The gastrocnemius muscle provides movement of the foot in the sagittal plane and stabilizes the body during movement. Sharp pain in the calf muscle can occur for many reasons. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital, when examining a patient, find out the cause of pain using modern examination methods.
Once the diagnosis is made, treatment is prescribed. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause of severe pain in the calf muscle, the mechanism of development of the pathological process and eliminating the pain syndrome. Rehabilitation specialists prescribe modern physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, and acupuncture. The senior instructor-methodologist draws up a special physical therapy program and conducts individual and group classes. Their goal is to relieve muscle spasm, increase the tone of the calf muscle and eliminate pain.
Aching calves: causes of discomfort
Sharp pain in the calf muscle at night or during the day can occur for the following reasons:
- damage to the calf muscles after excessive exercise;
- pathologies of blood vessels of the lower extremities (varicose veins, obliterating arterial diseases);
- sedentary or standing work, when oxygen starvation occurs due to venous stagnation, toxins accumulate in the leg muscles.
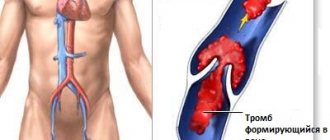
Severe pain in the calf muscle when walking develops in patients suffering from obliterating atherosclerosis or endarteritis. Pain in the calf muscle at the back is a sign of acute venous thrombosis. Pain may occur in the calf of the left leg due to injury. Heel pain radiates to the calf muscle due to inflammation of the Achilles tendon. Pain in the calf muscles can be a symptom of ankylosing spondylitis.
Spinal diseases provoke pain in the calf muscles. When the structure and function of the intervertebral discs are disrupted, radiating pain occurs that radiates to the legs. Peripheral nerve diseases can also cause pain in the calf muscles. With neuralgia, the pain is paroxysmal in nature and occurs along the nerve fibers. During the intervals between attacks, the patient does not feel pain.
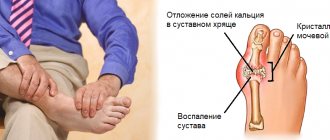
The most severe pain occurs with inflammation of the calf muscles - myositis. The patient is bothered by aching pain in the calves, which intensifies with movement. Often, dense nodules or cords can be felt in the calf. A peculiar form of the disease is parasitic myositis, which occurs when affected by muscle pain in the legs, fever, pain in the muscles of the limbs, tongue, face, chest. Acute, prolonged pain in the calf muscles occurs due to inflammation of the bone marrow - osteomyelitis.
Self-help for sore calf muscles
Before deciding what to do if your calves hurt, you need to understand why this happens. Try to determine the cause of the discomfort yourself - to do this, you need to remember whether you have recently had injuries, hypothermia, long walking, lack of fluid in the body, or insomnia. With dehydration, stress and fatigue, leg pain decreases after:
- light massage;
- warm foot bath with mint, chamomile or salt;
- taking enough fluids;
- recreation.
If injury, vascular pathologies or inflammatory processes are suspected, massage and foot baths are contraindicated. If the pain is very severe, you can take a pain reliever. Local agents in the form of gels and ointments help well.
If you experience frequent pain in your legs, you should consult your doctor as soon as possible. Self-medication can lead to the development of thrombosis, sepsis and other dangerous complications.
How to relieve pain in calf muscles
In order to relieve pain in the calf muscle after an injury, it is necessary to provide rest to the lower limb, place an ice pack on the back of the shin, apply an elastic bandage and elevate the leg. 72 hours after the injury to the calf muscle, a heating pad should be applied to the lower leg.
As soon as the swelling subsides, you need to rub the skin over the calf muscle with a pain-relieving balm (Bengay, Finalgon) and wrap it with an elastic bandage. If there is severe pain in the calf muscle, you should take a tablet of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug – ibuprofen, ketanov – orally. If the pain does not go away after 7 days, you should consult a doctor.
If you have pain in the calf due to an injury, you need to reduce the load on the heel. Heel pads can reduce stress on the tendons and calf muscles. You can make them yourself. To do this, just cut out pieces of cork 6 cm thick and put them in your shoes. It is necessary to avoid activities that involve additional stress on the calf muscles. No need to walk to the upper floors or ride a bicycle. Wearing comfortable shoes reduces pain in the calf muscle. Traumatologists recommend wearing sneakers and avoiding stiletto heels during illness.
If the cause of pain in the calf muscles is varicose veins of the lower extremities, it is useful to use compression stockings. Arch supports, which are installed in shoes under the instep of the foot, help correct imbalances that affect gait and cause pain in the calf muscles.
If acute pain suddenly appears in the calf muscles, you must stop, lie down on a bench, place a cushion under your feet, and call an ambulance. In this case, the patient needs to consult a phlebologist and provide emergency care. Sharp pain in the calves, reminiscent of a whiplash, goes away after resting for a few minutes. If it appears again, you should contact an angiosurgeon.
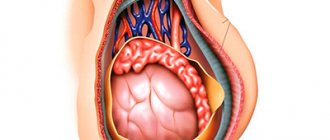
Baker's cyst
This is an outgrowth of the synovial membrane of the joint, filled with joint fluid. It occurs quite often, usually in women after 40 years of age. A Baker's cyst can cause aching pain under the knee and swelling in the popliteal fossa; with large cysts, the leg does not bend at the knee completely, and a “bump” can be felt behind the knee. To clarify the diagnosis, ultrasound of the knee and MRI are used.
Baker's cysts can be caused by inflammatory diseases, injuries, or arthrosis of the knee. Despite the fact that it is not a tumor, the cyst must be removed or punctured, since it can compress the vessels under the knee and cause complications such as thrombophlebitis and thromboembolism.
Exercises to Prevent Leg Pain
Stretching and strengthening your calf muscles will help prevent future pain. Before classes, you need to warm up your feet. It is better to do the exercises immediately after a hot shower.
Stand facing the wall, touch it with your palms. Place the toe of one foot towards the heel of the other. Leaning on the floor with the heel of your “back” leg and slightly raising your toes, bend the knee of your “front” limb. Lean against the wall, resting your palms on it. Stay in this position for 30 seconds.
Sit on the floor with your legs extended in front of you, toes pointing up. If you can reach your toes, grab them with your hands and pull them towards you, stretching the calf muscles. If you can’t reach your toes, you can hook your toes with a towel and pull on the ends for 30 seconds.
While sitting on a chair, raise and lower your heels. You can rise on tiptoes, or lower yourself, leaning on the back of a chair or table. Repeat each exercise 20 times, eventually increasing the number of repetitions to 40. If during the exercise you experience pain in the calf muscle, you should stop doing it.
Strengthening your lower leg helps relieve pain in the calf muscle. Place 1 kilogram of rice in a stocking and place it on your toes while sitting on a chair with your knees bent. Without lifting your heels off the floor, lean forward and pull your toes toward your shins. This exercise strengthens the finger extensor muscles, which reduces the load on the calf muscle.
Diseases of the nerves and blood vessels of the popliteal fossa
There are three large structures running beneath the knee: the tibial nerve, the popliteal artery, and the popliteal vein. Acute pain radiating to the lower part of the leg accompanies damage to the tibial nerve, for example, due to injury and pinching. A throbbing, aching pain under the knee is characteristic of a popliteal artery aneurysm. Popliteal vein thrombosis is not common and may be a complication of Baker's cyst. The pain is aching, not severe, and often the disease can only be recognized at a late stage. Ultrasound with Doppler is of decisive importance, which allows identifying a blood clot in the popliteal vein.
Taping
The gastrocnemius muscle is located on the back of the lower leg and consists of two heads that are parallel to each other. They smoothly transition into the Achilles tendon, which is very often injured. Given this structural structure, rehabilitation specialists at the Yusupov Hospital use only Y-tapes or lymph tape for taping the calf muscle. Y-tapes are more effective for sprained or torn ligaments. Lymph tape is used to accelerate the resorption of swelling and hematomas after bruises.
Tape is applied for pain in the calf muscle caused by contusion of muscle fibers, sprain of the calf muscle, tears of ligaments and muscle fibers. If the calf is torn or sprained, you can apply the tape to the calf muscle from bottom to top. In case of a bruise, lymph tape is applied from top to bottom. Before gluing the tape, the hair is shaved off and the surface of the shin is thoroughly wiped with alcohol.
The patient's position should help stretch the muscles of the lower leg - the foot should be in the direction towards itself. This can be done while lying on your stomach with your leg bent and your foot pointing towards you, or standing with your leg back and your heel on the floor.
The doctor selects the optimal tape length. It should correspond to the anatomical length of the calf muscle, taking into account the percentage of elongation of the middle part of the elastic band. The tape is placed from the plantar surface of the heel to the knee joint. The first and last 2-3 cm are glued without tension. When the calf is stretched, a tension of 20-30% is applied, and when there is a bruise, the tape is applied without any tension at all.
The rays of the tape should be located according to the location of the muscle fibers in the calf muscle - along the lower leg. If there are signs of injury to the Achilles tendon at the site of attachment to the calf muscle, apply a short tape perpendicular to the axis of the lower leg.
Infections of the popliteal fossa, enlarged lymph nodes
The soft tissues of the popliteal region can become inflamed after undetected injuries, cuts, or punctures of the skin. Severe pain, swelling and temperature are caused by an abscess of the popliteal fossa, in which pus accumulates under the skin. Treatment is only surgical.
Enlarged lymph nodes under the knee can also be accompanied by discomfort and swelling. Since lymph from the lower part of the leg flows into the popliteal lymph nodes, their increase indicates an inflammatory process somewhere below. It is necessary to check the condition of the veins, the presence of ulcers on the lower leg or foot, suppuration, cuts and deep punctures, which can cause infection and suppuration.
How to treat pain in the calf of the left or right leg
If you feel pain in your calf muscles, contact the Yusupov Hospital. Doctors will prescribe anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory treatment. After a comprehensive examination using x-rays, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, blood and urine tests, a collegial decision will be made on treatment for the syndrome that causes pain in the calf muscles.
Severe cases of diseases that cause pain in the lower leg muscles are discussed by professors and doctors of the highest category at the Yusupov Hospital at a meeting of the expert council. Leading neurologists, rheumatologists, orthopedists, and rehabilitation specialists establish an accurate diagnosis and jointly develop tactics for further patient management. A comprehensive treatment is carried out aimed at eliminating the cause of pain, the mechanisms of development of the pathological process and relieving the pain syndrome. Therapy is carried out with effective drugs that have a minimal range of side effects.
After treatment, patients are offered a comprehensive rehabilitation program. It allows you to get all the necessary procedures at a stable price and save money. If you experience pain in the calf muscle, call the Yusupov Hospital, where the call center is open every day 24 hours a day, without days off or lunch breaks. Doctors provide emergency medical care around the clock.
Diseases of the soft tissues of the joint, tendons
The knee joint has 6 ligaments and up to 10 bursae (depending on individual characteristics), a thin capsule surrounding the joint. In untrained people, even minor long-term exercise can cause tendonitis (inflammation of the tendon) or bursitis (inflammation of the bursa). With awkward movement, the joint capsule can be pinched between the ligaments. All this causes pain, which is often nagging in nature and is often localized in the back of the knee and under it.
Diagnosis of knee ligament diseases necessarily includes MRI. Treatment uses cold, rest and anti-inflammatory drugs. We perform osteopathic manipulations on our patients that allow us to release the pinched joint capsule or relieve tension from the ligaments and fascia of the knee. Pain under the knee goes away several times faster after complex treatment.