Cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular diseases most often cause characteristic chest pain on the left. These may be conditions that threaten a person’s life or indicate the development of serious diseases.
Heart attack and ischemia
Chest pain on the left, radiating to the arm, is a typical sign of a heart attack, when the heart muscle becomes inflamed and atrophies. The precursor to this disease is coronary heart disease, which occurs as a result of impaired blood flow due to atherosclerosis.
Pericarditis
If the chest pain on the left side is sharply stabbing, this may be a sign of pericarditis. Pericarditis is an inflammation of the heart sac that is caused by infections and autoimmune processes. Pericarditis can easily be mistaken for a heart attack, but the pain associated with pericarditis is reduced when the person is standing.
Angina pectoris
Angina is an attack of pain in the chest on the left, as during a myocardial infarction. But it arises as a result of strong experiences, emotional upheavals and lasts no more than 5 minutes. Angina occurs due to insufficient blood supply to the heart. If chest pain on the left side lasts more than 5-7 minutes, it may be a sign of myocardial infarction.
Aortic aneurysm
Acute tearing pain in the chest on the left is one of the signs of an aortic aneurysm. An aortic aneurysm is a pathological enlargement of an artery that threatens human life. It is accompanied by difficulty breathing, numbness of the limbs, and difficulty speaking. Death is possible as a result of aortic rupture, so this pathological condition is especially dangerous.
Respiratory diseases
The human chest contains not only the heart, but also the bronchi and lungs. Therefore, chest pain on the left may be a sign of diseases of the respiratory system, among which there are also serious pathological conditions.
Pleurisy
Acute pain in the chest on the left, intensifying with inspiration, is characteristic of pleurisy. The lining of the lungs - the pleura - becomes inflamed during infectious diseases and secretes a special secretion that irritates the nerve endings and causes pain. Pleurisy accompanies pneumonia and other infectious lung diseases.
Spontaneous pneumothorax
If the integrity of the pleura is compromised (usually due to injury), air enters the lining of the lungs during inhalation, which causes pain. Pain in the chest area on the left side is accompanied by difficulty breathing, weakness and dizziness. The cause of spontaneous pneumothorax may be damage to the pleura as a result of chronic diseases.
Emphysema
With emphysema, the lungs lose their ability to get rid of excess air, which occurs due to loss of elasticity in the walls of the bronchi. Chest pain on the left or above the chest can occur due to this serious disease, which causes complications such as pneumothorax and respiratory failure. This dangerous condition requires immediate treatment.
Pulmonary embolism
The lungs are supplied with oxygen through the blood vessels, and a blood clot entering the pulmonary artery is called an embolism. This disease manifests itself as aching pain in the chest on the left and problems with breathing. Pulmonary embolism is characterized by increased pain with deep inspiration. It is not associated with cardiovascular diseases, but poses a potential threat to human life.
Burning behind the sternum
Gastritis
Ulcer
Pancreatitis
26094 May 28
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Burning sensation behind the sternum: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
A burning sensation behind the sternum is a symptom characteristic of many diseases - this is how patients with pathologies of the cardiovascular system, spine, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system, neuralgia and panic attacks describe their sensations.
In some cases, this symptom is not dangerous, but some pathological conditions require immediate medical attention.
Types of burning behind the sternum
There is no generally accepted classification of burning behind the sternum. When patients are asked about their sensations, they talk about pressing, pulling, stabbing, burning, and encircling pain.
Thus, the burning sensation is as varied as the causes that cause it.
Possible causes of burning behind the sternum
Burning in the sternum, a feeling of fullness and heaviness, especially in older people, can be a symptom of serious cardiac problems, and all of them equally require seeking medical help.
In diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the burning sensation is usually diffuse, often radiating to the back. In many patients it occurs during or after eating.
Disruption of the musculoskeletal system often leads to unpleasant sensations in the chest. The burning sensation intensifies when inhaling or exhaling, and changes when changing body position.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine can cause numbness in the hands and decreased sensitivity.
Neuroses and panic attacks are often accompanied by a burning sensation in the chest.
When the neuroendocrine regulation of internal organs is disrupted, patients complain of a burning sensation behind the sternum. The cause may be either insufficient maturity of the body's systems during adolescence, or previous infectious diseases, stress, bad habits, or overwork. Short-term vasospasm directly leads to the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the heart area. The attacks pass at rest and are accompanied by weakness, rapid heartbeat, and cold hands due to deterioration of blood flow.
Diseases leading to a burning sensation behind the sternum
Cardiovascular pathologies:
- Angina pectoris. Impaired blood circulation in the vessels of the heart due to atherosclerosis leads to deterioration in the nutrition of the heart muscle. During physical activity or anxiety, the heart requires more oxygen - if there is not enough oxygen, then the first signal will be discomfort in the chest area. A burning sensation, a feeling of squeezing, a tingling sensation can radiate (radiate) to the left arm, under the shoulder blade, rarely to the lower jaw, lasting no more than 15 minutes and passing with rest and after taking nitroglycerin.
- Myocardial infarction.
During a heart attack, a sharp disruption of the blood supply to the heart muscle occurs due to blockage of most of the lumen of the vessel supplying the heart by thrombotic masses. Most often, intense pain occurs, but a strong burning sensation in the chest may also be present. The attack lasts a long time, is not relieved by nitroglycerin, does not go away with rest, and is accompanied by shortness of breath, severe weakness, and decreased vision. Myocardial infarction is a life-threatening condition, so the patient needs urgent hospitalization. - A sharp rise in blood pressure may occur with a burning sensation in the chest. During a hypertensive crisis, the patient feels weakness, headache, dizziness, nausea, spots appear before the eyes and tinnitus.
- Inflammatory processes in the heart can also be manifested by a burning sensation in the chest. Typically, this condition is preceded by an infectious disease, most often of viral origin, or a severe bruise in the chest area. Unpleasant sensations can spread to the right or left side and intensify with changes in body position.
- A very dangerous condition is pulmonary embolism.
It occurs if blood clots are present in the vessels of the lower extremities - when they break off, they rise up the bloodstream and clog the pulmonary vessels. In addition to a burning sensation behind the sternum, the patient is bothered by severe shortness of breath, coughing (sometimes with blood), and severe cyanosis appears. In such a situation, emergency hospitalization is necessary. At risk are patients with varicose veins, smokers, and patients on the first day after surgery.
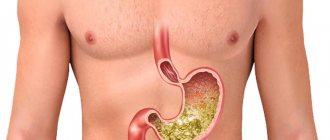
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract:
- Esophageal pathology is considered perhaps the most common cause of burning in the chest. It occurs as a result of the reflux of acidic gastric contents into the esophagus, which leads to damage to its mucous membrane. A burning sensation appears after eating food (especially spicy, fatty, smoked and fried), when wearing tight belts and taking a horizontal position immediately after eating.
- Inflammatory processes in the pancreas and gall bladder are often accompanied by a burning sensation in the chest. This symptom appears a couple of hours after eating and may be accompanied by nausea and heaviness in the stomach.
Respiratory diseases:
In case of inflammation of the bronchi or lungs (bronchitis, pneumonia, pleurisy), in addition to coughing and fever, the patient may be bothered by a burning sensation in the chest.
In addition, diseases characterized by a burning sensation behind the sternum include intercostal neuralgia, osteochondrosis, intercostal myositis, and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Which doctors should I contact if I have a burning sensation in the chest?
If a burning sensation behind the sternum is accompanied by a sharp deterioration in condition, weakness, an increase in pain, shortness of breath, coughing, or dizziness, you must immediately call an ambulance.
In other cases, you should also not postpone your visit to the doctor. Since this symptom has many causes, it is advisable to first turn to. He will prescribe examinations and, if necessary, refer to other specialists: a cardiologist; gastroenterologist; pulmonologist; neurologist.
Diagnosis and examinations for burning sensation behind the sternum
Making a diagnosis begins with a thorough history taking into account all the patient’s complaints and a physical examination.
To exclude cardiovascular pathology, first of all, a chest x-ray or CT scan of the chest and mediastinum is performed, as well as an electrocardiographic study (ECG) or echocardiography (EchoCG).
Spinal problems
The spine is connected to many organs, so spinal pain often radiates to the sternum. Often, a pressing dull pain on the left side of the chest may indicate problems in the thoracic spine.
Osteochondrosis
Pain in the chest and back on the left with osteochondrosis usually appears at a serious stage of the disease, when complications arise in the form of a vertebral hernia. In the thoracic region, osteochondrosis is most complex, since it is often accompanied by difficulty breathing and limited freedom of movement.
Injuries
With injuries to the sternum, aching or sharp pain in the left chest may appear, sometimes this is a sign of a rib fracture on the left side of the chest. The nature of the pain depends on the severity of the injury. In some cases, with spinal injuries, pain radiates to the left side of the chest.
Diagnostics
Such a complex symptom as aching or acute pain in the left chest requires careful diagnosis. The therapist decides where exactly to look for its cause.
by collecting detailed information about the circumstances under which the pain occurs and the patient's health status.
If necessary, the patient can be sent to a specialist neurologist
.
Diagnosis often begins with the exclusion of diseases of the cardiovascular system - an ECG
and a visit to
a cardiologist
; if necessary, the patient is prescribed
an echocardiogram
. In other cases, to diagnose diseases that cause chest pain on the left, blood tests, endoscopic, ultrasound and x-ray examinations can be prescribed.
Diagnosis of rib pain
If you are suffering from rib pain, contact the CELT Pain Clinic. We employ doctors of various specialties who will use the entire arsenal of diagnostic and treatment capabilities of our multidisciplinary clinic to solve your problems. Since there are many reasons that cause pain in the ribs, it is very important to correctly diagnose. This is the only way to correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
If you experience pain, contact one of our specialists:
- therapist;
- neurologist;
- traumatologist;
- pulmonologist;
- cardiologist.
Diagnosis in our Pain Clinic, in addition to examination by a doctor and medical history, may include:
- laboratory research methods;
- cardiography;
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging.