The name of the disease, gout, is probably known to everyone. But when the first symptoms of gouty arthritis appear, few people remember it. It happens that after festive libations or a rich table at a corporate party, sudden pain in the legs may occur - it risks remaining unrecognized until the first tophi appear. It is these nodes, disfiguring the joints of the limbs, that are commonly considered the main sign of gout. But these compactions in the subcutaneous tissue do not appear soon, 5-10 years after the onset of the disease.
Meanwhile, gouty arthritis affects every 20th elderly person and can be a harbinger of other, even more serious diseases. Let's figure out what this disease is and how you can fight it.
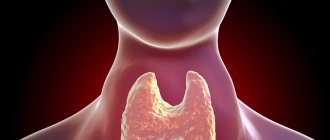
What happens to joints with gouty arthritis?
Being a metabolic disorder, gout is associated with insufficient excretion of uric acid by the kidneys. Because of this, breakdown products begin to accumulate in the blood (in particular, in plasma), causing hyperuricemia. Hyperuricemia itself does not mean the onset of gout - it can occur as a result of excessive fatty foods or physical overload. However, this pathology causes damage to the renal glomeruli and gradually leads to kidney damage and, as a consequence, gouty arthritis. The symptoms of gouty arthritis cannot be ignored - they seem to warn the patient of even more serious complications. Thus, excess uric acid in the blood negatively affects the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
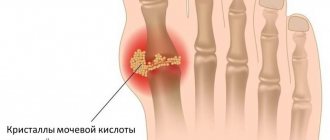
Over time, monosubstituted sodium urate crystallizes in the joints, kidneys, forehead, earlobes and other tissues 5-6 years after the onset of the disease, causing thickening of the connective tissue (tophi). Over time, tophi can grow in clusters on the affected areas, reducing the quality of life of patients and requiring treatment of gouty arthritis with drugs.
Often the consequence of gouty nodes is inflammation of the periarticular bursae and tendons. It not only causes pain in the joint, but also gradually leads to a limitation of its mobility. Gout is accompanied by extensive erosion of the articular surfaces caused by calcium deposits in adjacent tissues, as well as impaired formation and destruction of bone tissue.
The disease also leads to the formation of kidney stones (uric acid stones), a chronic inflammatory process and renal colic.
Sources of Selenium – Important Prerequisites for Taking Selenium Supplements
- Large amounts of selenium are found in meat and offal, fish and crustaceans, grains and dairy products, chocolate and fruits.
- Garlic, onions, dry legume seeds, broccoli, white cabbage and asparagus are rich in this mineral.
- Nuts and mushrooms are also good sources of selenium.
Selenium is best absorbed together with protein and vitamins A, C, E. The absorption of the element increases with its deficiency in the body. High levels of sulfur and heavy metals in food reduce its absorption.
You can compensate for selenium deficiency in the body by eating foods rich in this element or using medications from the pharmacy. In case of excess, it is recommended to include foods with reduced selenium content in the menu and stop taking supplements.
We must not forget that adding any elements or vitamins cannot replace a healthy and balanced diet and should not be done without consulting a doctor. In some cases, selenium supplementation may be required in appropriate doses. However, before you start taking it, you should check the level of selenium in the blood, because its excess leads to side effects, and the difference between a therapeutic and a toxic dose is small.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Risk group for gouty arthritis
Gout is a disease with severe comorbidity, i.e., it often accompanies other chronic diseases, such as type II diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension and other cardiovascular pathologies, Gierke's disease, and chronic renal failure. When deciding how to treat gouty arthritis, these pathologies cannot be left without treatment. In addition to the factors mentioned, an increased risk of gouty arthritis creates:
- excessive consumption of foods containing purines, chemical precursors of uric acid;
- antitumor therapy;
- the presence of autoimmune diseases and problems with the genitourinary system;
- alcohol abuse;
- shock and stress (including due to overwork);
- genetic predisposition;
- hormonal imbalance;
- taking medications that increase the production of uric acid;
- high-carbohydrate diet, especially with active consumption of processed foods;
- insufficient or unbalanced nutrition;
- infectious diseases;
- injuries;
- hypothermia.
It is noted that men over 40 years of age need treatment for gouty arthritis approximately 12 times more often than women.
Causes of selenium deficiency
The level of selenium in food depends greatly on its content in the environment: soil and water. In areas where the soil is poor in selenium, deficiency is more common in people. The classic example is China. But the selenium content in the soil in Poland and other European countries is also low, so the amount of selenium in the diet may not be enough.
Selenium deficiency can also be caused by an improperly balanced, heterogeneous and unhealthy menu. Malnutrition, bowel disease, kidney or liver failure, and cancer can all contribute to selenium deficiency in the body.
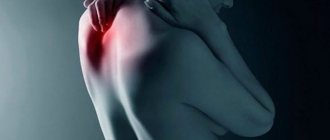
Symptoms of gouty arthritis
Symptoms and treatment of gouty arthritis may vary depending on the period of the gout disease - latent, acute or chronic. And if during the latent stage only a biochemical test of blood or urine helps to reveal the disease, then an acute gouty attack cannot be missed. The attacks occur irregularly, the intervals between them vary from a couple of weeks to a year or more. Gout is characterized by pain when moving and pressing on the tissue around the affected joint: negative symptoms usually increase at night.
The disease usually affects the small joints of the extremities; in 9 out of 10 cases, the big toe is the first to be affected.
The clinical picture of gouty arthritis in the chronic stage (when pain lasts 3 months or more) implies the presence of exacerbations and remissions. In later stages, deformation of the affected joints and limbs is observed.
By the way, the level of urate in the blood can remain low even despite solid deposits in the joints, ears and adjacent tissues.
Important: arthritis and osteoarthritis contribute to the localization of gouty joint lesions in the affected areas. In this case, differential diagnosis of the two diseases, which can only be carried out by a doctor, is especially important.
Diet for gout: diet
If you have gout, it is very important to follow a proper diet. You should eat regularly, 4 times a day. Overeating and starvation are unacceptable - this can provoke an attack. Patients with gout need to fight excess weight, but sudden weight loss is undesirable.
The diet for gout must include a sufficient amount of fluid - at least 1.5 - 2 liters, and during an exacerbation - up to 3 liters. This can be mineral water, compotes, fruit drinks, weak tea. Rosehip decoction is very useful. It is advisable to drink between meals.
Acute gouty arthritis
Acute gouty arthritis occurs as a consequence of hyperuricemia, which is asymptomatic. At the same time, kidney stones may occur. If left untreated, this condition can lead to frequent pyelonephritis, nephrosclerosis and renal failure within 3-4 years. Symptoms of this pathological condition include:
- fever, which is accompanied by severe pain and inflammation in the joints;
- The 1st day of pain is the most painful;
- the skin over the sore joint turns red and becomes hot;
- the joint of the big toe (first metatarsophalangeal) is swollen and very painful;
- asymmetric swelling of the joints.
Symptoms and treatment of acute gouty arthritis should be determined by a doctor by palpation, radiography and culture of synovial fluid.
Our advantages
In medical diagnostics of gout and its treatment is carried out using the latest methods. Reception is carried out by highly qualified doctors with many years of experience in the treatment of rheumatic diseases.
Here you can consult with doctors who are directly involved in the diagnosis and treatment of gout.
Our clients are provided with information about:
- the causes of gout in your particular case;
- modern diagnostic methods using the latest equipment, eliminating the possibility of error;
- suitable treatment methods - therapy is selected individually, taking into account the presence of concomitant diseases;
- diet to prevent disease.
The professionalism of our specialists and the use of progressive techniques allows us to achieve significant success in the treatment of complex rheumatic pathologies.
How to treat gouty arthritis
Being, in fact, one of the chronic arthritis, gout is treatable much better than other joint diseases. Although a complete cure is not possible, metabolic disorders can be controlled through medication, physical therapy and diet.
The treatment regimen is determined individually. It may include measures to relieve exacerbations and pain attacks, prevent relapse, and eliminate discomfort from a chronic disease
If a patient's gouty arthritis does not have a genetic etiology and is not associated with other chronic diseases, its course depends entirely on the patient's compliance with the therapeutic regimen, in particular, a diet with a reduced purine content.
Regular monitoring of uric acid levels and a course of enterosorbents are also recommended. Gout is not treated surgically, however, if the tophi grows excessively, a minor operation may be performed for the patient’s convenience.
Clinical recommendations for gouty arthritis necessarily include losing excess weight.
Treatment of gouty arthritis with medications
A comprehensive treatment regimen for gouty arthritis with medications includes anti-inflammatory drugs (steroidal or non-steroidal, depending on the condition), uricodepressive, uricosuric and uricolytic drugs. After the inflammation is relieved, the primary goal of therapy is to stimulate the excretory function of the kidneys, due to which the level of uric acid in the patient’s body decreases.
Physiotherapy in the treatment of gout
Physiotherapeutic techniques for the treatment of gouty arthritis are primarily aimed at alleviating pain symptoms and stimulating metabolic processes in tissues. The best effect is demonstrated by:
- high-frequency magnetic therapy;
- UV irradiation in erythemal doses;
- Low intensity UHF therapy;
- centimeter wave therapy;
- DMV therapy for the adrenal glands.
If the mentioned types of therapy are contraindicated for the patient, treatment with leeches is possible.
Diet for gouty arthritis
Diet plays a leading role in discussions about how to treat gouty arthritis. To keep the symptoms of gouty arthritis under control, it is essential to follow a low-carbohydrate diet with minimal purine levels. And although these compounds are found in all foods without exception, it is important to exclude their main sources:
- meat, fish and other broths;
- offal, lard;
- canned food;
- tomatoes, potatoes and other nightshade plants;
- legumes (especially beans, peas, lentils).
Consumption of meat and fish should be reduced as much as possible. Milk and fermented milk products and eggs are used as sources of protein in the anti-gout diet. It is recommended to minimize the consumption of chocolate, mushrooms, and fructose.
Everything fried is also prohibited. Preference should be given to dishes prepared by steaming, stewing or boiling. Alcohol must be completely avoided; it not only causes hyperproduction of urate, but also reduces the effectiveness of drug treatment for gouty arthritis. Remember that alcohol is one of the main “provocateurs” of exacerbation.
Under no circumstances should you go hungry. Fluid intake (from 2 liters per day) should include mineral and purified water, green tea, unsweetened fruit drinks to prevent uric acid kidney stones.
Following a diet helps to significantly reduce the patient’s need to treat gouty arthritis with medications.
Functions of selenium in the body - one of the main microelements
The content of the article
Selenium (Se) is one of the trace elements that performs a number of important functions in the human body.
Physiologically active Se is part of proteins: selenoprotein in the form of Se-cysteine, a derivative of the simplest amino acid, and cysteine, in which it replaces sulfur in the thiol group (-SH). It is a component of two essential amino acids, selenomethionine and selenocysteine, involved in the construction of certain enzyme proteins, and a component of many key enzymes necessary for life.
As part of enzymes that catalyze redox reactions, selenium performs a number of functions:
- protects cells from the harmful effects of free radicals, having antioxidant activity;
- participates in the reduction of ascorbic acid from oxidized metabolites, in the processes of DNA synthesis and apoptosis (programmed cell death);
- By separating iodine, it plays an important role in the metabolism of thyroid hormones.
Selenoproteins promote the development and regeneration of muscle tissue.
Selenium in the body has a positive effect on the functioning of the immune system, affecting the activity and differentiation of macrophages and the proliferation of lymphocytes. By scavenging reactive oxygen species, inhibiting cancer cell division, and targeting carcinogenic compounds, selenium may reduce the risk of cancer. By forming inactive complexes with heavy metals such as cadmium, lead, mercury, arsenic and thallium, it neutralizes their toxic effects.
Selenium protects nerve cells and heart muscle cells from oxidative stress. It plays a positive role in sperm production and has a beneficial effect on the condition of hair and nails. Selenium may be useful in the treatment of some neoplastic and neurodegenerative diseases, and through controlled supplementation or diet, it may become an important element in the prevention of neoplastic diseases.