What is duodenitis? Functions of the duodenum duodenum
Duodenitis is an inflammatory disease of the duodenum. At the first consultation at Sarklinik, the doctor will tell you what duodenitis is , what are the causes, symptoms and signs of duodenitis. What is the difference between gastritis (inflammation of the stomach) and duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum, 12 duodenum) and enteritis (inflammation of the intestines)? How to treat acute and chronic duodenitis , esophagitis, exacerbation of duodenitis, gastric reflux? Where is the duodenitis clinic located? What are the characteristics of erosive (incorrectly erosive) duodenitis, catarrhal, superficial, proximal, distal duodenitis, reflux duodenitis, giardiasis duodenitis in children? Why does reactive duodenitis occur in adolescents, atrophic, follicular, hemorrhagic, ulcerative, hypertrophic, diffuse duodenitis in adults? How to cure the diagnosis of weak, moderate, moderate, moderately severe, strong, severe duodenitis, bulbitis, cholecystitis, postbulbar duodenitis? What diet , nutrition , menu for duodenitis, gastritis? folk remedies , folk remedy treatment , herbal treatment, folk medicine, herbs, folk medicine, antibiotics, antibiotic treatment, diet 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 not help How to choose drug treatment if there is primary or secondary duodenitis, DGR? How dangerous is the disease, how to treat duodenitis? How to relieve pain due to duodenitis, why temperature, fever, hyperthermia? How is focal chronic duodenitis ? How to get rid of duodenitis , how to remove duodenitis? What does the army think about duodenitis? Where is the diagnosis of duodenitis , FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy) with biopsy done? How does the duodenal bulb, gallbladder, stomach, intestines, pancreas suffer during inflammation? What can you eat for duodenitis, where to treat? Why does catarrhal gastritis, helminthic infestation, bulbitis, superficial gastritis, gastroduodenitis, esophagitis, dyskinesia, colitis, enterocolitis, gastritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, duodenal gastric reflux, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, thyrotoxicosis, gallbladder dyskinesia occur?
Functions
Let us highlight the main functions of the duodenum:
- production of enzymes and duodenal juice necessary for normal digestion;
- motor and evacuation function, that is, responsible for moving food gruel;
- secretory;
- regulation of bile pancreatic enzymes;
- supporting communication with the stomach. She is responsible for opening and closing the gatekeeper.
- adjusting the acid-base balance of food. It makes the food bolus alkaline.
Since the duodenum is the initial section of the entire intestine, it is here that the processes of absorption of nutrients that come with food and drink actively occur. This is where the stage of intestinal digestion begins.
Digestion
After the food bolus enters the initial part of the colon, it mixes with bile, secretions of the intestinal walls, as well as fluid from the pancreatic ducts. The acidic environment of food is then neutralized by bile, thereby protecting the mucous membrane. In addition, bile breaks down fat and breaks it down into small emulsions, which speeds up the digestion process.
Under the influence of bile secretion, fat breakdown products dissolve and are absorbed into the intestinal walls, and complete absorption of vitamins and amino acids occurs. It is also worth noting that bile regulates intestinal motility, stimulating the contraction of its muscles. Thanks to this, the food bolus moves faster through the intestinal lumen and is promptly evacuated from the body.
Pancreatic juice also plays an important role, with the help of which starch is digested, as well as proteins and fats. The duodenal glands produce intestinal juice, which mostly consists of mucus. This secret promotes better breakdown of proteins.
Considering all of the above, we can say that the duodenum plays a huge role in the digestive process. It saturates the food bolus with the necessary enzymes and ensures further digestion.
DPC ensures the normal course of digestive processes
Duodenum, 12 duodenum: treatment
The duodenum is an important organ of the digestive system and digestive behavior. The intestinal cavity is a reservoir into which digestive juices flow from the pancreas, liver and glands of the wall of the small intestine. Here, cavity digestion begins to take place, preparing the food bolus for the final breakdown of nutrients in the brush border of the cells of the duodenal mucosa. Between the microvilli, abundantly covered with enzymes, the bulk of the nutrients entering the human body are digested and absorbed at high speed. This digestion in the brush border is called parietal. The duodenum is richly innervated, especially in the initial section and in the area of confluence of the ducts from the gallbladder and pancreas. In the muscular lining of the intestine there are sensors for the rhythm of contractions of the entire small intestine.
The duodenum is also a hormonal organ. In the intestinal wall, under the influence of gastric contents, enterogastron is produced, which suppresses the secretion of gastric juice and relaxes the muscles of the stomach wall. Enterogastron prevents the digestive hormone gastrin from stimulating the activity of the gastric glands. Gastrin is produced by the pyloric zone of the stomach, which is close in origin and structure to the duodenum. The duodenum secretes pancreozymin, cholecystokinin, secretin and other hormones that regulate the activity of the pancreas and gallbladder, while simultaneously stopping gastric secretion. Digestive hormones from the duodenum stimulate the intestinal glands, which actively begin to secrete juice and stimulate intestinal motility. In the duodenum, hormones of general action are found that affect the body’s metabolism, endocrine, nervous, and cardiovascular systems.
Diseases of the duodenum
Duodenum
- this is the initial section of the small intestine, which is anatomically connected not only with the stomach, but also with the liver and pancreas through the ducts of Oddi entering through the sphincter of Oddi. Therefore, on the one hand, diseases of the duodenum may have their “roots” in disruption of the functioning of different parts of the digestive tract; on the other hand, diseases of the duodenum may affect other organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Accordingly, good results in the treatment of diseases of the duodenum make it possible to prevent dysfunction and problems of the organs concerned. Currently, gastroenterologists note a significant “rejuvenation” of patients with diseases of the duodenum and an increase in the prevalence of these diseases among schoolchildren.
Duodenal ulcer.
Duodenal ulcer is a disease that is caused by a combination of many etiological factors, while the morphological manifestation of the disease is an ulcer - a defect in the duodenal mucosa. Localization of ulcers in the duodenum is more common than in the stomach.
The cause of the ulcer can be psycho-emotional stress, stress, irregular diet, alcohol abuse, smoking. But, basically, the development of the disease is predetermined by internal factors: heredity, metabolic disorders in the body, pathological neuro-humoral regulation of gastric secretion, age-related changes in hormonal levels. Peptic ulcer is a serious and complex disease that often occurs with the development of various complications, such as perforation, bleeding, development of cicatricial narrowing of the outlet of the stomach with disruption of food passage. Classic signs of duodenal ulcer are the seasonality of exacerbations and the daily rhythm of pain. The seasonality of exacerbations (spring, autumn) is explained by changes in the state of the body at different periods of the year, hormonal levels, and neuroendocrine changes. Typically, pain increases on an empty stomach and at night. The pain often decreases after eating or drinking cold milk. Heartburn is also a concern, vomiting and belching occur periodically. Vomiting sometimes occurs at the height of pain and relieves it. If vomiting begins to occur regularly and in large quantities with an admixture of undigested food with a rotten smell, then in this case we may be talking about the development of a narrowing of the lumen of the duodenum due to scar changes in it. The most serious complications of peptic ulcer disease are bleeding, which can be obvious or hidden, and perforation of the ulcer. Bleeding may include bloody vomiting and tarry stools. Perforation of the ulcer causes acute pain and leads to the development of peritonitis.
Duodenitis.
Duodenitis is an inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the duodenum. The manifestations of duodenitis visible during endoscopy are swelling and hyperemia (redness) of the mucous membrane; as the disease progresses, erosions appear. If exposure to disease-causing factors continues, ulcers may develop from erosion. The reasons for the development of duodenitis are stress, irregular diet, alcohol abuse, smoking, as well as diseases of other internal organs - liver, gallbladder, pancreas, colitis with impaired intestinal motility. Duodenitis may develop if you are allergic to certain foods. Symptoms of duodenitis: pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, gas formation, feeling of fullness in the stomach, fatigue, lack of appetite, unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Polyps.
Polyps are benign growths of the mucous membrane in the form of formations of various sizes and shapes protruding into the lumen. Small polyps are not felt in any way, large ones (more than 2 cm) can interfere with the passage of food through the duodenum, which causes bloating, nausea and vomiting. The danger of polyps is that they can change their structure over time, even to the point of developing cancer. Therefore, when polyps are detected, regular monitoring with biopsies is necessary.
Tumors.
Tumors of the duodenum are rare. Usually these are tumors of the duodenal papilla - both benign and malignant, or the germination of tumor tissue from nearby organs - the pancreas or intestines. Symptoms of duodenal tumors are weakness, sweating, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, pain in the upper abdomen; with a tumor of the duodenal papilla, pain in the right hypochondrium. All of the above-described diseases of the duodenum are detected by endoscopy, and polyps are treated with endoscopic polypectomy (if the polyp is no more than 1 cm in size).
AT THE FAMILY CLINIC, fibrogastroduodenoscopy and endoscopic removal of polyps of the stomach and duodenum are performed using modern high-quality equipment by experienced endoscopists. If necessary, endoscopic procedures and operations can be performed under general anesthesia.
Acute duodenitis
Acute duodenitis usually occurs in combination with acute inflammation of the stomach and intestines as acute gastroenteritis, gastroenterocolitis. Morphologically there are:
1) catarrhal acute duodenitis;
2) erosive-ulcerative acute duodenitis;
3) phlegmonous acute duodenitis.
According to the predominant clinical manifestations, various forms of duodenitis are distinguished:
1) resembling duodenal ulcer;
2) resembling chronic gastritis;
3) resembling cholecystitis;
4) resembling acute gastritis;
5) resembling appendicitis.
Acute duodenitis occurs as a result of exposure to a number of factors on the body:
1) food toxic infections;
2) poisoning with toxic substances that have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the digestive tract;
3) excessive intake of very spicy food, usually in combination with large amounts of strong alcoholic drinks;
4) damage to the duodenal mucosa by foreign bodies.
Stages of duodenal cancer
In the overwhelming majority, mucous adenocarcinoma develops in the duodenal wall; anatomical features make it possible to diagnose it in the early stages.
Staging is based on the degree of involvement of the intestinal wall in the malignant process and the presence of metastases in the lymphatic collector:
- Tumor within the mucous membrane - stage 1;
- Neoplasm within the wall with metastasis to the lymph nodes near the organ - stage 2;
- Cancer of the intestinal wall grows into the abdominal cavity and involves nearby anatomical structures - stage 3;
- With any size of tumor lesion of the duodenal wall, the appearance of metastases in other organs - stage 4 is unconditionally established.
Acute duodenitis: symptoms, signs
What are the signs and symptoms of acute duodenitis ? The clinical picture of acute duodenitis is characterized by symptoms such as epigastric pain , nausea, vomiting, general weakness, pain on palpation in the epigastric region, and increased temperature. The diagnosis is confirmed by FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy), which detects inflammatory changes in the duodenal mucosa. With phlegmonous duodenitis, the patient’s general condition sharply worsens, tension in the abdominal wall muscles in the epigastric region is determined, a positive Shchetkin-Blumberg sign is detected, and an increase in temperature is noted.
Acute catarrhal duodenitis and erosive-ulcerative duodenitis often end in self-healing within a few days. With repeated duodenitis, a transition to a chronic form is possible. Complications of acute duodenitis are intestinal bleeding, perforation of the intestinal wall, and the development of acute pancreatitis.
Treatment
Treatment of chronic duodenitis during periods of exacerbation of the disease is carried out in a hospital. Treatment is prescribed depending on the cause of the disease.
In the presence of giardiasis and helminthiases, appropriate drug therapy is prescribed. When a Helicobacter pylori infection is detected, antibiotics are used. For increased acidity - drugs that reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid and antacids that neutralize the acidity of gastric juice.
To protect the mucous membrane, enveloping drugs are prescribed. For anti-inflammatory purposes, it is recommended to use decoctions of chamomile and yarrow. Enzyme preparations are prescribed to restore digestion.
Frequent meals in small portions, drugs that bind bile and promote its secretion (choleretic) are indicated. Duodenal intubation with duodenal lavage is effective.
In the presence of adhesions, mechanical barriers and other types of obstruction that are not amenable to therapeutic treatment, surgical treatment of duodenitis is indicated.
Chronic duodenitis: causes
Chronic duodenitis is a chronic inflammation of the duodenum. The occurrence of chronic duodenitis is facilitated by irregular nutrition with frequent consumption of spicy, irritating, too hot foods ( primary chronic duodenitis ). Secondary chronic duodenitis is observed in diseases such as chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, chronic pancreatitis, food allergies, giardiasis, uremia. In the pathogenesis of chronic duodenitis, the direct effect of the irritating agent on the mucous membrane of the duodenum and the proteolytic effect of active gastric juice on it are important.
Causes and risk factors
Expert opinions differ regarding the reasons for the development of oncology in the duodenum. There is evidence that the causes of cancer in this location are similar to the causes of stomach tumors.
It is believed that there is a connection with a long-term infection caused by H. Pilori, an acid-fast bacteria. Ulcerative defects caused by this microorganism occur more often than in the stomach area. They occur in 8 out of 10 patients, while in the stomach only 6 out of 10 people. Duodenal ulcers are more common in women, although the incidence of cancer in them is equal to that in men. There are publications about the connection between cancer and obesity, dietary habits, including some national cuisines of the world.
Malignant tumors of the duodenum can occur against the background of certain provoking factors. These include:
- chronic inflammatory processes (duodenitis) and ulcerative lesions, the presence of Crohn's disease;
- diffuse intestinal polyposis (benign lesions - polyps of different sizes on the intestinal walls);
- poor nutrition with a predominance of animal fat and a deficiency of fiber;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- decreased immune defense, including antitumor.
In addition, some of the risk factors include viral infections, diabetes, and pancreatitis. Unfavorable heredity also plays a role.
Classification of chronic duodenitis
Classification of chronic duodenitis:
1) chronic duodenitis , mainly bulbitis , of acidopeptic origin;
2) chronic duodenitis, combined with atrophic gastritis or enteritis;
3) chronic duodenitis that developed against the background of duodenostasis;
4) local duodenitis (papillitis, peripapillary diverticulitis).
According to the endoscopic picture there are:
1) superficial chronic duodenitis;
2) atrophic chronic duodenitis;
3) interstitial chronic duodenitis;
4) erosive-ulcerative chronic duodenitis.
Chronic duodenitis, symptoms of chronic duodenitis
What are the signs, manifestations, symptoms of chronic duodenitis ? The clinical picture of chronic duodenitis is characterized by such signs as constant, dull or ulcer-like pain in the epigastrium , a feeling of fullness or distension in the upper abdomen after eating, decreased appetite (poor appetite), vomiting, nausea. On palpation, pain is noted in the epigastric region.
With proper treatment, the prognosis is favorable. With the erosive-ulcerative form of duodenitis, various complications can often occur, most often intestinal bleeding.
The clinical picture of duodenitis is diverse and nonspecific. Isolated chronic duodenitis is rare. It is combined with chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer, enteritis, pancreatitis, and diseases of the biliary tract.
Duodenal cancer: main symptoms and signs
Typical symptoms of duodenal cancer are practically not detected in the early stages. The disease can be asymptomatic for quite a long time. The tumor can be detected by chance at this time during examinations for other diseases. In a later stage, pain may occur with duodenal cancer. But they do not always alert the patient, as they can be mistaken for signs of indigestion or overeating. The pain is dull and diffuse, usually localized in the upper abdomen, under the ribs or epigastric region. Painful sensations may occur at night or after prolonged fasting. As the disease progresses, intoxication with tumor decay products may occur. This is manifested by weight loss, severe pallor, and constant weakness.
Manifestations of cancer largely depend on the stage of cancer, the size of the lesion and additional pathologies that complicate the condition. In later stages, cancer may manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- apathy, depression, weakness with fatigue, lethargy;
- sleep disturbances with drowsiness or insomnia;
- dizziness and headache;
- a sharp decrease in appetite, which leads to sudden weight loss, loss of up to 10% of weight or more;
- pale skin with a waxy or bluish tint, yellowness of the sclera;
- dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth, eyes and nose;
- constant low-grade fever;
- sweating at night;
- persistent anemia;
- nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort;
- frequent colds, decreased immunity.
If the tumor tissue disintegrates, blood vessels are damaged and bleeding begins, black stool may appear.
Diagnosis of chronic duodenitis, differential diagnosis
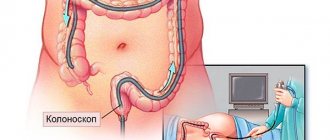
Diagnosis of chronic duodenitis is carried out using diagnostic methods such as fibrogastroduodenoscopy with biopsy, duodenoscopy, pH-metry, floor-by-floor manometry, impedance measurement. In parallel with the diagnosis of duodenitis, other digestive organs are examined.
Often duodenitis simulates duodenal ulcer. People of all age groups suffer from duodenitis. More often, inflammation of the duodenum occurs in young women, in whom duodenitis can be severe, accompanied by various disturbances in the activity of the central nervous system and endocrine glands. Duodenitis often occurs in childhood, which is facilitated by the inherited weakness of the hormonal apparatus of the duodenum, the variability of its shape, mobility and location in relation to the axis of the body.
The duodenum does not have a mesentery. In the case where the embryonic mesentery is preserved, the intestine is abnormally mobile and forms additional loops. Part of the liquid food mass flowing through the duodenum gets stuck in the additional elbow, creating favorable conditions for the proliferation of microorganisms in the intestinal cavity. When exposed to alcoholic drinks or irritating foods, an inflammatory process occurs. An obstacle to the passage of food through the duodenum also appears when it is located in the opposite direction relative to the axis of the body.
Treatment of bulbitis
Treatment of the digestive system is extremely variable. In the early stages, sometimes it is enough to reconsider your diet, and perhaps go on a strict diet and give up bad habits, such as:
- smoking;
- excessive caffeine consumption;
- alcohol consumption;
- abuse of spicy foods and synthetic carbonated drinks.
At this stage, it is important to exclude stress factors that affect the patient’s psycho-emotional state. Most diseases can be successfully treated with courses of drug therapy, which must be completed several times a year with regular adjustments of medications by a specialist who will also tell you where to do a gastroscopy to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Complex therapy and an individual approach are the main principles that guide the doctors of the Gorbakov Clinic when choosing treatment methods for each patient. Specialists develop a diet and prescribe drug therapy. The patient is prescribed drugs that reduce acidity, regulate gastrointestinal motility, as well as those that have an enveloping effect. If necessary, treatment for Helicobacter pylori and parasitic infections is prescribed. In some cases, the patient is examined by an immunologist who prescribes additional restorative drugs, an endocrinologist, if there is concomitant endocrine pathology, and other specialists.
What contributes to the development of duodenitis?
What diseases contribute to duodenitis? Giardiasis , ascariasis, chronic infection in the oral cavity, pharynx, genitals, gall bladder, and renal failure contribute to the development of duodenitis.
The inflammatory process can be sluggish, manifested by disturbances in appetite and general well-being, and mild dyspeptic symptoms. Patients experience lethargy and mental instability. Children grow up thin and develop poorly.
When infected with Giardia, the clinical picture of duodenitis can develop rapidly. Suddenly, usually after an error in diet, an attack of severe abdominal pain occurs, causing patients to squirm. The pain is not relieved by antispasmodics. The patient's face becomes hyperemic and becomes covered with drops of sweat.
Diagnostics
The basis of diagnosis is instrumental examinations. Duodenoscopy is performed
with a biopsy taken to determine the nature of the tumor, and
an X-ray of the intestine
.
Additionally an ultrasound of the abdominal organs
to determine tumor growth into blood vessels, the pancreas, damage to the lymph nodes, liver, and fluid accumulation in the abdomen (development of ascites).
Angiography
helps to determine the characteristics of the blood supply to the tumor, which is important for its prompt removal and detection of small metastases in the liver. Blood and urine tests for gastrin and serotonin levels are also important.
Dowdenitis complications
What are the complications of duodenitis ? A severe complication of long-term duodenitis is duodenal hormonal insufficiency. Inflammation, destroying the duodenal mucosa, causes death and inhibition of cells that secrete hormones. The appearance of symptoms of duodenal insufficiency is facilitated by congenital weakness of the endocrine apparatus of the duodenum, hypoxia, and concomitant chronic infectious diseases. Insufficiency of the hormonal function of the duodenum causes indigestion, carbohydrate metabolism, significant emaciation or weight gain. Severe neuropsychic and cardiovascular disorders occur.
In young women, duodenal hormonal insufficiency begins to manifest itself in the premenstrual period. Headaches, nausea, vomiting, irritability appear, and performance decreases. Attacks of severe weakness can last from one to four weeks. Weakness is accompanied by palpitations, heart pain, nausea, vomiting, often in the morning on an empty stomach. Patients lose their ability to work, interest in life and family. In a number of patients, attacks of weakness with trembling, pain in the heart, and frequent urination occur immediately after eating or several hours later, less often at night.
Duodenal hormonal insufficiency in acute and chronic duodenitis, duodenostasis is manifested by diencephalic, dumping, Meniere-like, hypoglycemic syndromes, attacks of severe weakness, dizziness, headaches, tachycardia, weight loss, muscle atrophy, depression. There is a dysfunction of other endocrine organs, especially the insular apparatus.
Anatomy
Most people have a variety of shapes. Even in the same person, the shape and location of the organ can change over time. First, let's talk about the structure of the duodenum.
Structure
The organ has several layers:
- outer shell;
- muscle layer with longitudinal and circular layers;
- submucosa, thanks to which the mucous membrane can be collected in layers;
- mucous layer covered with villi.
Location
The organ has four main parts:
- Upper, or initial. It is located approximately at the level of the first lumbar vertebra or even the last thoracic vertebra.
- Descending. It is located to the right of the lumbar region and touches the kidney.
- Bottom, or horizontal. It goes from right to left, and then passes next to the spine and bends upward.
- Rising. Forms a bend and is located at the level of the second lumbar vertebra.
Where is the duodenum located? Most often it is located at the level of the second or third lumbar vertebrae. The location may differ for each person and is influenced by a large number of factors, such as age and weight. For example, in elderly and thin people the organ is located slightly lower than in young and well-fed subjects.
The photo clearly shows where the duodenum is located in humans
The intestine is in contact with other abdominal organs on all sides:
- liver;
- bile ducts;
- pancreas;
- right kidney;
- ureter;
- ascending colon.
The length of the duodenum is 25-30 cm.
Treatment of duodenitis in Saratov, treatment of chronic duodenitis
Complex differentiated treatment of duodenitis in Saratov, treatment of chronic duodenitis in Saratov, treatment of patients with chronic duodenitis and gastroduodenitis with the widespread use of new reflexology techniques allows you to achieve satisfactory results even with a pronounced clinical picture of the disease! Sarklinik knows how to treat duodenitis, how to cure duodenitis, how to get rid of duodenitis.
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: Wacpan | Dreamstime.com\Dreamstock.ru. The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Spasm of the esophagus: treatment, causes, how to relieve, treat cardiospasm of the esophagus, esophagospasm
Hepatomegaly, steatosis, fibrosis, alcoholic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, alcohol damage
Belching, treatment, frequent rotten belching of air, eggs, food
Reflux esophagitis: symptoms, treatment, gerb, gastroesophageal reflux disease
Stomach ulcer, duodenal ulcer, peptic ulcer: treatment in Saratov
Comments ()
Duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum). Treatment
Duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum). Treatment in adults
In the acute phase, rest - fasting for one to two days - can save the situation. This will avoid additional damage, reduce intoxication and provide material and energy resources for tissue restoration. What should not be forgotten is the drinking regime. Water is vital for the body, and doubly necessary for those actively recovering. Water is a purifier, a solvent, and a source of energy. But the water should not be very hot or cold!
Rest concerns not only eating, but also general motor and emotional activity. This principle of energy saving will help the body concentrate fully and effectively on the main task.
Food . At the end of the fast, at first it should be gentle. And in consistency, and in temperature, and in composition, so as not to provoke too much juice secretion, which can slow down tissue regeneration.
Medicines can also help the body get more confidently on the path to recovery: painkillers, antacids, enzymes, vitamins, etc.
In rare complicated cases (with erosive-ulcerative duodenitis), emergency surgical measures may be required.
In the remission phase, on the contrary, physical activity is important . It helps the gastrointestinal tract better absorb food and maintain the natural rhythm of cell repair. But it is also important not to forget about the nuances of nutrition.
Duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum). Treatment in children
In treating children, as well as adults, it is important to remember that symptomatic therapy (painkillers, anti-inflammatory, enzyme replacement) deals with consequences. And our task is to prevent their reappearance (or even better, their initial appearance). The gastrointestinal tract is a mirror of the lifestyle as a whole, both from a physical and psycho-emotional point of view. Scientific discoveries clearly indicate a close physiological connection between the organs of the digestive system and the brain. Therefore, not only poor nutrition (and this concept has both general principles and individual characteristics), but also “wrong” emotional reactions (stress) disable the food absorption system, which affects the functioning of the body as a whole.
The younger the child, the more his condition is influenced by the habits and reactions of his parents (especially his mother). Therefore, the main role in the formation of healthy habits is played not so much by the instructions of adults, but by the living example of their own behavior.
Make an appointment