general information
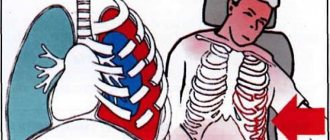
There are 12 pairs of intercostal nerves in the human body. They originate from the roots of the thoracic spinal cord and cover the entire chest, adjacent to the peritoneum, muscles, skin and mammary glands. The individual fibers of each nerve are responsible for tissue sensitivity, motor function and regulation of the functioning of all structures. Accordingly, damage or inflammation in any area can radiate pain to a variety of parts of the body.
The sensations can imitate diseases of internal organs: myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, pancreatitis, gastritis, cholecystitis, etc. In some cases, only a doctor can accurately determine the nature of the pain after a full examination. That is why it is important to seek help promptly if chest pain occurs.
Make an appointment
Localization of pain
- Referred pain. Referred pain, as a rule, is a consequence of the development of a pathological process in the internal organs (diseases of the retroperitoneum, aortic aneurysm, pathology of the digestive tract, coronary artery disease).
- Radiating pain. The mechanism of development of this pain has not been fully studied to date. According to experts, parts of the nervous system may misinterpret the source of pain due to the presence of common pathways through which both visceral and somatic pain are carried out. Referring pain, resulting from stretching, irritation or compression of a somatic nerve or nerve root, is more intense. With physical activity, sneezing or coughing, the pain may intensify, and can often spread to the affected area of the body.
- Local pain. Its cause can be any pathological process aimed at pain receptors of various tissues, muscles, ligaments, skin, tendons, bones, joints, etc. In this case, pain develops directly in the area of damage.
Forms
There is no special classification of the disease. There are several separate forms depending on the mechanism of occurrence:
- radicular: associated with irritation of the spinal cord roots at the point of their exit from the spinal column;
- reflex: associated with overstrain of muscle fibers at the site of the nerve passage.
There is also a classification of neuralgia depending on:
- causes: primary (associated with damage or inflammation of the nerve itself) and secondary (due to other diseases);
- localization: unilateral and bilateral;
- course of the disease: acute and chronic.
Consequences
Patients are concerned about the dangers of thoracalgia. The pathology itself is not fatal, but due to constant pain, which is accompanied by nervous tension, the risk of angina pectoris, hypertensive crisis (a sharp increase in pressure), and sometimes heart attack increases.
If left untreated, thoracalgia can cause heart disease
The consequences affect the patient’s daily life, insomnia occurs, work ability and quality of life decrease due to severe pain. In the absence of timely treatment, the disease becomes chronic.
Causes
The list of main causes of intercostal neuralgia includes:
- degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine: osteochondrosis, arthrosis, hernias and protrusions of discs, etc.;
- uneven or excessive load on the spine and back muscles (due to carrying heavy objects, poor posture, etc.);
- spinal column deformities (primarily scoliosis);
- diseases of the nervous system, in particular multiple sclerosis;
- infectious lesions: tuberculosis, herpes zoster, influenza;
- injuries of the spine and chest, surgical interventions in this area;
- tumors in the ribs, sternum, spinal column;
- taking certain medications;
- increased load on the respiratory muscles and abdominal muscles;
- increased intra-abdominal pressure, including during pregnancy.
In addition, intercostal neuralgia can occur secondary to other diseases, for example, pleurisy, pathology of the digestive system, kidney disease, thyrotoxicosis, and immunodeficiency states. Adolescents during the period of active skeletal growth may also experience similar symptoms.
Symptoms
The main symptom of intercostal neuralgia is severe pain in the chest along the nerve. As a rule, it occurs suddenly and resembles an electric shock, gradually spreading along the ribs. The nature of the sensations can be different: shooting, pulsating, constant, burning or dull.
Deep breathing, turning the head or body, bending, pressing or simply touching the chest causes a pronounced increase in pain. In addition, characteristic signs of neuralgia are:
- persistence of pain at night;
- the ability to determine the epicenter of pain;
- redness or paleness of the skin in the affected area;
- a feeling of tingling, crawling or, conversely, numbness along the affected nerve;
- slight muscle twitching in the affected area.
As a rule, during an attack of neuralgia, a person tries to lie or sit motionless in a position in which the pain becomes slightly less.
If the cause of the pain syndrome is herpes zoster, first redness appears on the skin along the affected nerve, then numerous blisters that burst, forming crusts. After recovery, increased pigmentation remains in this area for some time.
Differences from myocardial infarction
Chest pain, especially on the left, can be a consequence not only of intercostal neuralgia, but also of more serious problems. The most dangerous is myocardial infarction. This condition requires emergency medical attention. The characteristic differences in pain are:
- occurrence against the background of physical, less often psycho-emotional stress;
- spread to the left arm, shoulder, left half of the neck and lower jaw;
- no changes when turning the body, bending, pressing on the sore area;
- decreased intensity when taking nitroglycerin and its analogues.
A heart attack is often accompanied by cold, sticky sweat, pale skin, dizziness, and fear of death.
It is important to remember that the signs of a cardiovascular accident and intercostal neuralgia are not always so radically different. An accurate diagnosis can only be made by a doctor.
Analgesics
A number of patients do without medications in this group, but if the patient experiences severe pain attacks, then it is necessary to relieve them with painkillers. The most popular analgesics based on analgin are Baralgin, Sedalgin, Spazmalgon. As soon as severe pain subsides, you should stop taking them.
These tablets also have a number of disadvantages and side effects, in particular on the digestive tract. If the patient additionally uses ointments and creams with an anesthetic component, then it is necessary to take into account the total amount of the product that the patient receives.
Diagnostics
Intercostal neuralgia, regardless of the severity of the pain syndrome and its location, requires a full diagnosis. The following examinations will help distinguish it from other pathologies:
- questioning and medical history: identifying the nature of the sensations, the conditions of their occurrence, the duration of the attack, concomitant diseases;
- examination and palpation: the doctor evaluates the appearance of the skin, checks the reaction to movements, pressing, turning, bending, assesses the severity of reflexes;
- laboratory diagnostics: general and biochemical blood tests, general urine tests: allows to identify signs of damage to the heart muscle (tests for troponins, CPK), inflammation, renal pathology, gastrointestinal diseases, etc.; the exact set of tests depends on the location of the source of pain;
- ECG, ultrasound of the heart: allow you to identify or exclude cardiovascular pathology;
- X-ray, CT or MRI of the thoracic spine: helps to identify osteochondrosis, osteoporosis, tumors, hernias and protrusions of intervertebral discs, etc.;
- Chest x-ray: allows you to assess the condition of the lung tissue and identify signs of tumors;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, abdominal organs (excludes relevant pathology);
- FGDS to exclude pathologies of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum;
- myelography, contrast discography, electrospondylography to assess the condition of the spine, intervertebral discs, spinal cord and its roots.
If necessary, consultations with narrow specialists and additional examinations are prescribed.
Make an appointment
Treatment
Intercostal neuralgia requires complex and often long-term treatment, including medication, physiotherapy, massage, etc.
Drug therapy
In the acute phase of the disease, therapy is aimed at relieving pain and improving the patient's condition. Depending on the specific clinical situation, the following are prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): products based on diclofenac, nimesulide, ibuprofen, meloxicam and their derivatives; used in tablet, injection and local (creams, ointments, patches) form;
- analgesics: analgin and products based on it; like NSAIDs, they relieve pain;
- muscle relaxants to eliminate muscle spasms: mydocalm, etc.;
- group vitamins: milgamma, neuromultivitis, etc.; necessary to restore normal functioning of nerve fibers;
- sedatives to reduce the psycho-emotional component of pain and improve sleep.
If necessary, the following may additionally be prescribed:
- anticonvulsants: inhibit the passage of pain impulses;
- antidepressants to relieve tension;
- antihistamines and diuretics: relieve tissue swelling, especially relevant for pinched nerve roots;
- antiviral drugs for herpes zoster;
- glucocorticosteroids for persistent pain and severe inflammation that cannot be relieved by milder means.
Physiotherapy and exercise therapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed after the acute pain subsides. Help speed up recovery:
- UHF;
- reflexology;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- laser treatment;
- paraffin applications;
- mud therapy.
These procedures help improve blood circulation and metabolism in the affected area and accelerate the regeneration of nerve tissue.
Physical therapy exercises are prescribed after complete recovery. The main goal of gymnastics is to unload the back muscles. The complex is developed individually. The first classes should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist; in the future, home exercises are allowed.
Other treatments
Since very often the cause of intercostal neuralgia is pathology of the spine and spinal cord, the following are often used as additional methods of influence:
- acupuncture;
- manual therapy;
- therapeutic massage, including the use of warming agents;
- Shiatsu massage (acupressure);
- osteopathy;
- underwater traction and other techniques.
Like all medical procedures, these techniques are used only in a clinical setting and are carried out by specialists with medical education and the appropriate certificate.
Intercostal neuralgia is
Intercostal neuralgia or thoracalgia is acute pain in the area of the nerve between the ribs . The disorder is provoked by injury, inflammation, osteochondrosis, displacement of spinal discs and some other factors.
When the nerve roots between the ribs become inflamed or irritated, intercostal neuralgia is diagnosed.
Malaise due to neuralgia is localized in the intercostal spaces, along the spinal column and chest, in the back area. Often the manifestations of the disease radiate to the shoulder, arm or shoulder blade. Pain occurs especially often in the area between the fifth and ninth ribs on the left side.
Classification
Thoracalgia can be classified on several grounds:
| According to the nature of the flow: | By external manifestations: | Due to development: |
| acute - rapidly progressing | unilateral - pain appears on only one side | radicular - formed as a result of pinching of nerve roots in the spinal column |
| chronic - has a protracted nature | bilateral - pain can radiate to both the right side and the left | reflex - is a consequence of muscle spasm in the space between the ribs |
Complications
Complications of intercostal neuralgia occur quite rarely, however, in severe cases, without appropriate treatment, the patient may encounter the following problems:
- severe spasm of the respiratory muscles, limiting inhalation and exhalation;
- inability to get out of bed due to significant increase in pain;
- excessive pain syndrome that is not relieved by conventional analgesics and NSAIDs;
- heart rhythm disturbances due to muscle spasms and nerve pathology;
- decreased leg mobility.
In addition, complications can be caused by attempts to be treated outside the clinic. Abscesses and cellulitis after acupuncture, paralysis and decreased sensitivity after manual therapy are not a complete list of problems. That is why you should not treat intercostal neuralgia either independently or with the help of dubious specialists.
Non-drug therapy
Intercostal neuralgia can be treated without the use of medications using the following methods:
- Using massage movements of the hands with a warming ointment or cream applied to them, deep warming and relaxation of the muscles that create a protective “corset” (or, conversely, leading to compression of the intercostal nerve) is achieved. It is performed in a sitting position with rubbing and stroking the intercostal spaces with the fingertips and subsequent kneading of all the spinal muscles.
- Unlike the previous method, acupressure applies pressure to the physiologically and bioenergetically massaged chest points associated with the diseased organ, leading to pain relief, relaxation and a quick effect by stimulating the body’s own defense mechanisms.
- Similar physiologically and bioenergetically justified effects are the methods of acupuncture (acupuncture), cauterization, and laser therapy, which make it possible to quickly neutralize muscle imbalance in the deep back muscles with the elimination of pain.
- Treatment of intercostal neuralgia by placing massage cups on the back pursues the same goals, being a simple and harmless technique for the body (provided there are no contraindications to its use).
- Manual techniques are resorted to after the end of the acute period. They consist in returning to their proper places the bone structures and muscles and ligaments that serve them that have been displaced during the disease and are carried out exclusively after manual diagnosis. As a result of the impact, the diameter of the narrowed tunnels (bone-tendon and musculoskeletal) returns to normal and the function of the pinched nerve is restored.
Like all the above methods, physiotherapeutic methods using:
- magnetic or electromagnetic field;
- ultrasonic, ultraviolet and infrared radiation;
- electro- and iontophoresis, with a dose of the drug substance that is minimal for the risk of the fetus.
Prevention
Prevention of intercostal neuralgia is mainly general measures aimed at strengthening the muscle frame and improving the health of the body. Neurologists recommend:
- lead an active lifestyle, play sports at an amateur level;
- minimize hypothermia and colds;
- watch your posture;
- avoid lifting heavy objects;
- maintain a high level of immunity;
- eat a balanced diet, if necessary, take additional vitamins, especially group B;
- treat chronic diseases in a timely manner;
- avoid stress, get proper rest and ensure yourself at least 8 hours of sleep every night.
Following these simple rules will significantly reduce the risk of developing intercostal neuralgia.
Antiviral agents
They are similar to NSAIDs, but act against other pathogens: not bacteria, but exclusively viruses. In practice, they are used extremely rarely in the treatment of joint and neurological diseases. A viral infection of the onset of inflammation can be suspected if intercostal neuralgia occurs in a herpetic nature. Among the external manifestations is herpes zoster.
The most well-known remedy that will help the patient cope with the herpes virus is Acyclovir. Its analogues: Zovirax, Cyclovir, Vivorax. People with weakened immune systems most often suffer from local exacerbations of herpes infection, and therefore it makes sense to check the body for a number of other chronic diseases that lead to a similar weakened state.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
Doctors at the Energy of Health clinic will always come to the aid of patients with intercostal neuralgia. We offer each client:
- a full examination with consultations with specialists for an accurate diagnosis;
- individual selection of treatment regimen;
- services of a qualified chiropractor;
- own exercise therapy room for the most effective and safe exercises;
- modern methods of physiotherapy;
- massotherapy;
- drug blockades for severe pain syndrome.
Regular observation by a neurologist after the acute period of the disease has subsided will help prevent recurrent attacks.
Advantages of the clinic
In the neurology department of the Energy of Health clinic, every patient receives the highest level of specialists and modern equipment for diagnosing and treating diseases. We take an integrated approach to therapy and use not only medications, but also physiotherapy, exercise therapy and massage.
Treatment is prescribed only after a thorough examination and is monitored by a specialist until the patients fully recover. Adequate prices, convenient location, private parking - we do everything for the convenience of our clients.
If intercostal neuralgia interferes with living, walking and moving, do not delay treatment. Sign up for the Health Energy clinic and get rid of pain.