Causes of neck pain in the front
Thyroid diseases
Organ damage can occur in people of all ages, including children. Pain in the front of the neck can be a consequence of both inflammatory processes and endocrine pathology. The pain intensifies with head movements, especially when tilting the head forward. The symptom is accompanied by elevated temperature, increased sweating, constant feeling of heat, and rapid heartbeat. Pain is often caused by the following reasons:
- Acute thyroiditis
. Soreness develops suddenly, more often after an acute respiratory viral infection or other infections. Characteristic complaints are severe acute pain in the anterolateral part of the neck, which extends to the mastoid process and collarbone. - Toxic goiter
. Painful sensations of a pressing or bursting nature are localized along the cervical midline; in the case of a single thyroid nodule, the pain is more pronounced on one side. Patients themselves notice an enlargement of the neck. - Hashimoto's thyroiditis
. In the phase of thyrotoxicosis, patients note severe discomfort in the front of the neck, which is not associated with changes in head position. Neck pain is accompanied by irritability, tremors (shaking) of the limbs, and sleep disturbances.
Sialadenitis
When the submandibular salivary glands are affected, complaints are usually made of sharp pain in the front of the neck, radiating to the ear and lower jaw. Unpleasant sensations tend to intensify when turning the head, chewing and swallowing movements. A swelling and compaction up to several centimeters in size very quickly forms. Due to a decrease in the amount of saliva, it becomes difficult to eat, and there is a constant dry mouth. Often sialadenitis occurs with disturbances in the general condition - low-grade fever, chills, weakness.
Purulent inflammation
Frequent causes of sharp pain are purulent processes in the pharynx, which spread to the adjacent tissue with the development of a retropharyngeal abscess. Patients complain that the neck begins to hurt in the front, the skin in this part is hot to the touch and bright pink. The pain is strong and throbbing. Due to severe discomfort, a person refuses food and water. The symptom occurs against the background of febrile fever. Similar manifestations can be detected with extensive paratonsillar abscesses, complicating bacterial tonsillitis.
Myositis
Inflammation of the neck muscles causes sharp shooting or dull pain in the neck that lasts for several days or even weeks. Pain with myositis often occurs after hypothermia or exposure to drafts. As a rule, pain is noted in the front of the neck, moving to the chin, collarbone and shoulders. The intensity increases with prolonged stay in one forced position and heavy physical activity. If symptoms worsen over time and interfere with daily work, you should consult a specialist to determine the cause of your neck pain.
Cervical plexitis
The severity of symptoms depends on the number of damaged nerves. The most common symptoms are sharp pain on the anterolateral surface, difficulty when trying to talk loudly or cough. Painful sensations can radiate to the ear, occipital region, and chest. Characterized by paresthesia, a feeling of “crawling goosebumps.” Patients associate the appearance of unpleasant symptoms with hypothermia, complications after vaccination, and injuries. Damage to the cervical plexus - plexitis - is also provoked by other causes: diabetes mellitus, infectious diseases.
Rheumatic diseases
Pain in the front of the neck is observed in systemic pathologies of connective tissue (collagenosis) with predominant damage to muscle tissue and skin - scleroderma, dermatomyositis. Typical are constant painful sensations of a pulling or aching nature, which are accompanied by thickening and swelling of the skin. Shooting pains radiating to the anterior surface of the neck are possible when the spinal column is involved due to rheumatoid arthritis. With collagenosis, along with local symptoms, signs of damage to other systems develop.
Lymphadenitis
Frequent causes of pain in the upper neck are inflammatory processes in the lymphoid tissue. Patients report severe local pain in the submandibular region on one side. The discomfort is aggravated when talking or tilting the head towards the affected area. The symptom is accompanied by a swelling ranging in size from a pea to a walnut. The skin over the formation is swollen and hyperemic. With inflammation of the lymph nodes, high body temperature, general weakness, and possible myalgia are observed. A similar clinical picture is also typical for lymphangitis.
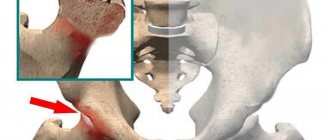
Damage to the cartilage of the larynx
Severe dull pain in the midline of the neck may be a manifestation of a tuberculous process in the cartilaginous tissue of the larynx. Men note local discomfort in the Adam's apple area. In addition to pain, prolonged low-grade body temperature and increased night sweats are detected. With chondroperichondritis of the larynx, sharp pain occurs in the upper and middle third of the neck. Also in this area, a round, painful formation is palpated, the skin over which becomes bright red. Symptoms are also caused by other causes: recurrent perichondritis, developmental abnormalities.
Angina pectoris
With atypical variants of angina attacks, instead of squeezing pain in the heart, patients feel pain in the front of their neck. The pain is very strong, combined with a feeling of lack of air, it becomes difficult to talk and swallow. In addition to pain, other symptoms are noted: severe weakness, cold sweat and paleness of the extremities, shortness of breath. Intense pain in the cervical region, arising against the background of discomfort in the heart, accompanied by a faint state, pallor and fear of death, may indicate the development of myocardial infarction.
Injuries
Severe pain can occur after blows to the front of the neck, sports injuries, or car accidents. In case of minor injuries or bruises, the pain syndrome persists for several days; breathing and swallowing problems are usually absent. With injuries to internal organs, primarily injuries to the larynx, patients complain of unbearable pain, which is combined with shortness of breath and hemoptysis. In any case, after injuries to the cervical region, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible to determine the extent of the damage and provide medical assistance.
Diseases of internal organs
In inflammatory diseases of the mucous membrane of the trachea or esophagus, pain can be localized in front along the surface of the neck. In this case, they are called referred pain. With esophagitis, in addition to pain, problems with swallowing are disturbed, constant heartburn and chest discomfort are observed. In the case of tracheitis, pain in the front of the neck occurs against the background of a painful dry cough, an increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels, and sometimes shortness of breath develops. Pain syndrome can be a sign of widespread mediastinitis involving the cervical tissue.
Rare causes
- Spinal lesions:
spinal osteochondrosis, ankylosing spondylitis, spinal stenosis and intervertebral hernia. - Tumor metastases.
- Staying in an awkward position for a long time
. - Congenital pathologies
: short neck syndrome (Klippel-Feil), hypoplasia of the axis tooth, accessory cervical rib syndrome. - Cervical compression syndrome
.
Why is this muscle needed?
It is this muscle that allows the cervical vertebrae to straighten when the spine is in the correct position. If the cervical flexure turns out to be straightened by the long muscle or the anterior major muscle, then it is this muscle that is responsible for flexing the neck. At the same time, it originates in the mastoid processes and is attached to the sternum and clavicles.
Functions include the ability to straighten the neck, as well as increase bilateral muscle contractions. It also provides a combination of tilting to the sides, in which the tilt is made towards the muscle that is contracting, and turning the neck in the opposite direction. Due to forced inhalation, the sternum and collarbone rise.
Diagnostics
If a patient’s neck hurts in the front, he needs to consult a general practitioner, who either prescribes an examination on his own or refers the patient to a specialist. The diagnostic search includes instrumental imaging techniques to identify pathological changes that are causing pain in the front of the neck. Laboratory methods are used to clarify the diagnosis. The most informative for identifying the cause of the disorder are:
- Ultrasonic method
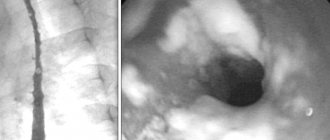
. Ultrasound of the neck allows you to study in detail the condition of soft tissues and organs in order to detect signs of inflammation, neoplasms and structural anomalies. A targeted scan of the thyroid gland is required to exclude an endocrine cause of pain in the front of the neck. - X-ray examination
. X-rays of the neck are performed to identify damage to the cartilage of the larynx and vertebrae. For more detailed visualization, computer and magnetic resonance imaging methods are used. During the examination, attention is paid to the presence of space-occupying formations, ulcers and median cysts of the neck. - Radioisotope scintigraphy
. A highly informative research method using a contrast agent is prescribed to assess the functional capacity of the thyroid gland and the degree of degenerative changes. If there is a defect in contrast accumulation, nodular formations are visualized; diffuse changes are characteristic of thyroiditis. - Electromyography
. To study the functional state of the neck muscles, the bioelectrical activity of individual muscle fibers is recorded. Depending on the method of performing the study, surface, stimulation and needle electromyography are distinguished. The technique allows us to identify the level of damage to the neuromuscular system. - Electroneurography
. A special study is recommended for plexitis and injuries of the cervical region to assess the speed of impulses along the peripheral nerves. This painless and non-invasive diagnostic method is necessary to accurately determine the location of nerve fiber damage and clarify the condition of the myelin sheath. - Laboratory research
. To confirm the cause of pain in the front of the neck, general and biochemical blood tests and a coagulogram are performed. Be sure to examine the level of thyroid hormones and insulin. If an infectious process is suspected, bacteriological culture of blood, throat swabs, and serological tests are indicated. - ECG
. To exclude myocardial ischemia, with a sudden onset of neck pain, which is accompanied by pale skin, dizziness, and cold sweat, an electrocardiogram is required. If pathological signs are detected on the ECG, an ultrasound of the heart and Dopplerography of blood vessels are additionally prescribed.
If suspicious mass formations of the thyroid gland are detected on radiographs, it is necessary to perform a biopsy of the node to exclude malignant degeneration of the cells. A diagnostic puncture of the lymph node may also be performed. To verify the rheumatic cause of neck pain, blood is examined for rheumatoid factor and specific antibodies. The patient may need to consult an osteopath or endocrinologist.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland
What will the specialist do at the appointment?
Approximate actions of a doctor, if there is a suspicion that the sternocleidomastoid muscle of the neck is damaged, would be as follows:
- To begin with, the specialist must study the patient’s complaints, which will suggest the direction in which to look for the cause.
- The doctor evaluates the movements that the patient can and cannot perform.
- Testing and diagnostics.
- Prescription of treatment.
- After treatment, a re-examination should be carried out.
- Treatment can be cyclical and may not help immediately, but only after several courses.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
The appearance of pain in the anterolateral cervical region is a sign of various diseases, therefore, to identify the immediate cause, consultation with a specialist is required. Before the diagnosis is verified, for severe pain in the front of the neck, it is allowed to take analgesics from the NSAID group to eliminate discomfort. Without a doctor's prescription, it is not advisable to use warm compresses or other local treatments on the cervical area, as this may aggravate the symptoms. It is important to limit movements in the cervical spine as much as possible.
Conservative therapy
Drug treatment is primarily aimed at eliminating the underlying disease as the cause of pain; symptomatic therapy is also required to relieve pain. For chronic pain, physiotherapy methods are indicated - electrophoresis with anti-inflammatory drugs and local anesthetics, laser therapy and UHF. In the acute period, physiotherapeutic treatment is undesirable. It is necessary to ensure maximum functional rest for the neck and head. The following groups of pharmaceutical drugs are most often prescribed:
- Analgesics
. Anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are widely used, which have a pronounced analgesic effect. They reduce the amount of pathological cytokines that irritate nerve endings and eliminate local signs of inflammation. - Antibiotics
. For purulent lesions, massive etiotropic therapy is needed to eradicate the pathogen. For common processes in the cervical tissue, a combination of two drugs is indicated. For tuberculosis, specific treatment regimens are selected. - Corticosteroids
. If the causes of pain in the neck are rheumatic diseases, long-term use of hormones is necessary. To quickly relieve exacerbations, pulse therapy with prednisolone is recommended. If ineffective, cytostatics may be added. - Antithyroid drugs
. For thyrotoxicosis of various etiologies, medications that selectively inhibit thyroid function are indicated. If a decrease in the endocrine function of an organ is determined, thyroid hormone replacement therapy is used. - Antianginal agents
. To prevent angina attacks, drugs that improve blood supply to the myocardium and antiplatelet agents are effective. The best therapeutic effect is provided by beta-adrenergic receptor blockers, calcium antagonists, and myotropic antispasmodics. - General strengthening therapy
. For lesions of peripheral nerves, B vitamins (especially thiamine) are prescribed, which improve the nutrition of nerve fibers and the speed of impulse conduction. Additionally, agents with an anabolic effect are recommended.
Surgery
For unbearable pain in the neck, local anesthesia is performed in the form of novocaine blockades. When an abscess forms in the retropharyngeal space or in the case of suppuration of a median neck cyst, prompt opening of the abscess and provision of adequate drainage is necessary. After dissecting the abscess capsule, be sure to wash the cavity with solutions of antibiotics and antiseptics. When sialoadenitis is complicated by strictures of the excretory duct, its bougienage is required, followed by the introduction of proteolytic enzymes.
In case of proliferation of nodular goiter of the thyroid gland, which is accompanied by pain and compression syndrome, surgical interventions of various volumes are indicated. If the function of the rest of the organ is preserved, enucleation of the node is performed; in case of diffuse pathology, hemithyroidectomy or subtotal resection of the thyroid gland is performed. In case of severe neck injuries with damage to internal organs, revision, removal of bone fragments and elimination of defects of hollow organs are performed.
Is it possible to train muscles at home?
Naturally, you can train your neck muscles at home. The main thing is to choose the right exercises that will suit your characteristics. The ideal option would be for the complex to be selected by a specialist in this field. The workout does not require any special equipment, making it accessible to most people.
This way you can use self-resistance exercises, and you only need to do six exercises, which won’t take much time. Decide for yourself, because the complex can be used as a main one and as a warm-up. The exercise should be performed in three sets of about 10 repetitions each time.
- The base of the palms should rest against the chin, the neck muscles should fight against the resistance exerted by the arms, and the neck should bend towards the chest. Then, using our hands, overcoming the resistance of the neck, we move our head back. The method is attractive because you can independently regulate the resistance force exerted and, if necessary, increase or decrease it.
- Palms clasp at the back of the head, you will need to overcome the resistance of your hands and tilt your head back. And also, through the effort of the hands, return the head to its original position until the chin touches the chest.
- The right palm should be leaning against the cheek, while you will have to overcome the resistance of the hand and tilt your neck to the right side. And then, with the help of the right hand, the resistance will be overcome until the head tilts to the left.
- We perform a similar action on the left side. That is, the left palm is applied on the left side, the neck tries to cope with the resistance provided.
- The heel of the palm of the right hand rests on the chin, the neck muscles must fight against the resistance that the hand provides. At the same time, the head turns to the right side. From the same position, the hand applies force and turns the neck and head to the left.
The exercise is similar to the previous one, only the left hand should work.
Remember that you should first stretch your neck, move your head, bend, and twist to prepare the muscles.
In many ways, the condition of the neck and sternocleidomastoid muscle depends on the person himself; when problems arise, we go to a specialist or rush to take a pill. But it’s worth first wondering if we did anything to prevent such a problem.
Vessels
Arteries of the Head and Neck: Anatomy, Diagram, Atherosclerosis
Feb 06, 2021 Kokh V. A.
19196
Vessels
Transverse Cervical Artery
Feb 06, 2021 Kokh V. A.
10697
Vessels