growth and threat of malignancy of the tumor;
- disruption of the normal functioning of organs - for example, if there is a tumor on the eyelid or tongue;
- impaired blood circulation – if the tumor is on a large vessel;
- infection and bleeding – for example, when on the genitals.
The priority is gentle, minimally invasive methods for removing hemangioma or vascular surgery methods to reduce blood flow in it. The excised tissue is sent for histological analysis.
If the neoplasm is small, it is possible to use electrocoagulation, radio wave or laser surgery, or cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen. For some forms of hemangiomas, sclerotherapy is effective - “gluing” damaged capillaries by injecting special solutions. Source: Hemangiomas and vascular malformations. Modern theories and therapeutic tactics. Goncharova Y.A.: Child’s health, 2013.
For slow-growing tumors with a low risk of malignancy, conservative drug therapy with drugs from the group of beta-adrenergic receptor blockers is possible. Source: Wong A., Hardy K., Kitajewsky A. Propranolol causes functional changes in hemangioma stem cells and hemangioma endothelial cells // Abstract book. ISSVA the 19th International Workshop on Vascular Anomalies. — 2012. – p. 245.. In some cases (if the tumor does not grow, does not bother, or there is a tendency towards its reverse development), they resort to wait-and-see tactics.
To ensure the effectiveness of treatment, after its completion, a control study is prescribed - ultrasound, tomography or dermatoscopy. To consult with a specialized specialist in St. Petersburg, fill out the online form.
Sources:
- What a pediatrician needs to know about infantile hemangiomas. Zakharova I.N., Kotlukova N.P., Roginsky V.V., Sokolov Yu.Yu., Zaitseva O.V., Maykova I.D., Idrisova G.R., Pshenichnikov I.I.: Medical Council , 2016
- Infantile hemangioma: classification, clinical picture and methods of correction. Sheptiy O.V., Kruglova L.S.: Russian Journal of Skin and Venereal Diseases, 2021.
- Hemangiomas and vascular malformations. Modern theories and therapeutic tactics. Goncharova Y.A.: Child’s health, 2013.
- Sires V. Systemic corticosteroid use in orbital lymphangioma /V. Sires, C. Goins, R. Anderson // Ophthal. Plast.Reconstr.Surg. — 2001. Mar. - Vol. 17(2). — P. 85 — 90.
- Wong A., Hardy K., Kitajewsky A. Propranolol causes functional changes in hemangioma stem cells and hemangioma endothelial cells // Abstract book. ISSVA the 19th International Workshop on Vascular Anomalies. — 2012. – p. 245.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
How can the disease be diagnosed?
The capillary form in the vast majority of cases is diagnosed based on history and examination. The pediatric surgeon finds out when the tumor was first noticed, whether it has changed in shape, color and size, and whether there are signs of regression.
If this data is not enough and there are doubts about making a diagnosis, the specialist prescribes additional studies:
- ultrasonography;
- Dopplerography;
- computed tomography with contrast;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- biopsy of the tumor site
- And so on.
Causes and course of the disease
The first signs of the development of benign middle ear tumors largely depend on the location of the tumor itself.
Chemodectoma of the middle ear arises from glomus bodies, which are found in the mucous membrane of the tympanic cavity and are located along the blood vessels and nerve fibers. Glomus accumulations are localized, as a rule, in the adventitia (outer shell) of the superior bulb of the internal jugular vein and thicker than the pyramid of the temporal bone.
Causes of hemangioma formation in a child
The main reason is congenital anomalies of vascular development.
Tumors are formed from endothelial cells (vessels grow from them) with involutional (that is, reverse) development. The cells of the vascular wall grow abnormally. The neoplasm usually grows for 6-12 months, and then involutions - “resolves.” According to scientists, up to 50% of hemangiomas go away on their own by the age of 5, up to 70% by the age of 7, and almost all by the age of 12.
This type of tumor always remains benign and is not prone to degeneration into malignant. Accordingly, they do not grow into nearby tissues and organs, but when they grow to a large size, they compress them. This can cause enormous harm to the body and even threaten life:
- cause severe bleeding;
- cause tissue atrophy;
- lead to dysfunction of internal organs.
For this reason, doctors strongly recommend that parents not wait until the tumor goes away on its own and show the baby to a specialist.
The disease is diagnosed in 10% of infants, 4 times more often in girls. The risk of formation is higher in premature babies with low body weight. Hemangioma in adults is a rare phenomenon. Basically, these are neoplasms in internal organs that are accidentally detected during an ultrasound and do not cause any discomfort to the patient.
Hemangioma is a benign tumor. Photo: gsermek/Depositphotos