October 28, 2021
53 283
18 minutes
Author, editor and medical expert – Klimovich Elina Valerievna.
The term “tonsillitis” or “acute tonsillitis” refers to an infectious inflammatory disease that occurs with damage to one or more tonsils of the pharyngeal lymphoid ring.
The pharyngeal lymphoid ring surrounds the entrance to the respiratory tract and digestive tract and performs a protective function. It participates in the formation of immunity, neutralizes viruses, bacteria and other microorganisms that enter the body from the external environment through the mouth and nasal openings.
The pharyngeal ring includes six large accumulations of lymphoid tissue - tonsils:
- 2 palatine (tongs), located on both sides of the entrance to the pharynx;
- 1 lingual, located at the root of the tongue,
- 1 pharyngeal - in the upper part of the nasopharynx on its back wall,
- 2 tubes - directly at the entrances of the auditory tubes.
Sore throat is usually called inflammation of the tonsils, although the term is also applicable to other localizations of the inflammatory process1.
Up to contents
Causes of sore throat in children
The disease is more common in school-age children and teenagers2. Sore throat in a child under 2 years of age is rare and is caused by insufficient development of the lymphoid tissue of the pharynx2.
In the vast majority of cases, tonsillitis develops as an infectious process2.
- Primary (banal) it can be caused by:
- beta-hemalytic streptococcus A;
- streptococci C G;
- staphylococci, pneumococci and other bacteria;
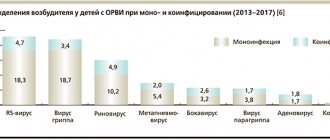
- viruses: respiratory parainfluenza viruses, adenoviruses, coronaviruses, respiratory syncytial viruses, roto- and enteroviruses, Coxsackie viruses, herpeviruses, etc.2
- Secondary inflammation can develop:
- for childhood infections (measles, rubella, scarlet fever);
- for syphilis, tuberculosis;
- as one of the symptoms of leukemia or agranulocytosis2.
The high susceptibility of children to viruses and streptococcus causes the widespread prevalence of tonsillitis. The source of infection is always a person – a patient or a carrier of the pathogen.
In the case of viral processes, these are patients with ARVI, measles, rubella, etc., in the case of catarrhal or purulent tonsillitis caused by streptococci, these are patients with tonsillitis.
The route of transmission of pathogens is airborne droplets or contact. Microbes are transferred from the patient into the environment along with sputum when sneezing and coughing. They are introduced into the body of a healthy baby with dirty hands, when using shared dishes, household items and hygiene items, during close contact, for example, when kissing.
The development of tonsillitis is promoted1,2:
- hypothermia, which often happens in the autumn-winter period and early spring;
- overwork, in particular excessive loads associated with training, attending numerous clubs and studios;
- unbalanced diet - predominance of carbohydrate foods in the diet, lack of vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins and essential microelements,
- the presence in the body of a focus of chronic infection (runny nose, sinusitis, caries, otitis media and others);
- decreased immunity after acute respiratory viral infections and other diseases suffered the day before;
- primary immunodeficiency.
Up to contents
Forms of the disease in children
All types of acute tonsillitis occur in children, but their prevalence depends on age.
Sore throat in a child 1-3 years of age is more likely (44% of cases) associated with a herpetic infection2. Only 35% of cases of the disease are the result of the activity of streptococci2.
In children aged 3 to 7 years, tonsillitis is more often bacterial, but streptococci are found only in 28% of cases2. Further, the picture changes towards the predominance of streptococcal infection and in adolescents it already accounts for up to 52% of cases of inflammation.
According to the picture of pathological changes in the tonsils1, inflammation of the tonsils can be:
- Erythematous (catarrhal), accompanied by redness of the tonsils and palatine arches. Viral tonsillitis, streptococcal (in the initial stages of development) or atypical, caused by Yersinia, mycoplasma, chlamydia, have such a clinical picture.
- Vesicular, characterized by the appearance of vesicles with turbid liquid on the tonsils, after opening of which small erosions form on the mucous membrane. This is how herpetic sore throats, tonsillitis with measles, and chickenpox occur.
- Membranous, in which purulent or necrotic films appear on the tonsils1. In lacunar forms, the film forms pus flowing from the lacunae, which is easily removed with a swab2. True films in diphtheria are firmly connected to the underlying tissue of the tonsils2.
According to the severity of the course, acute tonsillitis in children can be:
- light,
- moderate severity,
- heavy.
With the flow:
- without complications,
- with complications.
Up to contents
Symptoms of the disease
Despite the variety of forms, the signs of tonsillitis in children are largely similar. Let us analyze the clinical picture of the disease using the example of the most dangerous streptococcal inflammation1,2.
The incubation period ranges from several hours to 4-5 days - on average 2-4 days3. The onset of the disease is acute - symptoms of infection appear and develop quickly. The introduction of microbes into the tissue of the tonsils leads to their inflammation and the formation of a large amount of toxins. Their absorption causes poisoning of the body and the appearance of general symptoms of intoxication.
General symptoms:
- From the nervous system, weakness, drowsiness, lethargy, tearfulness and headaches are noted. A child of 2-3 years old during a sore throat usually becomes lethargic, begins to be capricious, cry for no reason, goes to bed in the daytime, although he usually refuses to sleep during the day. Older children complain of fatigue.
- Fever occurs as a result of irritation of the thermoregulation center by streptococcal toxins2,4. Sore throat in children is usually characterized by a rapid rise in temperature to 390 C and above, accompanied by chills, pale skin and lips, and cold extremities4.
- Febrile seizures in children (usually under 3 years of age) can occur against the background of a rapid rise in temperature4. They are expressed in twitching of individual muscle fibers or muscles, or in the form of a general seizure, in which the baby’s entire body tenses and bends in an arc.
- Nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain indicate a severe course of the disease1.
- Body aches, muscle and joint pain : Young children may complain of pain in their arms and legs1.
Local symptoms
These are the visible changes occurring in the throat and the sensations they cause. Depending on their nature, catarrhal, follicular, lacunar tonsillitis, as well as necrotic (ulcerative-necrotic, membranous-necrotic) acute tonsillitis are distinguished.
Catarrhal inflammation develops in all cases as the initial stage of the pathological process 1.3. If the immune system is strong and antibacterial treatment of a child’s sore throat is started on time, the disease can stop at this stage and then begin its reverse development3.
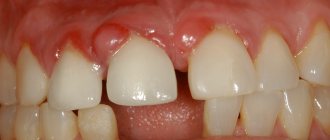
The tonsils, arches, soft palate and uvula look red and swollen. There are no raids on them. The baby develops a foreign body sensation, sore throat and sore throat when swallowing, and drooling.
Follicular tonsillitis is characterized by purulent melting of the follicles of the tonsils. Through the inflamed bright red mucous membrane of the tonsils, whitish-yellowish islands, the size of a grain of rice (3-4 mm), are visible. In this case, there is no pus on the surface of the tonsils - it is located inside under the mucous membrane.
In the case of lacunar tonsillitis, yellowish-white pus is secreted from the lacunae onto the surface of the tonsils and covers them with a thin layer, forming easily removable films. The smell from the mouth becomes sweetish-sweet, putrid, the pain in the throat becomes constant, independent of food intake. The baby's appetite decreases and he refuses to eat.
With necrotic sore throat in children, the throat looks uniformly red, large, 1-2 cm in size, areas appear on the tonsils, covered with a “pearly” dirty gray coating. The plaque is tightly bound to the underlying tissues. After its rejection, deep bleeding ulcers form on the surface of the tonsils. The development of necrotic processes indicates a severe course of the disease.
In all cases, streptococcal inflammation spreads to nearby (regional) lymph nodes. They are felt on the neck, below the corners of the lower jaw in the form of painful round formations, the size of which depends on the severity of the disease.
Severity
The disease can occur in mild, moderate and severe forms.
| 1. Light | A sore throat in a child over 5 years old can occur without pronounced symptoms of intoxication with mild weakness, low-grade fever (below 380 C) for 1-5 days, mainly with catarrhal changes in the tonsils, some pain and enlarged lymph nodes up to 1 cm3. This type of flow is considered mild . In children in the first years of life, the disease is often more severe. |
| 2. Medium-heavy | The moderate severity of the disease is indicated by the moderate severity of the general symptoms of angina: temperature above 38.50 C, weakness, headaches and body aches last for 6-8 days3. The tonsils are covered with purulent films and clear no earlier than after 4-6 days3. The lymph nodes are enlarged to 2 cm, but, despite the severity of the condition, there are no complications3. |
| 3. Heavy | A severe course is characterized by the appearance of severe symptoms of intoxication, including vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. A temperature above 39.50 lasts up to 9 days, exhausts the little man, and is often accompanied by febrile convulsions. In the pharynx there is a picture of filmy or ulcerative necrotic tonsillitis. Lymph nodes reach 3 cm in size. The tonsils are cleared after a week or even later. |
Up to contents
Symptoms of tonsillitis in children
The first symptoms of the disease appear suddenly. The child complains of a sharp sore throat. This makes it difficult for him to swallow. There is a lump in the throat. The patient refuses to eat. In this case, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck can be clearly felt.
In acute tonsillitis, body temperature rises sharply to 39-40℃. As the disease progresses, symptoms of intoxication become more and more apparent: nausea, vomiting, headaches, dizziness. Possible unpleasant reactions from the gastrointestinal tract.
Another characteristic symptom of angina is the appearance of a white or yellowish coating on the tonsils. It may differ depending on the type of sore throat (for example, in the form of a white film or pustules).
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
When a child is ill, he does not feel like eating, he quickly gets tired, weak and drowsy.
If you start treating the disease on time, the symptoms of inflammation gradually disappear and recovery occurs.
If treatment is delayed or the acute form of the disease was initially treated incorrectly, without consulting a doctor, the course of a sore throat may be aggravated by severe complications.
Diagnostics
Inflammation of the palatine tonsils is sometimes accompanied by severe swelling, which can spread to the underlying parts of the respiratory tract and lead to severe difficulty breathing. Against the background of intoxication, cardiovascular failure and shock may develop3. Therefore, it is impossible to treat sore throat in children at home without consulting a doctor.
The clinical picture of angina is obvious. Whether or not there is inflammation can be seen when examining the throat. The main question that the doctor has to answer before starting treatment is what infection caused the inflammation.
- Viral tonsillitis caused by respiratory viruses is usually catarrhal1 and is accompanied by other symptoms of ARVI: discharge from the nasal passages, sneezing, nasal congestion, cough, conjunctivitis and others2. In the herpetic form, small blistering rashes are visible on the mucous membrane of the palate, uvula and tonsils.
A viral infection does not require antibacterial therapy; it can be treated with symptomatic means1,2.
- Diphtheria is the main danger2. Its main feature is the discrepancy between the severity of intoxication and sore throat and the changes occurring in the tonsils2. By the end of the first day of the disease, against the background of malaise, low-grade fever and mild sore throat, the tonsils become covered with a white-gray “pearly” film. In this case, the surrounding mucosa looks more bluish than red, and the lymph nodes practically do not enlarge.
As the pathological process develops, the temperature increases to 400 C, the baby begins to become delirious, and plaque covers not only the tonsils, but also the palate and uvula2. Swelling can spread to the airways and neck, making breathing very difficult.
Treating such a sore throat in a child at home is strictly prohibited!
- Candidal tonsillitis is one of the manifestations of a common fungal infection that accompanies HIV and other severe immunodeficiency conditions2. Since they are rare in childhood, candidal tonsillitis in a child 4-7 years old is more of a casuistry than a reality.
With candidiasis, the plaque is curdled; it covers not only the tonsils, but also other areas of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and pharynx. There is no fever, the lymph nodes are not enlarged. Treatment primarily includes antifungal drugs2.
To accurately determine the causes of the disease, laboratory diagnostics are performed. It includes:
- microbiological analysis of a smear from the surface of the tonsils and the back wall of the pharynx to identify the causative agent of infection and determine its sensitivity to antibiotics1 (result after 1-2 days);
- rapid tests for streptococcus, allowing diagnosis within 10-15 minutes1,2;
- swab from the throat on a Lefler stick (to exclude diphtheria).
Based on the results obtained, treatment for acute tonsillitis is prescribed.
Up to contents
Why does chronic adenoiditis provoke frequent sore throats?
The cause of frequent sore throats is often a complete or partial block of nasal breathing caused by enlarged adenoid vegetations. Difficulty in nasal breathing provokes mouth breathing, while unheated, undisinfected air passes through the mouth, which helps to cool the tonsil tissue, increases the immune load on the tonsil tissue, and also often becomes contaminated with pathogenic flora due to the leakage of mucopurulent discharge along the back wall of the pharynx from inflamed areas. adenoids, and as a result, decompensation and the occurrence of purulent inflammation in the tonsil tissue.
Treatment of sore throat in children
Mild forms of the disease can be managed at home, under the supervision of a local doctor3. An exception is sore throats in children under one year of age: they need to be treated only in a hospital3.
Moderate and severe tonsillitis at any age is an indication for hospitalization, as are any forms of inflammation in children with immunodeficiencies, developmental defects and diseases of the nervous system3.
Mode
In the first 3-4 days of illness, bed rest is indicated2.
Diet
The diet is gentle, with a predominance of dairy and vegetable dishes, limiting salt, sugar, and excluding spices and herbs.
Drink plenty of fluids
It prevents dehydration due to fluid loss during fever and helps reduce symptoms of intoxication.
Antibacterial and antiviral therapy
Bacterial inflammation requires treatment with antibacterial drugs in the form of tablets, injections or intravenous infusions - it is prescribed by a doctor. Regardless of how long the temperature lasts, if a child has a sore throat, the duration of treatment with antibiotics is at least 10 days2,3.
It makes no sense to give your baby antiviral drugs, since respiratory viruses, which most often cause tonsillitis, are practically insensitive to them1. In addition, viral forms of the disease are mild1,2.
Antipyretic drugs
WHO recommends the use of antipyretic drugs in previously healthy children only if the temperature rises above 390 C, and if heat is poorly tolerated: headache, aching muscles and joints2. For babies under one year of age, as well as children prone to seizures, fever medicine should be given earlier - as soon as the temperature reaches 380 C.
In other cases, you need to use physical methods to combat the fever: light clothing, a fan, rubbing, cold compresses on the forehead, armpits and groin area2.
Local treatment
It includes gargling with special solutions, irrigating the tonsils, and sucking special tablets containing antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and analgesic components.
To gargle with a sore throat, children from the age of three can use HEXORAL® SOLUTION for gargling based on hexethidine5. Hexetidine is active against bacteria, including beta-hemolytic streptococcus, respiratory viruses and fungi, and has a mild analgesic effect, so it can be used as an adjunct to the main treatment of tonsillitis5.
HEXORAL® SOLUTION is not suitable for children who, due to age and lack of skill, simply do not know how to gargle. For such cases, there is HEXORAL® in the form of an AEROSOL, which is evenly sprayed over the entire surface of the pharyngeal mucosa and provides the necessary therapeutic effect6.
For a 4-year-old child, HEXORAL® TABS7 is suitable, and for sore throat in a child 6 years of age and older, HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC8. HEXORAL® TABS7 contains, in addition to the antiseptic component, the local anesthetic benzocaine, which helps fight sore throat and facilitate swallowing7,8. The composition of HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC8 includes two antiseptic components, amylmetacresol and dichlorobenzyl alcohol, which enhance the antiseptic effect of each other. The pleasant orange, lemon, honey-lemon, and blackcurrant taste of the tablets is usually liked by children and encourages them to undergo treatment8.
HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA is intended for children over 12 years of age9. It contains lidocaine, a powerful pain reliever that helps fight even the most severe sore throat9.
Please note that after using the drugs, the patient should not be allowed to eat or drink for half an hour.
Up to contents
Sore throat is a type of acute inflammation of the tonsils (the same ones that are colloquially called “tonsils”). ... Such increased attention to one single form of tonsillitis is due to the fact that angina is often very severe and gives dangerous complications (including fatal ones!).
Symptoms and treatment of sore throat in children have certain specifics. The course of the disease in older children is accompanied by weakness and drowsiness, while in younger children, on the contrary, one may notice manifestations of anxiety and irritability. Enteroviral tonsillitis in children is accompanied by the appearance of a vesicular rash with liquid inside on the mucous membranes of the tonsils, arches and pharynx. When the blisters burst, ulcers with a white coating appear. There are no scars left after they heal.
Sore throat in children under five years of age is dangerous because a dangerous condition such as false croup can develop. In this case, swelling of the larynx is observed, its lumen narrows, resulting in a clinic of suffocation. If a child has breathing problems, you need to call an ambulance immediately, and before it arrives, ensure access to fresh air in every possible way, for example, take the baby out to the balcony or simply open a window.
For angina, it is necessary to use antiviral drugs (prescribed by a pediatrician).
Treatment of viral sore throat in children should include measures to cleanse toxins.
You should not give your child aspirin or alcohol tinctures. Gargles are usually done if the child is over 4 years old. A young child usually cannot hold his breath and simply drinks the rinse.
Antibiotics for viral tonsillitis are prescribed to children much less often than to adults, that is, only in extreme cases.
Types of sore throat
There are no significant differences in the classification of the disease in children and adults. The disease can be catarrhal, lacunar, follicular, necrotic. The mildest is catarrhal, and the most severe is necrotic.
Catarrhal tonsillitis - superficial damage to the tonsils and moderate signs of intoxication, temperature up to 38 degrees, changes in the blood are minor. When examining the throat, bright hyperemia is detected, covering the back wall of the pharynx, hard and soft palate. The tonsils enlarge mainly due to swelling and infiltration.
Lacunar and follicular tonsillitis. These types of sore throat have similar symptoms and often develop simultaneously: accompanied by a temperature of up to 39-40 degrees, signs of intoxication are clearly expressed
Fibrinous tonsillitis - characterized by the presence of a whitish-yellow fibrinous plaque on the tonsils, regional lymphadenitis is observed. It is necessary to note the following feature of this type of sore throat - it occurs more often in children with severely weakened immunity. This disease can be the result of lacunar tonsillitis or develop independently.
Phlegmonous tonsillitis is a purulent melting of the tonsil area. People between the ages of 15 and 40 are mainly affected. The tonsil is hyperemic, enlarged, and painful on palpation. The throat hurts severely when talking and swallowing, and signs of intoxication are clearly visible. The patient's temperature rises to an alarming level of 39-40 degrees.
Necrotizing tonsillitis. In this case, general and local symptoms are more pronounced than in the forms described above. The patient has a persistent fever, signs of confusion, and constant vomiting. A plaque with a pitted surface is found on the tonsils. Its color can be grayish or greenish-yellow. The affected areas are often saturated with fibrin, that is, they become dense.
How is angina transmitted?
Pathogenic microorganisms live in the tonsils of every person, including absolutely healthy ones, usually without manifesting themselves in any way. But if any provoking factors arise, the pathogenic microflora is activated, as a result of which the tonsils become inflamed and a sore throat develops.
Typically, the peak incidence occurs in the winter and off-season, when people cough and sneeze especially often. This is due to the fact that sore throat is transmitted by airborne droplets.
You can become infected from a person through a kiss or sharing personal hygiene items.
Prevention of sore throat
Prevention of angina is aimed at overall strengthening of the body and eliminating various infections that provoke the disease. It requires an integrated approach:
· Maintaining personal hygiene. During illness, the patient must use a separate towel, toiletries and utensils.
· If you have a sore throat, the patient should be isolated from other family members and people. The room should be cleaned regularly.
· Support proper nutrition. It should be healthy, nutritious, contain vitamins and minerals.
· Regular examination and treatment of helminthiasis, as well as all sources of chronic infection: caries, pyelonephritis, sinusitis, chronic tonsillitis, various purulent skin diseases. Maintain oral hygiene and get examined by a dentist. If necessary, carry out partial or complete removal of adenoids or tonsils.
· Hardening a child from an early age. It is best to start hardening in childhood, but it can be done at any age. Among the methods of hardening are dousing, rubbing, contrast showers, swimming, walking barefoot on stones and sand. The process should be gradual so that the body gets used to the stress. Hardening can only be carried out in a healthy state.
· Increased immunity level. It is necessary to protect the mucous membranes from damage with dry and warm air. Do not frequently use local antiseptics in the form of sprays. Cold drinks and foods can be consumed only in small quantities so that the mucous membranes get used to low temperatures. It is necessary to increase the body's defenses. To do this, you can make an appointment with an immunologist who will prescribe medications that stimulate cellular and humoral immunity, immunomodulators of bacterial origin, and a complex of vitamins.
For this disease, therapy must be comprehensive. Its basis is complete rest in bed rest. Even with proper medical treatment without bed rest, viral tonsillitis can cause complications that will require much more radical and expensive methods of intervention.
As for nutrition, it is better to avoid heavy and sweet foods during illness. Some of them irritate the throat, their digestion requires additional strength from the body, in addition, sugar creates a very comfortable environment for pathogenic bacteria. While the sore throat caused by the virus lasts, it is better to focus on fresh fruits.
Drinking plenty of fluids will help the body cope with the infection much faster. In this case, toxins will be excreted along with urine. While the symptoms characterizing viral tonsillitis are present, it is better to drink warm homemade berry fruit drinks rich in vitamin C. A variety of jelly is also suitable - they soften the throat and soothe pain. During this period, it is better to drink tea with honey and lemon, and you should avoid coffee (it increases nervous activity).
To gargle, you can use decoctions and infusions of various herbs, in particular sage, chamomile, mint, and plantain. A saline solution with iodine is often used. It is advisable to start rinsing on the first day of symptoms.
In some cases, inhalations can lead to a speedy recovery of the patient and eliminate the infection from the body. Raspberry fruits, thyme tincture, eucalyptus oil are very effective for purulent sore throat without fever. You can also use the old grandfather’s method - “breathe over the potatoes.” To do this, bring the washed potatoes to a boil and add a couple of drops of cinnamon oil. Then you should carefully inhale the steam for 15 minutes. Include both your nose and mouth in this process.
Regular gargling can remove the infection from the body as quickly as possible and reduce pain. In this matter, the main thing is to maintain stability.
Antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to reduce swelling and soreness in the throat, as well as to alleviate general toxic effects.
Some forms of tonsillitis require surgery, as the patient may suffocate or the infection spreads to other organs. In this case, complete or partial removal of the affected tonsils and pus is performed. The patient is recovering in hospital. After surgery, it is necessary to limit physical activity, protect yourself from hypothermia, and strengthen your immune system and health.
Complications of sore throat
The reason for the development of complications is often a late start of treatment, incorrect selection of antibiotics and a sharp weakening of the immune system2.
- Streptococcus has an allergenic effect on the body3, creates the preconditions for the development of nephritis (inflammation of the kidneys), myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle), rheumatism, manifested by the development of heart defects and inflammation of the joints, systemic connective tissue diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome, systemic vasculitis , scleroderma.
- Aggressive streptococcus can penetrate from the tonsils into the surrounding tissues, causing the formation of paratonsillar and retropharyngeal abscesses, periadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes), phlegmon - diffuse purulent inflammation of the tissues.
- The list of complications of tonsillitis includes otitis (inflammation of the middle ear), sinusitis (damage to the paranasal sinuses).
- The infection can enter the blood, spread throughout the body and cause the formation of purulent foci in other organs (septicopyemia).
Sore throat and acute tonsillitis in children should be taken seriously.
Consultation with a pediatrician and ENT doctor is necessary in any case, even if at first glance the patient’s condition does not cause much concern!
Self-medication is fraught with the development of complications - all parents should understand this.
Up to contents
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.
Angina
ANGINA. CLINIC, DIAGNOSTICS AND TREATMENT AT THE CLINIC ENT CENTER IN MOSCOW
Sore throat is an acute nonspecific infectious disease, characterized by severe inflammatory damage to the palatine tonsils (tonsils - paired formations that are located in the pharynx symmetrically on both sides of the uvula and soft palate), therefore, “angina” means an acute inflammatory process in the palatine tonsils (from the Latin . tonsillae) or acute tonsillitis.
CAUSES OF SOLISH
The cause of sore throat is pathogenic bacteria, usually streptococci, which are present in the pharynx in a conditionally pathogenic state and usually do not cause disease, but under unfavorable conditions (hypothermia in autumn-winter and spring, temperature changes) are activated and become pathogenic , as a result, an inflammatory process develops.
THE FOLLOWING MOMENTS CONTRIBUTE TO THE ACTIVATION OF SOLISH CAUSES ON THE MUCOSA:
- previous influenza or other acute respiratory infections;
- the body's predisposition to sore throat;
- the presence of a purulent inflammatory process in the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, oral cavity or pharynx (rotten teeth affected by caries).
CLASSIFICATION OF ENGINES (PHARINGOSCOPIC SIGNS ACCORDING TO B.S. PREOBRAZHENSKY):
- catarrhal tonsillitis (there is hyperemia of the palatine tonsils, the edges of the arches and the soft palate; the tongue is coated, dry);
- follicular tonsillitis (inflammation occurs in the area of lymphadenoid follicles with their suppuration and subsequent opening);
- lacunar tonsillitis (appearance of exudate or plaque at the mouths of lacunae);
- fibrinous tonsillitis (plaques take on a fibrinoid character and completely cover the tonsil);
- herpetic sore throat is characterized by herpetic rashes on the tonsils, soft palate and arches;
- phlegmonous tonsillitis develops when pyogenic bacteria penetrate into the tissue behind the tonsil with the formation of an abscess, both in the tonsil itself and behind it;
- mixed forms.
To select the correct treatment tactics, an otolaryngologist needs a routine examination, but in some cases laboratory tests are required.
DIAGNOSIS OF SOLISH. METHODS.
- Clinical examination. Includes a survey and examination of the patient with palpation of the lymph nodes, examination of the oropharynx and tonsils, and listening to the lungs. Based on the data obtained, a preliminary diagnosis is made.
- Pharyngoscopy (examination of the oropharynx using a spatula under artificial bright light.
- Bacteriological analysis.
- Nasal cavity test.
- General blood analysis.
When a sore throat becomes chronic or severe, complications are diagnosed:
- Laboratory blood test.
- Echocardiogram.
- Radiography.
CLINIC OF SOLISH
Sore throat, as a rule, begins acutely.
SYMPTOMS OF SOLISH
- general symptoms: weakness, malaise, “heavy” head, increased body temperature to 39-40°C, chills, a feeling of weakness in the body with joint pain and pain in the muscles of the extremities;
- dryness, rawness, soreness, burning in the throat and pharynx;
- a feeling of narrowing, tightness, squeezing in the throat, making breathing difficult;
- hoarseness;
- pain when swallowing (may radiate to the ear, temple);
- redness of the tonsils, with severe damage, the appearance of purulent plaque on them.
COMPLICATIONS OF SOLISH
With incorrect diagnosis and inadequate treatment of angina, serious complications are possible, such as peritonsillar abscess, retropharyngeal abscess, neck phlegmon, postanginal sepsis (Lemierre's syndrome), streptococcal meningitis, acute rheumatic fever, glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, polyarthritis, etc.
TREATMENT OF SOLISH AT THE CLINIC ENT CENTER
Mainly local and systemic antibacterial therapy, anti-inflammatory therapy are carried out, in severe cases - steroid, detoxification therapy, etc.
A frivolous attitude towards sore throat is unacceptable, especially independent treatment. Treatment must be carried out under the supervision of an otolaryngologist. Only timely and correct comprehensive treatment of sore throat will protect the patient from serious complications.
PREVENTION OF SOLISH
- Indoor air humidification. The humidity of the air in which a person is located must be at least 45%, otherwise the mucous membranes dry out and become susceptible to inflammation.
- To give up smoking. Cigarette smoke impairs blood circulation in the mucous membranes and destroys the protective mechanisms of the upper respiratory tract.
- Breathing is not through the mouth (with cooling and drying of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx), but through the nose. The nasal mucosa absorbs many foreign bodies before they enter the throat, warms and humidifies the air.
- Maintaining a gentle voice regime.
- Hardening the body.
Literature
- T.I. Garashchenko. Sore throats in children and their systemic antibacterial therapy. Consilium Medicum. Pediatrics. (Add.) 2008; 02: 14-20.
- E. I. Krasnova, N. I. Khokhlova. Differential diagnosis and treatment tactics for acute tonsillitis (angina) at the present stage. Attending physician No. 11/2018; Page numbers in the issue: 58-63.
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocol) for providing medical care to children with tonsillitis (acute streptococcal tonsillitis), FSBI NIIDI FMBA of Russia, 2015.
- Tatochenko V.K.. Once again about antipyretics. Issues of modern pediatrics. Volume 6 No. 2 2007, p. 128-130.
- Instructions for the drug HEXORAL® SOLUTION.
- Instructions for the drug HEXORAL® in AEROSOL form.
- Instructions for the drug HEXORAL® TABS.
- Instructions for the drug HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC.
- Instructions for the drug HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA.
Up to contents