16 June 2020
45538
2
3.9 out of 5
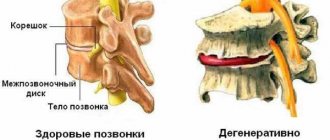
Hemangiomas are vascular tumors that can occur in the skin and any internal organs that contain a network of blood vessels. Thus, such formations cannot form only in the articular surfaces and optically transparent environments of the eyes. The spine is one of the places where it can form. In such cases, a hemangioma of the spine, or more correctly, a vertebra, is diagnosed.
A tumor of this kind in 100% of cases is a benign neoplasm and never becomes malignant, i.e., does not turn into malignant. Vertebral hemangioma is localized in its thickness, which is due to the peculiarities of the blood supply to the structural elements of the spine, and is, so to speak, an advantageous location for a tumor of this type. Growing inside the spongy tissue of the vertebra, the vascular formation is reliably protected from external influences by the bone, which reduces the risk of injury to a minimum. At the same time, hemangiomas formed in the parenchyma of internal organs are easily damaged and can become a source of severe bleeding.
In recent years, the frequency of diagnosing vertebral hemangiomas has increased significantly, but not due to an increase in the number of cases of their formation, but due to the introduction of modern diagnostic methods: CT and MRI.
How dangerous is the disease?
A small hemangioma does not pose any danger. Such a benign tumor rarely manifests itself. About 10% of patients do not even suspect its presence. If the tumor is less than 1 centimeter, then it is only observed; if it begins to grow, it is removed.
Developing between the vertebrae, the tumor can invade several neighboring vertebrae, usually 2-3 vertebrae. Large tumors cause pain and can also cause vertebral collapse. In this case, compression of the nerve endings of the spine occurs, which leads to both pain and numbness in this area of the back. In addition, a vertebral hemangioma of significant size can cause its fracture.
A large tumor in the lumbar spine can cause:
- urinary disturbance;
- problems with bowel movements;
- numbness of limbs and so on.
Forecast
As you may have guessed, in the vast majority of cases, a stable, small hemangioma does not affect either the quality of life or its duration. Before the widespread use of tomography, tens and even hundreds of generations lived perfectly well with hemangiomas, with calcification of the pineal gland in the brain, and with other random findings that nowadays cause stress and panic. It is not always necessary to take any emergency measures when you discover unfamiliar formations in your body.
Perhaps, if a “silent” vertebral hemangioma is detected, we can only advise you to keep your weight close to ideal, avoid heavy lifting, weightlifting, and contact, hard types of martial arts. Women can be advised to regularly perform densitometry after menopause, since in the presence of osteoporosis, a pathological fracture can occur long before the hemangioma reaches the theoretical strength limit in the region of 50-60% of the vertebral volume.
And if a compression fracture already occurs, then you will have to undergo extensive surgery. Yes, some vertebral compression fractures do not require surgical treatment; they heal on their own. But keep in mind that in this case there will be a vascular tumor between the bone fragments, and the hemangioma will be a factor of “non-union”, it will create tissue interposition between the fragments, and, lying freely, no longer covered by the vertebra, will create an additional risk of bleeding.
Therefore, the basis of the correct approach to the treatment of hemangiomas will be dynamic observation, taking into account additional risk factors.
Causes of hemangioma
Spinal hemangioma occurs when improper (chaotic) division of vascular tissue cells occurs. What this depends on is still a matter of debate in scientific circles. However, it has been noted that the main factor in most cases is heredity. Studies have shown that such a tumor can also occur with increased levels of estrogen, so it is most often found in women. The disease also occurs when there is heavy load on the spine, for example, during pregnancy or when lifting heavy objects.
Diagnostics
To detect spinal hemangioma, in addition to examination and clinical tests, the following is prescribed:
- fluoroscopy to see changes in bone tissue. But due to the fact that a tumor can only be detected when it is large enough, this study is not very informative;
- magnetic resonance imaging to determine the type, location and size of the tumor;
- CT scan to look for small growths.
Most often, the disease affects the thoracic region - almost 80% of cases. In second place is the lumbar region, and the sacral and cervical regions are least affected. For an initial consultation, you can contact a therapist.
Types of tumors
There are two types of hemangiomas:
- non-aggressive - the tumor behaves calmly, it is discovered by chance during a medical examination or after a computed tomography);
- aggressive - the tumor grows quickly and causes severe pain during movement).
Based on their structure, hemangiomas are divided into the following types:
- capillary (vascular);
- cavernous;
- mixed (vascular-cavernous).
In most cases, spinal hemangioma is a non-aggressive tumor that does not pose any threat. But in exceptional cases, the disease destroys bone tissue.
By location
Depending on the location of occurrence, hemangiomas of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine are distinguished.
Cervical hemangioma
A tumor of this localization causes headaches and frequent dizziness. Vision may be impaired, and insomnia is a common symptom. This is affected by compression of the artery and poor circulation.
Hemangioma of the thoracic region
The initial stages of the disease are asymptomatic. Typically, such a tumor grows very slowly. When a hemangioma in the thoracic spine grows to a size of more than 1 cm, it begins to compress the vertebrae. At first, the pain occurs periodically, but over time it becomes constant. This all happens due to compression of the nerve endings. Symptoms and treatment of hemangioma of the thoracic spine differ from the symptoms, as well as methods of conservative treatment of a tumor located in the cervical spine.
Hemangioma of the thoracic spine causes:
- numbness of hands and feet;
- gastrointestinal problems;
- constant weakness;
- pain in the spine;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- infertility in women.
In this regard, cardiological drugs are used along with conventional conservative treatment methods. It is also recommended to consult a gastroenterologist and gynecologist in case of illness.
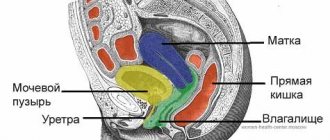
Lumbar hemangioma
Appearing in the lumbar spine, hemangioma disrupts the functioning of the pelvic organs. Symptoms usually become noticeable when the tumor is already quite large. Thus, a tumor measuring 1 cm or more can cause:
- numbness of the limbs;
- lower back pain;
- the appearance of problems with urination;
- fecal incontinence.
In count
In one patient, one to several formations may occur simultaneously. After making an appointment with a doctor, the patient will be told the exact number of formations.
Single
Single hemangiomas are most common. They can be localized in any part of the spine.
Multiple
The rarest and most dangerous type is multiple hemangiomas. They can be located in different parts of the spine at once, which aggravates the patient’s condition.
By content
Based on their contents, spinal hemangiomas are divided into the following types:
- vascular;
- cavernous;
- mixed.
Vascular
Vascular neoplasms consist of several fused thin-walled vessels, between which fibrous or adipose tissue accumulates.
Cavernous
They consist of several thin-walled vessels that communicate with each other.
Vascular-cavernous
A mixed (vascular-cavernous) benign tumor consists of blood vessels, as well as vascular cavities.
Percutaneous puncture vertebroplasty
Puncture vertebroplasty is a modern and very convenient method of removal. The goal is to eliminate the cavity inside the vertebra, filling it with special cement, which, when slightly heated, expands, completely destroys the tangle of blood vessels, and completely fills the entire space inside the vertebra.
Schematic representation of the procedure.
You don't need to make any cuts for this. It is enough to accurately determine the projection of the desired vertebra on the skin. Under X-ray control, to avoid mistakes, a needle is inserted into the vertebra under local anesthesia. After the needle falls into the internal cavity filled with a vascular tumor, a special biopolymer is fed inside, which is heated to a relatively high temperature, about 60 C°. This temperature is quite enough to completely destroy tumor cells, and the ability of the polymer to slightly expand during hardening makes it possible to guarantee that all voids are filled. Thus, the vertebra again becomes a single monolith.
In this case, a cementing substance consisting of:
- cement itself;
- radiopaque material (so that you can see the filling process directly under X-ray control “in real time”);
- antibacterial additive is approximately similar in density and mechanical characteristics to bone tissue, so that the vertebra continues to perform its function as before.
Cement.
Roughly speaking, this surgical intervention resembles filling a diseased tooth. No cuts, no blood, no long hospital stay. The next day, the patient can leave the hospital on his own, and local anesthesia allows percutaneous puncture vertebroplasty to be performed in patients with concomitant pathologies, including the elderly.
Symptoms and signs
The symptoms of the disease depend on the size of the tumor and where it is located:
- a tumor less than 1 cm may not bother you, but sometimes causes periodic back pain;
- a tumor that has grown to a size of more than 1 cm causes severe, constant back pain.
Spinal hemangioma is a benign formation that can destroy the structure of the vertebrae. As the tumor body grows, the vertebrae can be compressed and cause disruption of the intestines and bladder, causing numbness in the arms and legs.
A little history
It must be said that vertebroplasty is an extremely successful and beautiful way to eliminate a tumor and create a single bone block. Previously, before the introduction of this technique, sclerotherapy was used. In this case, a sclerosing substance, such as ethyl alcohol, was injected into the hemangioma. But the cavity remained: although the hemangioma itself died, the alcohol reduced the strength of the bone tissue, and as a result, a pathological fracture quite often occurred. In some cases, the tumor did not die completely, and a relapse occurred.
In addition to sclerotherapy, tumor embolization was also used, that is, an attempt to eliminate blood flow through the vessels. It was technically more difficult, and the matter could not be done with just a puncture. It required the skill of a vascular surgeon, which is not at all needed in modern vertebroplasty. But since the tumor itself remained, the death of the embolized vessels did not play a big role. The vessels actually died, but new vascular bundles were constantly being formed, because the pressure in the arterial section was maintained.
Treatment of hemangioma
Only a doctor determines the diagnosis, stage of the disease and prescribes treatment for spinal hemangioma. So, the treatment process can be:
- medicinal (conservative);
- operational;
- special.
Treatment is prescribed after all necessary measures and examinations. If the tumor is small and non-aggressive, then it is observed and conservative treatment is applied. If the tumor begins to bother you and its size increases, then it is operated on or special treatment methods are used (X-ray irradiation, embolization, etc.)
Drug treatment
With drug treatment, the tumor will not disappear. This treatment is aimed at reducing pain and unpleasant symptoms.
The following drugs are usually used:
- painkillers, analgesics;
- anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs;
- vitamin complexes;
- hormonal drugs;
- various muscle relaxants.
Surgical intervention
If a hemangioma occurs on the spine, is surgery necessary? The main thing in treating such a disease is to do no harm. Surgical intervention is prescribed only when conservative treatment does not improve the condition, and the tumor grows rapidly, hurts unbearably and poses a threat to the entire body.
Massage and physiotherapy
In case of spinal hemangioma, any physiotherapy and massage are strictly prohibited. Various rubbing with warming ointments, compresses, etc. are prohibited, as these methods can provoke a sharp growth of the tumor.
Traditional methods
It is believed that treatment with traditional methods for spinal hemangioma is absolutely ineffective and useless. Traditional medicine will not relieve pain or reduce swelling. In addition, such interference can only cause harm.
Contraindications for surgery
Taking advantage of the illiteracy of the population, many private clinics warm their hands well by doing the opposite - imposing unjustified surgical treatment. So, if they found a vertebral hemangioma on an MRI in a gullible, suggestible person, then they can make good money on this. Arguments such as “potential danger”, “risk of rapid, uncontrolled growth”, and “vertebral fracture in just a few weeks, or, in extreme cases, months” are used. Usually, urgent vertebroplasty is suggested, and the conversation ends with the words: “you are very lucky that you came to us, and we did the MRI on time.” Particularly arrogant “specialists” may even hint at the possibility of malignancy and “turning into cancer.” As we remember, this is impossible: hemangiomas of any location do not turn into “cancer”.
This is a very winning situation. Vertebroplasty is an operation with minimal risk for the patient, quite simple, but it can cost quite a lot of money. So, for the injection of bone cement into one vertebra you can easily charge 20 thousand rubles, and even more. Patients should know that this is not necessary at all, and they should not follow the lead of such doctors.
The contraindication to this small surgical intervention will be precisely the small size of the hemangioma and its stability. Therefore, if you are assured of the need for urgent vertebroplasty, then in any case, it is necessary to do a repeat tomography at least 6 months after the discovery of the tumor to make sure that the tumor is really growing and the potential danger.
Preventive measures
Having learned what spinal hemangioma is, you can now prevent the development of complications. Preventive measures will prevent the disease from starting and not worsening the condition. It is necessary to see a doctor annually and monitor tumor growth. Benign neoplasms react very poorly to sunlight. With this disease, it is recommended to avoid solariums, long stays on the beach, avoid engaging in traumatic sports, and stop using immunostimulants.