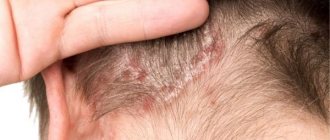
For many people, cleaning their ears is a habit they have developed over the years. This simple manipulation seems as mundane as brushing your teeth. However, few people clean their ears correctly: information about this arises at a time when it is too late to do anything. Improper ear cleaning can lead to ear infections, hearing problems, eardrum damage, and even cardiac arrest.
Most ear diseases are associated with poor hygiene.
However, there is another position. Many experts say that you don’t need to clean your ears at home at all.
What is wax plug in the ear?
The cerumen plug itself is a collection of ear secretions produced by the sulfur glands of the ear canal, which leads to blockage of the ear canals.
But did you know that the presence of earwax is a normal physiological process? Moreover, sulfur protects the ear canal from dust and small particles; the fats in its composition prevent the ear from getting wet and do not allow pathogenic fungal microflora to multiply, thereby performing an antiseptic function.
As a rule, in a healthy person, sulfur is independently removed due to movements of the temporomandibular joint when talking or chewing. However, in some cases, sulfur accumulates in the ear canal, clogs it, forming a plug and, thus, often causes unpleasant sensations in a person.
How to remove a plug by washing
Dried sulfur must be softened.
To do this, use a solution of baking soda (3%) or hydrogen peroxide. For two days, drops are applied to the ear three times a day. Then wash the plug out of the ear using a syringe or syringe. How to remove a cork correctly:
- Tilt your head over a basin or sink so that water flowing from your ear does not get on your clothes or floor.
- Fill the syringe with warm boiled water (not hot), squeeze out the air and gradually pour water along the ear wall.
- Wax from the ear should be washed out until all the plug is removed from the ear and the discomfort from its presence goes away.
So what causes wax plugs to form?
- The very first and most common cause of earwax in the ear is the use of cotton swabs for ear hygiene. Many people, using cotton swabs irrationally, push and compact earwax further, which provokes the formation of a plug. You can clean out wax only at the entrance to the ear canal, otherwise inserting sticks and turundas can damage the skin, injure the eardrum, and disrupt the natural process of self-cleaning.
- Too much sulfur can be produced due to overactive sulfur glands. The auricle does not have time to clean itself and wax quickly accumulates. Increased secretion of the sebaceous glands can be a consequence of high cholesterol levels in the blood, as well as diseases such as eczema, atopic dermatitis, chronic otitis media and external otitis.
- Large amounts of wax can be produced as a result of overzealous ear care. Of course, you need to wash your ears, but an excessive desire for cleanliness, when the patient cleans his ears with cotton swabs every day until they shine, leads to skin irritation, and very often to an increase in sulfur formation.
- If the anatomical ear canal is tortuous and narrow, then accumulation and compaction of wax into the ear plug is also possible. This is not a pathology when the ears are prone to the accumulation of wax, however, more attention should be paid to the hygiene of such ears.
- It is not common, but it happens that patients' earwax has increased viscosity. In addition, rapid hair growth in the ear canal, headphones, hearing aids, very dusty conditions, and dry indoor air can also cause wax plugs in the ears.
How to clean your child's ears
If for an adult proper ear hygiene quickly becomes a habitual manipulation, then a child needs a special approach in this matter. The main principle is that less is better. A caring mother often examines her baby’s ears and hurries to remove all the accumulated wax. Of course, you can't do that.
According to the observations of pediatricians, more than 50% of childhood otitis media are associated with ear injuries during their cleansing by parents.
Children's cotton swabs (with an enlarged soft tip) should also be used with caution, do not screw them in or rub them too hard. After bathing, it is enough to carefully apply the stick to the ear canal and allow the soaked dirt to be absorbed.
In both children and adults, the main natural mechanism for removing wax from the ears is the movement of the jaws. This is why too much wax can accumulate in a baby: intensive breast or bottle sucking intensifies the process. But even this is not a reason to clean the ears too diligently: in the first 1-2 years of the baby’s life, try to reduce this procedure to a minimum.
The main symptoms of wax plug
Often, the patient may not realize that there are wax plugs in the ears, because they do not present any particular discomfort. However, symptoms such as tinnitus, autophony (resonance of one's own voice), a feeling of fullness and, finally, severe hearing loss signal the formation of earwax.
Often, when water gets into the ear, the wax mass swells and completely blocks the ear canal. If the formed plug is located near the eardrum, irritation of the nerve endings occurs and the patient may feel nausea, dizziness and headache.
It is also worth remembering that due to prolonged irritation of the eardrum, inflammatory processes may develop in the middle ear, where our hearing aid is located.
Treatment methods for ear plugs
{banner_banstat3}
It is better to entrust the removal of sulfur clots to an ENT specialist; only a doctor will be able to assess the degree of pathology, the consistency of the mass, and choose the appropriate method of cleansing the ear canal.
What methods are used to remove the plug:
- To begin with, the clots need to be softened - for this, hydrogen peroxide and special drops for dissolving sulfur (cerumenolytics) should be instilled into the ear three times a day for 2-4 days.
- Washing is carried out using a special Janet syringe to remove clots - its special design avoids sudden injection of liquid. The syringe is filled with water or saline solution, the temperature of which is about 37 degrees. The jet is directed along the wall of the ear canal, while the head should be tilted in the direction opposite to the blocked ear. For adults, the shell is pulled down a little, for children - a little back and down. After 2-3 minutes, you need to change the position of the head, the doctor removes the wax with sterile cotton wool, and a cotton swab soaked in boric acid is temporarily inserted into the ear.
- The dry removal method is used for large plugs, or when the integrity of the eardrum is compromised. The procedure is carried out using an aspirator, which sucks out the clot under pressure. Or they use a probe with a hook - you can use it to break through and remove the clot. To avoid damaging the tissue, the progress of the manipulation is monitored through a microscope.
Important!
Washing is contraindicated when diagnosing pathologies of the eardrum, hearing loss, or a history of chronic otitis media. Self-removal of plugs is absolutely not suitable for treating children - unpleasant sensations often indicate an infectious process, and any unprofessional intervention will cause complications.
When should you see a doctor?
If a person notices any of these symptoms, he needs to visit a doctor. An experienced otolaryngologist will examine the patient using an otoscope to determine if a problem exists.
How to get wax plug? Your doctor may be able to remove the wax yourself using a device called a curette. In some cases, the specialist will prescribe wax softening medications or drops suitable for use at home to soften the wax before removing it. You don’t need to buy special medications yourself - this can make your health worse.
Safe ways to rinse the ear cavity. Syringe Janet
Today, problems of the ear cavity such as wax plugs and purulent inflammations are the most common in otolaryngology. They cause pain and discomfort in the middle ear area and cause loss of hearing acuity for the patient. However, they are not difficult to fight. There is a proven way to get rid of such problems - rinsing the ear in the ENT office.
Washing methods
Methods using surgical devices and any piercing/cutting objects are a thing of the past at the end of the 9th century, when a French psychophysiologist named Pierre Marie Felix Janet created an enlarged design of a conventional syringe that could flush the urethra. In the future, otolaryngology also found its application.
This syringe began to be actively used by ENT doctors to combat problems of blockage of the ear cavity by rinsing with warm water. Moreover, today this method remains the most common, but no longer the only one.
Medical technology continues to evolve, and this procedure is now being performed in some institutions using the safe, innovative ProPlus ear rinsing device.
Rinsing with a Janet Syringe
In modern ENT practice, the method of rinsing the ears using a Janet Syringe is widely used. The French doctor's syringe is similar to a regular injection syringe down to the last detail, but it is not used for injections; moreover, this is prohibited by law in some countries. Structurally, the syringe is made in the form of a hollow cylinder, one side of which is topped with a cone for nozzles, and the end side is open, where the rod with the piston is inserted. In fact, the only way it differs from trivial syringes is its large volume: 100, 150, 200, 250 and even 500 ml.
This method is the most conservative, simple and inexpensive in the field of ear rinsing. But perhaps that's where the advantages end. The Janet syringe is not always disposable, because public clinics often use reusable models for a large number of patients with ear problems.
In this regard, there is always a risk of negligence or “human factor” when medical workers accidentally forget to completely disassemble the syringe before disinfecting and sterilizing it or putting it in autoclaves after use, which may subsequently result in a risk of infection for future patients.
Note that the operation of this syringe is carried out exclusively with the help of the hands of an ENT doctor, and also in a hanging position. In most cases, there is an uneven supply of solution (pressure) into the ear cavity, creating discomfort for the patient. Also, we can say with confidence that the use of this method is already considered obsolete, because it has been replaced by modern mobile devices for automated ear rinsing ProPulse, which are much more functional and safer than the traditional method using the Janet Syringe.
Figure 1. ProPulse Ear Irrigation System
The ProPulse ear rinsing device is a modern product with innovative technology for rinsing the ear cavity. Thanks to its unique design, all conditions are created for comfortable and safe washing. The system includes a warm water pressure control function that automatically controls the water jet, avoiding any discomfort for the patient and thereby making the doctor's work easier. The simple design and high ergonomics make the procedure very fast.
Most importantly, the use of this design allows you to completely avoid the risk of infection by using disposable tips for supplying water to the ear cavity.
Hydrogen peroxide
You can remove ear plugs at home using hydrogen peroxide. The solution should be 3% to avoid burning the ear canal.
It is necessary to fill the pipette with peroxide and take a lying position. Apply drops to the ear and cover with a cotton swab; do not push the swab deep into the ear.
Immediately after instillation, a hissing sound and a slight tingling sensation may appear in the ear. This is a reaction of hydrogen peroxide, if there is no pain, there is no need to worry.
It is necessary to drip into the ear for a week. The cork will dissolve and come out on its own.
When should you see a doctor?
If a person notices any of these symptoms, he needs to visit a doctor. An experienced otolaryngologist will examine the patient using an otoscope to determine if a problem exists.
How to get wax plug? Your doctor may be able to remove the wax yourself using a device called a curette. In some cases, the specialist will prescribe wax softening medications or drops suitable for use at home to soften the wax before removing it. You don’t need to buy special medications yourself - this can make your health worse.