Renal failure is a disorder of the kidneys, in which the function of the organs is insufficient, that is, the filtration, formation and excretion of urine are impaired.
The disease can be acute or chronic.
There are many causes of kidney failure. How to find the problem and check the health of the organ?
Causes of poor kidney function
The causes of kidney problems can be different:
- Impaired blood supply. Urine is formed as a result of glomerular filtration. In this case, water with substances dissolved in it comes from the blood. If the pressure drops, then not enough blood flows to the kidneys and urine production is reduced. Blood pressure may drop due to injury, heart attack, bleeding, septic shock, or anaphylactic shock. The condition is acute and requires immediate response.
- Damage to the renal parenchyma. We are talking about the tissue that covers the surface of the kidneys. The outer layer is the glomeruli that filter the blood, the inner layer is the tubules through which the fluid passes before entering the calyces and pelvis. Here the necessary substances enter the blood, that is, readsorption occurs. Thus, when the parenchyma is damaged, a disturbance occurs in the processes of filtration and readsorption. How can parenchyma be damaged? With nephritis, pyelonephritis, glomeruloneritis, urolithiasis, the parenchyma can degenerate into connective tissue. As a result, function is impaired and kidney failure occurs. Such a process will not be acute, but chronic. If the parenchyma is damaged due to injury, kidney infarction, then renal failure will be acute.
- Obstruction of the urinary tract. Due to various processes, obstruction of the ureters, that is, their obstruction, can occur. As a result, the outflow of urine from the kidneys is disrupted. Obstruction can be caused by obstruction by a calculus, that is, a stone, hematoma, or as a result of compression by a tumor. Usually the blockage occurs in one ureter.
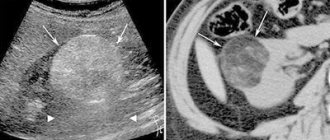
Kidneys. Norm and pathology
Structure
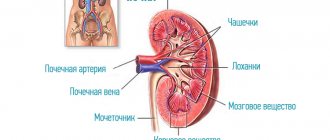
The kidneys are a paired organ of the excretory (excretory) system, which, due to their external similarity, is most often compared to a bean or bean.
However, the size of the kidney is much larger: if you average individual variations, then the dimensions of the kidney of an adult are approximately 11 x 3.5 x 5.5 cm, weight from 120 to 200 g. The kidneys are located in the retroperitoneal space, at the posterior abdominal wall, on both sides from the spinal column, usually at the border of the lumbar and thoracic regions. The asymmetry of the visceral space (anatomical structure and relative position of internal organs) determines the slightly higher position of the left kidney over the right; in addition, the left kidney is slightly larger. The membrane of the kidney is adipose tissue, under which there is a layer of dense connective tissue (fibrous capsule). The concave, in-depth part of the “bean” (renal gate) includes the renal pedicle - a complex tourniquet containing the blood supply system (the renal artery supplying blood and the efferent vein), the nerves innervating the kidney, lymphatic ducts, as well as the ostium-pelvis (the cavity where open calyxes of the excretory papillary ducts) and the ureter - a narrow tubular canal that goes down to the bladder. Together, the renal bed (external connective tissue fascia), pedicle, fatty and fibrous membranes ensure the integrity, fixation and relative immobility of the kidney - at least normally it should remain within the space allotted to it and in a vertical orientation, where the upper and lower ones are distinguished poles. In cross-section, the kidney has a complex structure: there is a dark red-brown cortical layer and a light gray medulla, deep. The medulla is formed by pyramidal-shaped drainage elements (the number of renal pyramids varies from 8-10 to 20-24), which open into the pelvis through the small and large calyces.
Parenchymatous, – i.e. The main, functional, specialized structural unit of the kidney is the nephron (similar to hepatocyte cells in the liver or cardiac muscle cardiocytes). However, a nephron is not a cell; in fact, it is an organ, a multicellular organ and a very complex structure, despite its microscopic size (an ideally healthy human kidney contains from one to two million continuously functioning nephrons). We will not remember or write down the proper names of the components of the nephron—Shumlyansky-Bowman capsule, loop of Henle, etc.—now. It is more important for us to understand that the “famous” glomerulus is a plexus of microcapillaries where the primary filtration of blood plasma begins. The term “ultrafiltration” is often (and rightfully) used: the membrane pores of the glomerular filter are so small that they do not allow protein macromolecules to pass through, separating them from the amino acids (protein components) necessary for the body, as well as from water, glucose, electrolyte ions, useful low-molecular compounds, – which is absorbed as primary urine is transported through the tubules “to the exit” of the kidney.
No less famous renal tubules, proximal and distal (respectively, nearest and distant) excrete secondary, final urine containing concentrated waste products of metabolism into the renal calyces. From the renal pelvis it enters the ureter, then into the storage bladder, from where it is expelled through the urethra in a known manner.
The danger of poor kidney function
Impaired kidney function at any stage of urine excretion or formation is fraught with problems. The fact is that urine contains a large amount of toxins and metabolic products. If the outflow of urine is impaired, then these substances will accumulate in the body and poison it. This process is called autointoxication. Substances such as:
- ammonia;
- urea;
- creatinine;
- protein breakdown products that are highly toxic.
The result will be disruption of the functioning of organs and metabolic processes. In high concentrations, substances can cause irreversible damage and death. It is important to know what symptoms indicate poor kidney function.
Features of diseases
- Understanding what a kidney is, you also need to know what pain symptoms occur when the organ malfunctions. Despite the fact that pain always occurs in the lumbar area, only a doctor can identify it based on the tests and examinations performed.
- Kidney pathologies are always accompanied by pain of varying intensity. Against this background, there is a deterioration in general well-being, which is expressed by increased weakness, frequent and painful urination, change in the color of urine and other unpleasant symptoms.
All kidney diseases are dangerous, so it is necessary to undergo timely treatment. Factors that can lead to malfunctions of the organ:
- Hypothermia.
- Promiscuous sexual contacts.
- Unbalanced diet.
- Bad ecology.
- Heredity.
According to the place of development of the pathological process, four categories of diseases are distinguished:
- Urolithiasis, caused by the appearance of increments in the organ
- Pyelonephritis, manifested by inflammation of the kidneys due to infection.
- Hydronephrosis, which develops when the outflow of urine is disrupted.
- Glomerulonephritis, which occurs when tissue is damaged and is manifested by inflammation.
When, against the background of various diseases, the functioning of the kidneys is disrupted and pathological processes occur, they speak of the development of renal failure. In this case, the organ does not perform its functions fully, which leads to malfunctions in many systems of the human body.
Signs of kidney problems
- Intoxication – fever, poor health, fatigue and lethargy, even at rest, loss of appetite.
- Swelling – if you notice swelling in the morning, it means that fluid has accumulated in the body, that is, the kidneys have not removed it. In the morning, swelling is localized on the arms and face, but during exacerbation it can be present throughout the body, spreading to the legs. Swelling first appears under the eyes, so the first symptoms will be noticeable on the face. If you press on the swollen tissue with your finger, it will become faded.
- Problems with urination - if you notice that there is less or more urine, urine has begun to be excreted frequently and in small portions, the urge is frequent, even at night, there is a burning sensation, pressure, then this sign will directly indicate that something is wrong with kidneys.
- Changes in urine - we are talking about its color, turbidity, the presence of impurities of pus and blood. The urine may become foamy or the color of meat slop, and the smell may become very unpleasant.
- Pain in the lumbar region - such sensations usually accompany acute disorders of the kidneys, such as urolithiasis. With chronic problems, pain rarely occurs. The pain can be localized on one side or both, can be sharp or aching in nature, and can radiate to the thigh, groin area or lower abdomen.
- Metallic taste in the mouth, dryness and bad breath - the smell of ammonia from the mouth may be present due to a violation of the outflow of urine, since as a result of poor kidney function, the urea content in the body increases. This may cause thirst and dry mouth.
- Vomiting, nausea – when the body is intoxicated, in particular when urea accumulates in the blood, vomiting and nausea may occur. More often this occurs in the morning.
- Increased blood pressure - if your blood pressure is high and it cannot be brought down with antihypertensive drugs, then hypertension may likely be caused by problems with the kidneys.
home
Message from the Chief Physician
I welcome you to the official website of the Orenburg Regional Clinical Tuberculosis Dispensary! Throughout the world, tuberculosis remains one of the serious medical and social problems. In modern conditions, when there is an increase in the number of stressful situations, global migration processes, as well as neglect of preventive measures and early detection of the disease, the disease can affect all segments of the population. And the rapid spread of drug-resistant strains of the pathogen threatens to turn tuberculosis into an incurable disease.
Therefore, today special attention is paid to the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis. A significant role is given to preventive work, because the level of morbidity depends not only on the living conditions of the population, but also on the level of culture of citizens, their responsibility for their health.
In June 1922, a regional tuberculosis dispensary was opened in Orenburg at the regional hospital. This was the period of formation of independent anti-tuberculosis service in the region. Of course, its capabilities were very limited and incomparable with what is in the arsenal of phthisiatricians today.
Currently, the Orenburg Regional Clinical Tuberculosis Dispensary is a large medical, organizational, methodological, training and scientific-clinical center for organizing anti-tuberculosis activities in the Orenburg region.
The scientific potential of the dispensary is two doctors of medical sciences V.R. Mezhebovsky and A.M. Mikhailovsky, seven candidates of medical sciences: A.V. Mezhebovsky, A.V. Zhigailov, V.S. Smolevsky, A.V. Donskov, T.N. Ignatova, E.M. Sheremetyeva, E.V. Goryunkova.
Modern medical technologies introduced in the dispensary, scientific achievements in the field of diagnosis and treatment make it possible to provide highly qualified medical care to patients with tuberculosis of all localizations. As a result, the incidence of tuberculosis decreases annually.
On our website you will find all the information about the treatment and diagnostic capabilities of our dispensary. In the question-answer section you can get expert advice on any question that interests you. On his personal blog, the dispensary's chief physician is ready to discuss problems associated with providing medical care to tuberculosis patients.
Sincerely,
Chief Physician of the Orenburg Regional Clinical Tuberculosis Dispensary,
Candidate of Economic Sciences
Shamshurin Mikhail Gennadievich
Signs of disease development
Different diseases have specific symptoms. But at the same time, it is necessary to undergo an examination if the following manifestations are present against the background of increased fatigue:
- Body temperature is 37°C–37.5°C, which increases slightly in the evening.
- Frequent and painful urination.
- Changes in the color of urine and the presence of blood traces in it.
- Swelling around the eyes and on the limbs.
- Aching pain in the lower back.
Renal colic is an acute pain attack that can cause vomiting and loss of consciousness. It occurs when pressure in the upper urinary tract increases. This condition often occurs when the ureter is blocked by a stone.
The best treatment is moving?
Help for kidney patients is an expensive type of medical care; a patient on dialysis costs the state more than a cancer patient. The cost of one procedure is 6,800 rubles; such procedures must be completed 3 times a week in a hospital. For life. If, of course, you manage to get there.
“The provision of dialysis for Russians is 212 people per 1 million population (tens of times lower than in developed countries”), explains Natalya Tomilina, head of the department of nephrology at Moscow State Medical University. Evdokimov.
Treatment of kidney patients is paid for from the local budget. Only rich regions can do this; residents from other places cannot get treatment.
The same thing applies to transplantation. There are several advanced transplant centers in Russia - in Moscow, Krasnodar, St. Petersburg. But they only treat “their” patients. It is easier for a person living in Vologda to get a kidney transplant in Pakistan than in St. Petersburg. Therefore, the most accessible type of treatment for a person with kidney disease is moving to a region that is prosperous in this regard.
It is possible to reduce the cost of treating kidney patients if the disease is detected at an early stage. Nephrologists are screening patients at risk - patients with hypertension, atherosclerosis, obesity and diabetes. They need to do an ultrasound of the kidneys, a urine test and a biochemical blood test once a year. And patients themselves should be more attentive to themselves.
Diet for the kidneys. Principles and menu of treatment table number 7
More details