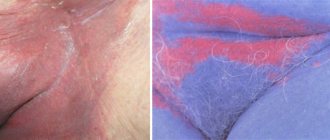
Gynecomastia in men is a disease based on unilateral or bilateral enlargement of the mammary glands. The disease can progress both against the background of hormonal disorders and in relatively healthy men who do not have problems with hormones, but are obese.
There are two forms of gynecomastia in men: physiological and pathological. The physiological variant of breast tissue enlargement occurs in newborns and adolescents, as well as in older people, in whose body the level of testosterone sharply decreases and female sex hormones - estrogens - begin to predominate. Gynecomastia during the newborn period occurs due to the influence of maternal hormones that reach the child in utero.
During puberty, many adolescents suffer from bilateral breast enlargement, which usually goes away on its own without any treatment. The problem is associated with changes in hormonal levels, namely with an increase in the amount of estrogens and their predominance over male sex hormones.
In most cases of gynecomastia in men, there is a bilateral increase in the volume of the mammary glands. At the CONSTANTA Clinic you can seek qualified medical care, make an appointment with experienced specialists who will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and determine the true causes of the disease. Doctors will develop individual treatment tactics for gynecomastia, in accordance with the diagnostic data obtained and the general well-being of the patient. Read more about the treatment of gynecomastia in men in our Clinic.
The main reasons for the development of gynecomastia in men
Normally, the mammary glands in men and adolescents are underdeveloped, formed by a small amount of glandular tissue. With obesity, adipose tissue begins to predominate. Breast volume is determined by the influence of female sex hormones - estrogens, as well as prolactin - a pituitary hormone. When, for various reasons, the androgenic index decreases and the amount of estrogen increases, excessive growth of the mammary glands in men is observed according to the female type with a predominance of glandular cells.
Unlike physiological gynecomastia in men, which is considered a passing phenomenon and in most cases resolves on its own, the pathological form of the disease is often associated with organic pathology and serious internal disorders. It is often necessary to involve highly specialized specialists in treatment: therapists, endocrinologists, oncologists, surgeons.
The main causes of true pathological gynecomastia:
- a similar condition is typical for neoplasms of the pituitary gland and testicles, primary hypogonadism, prostate adenoma and other hormonally active tumors;
- an increase in the amount of prolactin - increased secretion is associated with neoplasms of the pituitary gland and a lack of thyroid hormones;
- treatment with drugs that stimulate the synthesis of estrogen and prolactin;
- taking steroids;
- infectious and inflammatory processes, immunodeficiency states;
- chronic intoxication;
- excess body weight;
- liver and kidney diseases;
- diseases that are accompanied by metabolic disorders and dysfunction of the endocrine glands.
Drug addiction has an extremely adverse effect on the condition of the liver and mammary glands. Potent drugs, especially the opiate group, help increase the synthesis of prolactin, disrupt the functional abilities of the liver, disrupt the course of metabolic reactions, change the condition of the gonads and reduce the amount of testosterone produced. All this increases the synthesis of female sex hormones and leads to the development of gynecomastia.
Diagnostics
A thorough medical history is important to determine the underlying cause of gynecomastia and rule out breast cancer and other tumors. On the other hand, it should be noted that about 25% of cases of gynecomastia may be idiopathic (the cause is unknown).
Must be taken into account during examination
- patient's age,
- onset and duration of breast augmentation,
- symptoms of associated pain,
- recent weight change and
- possible endocrine disorders.
It is necessary to establish whether any medications or drugs are being taken, as they can cause up to 10–20% of cases of gynecomastia.
On physical examination, gynecomastia is defined as overgrown glandular tissue under the nipple-areolar complex and can vary in size.
True gynecomastia must be differentiated from pseudogynecomastia, or false gynecomastia, which is manifested by hypertrophy of adipose tissue without proliferation of the gland itself.
Breast cancer is rare and accounts for less than 1% of malignant neoplasms in men (according to UK and US data). It usually appears on one side and is felt as a hard mass located outside the nipple-areolar complex.
As part of a systematic review, the physical examination should include a search for signs of chronic disease of the thyroid gland, kidneys or liver, or genital organs. When examining the genitals, it is also important to monitor testicular weight or testicular atrophy. Sometimes liver enlargement may occur.
Laboratory research
Biochemical evaluation includes tests to determine liver, kidney and thyroid function, as well as serum levels of testosterone, prolactin, follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone.
Additional tests may be necessary in cases of recent or symptomatic gynecomastia to rule out tumors. For example, serum levels of estrogen, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), dehydroepiandrosterone and 17-ketosteroids in urine.
Routine mammography and breast ultrasound with or without biopsy are usually not recommended unless breast cancer is suspected or the patient has unilateral breast enlargement.
Similarly, a testicular ultrasound or CT scan of the abdomen may be performed if the testicle or adrenal gland becomes enlarged.
Diagnostic evaluation of gynecomastia
- Lab tests: testosterone
- estrogen-β-human chorionic gonadotropin
- prolactin, follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone
- urea and electrolytes
- ± dehydroepiandrosterone or 17-ketosteroids in urine
- Ultrasound of the breast
Patient selection
Various clinical and histological classifications have been proposed for gynecomastia. The Simon classification is the most practical because it takes into account not only breast size, but also the amount of excess skin.
Main symptoms of gynecomastia
The main sign of the development of gynecomastia is excessive growth of the mammary glands. As a rule, in men there is an increase in predominantly glandular tissue. When the amount of fatty tissue in the breast area increases, experts diagnose pseudogynecomastia. In addition to the appearance of mammary glands that are not typical for the male constitution, other signs of the disease may be present:
- pathological discharge from the nipples;
- pain in the chest area;
- increased nipple sensitivity;
- thickening of breast tissue;
- discomfort when the chest rubs against clothing.
If pathological growth of the mammary glands is detected, it is necessary to contact a specialist as soon as possible. Only doctors, having wide diagnostic and treatment capabilities, can make an accurate diagnosis and select an effective treatment regimen for gynecomastia in a man. Specialists are especially wary of unilateral enlargement of the mammary gland, which can be observed with the development of malignant pathology, as well as the appearance of bloody discharge from the nipple and suspicious lumps. Sometimes, against the background of male gynecomastia, the axillary lymph nodes become enlarged, which can also be considered an alarming symptom that requires consultation with a doctor and a detailed examination of the mammary gland and surrounding tissues.
Recommendations
It is often difficult for even experienced surgeons to choose the most appropriate treatment. Sometimes a combination of these methods is necessary. Surgical treatment of gynecomastia consists of three main stages, which may not all be necessary for a given patient: liposuction, open excision and skin tightening.
Liposuction should always be used for diffuse or large breast enlargement. It may not be necessary when correcting small breasts with a hard subareolar nodule, but facilitates subsequent open removal. Our results with ultrasonic liposuction have led us to the conclusion that, when available, it is preferable to conventional liposuction because it is more effective and stimulates better skin contraction. Additionally, there may also be less bruising. After liposuction, the consistency of the breast is again assessed and open excision is performed if residual gland tissue is present.
Skin tightening is indicated if there is noticeable excess skin after removal. The choice between a concentric, vertical scar (LeJour technique) and an elliptical skin excision largely depends on the amount of excess skin to be removed, as well as the experience of the surgeon.
Examination for gynecomastia
To make a preliminary diagnosis, the doctor only needs to conduct a standard examination and palpation of the breast tissue and nearby lymph nodes. But an accurate diagnosis of gynecomastia is carried out only on the basis of the results of modern research. Ultrasound is considered the main diagnostic method. Specialists conduct ultrasound examinations of the mammary glands, scrotal organs, and axillary lymph nodes.
Laboratory tests are actively used, which include determining the level of testosterone, hCG, estradiol and prolactin, as well as other hormones (as indicated). If the development of a malignant tumor is suspected, a breast biopsy is prescribed. Additionally, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography of internal organs are used.
At the CONSTANTA Clinic, patients have access to many types of modern diagnostic and laboratory tests, which allow them to obtain the most reliable information about the patient’s condition and the functioning of all his internal organs, including the endocrine glands. We provide professional assistance to men with gynecomastia and provide both symptomatic and surgical treatment.
Gynecomastia is a serious disease that requires an integrated approach and the participation of experienced specialists. Delayed visit to the Clinic or the use of questionable home methods for treating gynecomastia in men can lead to the development of serious complications. Our specialists have modern therapeutic and surgical methods to combat this disease, which are highly effective and safe. You can discuss treatment options with your doctor. Do not hesitate to ask a specialist any questions that interest you. The doctors of the CONSTANTA Clinic are focused on respecting the interests of their patients and maximum concentration of professional forces on solving the problems of each patient.
Preparation rules
If the doctor decides that surgery is necessary, the patient will have to undergo careful preparation. First of all, you need to undergo an examination, which includes:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Blood test for clotting.
- Blood test for HIV, hepatitis and syphilis.
- Study of the hormonal spectrum of blood (testosterone, prolactin, estrogen, FSH).
- Fluorography.
- Electrocardiogram.
- Ultrasound examination of the mammary glands.
- A certificate from a physician stating that there are no contraindications to surgery.
This is the minimum list of necessary preparatory procedures. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe other types of diagnostics.
It is also worth checking out the list of recommendations:
- Surgery is performed on an empty stomach, which means that the patient must abstain from food for at least 7-8 hours before surgery.
- 3 hours before the appointed time you need to refuse water.
- A few days before the procedure, it is recommended to include more fresh vegetables, fruits, dairy products, etc. in your diet.
- Be sure to remove excess hair in the chest area.
- If you are worried about the feeling of fear before surgery, consult your doctor about taking sedatives.
Gynecomastia and steroids
Taking anabolic steroids often leads to the development of male gynecomastia. Steroid hormones contribute to the excessive formation of female sex hormones, in particular estradiol. As a result of long-term use of anabolic steroids by athletes, female-type adipose tissue deposition and bilateral enlargement of the mammary glands are observed. Athletes taking steroids should take care in advance to prevent gynecomastia. It involves taking special medications that block estrogen receptors. Ideally, an athlete’s career should be built without the use of steroid drugs, which have a detrimental effect not only on hormonal status, but also on the entire male body.
Advantages of laser gynecomastia removal in our clinic
- Modern laser equipment made in Italy allows you to fully control the volume of tissue removed
- Tissue burns are avoided, the skin is not damaged, only several punctures with a diameter of no more than 1-2 mm are made
- The risk of fibrosis is minimized
- The operating area becomes sterile, because the laser has the ability to destroy all microorganisms
- Glandular and/or adipose tissue is removed evenly, ensuring that the skin does not become lumpy
- Skin turgor improves - laser radiation activates the formation of new collagen, thereby providing a lifting effect
- Side effects such as swelling and hematomas are mild
- Recovery is reduced to 36 hours, the procedure is so gentle that after a few days you can safely go to the beach
Gynecomastia in endocrine pathologies
Endocrine diseases often cause the development of gynecomastia in men. Various pituitary tumors lead to hyperprolactinemic hypogonadism. In this condition, the synthesis of gonadotropins and testicular function are impaired, and spermatoginesis may decrease. As a result, men note a decrease in potency and disappearance of libido. Adolescents in this state do not have clearly expressed secondary sexual characteristics.
Hyperprolactinemia is observed with the growth of prolactinoma, as well as with other pituitary adenomas and the presence of hormonally inactive adenomas. In childhood, gynecomastia can occur with hyperthyroidism. Thyroid hormones help increase estradiol levels. To get rid of gynecomastia caused by hyperthyroidism, it is first necessary to treat the underlying disease.
Video about the service
Where do hormonal imbalances come from? Medicine does not provide a clear and specific explanation. The development of gynecomastia can be triggered by internal factors (certain diseases, pathologies and functional disorders) and external factors (taking medications). In addition, in the life of every man there are three so-called “critical” periods when hormonal disorders often occur:
- the neonatal period, when enlargement of the mammary glands is observed in many male infants, usually after a certain time the problem resolves itself, since the hormonal balance is restored after adaptation;
- period of puberty, the body goes through hormonal changes, as a result of which teenage gynecomastia can occur (it manifests itself very often - in about 70% of adolescents to varying degrees), treatment is usually not required here either, after the completion of the process of puberty, the breasts take on normal sizes, only in some cases its reduction may not occur fully;
- old age (over 45 years), when a man’s testosterone production decreases due to age, as a result of which the hormonal balance can shift towards female hormones.
Gynecomastia and genetic pathologies
Genetic abnormalities often underlie the development of gynecomastia. Most often, excess growth of breast tissue is diagnosed in men with Klinefelter syndrome, in which an extra X chromosome is detected in the cells. These men have increased sensitivity to estrogen. With this disease, hyperprolactinemia occurs, which also increases the manifestations of gynecomastia.
In Klinefelter syndrome, puberty may occur on time, but puberty is often delayed. Patients exhibit predominantly tall stature and abnormal physique, in which the lower part of the body is significantly larger than the upper part. The size of the testicles is reduced. For chromosomal abnormalities, treatment of gynecomastia is predominantly surgical. The nodular form of the disease requires constant medical supervision and a biopsy after surgery or at the diagnostic stage.
Reifenstein syndrome occurs with increased estrogen synthesis and the development of gynecomastia. Symptoms of the disease usually appear during adolescence, when hormonal changes in the body occur. At the same time, experts identify signs of underdevelopment of the genital organs. Such patients require hormone replacement therapy with individual dosage selection.
True hermaphroditism also occurs with symptoms of gynecomastia. The patient usually learns about his problem at the beginning of puberty, when active growth of the mammary glands begins and other signs of the formation of a female-type figure appear.
Restrictions and contraindications
Absolute contraindications, in the presence of which the surgeon refuses to perform surgery to remove gynecomastia, are:
- severe heart disease;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- decompensated kidney and liver diseases;
- true, mixed gynecomastia without attempts at drug treatment;
- bleeding disorders;
- HIV and AIDS.
Relative contraindications (time restrictions) include:
- any acute conditions, infections, colds;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- fever;
- purulent-inflammatory processes in the area of the upcoming intervention;
- severe obesity.
Gynecomastia and liver diseases
Some liver pathologies can lead to the development of gynecomastia. Important metabolic processes occur in the liver tissues. This organ is responsible for the metabolism of steroids. Therefore, if its work is disrupted, with the development of hepatitis, alcoholic cirrhosis, the risk of mammary gland growth in men increases. Specific kidney enzymes lead to the destruction of prolactin and gonadotropins, as well as slowing down the release of body tissues from metabolic products. All this often leads to an increase in the level of prolactin and estrogen, causing the progression of gynecomastia.
Indications for removal of gynecomastia
- Persistent increase after puberty (>2 years)
- Inadequate response to treatment
- Severe breast enlargement
- Significant asymmetry or unilateral condition
- Patient request
- Post-massive weight loss
- Special clinical conditions
The boundaries between categories are not clearly defined, which leads to subjectivity. Therefore, in our practice, we classify gynecomastia into three stages:
- small to moderate in size with no or minimal excess skin (Grades I and IIA)
- medium to large in size with moderate to severe excess skin (grades IIB and III).
Gynecomastia and breast neoplasms
Tumors in the mammary glands are often mistaken for true gynecomastia. The process is most often one-sided, but sometimes the neoplasms involve two mammary glands at once. To the touch, the tumor has a dense consistency, is usually fused with adjacent tissues and has unclear contours. With breast tumors in men, bloody discharge from the nipples may appear, and sometimes the lymph nodes in the armpit become noticeably enlarged.
When a tumor is detected, specialists refer the patient for mammography, ultrasound, MRI and prescribe a biopsy, based on the results of which they can determine the nature of the tumor and make appropriate predictions for the future.
How is the operation performed?
Most often, the operation is performed under general anesthesia. However, the issue of anesthesia is decided individually with each patient.
Depending on the type of gynecomastia and the individual characteristics of the body, surgical intervention can be performed in various ways:
- Mastectomy – removal of gland tissue using an endoscope.
- Liposuction is the removal of excess fat in the breast area through an aspirator.
- Combined – mastectomy with liposuction.
With the endoscopic method of surgery, a tiny incision is made in the armpit through which the necessary instruments are inserted, including a miniature camera with which you can monitor the operation on a monitor.
Unnecessary tissue is excised (including excess skin). And at the end of the surgical intervention, the doctor applies stitches and elastic bandages. It is worth noting that the nipple and the surrounding areola are necessarily preserved. The duration of the operation is about one and a half hours.
If everything went without complications, the patient can go home after 3-4 days.
Iatrogenic gynecomastia
Iatrogenic gynecomastia occurs when taking certain medications. The risk group includes patients who undergo hormonal treatment with estrogens, as well as other hormones (gonadotropins, glucorticoids). Against the background of hypogonadism, specialists often prescribe testosterone, which is toxic to the liver and can cause signs of temporary gynecomastia. Cardiac glycosides have a similar effect, stimulating the active production of steroids and disrupting the functional abilities of the testicles.
Drug-induced gynecomastia is most often a reversible process that can be stopped after stopping the medication that caused excessive breast growth. But it is necessary to stop taking medications as soon as possible. If you do not pay attention to the appearance of gynecomastia during drug therapy for 6-12 months or more, irreversible fibrotic processes will begin to occur in the breast tissue. The advanced form of the disease is subject to predominantly surgical treatment.
Recovery after gynecomastia removal
Drains are not usually used except in major resections or when skin resection is performed, such as in patients with massive weight loss. Patients are advised to wear a special compression bandage for gynecomastia day and night for 4-6 weeks.
Oral antibiotics are taken for a total of 5 days. Painkillers should be used, as a rule, for 2-3 days.
Principles of treatment of gynecomastia
Treatment of gynecomastia in men can be therapeutic and surgical. The physiological form of the disease in adolescents and newborns usually disappears spontaneously and does not require specific therapy. According to indications, specialists can carry out hormonal correction with drugs that reduce the level of female hormones. But any medications used to treat gynecomastia in men should only be prescribed by qualified specialists who are familiar with your clinical case. Self-administration of medications, without studying hormonal status and diagnostic results, can lead to adverse health consequences and increased symptoms of the underlying disease.
Conservative therapy for gynecomastia consists of prescribing hormonal drugs containing testosterone. Such drugs are effective in the initial period of development of the disease, in the first months, when scarring and other complications requiring surgery have not yet occurred.
The severe form of gynecomastia does not respond well to conservative treatment. It is extremely important to seek medical help promptly when drug therapy can be highly effective. If the doctor recommends surgical treatment, you should not refuse it. Today, men with gynecomastia have the opportunity to undergo minimally invasive surgical interventions, which do not leave rough keloid scars in the mammary glands. These are the types of operations that are performed at the CONSTANTA Clinic. Excess tissue is removed through a subareolar approach or using an endoscopic method with access from the armpit. In the second case, absolutely no scars remain on the skin of the breast.
For false gynecomastia, liposuction is indicated. The surgeon sucks out excess fat through small punctures in the skin or removes it using the classic surgical method. The operation is performed under general or local anesthesia, depending on the patient’s condition and his wishes.
Recurrence of gynecomastia
Patients with gynecomastia in general are a surgically challenging group of patients, not least because of their high expectations from surgery. In patients who have undergone surgical treatment, it is sometimes necessary to undergo revision surgery several months after the initial surgery for various reasons. These include inadequate correction, patient dissatisfaction, painful residual lumps, asymmetry, and recurrence (often associated with weight gain). Overcorrection is rare.
Preparation for surgical treatment of gynecomastia in men
No complex preparatory activities are carried out. The patient undergoes a comprehensive examination, which allows him to assess his health condition and choose the appropriate tactics for surgical intervention. Based on the diagnostic data, the doctor makes predictions for the future and selects the correct treatment regimen that prevents the development of complications, both during surgery and in the postoperative period.
The operation is performed on an empty stomach. The doctor will tell you in detail about the features of the surgical stage and recovery period. You must strictly follow your doctor’s prescriptions; if you have any questions or feel unwell, it is recommended that you contact your doctor without delay.
Consequences of gynecomastia
Gynecomastia, which is not treated in time, will progress, the tissue will undergo scarring and it will no longer be possible to remove it with medications. In this case, you will have to resort to surgery to remove the overgrown mammary glands.
Since gynecomastia occurs due to dysfunction of the hormonal system due to disruption of the functioning of certain organs, prolonged absence of treatment can lead to the development of tumors, the formation of metastases and other diseases of organs and systems.
Also, patients with gynecomastia may experience psychological problems, this is especially common in adolescents.
Recovery period after surgical treatment of gynecomastia
In most cases, surgical treatment of gynecomastia in men proceeds without complications. As a rule, long-term hospitalization is not required. The patient is discharged home, given detailed recommendations about the rules of behavior and the prevention of complications.
Gynecomastia in men can develop due to many endocrine and non-endocrine pathologies, so treatment should primarily be aimed at the cause of increased estrogen levels and excessive growth of mammary gland tissue. Medical tactics must be strictly individual. It is necessary to determine the factors that provoke the development of the disease in order to eliminate their adverse effects on the male body. Then both drug and surgical treatment will be highly effective, and the risk of recurrence of the disease can be minimized.
If you have any questions or make an appointment with a specialist, please call: (4852) 37-00-85 Daily from 8:00 to 20:00
Sign up for a consultation
Outcomes, prognosis and complications
Only an integrated approach can lead to predictable results in the surgical treatment of gynecomastia. Our starting point for all cases of gynecomastia is liposuction, even in those with hard subareolar glands, as it facilitates subsequent open excision. It is also technically easier to perform liposuction at the beginning of the operation rather than after removal. We use conventional liposuction only when ultrasonic liposuction is not available.
In patients in whom open excision is not necessary due to appearance and consistency, we always agree to open excision if liposuction leaves significant residual stromal tissue.
Whenever there is excess skin and/or ptosis, we prefer to treat the excess skin with primary surgery, especially in cases of poor or borderline skin elasticity. This is done to avoid post-operative excess skin.
The choice of skin reduction technique largely depends on the surgeon's preference.
Possible consequences of gynecomastia
- Bleeding and hematoma formation
- Seroma formation
- Infection
- Skin/nipple necrosis
- Contour deformity such as nipple inversion or depression
- Altered nipple sensation
- Redundancy of skin
- Residual asymmetry
- Unfavorable scars (wide, hypertrophy, keloid, pigmentation)
- Overcorrection, undercorrection
- Occasional need for revision surgery: asymmetry, residual tissue, depressed nipples