Back pain is a common reason for patients to visit a doctor. There are many pathologies characterized by back pain: osteochondrosis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, spinal hernia. One of the effective drugs that can relieve pain is Movalis.
Active ingredient
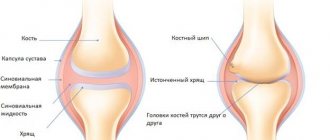
The active component of Movalis, meloxicam, relieves any inflammation. This has been proven by clinical trials. Meloxicam inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins (Pg), which are known to be mediators of inflammation. That is, Movalis acts precisely. As for cartilage tissue, it does not experience any negative effects during a course of Movalis.
The pharmacological market boasts a variety of dosage forms of the drug: tablets, injection solution, rectal suppositories (suppositories), suspensions.
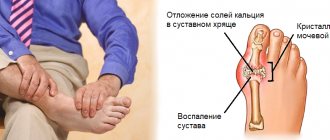
Movalis against arthritis of the fingers
It is worth noting that the injections are intended for the first 2-3 days of therapy, when the inflammatory and pain syndrome is most pronounced. After pain and inflammation are relieved, treatment continues using available dosage forms.
The analgesic effect can be observed after 30 minutes and lasts about a day after taking Movalis.
Also, if you follow the prescribed dose, the medicine does not affect bleeding time and does not change platelet aggregation. This sets Meloxicam apart from Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Diclofenac and Naproxen.
Indications
What do pills help with?
- symptomatic treatment of aggravated osteoarthritis;
- long-term treatment of infectious nonspecific polyarthritis and rheumatoid spondylitis.
What are Movalis injections for?
- short-term treatment of an acute attack of infectious nonspecific polyarthritis or rheumatoid spondylitis, when the rectal and oral routes of administration of the drug Movalis are impossible.
Why is the suspension prescribed?
- symptomatic treatment of osteoarthritis (including with a pain component), rheumatoid arthritis (including juvenile arthritis), rheumatoid spondylitis
Contraindications
The use of Movalis is prohibited in the following cases:
- active gastrointestinal bleeding, recent cerebrovascular bleeding or established diagnosis of diseases of the blood coagulation system;
- concomitant therapy with anticoagulants, because there is a risk of intramuscular hematoma formation;
- severe liver failure;
- severe heart failure;
- severe renal failure (if hemodialysis is not performed, CC <30 ml/min, and also with confirmed hyperkalemia);
- active liver disease;
- erosive and ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum in the acute phase or recently suffered;
- inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis in the acute phase);
- therapy of perioperative pain during coronary artery bypass grafting;
- pregnancy;
- lactation period (breastfeeding);
- age under 18 years;
- hypersensitivity to the active substance or auxiliary components of the drug.
- hypersensitivity (including to other NSAIDs), complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nose or paranasal sinuses, angioedema or urticaria caused by intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs (including a history) due to existing potential for cross-sensitivity.
Movalis should be used with caution in old age
Use with caution if you have:
- history of gastrointestinal diseases (presence of Helicobacter pylori infection);
- congestive heart failure;
- cerebrovascular diseases;
- dyslipidemia/hyperlipidemia;
- diabetes;
- peripheral arterial disease;
- renal failure (creatinine clearance 30-60 ml/min);
- IHD;
- elderly age;
- long-term use of NSAIDs;
- smoking;
- frequent drinking of alcohol;
- concomitant therapy with the following drugs: anticoagulants, oral corticosteroids, antiplatelet agents, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
Contraindications for use in pediatrics:
- tablets - age up to 16 years;
- d/i solution - age up to 18 years;
- candles - age up to 12 years;
- suspension - age up to 12 years (for juvenile arthritis, the restriction for use is age up to 2 years).
Drug interactions Meloxicam-ratiopharm
Pharmacodynamics: Concomitant use of several NSAIDs (including salicylates) may increase the risk of developing erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract due to a synergistic effect, therefore the use of meloxicam with other NSAIDs is not recommended. When using meloxicam with diuretics, the patient must drink sufficient fluids, and regular medical monitoring of renal function is required before and during treatment. Oral anticoagulants: combined use increases the risk of bleeding due to inhibition of platelet function and damage to the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines. Therefore, combined use with NSAIDs and oral anticoagulants is not recommended. Thrombolytic and antithrombotic drugs: when used in combination with meloxicam, an increased risk of bleeding is possible (periodic monitoring of blood coagulation parameters is necessary). ACE inhibitors and other antihypertensive drugs: simultaneous use in elderly patients with symptoms of dehydration may provoke the development of acute renal failure. In addition, combined use with meloxicam may reduce their hypotensive effect. Cyclosporine: the nephrotoxic effect of cyclosporine is enhanced. Contraception: The effectiveness of birth control may be reduced. Pharmacokinetic Lithium: NSAIDs may increase serum lithium concentrations to toxic levels (decreased renal excretion of lithium). Therefore, the simultaneous use of NSAIDs with lithium preparations is not recommended. If their combined use is necessary, the level of lithium in the blood serum should be carefully monitored before, during and after the end of the course of therapy with meloxicam and lithium preparations. Methotrexate: increases the negative effect on the blood system (threat of anemia and leukopenia). Periodic monitoring of the hemogram is necessary. Cholestyramine accelerates the elimination of meloxicam, increasing the clearance of meloxicam by 50%, reducing its half-life by 13±3 hours. This interaction is of clinical significance. When taken simultaneously with antacids, cimetidine and digoxin, no significant clinical interaction is observed. NSAIDs reduce the effectiveness of contraceptive intrauterine devices.
Side effects
Side effects of Movalis - Headache
As with therapy with other NSAIDs, while taking Movalis, there is a possibility of adverse reactions from the body:
- From the urinary system: edema, hypercreatininemia, increased urea concentration. In rare cases - interstitial nephritis, glomerulonephritis, renal medullary necrosis, nephrotic syndrome.
- From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, belching, abdominal pain, constipation or diarrhea, flatulence, increased activity of “liver” transaminases, hyperbilirubinemia, stomatitis, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal bleeding (hidden or obvious), perforation of the digestive tract canal, colitis, dyspepsia, gastroduodenal ulcer, esophagitis, gastritis, hepatitis.
- From the cardiovascular system: increased blood pressure, “flushes” of blood to the skin of the face and upper chest, palpitations.
- From the nervous system: dizziness, headache, drowsiness, mood lability, confusion, disorientation..
- From the hematopoietic organs: anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
- Allergic reactions: skin rash, itching, blisters, erythema multiforme, Lyell's syndrome, bullous dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, angioedema, hypersensitivity to UV radiation, urticaria, anaphylactoid reactions.
- Other: ringing in the ears, blurred vision, conjunctivitis.
The combined use of Movalis and drugs that suppress the functioning of the bone marrow can provoke cytopenia (deficiency of one or more types of blood cells). If gastrointestinal bleeding, perforation or ulcer occurs during therapy with Moralist, this can lead to death.
In the case of using a d/i solution, the following are also possible:
- glomerular or interstitial nephritis;
- papillary necrosis;
- nephrotic syndrome;
- swelling and pain at the injection site.
How to take Movalis
General advice for the use of any of the dosage forms of Movalis is that the drug is recommended to be used in the minimum effective dose, and the therapeutic course should last as short as possible. Moreover, during treatment with Movalis, it is recommended to evaluate the need to take the drug and the body’s response. During the day, you can take, regardless of the dosage form of Movalis, only 15 mg/day. This is the maximum for the day.
How to take Movalis medicine correctly?
Movalis tablets and suspension are taken orally during meals with a sufficient amount of water.
- osteoarthritis: 7.5 mg/day. If indicated and the severity of the pain syndrome, it is possible to increase the dose to 15 mg/day;
- rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis: 15 mg/day. (possibly reducing the dose by 2 times);
- Children under 12 years of age are prescribed Movalis in the form of a suspension for the treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. The dose is calculated based on body weight - 0.125 mg/kg (maximum - 7.5 mg per day).
- children 12-18 years old with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: 0.25 mg/kg, but not more than 15 mg per day.
It is recommended to use the following dosage regimen (amount of active substance/volume of suspension):
- 12 kg: 1.5 mg/1 ml;
- 24 kg: 3 mg/2 ml;
- 36 kg: 4.5 mg/3 ml;
- 48 kg: 6 mg/4 ml;
- From 60 kg: 7.5 mg/5 ml.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Meloxicam-ratiopharm
Meloxicam is an NSAID of the oxicam group with anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic properties that are associated with selective inhibition of the COX-2 isoenzyme. The selectivity coefficient IC50 for meloxicam is 2. Meloxicam is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Absolute bioavailability after oral administration is about 89%. After a single oral dose, the maximum concentration in the blood plasma is reached after 5–6 hours. With repeated administration, an equilibrium state is achieved after 3–5 days from the start of use. When taken orally at a dose of 7.5 or 15 mg of meloxicam 1 time per day, the concentration in the blood plasma (Cmin–Cmax) at steady state reaches 0.4–1.0 mg/l (7.5 mg) or 0.8– 2.0 mg/l (15 mg), respectively. With long-term use, the concentration in the blood plasma at steady state does not change. Absorption does not change when taken simultaneously with food. The bioavailability of meloxicam after intramuscular administration is 89%. The maximum concentration in the blood is achieved 1 hour after administration. Meloxicam has a high degree of binding to blood proteins, mainly albumin (99%). Meloxicam enters the synovial fluid, the concentration in it is equal to the concentration in the blood plasma. The volume of distribution is on average 11 liters. Individual variations are approximately 30–40%. Meloxicam is metabolized by liver enzymes. Four different pharmacologically inactive metabolites of meloxicam have been identified in urine. The main metabolite, 5'-carboxymeloxicam (60%), is formed by oxidation of intermediate metabolites 5'-hydroxymethylmeloxicam. The amount of 5'-hydroxymethylmeloxicam released unchanged is 9%. In vitro , it was found that the initial stage of this transformation is carried out mainly through CYP 2C9 with minor participation of CYP 3A4. The formation of two other metabolites (16 and 4% of the dose taken, respectively) is associated with the action of peroxidase. Meloxicam is excreted mainly in the form of metabolites, in equal parts with urine and feces. Meloxicam is detected in urine in insignificant (trace) quantities. The average half-life is about 20 hours. The total plasma clearance averages 8 ml/min. When administered orally in therapeutic doses (7.5 and 15 mg), meloxicam exhibits linear pharmacokinetics.
Injections with Movalis: instructions for use
Movalis in ampoules is used exclusively intramuscularly (intravenous use is prohibited). The medicine is administered once in a dose of 15 mg. Typically, injections with Movalis are used in the first 2-3 days of therapy.
The medicine is administered slowly, by deep injection into the gluteus maximus muscle.
The recommended daily dose is 7.5 mg or 15 mg 1 time/day, depending on the intensity of pain and the severity of the inflammatory process.
- Osteoarthritis with pain: 7.5 mg/day. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 15 mg/day;
- Rheumatoid arthritis: 15 mg/day. Depending on the therapeutic effect, the dose can be reduced to 7.5 mg/day;
- Ankylosing spondylitis: 15 mg/day. Depending on the therapeutic effect, the dose can be reduced to 7.5 mg/day.
Movalis suppositories: instructions for use
For adults with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis or spondylitis, rectal suppositories are administered at a dose of 7.5 mg 1 time / day. If indicated, the dose can be increased to the maximum possible per day - 15 mg.
Meloxicam tablets: main characteristics
Meloxicam is a non-steroidal drug that has anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. It helps in eliminating pain and works as an analgesic. Available in 3 forms:
- Pills.
- Solution (in glass ampoules).
- Suppositories.
The active ingredient is meloxicam, a derivative of enolic acid. Dispensed only with a doctor's prescription. The drug is stored at room temperature (no more than 25 degrees) within the general shelf life (no more than 2 years).
Special instructions for the use of the drug Movalis:
- for patients with an increased risk of adverse reactions (history of gastrointestinal diseases, presence of risk factors for cardiovascular diseases), the recommended initial daily dose is 7.5 mg;
- For patients with severe renal failure on hemodialysis and the elderly, a dose of 7.5 mg/day is recommended, which should not be exceeded;
- patients with insufficient renal function in which Clcr exceeds 25 ml/min., patients with mild/moderate liver failure, as well as clinically stable cirrhosis do not require dose adjustment.
Important! The required dosage and course duration are determined by the attending physician.
Indications and contraindications for use
Meloxicam tablets, suppositories and injections are used in the presence of the following diseases:
- rheumatoid type arthritis;
- inflammation, joint degeneration with severe pain;
- Bekhterev's disease;
- osteoarthritis.
Tablets should not be taken if you have the following pathologies:
- intolerance to aspirin, pyrazolone-based drugs;
- bronchial asthma;
- nasal polyposis (at the recurrent stage);
- severe kidney disease;
- pregnancy of any stage;
- GW period;
- peptic ulcers of the digestive organs;
- individual characteristics of the body (intolerance to non-steroidal drugs).
Suppositories should not be used in the presence of hemorrhoids, inflammation, or rectal wounds. Elderly people take all forms of the drug with caution. Before starting a course of treatment, you should consult your doctor.
Movalis during pregnancy and breastfeeding
As with other Pg (prostaglandin) inhibitors, meloxicam may have a negative effect on fertility. Therefore, when planning pregnancy, it is recommended to discontinue therapy with this drug.
Movalis during pregnancy
Suppression of prostaglandin synthesis has a negative impact on the development of pregnancy and/or the fetus. In particular, clinical data suggest that Movalis in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy increases the risk of miscarriages, as well as the chance of gastroschisis and heart defects in the fetus. Therefore, during this period, Movalis is prescribed by a doctor only if there is a real threat to the mother’s life.
As for the third trimester, taking the drug at this time can lead to abnormalities in fetal development:
- cardiorespiratory toxicity;
- renal dysfunction, which can develop into renal failure with oligohydramnios.
In addition, taking Movalis in the last weeks of pregnancy can provoke an increase in bleeding time, the development of an antiaggregation effect, inhibition of the ability of the smooth muscles of the uterus to contract, and this leads to a delay or disruption of the birth process.
The active component of Movalis easily passes into mother's breast milk, so it should not be taken during breastfeeding (breastfeeding).
Movalis and alcohol
Is it possible to combine Movalis with alcohol?
There is no clear prohibition on the simultaneous use of Movalis and alcohol in the instructions for use. True, this does not mean that such a combination will not cause harm. Thus, drinking alcohol during therapeutic treatment with Movalis can lead to acute renal failure. This occurs due to dehydration, which is caused by alcohol.
Meloxicam-ratiopharm overdose, symptoms and treatment
Symptoms of acute NSAID overdose are often accompanied by drowsiness, nausea, vomiting and gastralgia, which usually resolve with symptomatic therapy. Gastrointestinal bleeding may also occur. Severe poisoning can lead to increased blood pressure, acute renal failure, liver dysfunction, respiratory depression, coma, convulsions, collapse and cardiac arrest. Anaphylactoid reactions have been reported during therapeutic doses of NSAIDs in cases of overdose. After an overdose of NSAIDs, patients are given supportive and symptomatic therapy in accordance with the severity of the overdose and intoxication. Clinical studies have found that three doses of 4 g of cholestyramine orally accelerates the elimination of meloxicam.
Is it possible to take Milgamma, Movalis and Mydocalm at the same time?
If the pain is severe, causes discomfort, cannot be tolerated, and affects the usual rhythm of life, then the doctor may prescribe a combined treatment system. Milgamma and Mydocalm are often prescribed along with Movalis, which have shown good results in the treatment of certain diseases (intervertebral hernia, osteochondrosis). But before injecting Movalis, Milgamma and Mydocalm, you need to visit a doctor, since these drugs in any case have contraindications and the risk of developing negative reactions in the patient’s body.
- Movalis is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Its use is indicated in the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system to relieve inflammation, pain and lower temperature.
- Milgamma is a combined multivitamin product consisting of B vitamins. When diagnosing diseases of the musculoskeletal system, Milgamma injections are prescribed to improve blood circulation, nourish cartilage and bone tissue, and strengthen the nervous system.
- Mydocalm is a muscle relaxant. The drug relieves muscle spasms, reduces muscle tension, reduces compression of nerve endings and eliminates pain.
The classic treatment regimen with Movalis, Milgamma and Mydocalm looks like this: during the first three days, Movalis injections are administered once a day, then the patient is transferred to the tablet form of the drug. Milgamma is administered 2 ml IM once a day. Then injections are given two to three times a week, or the tablet form of Milgamma is prescribed.
Mydocalm injections (100 mg) are indicated 2 times a day, the dosage is 100 mg. To enhance the effect, injections can be given on the same day.
Thus, Movalis, Milgamma and Mydocalm are prescribed to eliminate the symptoms of the disease. Despite the fact that the drugs belong to different pharmacological groups, when used together they give positive dynamics during therapy.
It is worth remembering that for patients who are sensitive or intolerant to lidocaine, this treatment regimen is contraindicated.
Drug interactions
Combined use with myelotoxic drugs increases the side effects of Meloxicam on the blood. If you take the drug together with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications, the risk of bleeding in the stomach and intestines, as well as exacerbation of ulcers, increases.
If you take Cholestyramine, the drug promotes the rapid elimination of Meloxicam. When using Heparin, Ticlopidine, drugs to lower blood pressure, and indirect anticoagulants, the risk of bleeding increases. When taken together with Cyclosporine, the likelihood of kidney-related side effects increases.
Analogues of Movalis
Analogues of Movalis on the pharmaceutical market are the following drugs: Mirlox, Artrosan, Melox, Meloxicam, Mataren.
As for Movalis injections, the doctor can replace them with medications containing the same active ingredient: Amelotex, Arthrozan, Meloxicam, Melbek, Liberum, Bi-xicam, Movasin, Mesipol.
Analogues of the drug Movalis
Movalis/Meloxicam
The drugs are based on the same active substance, so their therapeutic effect is identical. The only difference is the price.
Movalis/Voltaren
The active substance of Voltaren is diclofenac. Frequent development of side effects is noted. Unlike Voltaren, Movalis has a positive effect on cartilage metabolism. Therefore, both drugs are effective for pain relief, but for osteoarthritis, Movalis is better.
Movalis/Nise
The active substance of Nise is nimesulide. Both drugs are characterized by effectiveness in treating heat, inflammation and pain.
But nimesulide is toxic to the liver, but Movalis is not and does not have a similar effect.
Movalis relieves pain more slowly, but its effect is prolonged, while Nise is good for quickly relieving pain.