- Answers
Kostevich Galina Vladimirovna - Category:
Gynecologist-oncologist of the highest category - Experience: more than 25 years
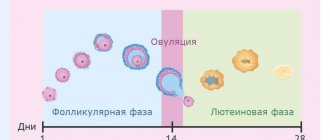
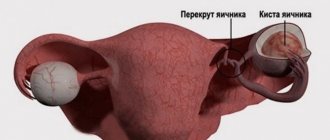
Among the dangerous gynecological diseases, rupture of ovarian tissue or apoplexy is especially distinguished. The pathology is accompanied by a sharp attack of pain in the lower abdomen and hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity. This serious disease usually affects women of reproductive age. An active inflammatory process provokes pathological changes in blood vessels. It is this that most often causes rupture of follicle vessels, follicular cysts or corpus luteum cysts. A favorable period for the occurrence of such a pathology is the period of ovulation or the stage of vascularization of the corpus luteum.
Classification of the disease: forms and degrees
Depending on the prevailing symptoms, the disease is expressed in certain clinical forms.
- Painful rupture of the ovary, in which severe pain and attacks of nausea are noted. There are no signs of internal bleeding.
- Anemic apoplexy with a predominance of weakness, dizziness, fainting and signs of hemorrhage in the abdominal cavity.
- A mixed form, combining the symptoms of painful and hemorrhagic forms of apoplexy.
Considering the fact that the disease is accompanied by bleeding of a certain level of severity, doctors classify the pathology according to severity. Mild, moderate and severe degrees depend on the amount of bleeding. In the first degree, the patient loses about 150 ml of blood. The volume of lost blood in the second degree approaches 500 ml. With the third degree of apoplexy, blood loss exceeds 500 ml.
Advantages of MC “HEALTHY FAMILY”
WE USE ONLY EUROPEAN, AMERICAN AND SOUTH KOREAN DRUGS ALL DRUGS ARE CERTIFIED YOUR COSMETOLOGIST HAS ABOUT 30 YEARS OF EXPERIENCE LOW PRICES FOR 100% US WE HAVE BEEN WORKING FOR COSMETOLOGICAL SERVICES OVER 1000 PATIENTS SINCE 2006 LOW COST OF BOTOX FROM 200 RUB. PER UNIT WE PROVIDE MORE THAN 5,000 COSMETOLOGY PROCEDURES PER YEAR
At what size does an ovarian cyst rupture?
A cyst whose diameter exceeds 2 centimeters is considered potentially dangerous. Without proper treatment and constant monitoring, it can lead to a number of serious complications: hemorrhage, suppuration, torsion.
The size of the formations can vary from 20 mm to 22 cm in diameter. Small formations up to 1 cm most often are not treated and resolve on their own within 1-3 cycles. Capsules with a diameter of 4 centimeters or more pose a serious health hazard. When they rupture they cause severe bleeding.
Rupture of an ovarian cyst in women
Apoplexy can happen at any time, but most often it is provoked by a combination of several factors. Cysts are particularly affected by:
- Pregnancy. During pregnancy, the possibility of apoplexy remains due to excess pressure on the uterus or possible hormonal imbalance. Therefore, if a pregnant woman is diagnosed with a capsule measuring 8 cm or more, surgical intervention is prescribed.
- Menstruation. At this stage, the formation is prone to resorption, but with regular exercise or intense sexual relations, a rupture may occur.
- Disruptions in the production of hormones. If there are disruptions in the menstrual cycle or lack of ovulation, multiple neoplasms may occur that tend to rupture under the influence of external factors.
- Poor blood clotting. The rupture of a cyst in combination with this feature of a woman can provoke severe bleeding.
When diagnosing a cyst, it is important to follow the doctor’s instructions to prevent new problems with the body.
What is the pathology fraught with?
When the first signs of the disease appear, the patient must be taken to the clinic immediately. Otherwise, apoplexy can cause serious complications. The main thing for a woman is to preserve her reproductive function. This is only possible with professional medical assistance.
Ovarian apoplexy can be treated conservatively. However, sometimes blood entering the abdominal cavity can cause aseptic inflammation. As a result, adhesions may form. They will provoke a violation of the ovary and the tissues located near it. In this case, it will not be possible to avoid such a complication as the development of infertility. The patient's reproductive function will cease to exist.
A minor degree of bleeding cannot be compared in terms of danger with severe blood loss. However, such a symptom cannot be ignored. After all, the consequences can be very different:
- inflammatory process of the pelvic organs;
- repeated hemorrhage in the ovarian area;
- inflammation of the abdominal cavity;
- development of the adhesive process;
- infertility or loss of reproductive function.
The severe clinical form of apoplexy already by its name speaks of dangerous complications. Removal of the ovary, infertility and even death if the bleeding is not stopped in time.
The presence of this pathology cannot prevent conception. The threat lies in the adhesions of the ovary and fallopian tube, which will not allow fertilization to occur. After apoplexy, a woman may have an ectopic pregnancy. If the disease occurs in a pregnant woman, a miscarriage may occur. Although the operation is possible by laparotomy.
Strictly following the advice of doctors and carefully observing all treatment conditions will help avoid negative consequences after surgery. Patients are prescribed physiotherapy sessions and a course of anti-inflammatory treatment. It is important to properly take hormonal and contraceptive medications prescribed by your doctor. Only competent treatment will ensure a favorable outcome of the disease.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is the main method of treatment for ruptured ovarian cysts. Laparoscopy minimizes the likelihood of adhesions forming. If symptoms appear, we recommend that you immediately seek qualified help, as any delay can lead to blood loss and serious consequences.
Currently, gynecologists perform the following types of surgical interventions when a cyst ruptures:
- unilateral oophorectomy - removal of the affected ovary;
- ovarian resection - excision of a section of a damaged organ while preserving its function;
- tubovariectomy - removal of the uterine appendage.
Operations are performed laparoscopically or laparotomically. In the first case, all manipulations are performed through small punctures in the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall, using special instruments. The laparotomy method involves making a large incision in the lower abdomen, along the midline.
The main advantages of minimally invasive surgery include:
- minor injuries;
- less medication load;
- fast recovery.
Despite this, the final decision regarding the method of surgical treatment is made by the attending physician, taking into account all the individual characteristics of the patient.
What kind of prevention should be carried out?
In order for a woman not to suffer the sad fate associated with this pathology, it is necessary to take care of her health. Even if you feel excellent, go to the gynecologist for an examination every six months. If there are gynecological problems, be observed regularly. Patients with adnexitis, oophoritis, polyendocrine syndrome or STDs must definitely treat their disease.
Women who have suffered from ovarian apoplexy should take care to ensure that there is no relapse. One of the preventive measures is complex treatment to normalize the menstrual cycle and improve blood supply.
Patients who have undergone surgery are required to monitor the restoration of hormonal levels and the normalization of blood circulation. They are advised to take nootropics and tranquilizers. Under no circumstances should you refuse such drugs. The use of multiphase oral contraceptives will ensure normalization of hormonal levels and help prevent ovulation. It is better not to plan pregnancy during this period. It is necessary to wait for the body to fully recover and become stronger. Then you can confidently hope for a successful pregnancy and birth of a healthy baby.
Observation by a doctor is considered mandatory.
Rehabilitation
After ovarian apoplexy, patients are shown rehabilitation to restore normal blood flow in the pelvic organs, as well as correct hormonal levels. The doctor will pay special attention to the central nervous system; you may need to consult a specialist.
Patients are prescribed Laennec therapy, massage, mud therapy, and gynecological massage. All these methods of postoperative recovery will help normalize blood circulation in the genital organs.
In the absence of contraindications, sanatorium-resort treatment is possible, where the above methods of rehabilitation of patients with gynecological diseases are practiced. With high-quality rehabilitation, women will be able to recover quickly enough both after surgery and after conservative treatment of the disease.
Why does ovarian tissue rupture?
This pathology occurs when the permeability of ovarian vessels is impaired. The reason may lie in the specific characteristics of the ovarian tissue itself. If the patient suffers from inflammation of the appendages, polycystic ovary syndrome, or has had abortions, sclerotic or degenerative changes in the tissue occur. This is the kind of disease that may appear. Ovarian apoplexy often occurs:
- if the woman had abdominal injuries;
- she was fond of horse riding;
- if the patient has experienced excessive physical activity;
- did douching;
- had an active sexual relationship with a partner.
Sometimes rupture of ovarian tissue is associated with a congenital pathology of the location of the uterus. Even ordinary squeezing of blood vessels can disrupt blood flow to the ovary. Quite often, rupture of organ tissue occurs spontaneously. Such an incident can occur while a woman is sleeping.
Inflammatory processes of the abdominal organs, blood diseases of various types, too long use of anticoagulants that disrupt the clotting process can provoke the onset of the disease.
Data from statistical studies show that ovarian apoplexy occurs at a certain period of the menstrual cycle. Usually this is the middle or second half. It is at this time that the level of vascular permeability in the ovarian tissue is very high. They undergo increased blood supply. Most often, the pathology is inherent in the right ovary. After all, the degree of blood circulation in it occurs much more intensely in comparison with its left counterpart. The reason is that the right ovarian artery arises from the aorta, and the left from the main vessel of the kidney.
Causes
Ovarian rupture can be provoked by both pathologies of the organ itself and other dysfunctions in the functioning of the body. Doctors identify the following reasons:
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- blood coagulation pathologies with long-term use of anticoagulants;
- acute and chronic adnexitis;
- pathologies of blood vessels - varicose veins, atherosclerotic changes;
- stimulation of ovulation with medications;
- abnormal position of the uterus, compression of the ovaries;
- the presence of adhesions;
- abdominal injuries;
- increased pressure in the peritoneum as a result of physical stress;
- hormonal disorders;
- emotional instability, stress.
Diagnosis of ovarian apoplexy
The rate of correctness of determining the clinical picture of the disease is only 5%. This indicates that there are no obvious symptoms of the disease. They are similar to other pathologies of the pelvic or abdominal organs.
When a patient's life is at stake, a diagnosis must be made immediately. What diagnostic methods are the most effective?
- Laparoscopy . A fairly accurate method of research. The clinical picture is a spot with a diameter of 0.5 cm. Hemorrhage is observed in the form of a corpus luteum with a rupture or a pronounced tissue defect. In this case, bleeding is detected.
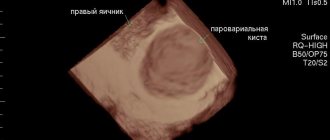
- Ultrasound diagnostics . Ultrasound of the pelvic organs allows you to clearly see the large corpus luteum of the ovary with bleeding into it. May detect the presence of free fluid in the abdominal area or posterior fornix.
- General blood analysis . A reduced hemoglobin level will be clear evidence of an organ rupture.
- Performing a puncture of the posterior fornix . It will allow you to clarify the presence or absence of hemorrhage in the abdominal cavity.
The final diagnosis will be made only during the operation.
Contraindications for surgery
Surgical treatment to eliminate apoplexy is contraindicated in the presence of:
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Colds.
- Previously suffered myocardial infarction.
- Heart failure.
- Hypertension.
- Oncological formations on other internal organs.
Laparoscopy is also not performed if the patient is highly obese, has poor blood clotting, or has a large formation.
Postoperative period
Upon completion of the operation, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, painkillers, vitamin complexes, as well as drugs for postoperative treatment of ovarian cysts. Additionally, you must adhere to a diet. You will only be able to eat:
- Liquid soups.
- Porridge.
- Freshly squeezed juices.
- Steamed vegetables and fruits.
Over time, restrictions are lifted.
To speed up the healing of sutures, the doctor prescribes wearing a special bandage. Full recovery of the body after surgery takes about 3-4 weeks. During this period, intimacy, as well as heavy lifting and physical activity, are contraindicated.