Doctors Cost
Price list Doctors clinic
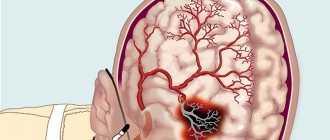
Cerebrovascular accident (CVA) is a reduction in blood access to the brain. This is a real vascular catastrophe. The brain weighs approximately 2% of a person's body weight. A relatively small organ consumes 20% of all incoming energy. The brain does not accumulate the substances necessary for its activity. For normal functioning, it needs a continuous flow of glucose, oxygen, and some other elements supplied with the blood.
Cerebral circulation is distinguished by a multi-level system of redundant vessels and several regulatory mechanisms. But sometimes this is not enough. Cutting off blood supply to the brain for 10 seconds is enough to cause irreparable harm.
Causes of circulatory disorders in the brain
- Systolic pressure is less than 60 or more than 180 millimeters of mercury.
- Insufficient metabolic control, accompanied by unreasonable dilation of cerebral vessels.
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels.
- Decreased blood oxygen saturation.
The compensatory capabilities of the brain are great. Vascular anastomoses allow blood to be distributed throughout the entire volume of the organ, even if the inflow through the left or right carotid artery is disrupted. However, these mechanisms do not work for long; after some time, oxygen starvation develops, and the first signs of the disease appear. This is why it is important to seek medical help immediately.
Most often, NMC develops against the background of:
- history of traumatic brain injury;
- chronic venous insufficiency;
- hypertension,
- atherosclerosis, ischemic heart disease,
- osteochondrosis,
- diabetes mellitus,
- hormonal imbalance,
- excess weight,
- stress, stress
- chronic fatigue,
- lipid metabolism failure,
- drinking alcohol,
- smoking.
How vascular lesions affect the brain
For proper functioning of the brain, it is important to maintain cerebral blood flow at a constant level. That is why this organ has a fairly intense blood supply. Blood flows to the brain through four main vessels in the neck: two carotid and two vertebral arteries. They connect at the base of the brain, forming the so-called Circle of Willis. From it, many smaller vessels diverge to different parts of the brain. This is a defense mechanism in case a catastrophe occurs in one of the four main vessels. The problem is that vascular diseases also affect smaller vessels that supply blood to distant parts of the brain and do not have collaterals (side or bypass blood flow paths) and compensatory mechanisms.
Acute cerebral circulatory disorders. Symptoms
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 17 million people are diagnosed with stroke every year. Five million of them die, another 5 million remain disabled.
Table 2. Types of NMC
| NMK | Kinds | Development mechanism |
| Ischemic. | Cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke). | Stopping the blood supply to a part of the brain. |
| Transient NMC. | Lasts up to a day. | |
| Transient cerebrovascular ischemic attack. | Occurs periodically. | |
| Hemorrhagic. | Intracerebral hemorrhage. | Rupture of a vessel with subsequent effusion of blood into the brain tissue. |
| Subarachnoid hemorrhage. | Hemorrhage into the subarachnoid space. | |
| Non-purulent thromboembolism. | Thrombosis. | Blockage of a vessel by a thrombus. |
| Embolism. | Blocking of a vessel with an embolus. |
Department of Vascular Surgery
History of the department
The Department of Vascular Surgery of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia was opened on October 14, 1988. The department was headed by Doctor of Medical Sciences, Gennady Vasilyevich Govorunov, one of the most respected vascular surgeons in Russia. G.V. Govorunov is the creator of an original highly professional school of vascular surgery, a brilliant surgeon and a talented scientist. Gennady Vasilyevich is the author of more than 70 scientific articles and 2 monographs devoted to the most pressing problems of vascular surgery: repeated operations on the great arteries and issues of surgical infection in patients with obliterating diseases of the aorta and arteries of the extremities
Distinctive features
The Department of Vascular Surgery is a powerful diagnostic and treatment unit, in which more than 800 operations are performed annually on various vascular systems, the operating room is equipped with the most modern equipment, and the department includes a consultation and methodological room.
Priority directions
- X-ray endovascular endoprosthetics of abdominal aortic aneurysms.
- Surgical treatment of cerebrovascular insufficiency caused by atherosclerotic lesions or tortuosity of the carotid and vertebral arteries.
- X-ray endovascular and hybrid operations for lesions of the aorta and arteries of the extremities.
- Treatment of critical ischemia of the lower extremities (including “diabetic foot”).
- Treatment of rare forms of vascular diseases (Buerger's disease).
- Thrombolytic therapy for pulmonary embolism.
- Radiofrequency obliteration of varicose veins, sclerotherapy.
Detailed description:
The Department of Vascular Surgery provides diagnosis, prevention and treatment of vascular diseases:
- Diagnosis of pathology of arteries supplying blood to the brain (atherosclerotic stenosis, pathological tortuosity, aneurysmal dilation, nonspecific aortoarteritis).
- Chemodectomas of the neck - diagnosis, surgical interventions.
- Diagnosis and treatment of arteries of the upper extremities (stenosis, Buerger's thromboangiitis).
- Diagnosis and treatment (including endoprosthetics) of the thoracic and abdominal aorta.
- Diagnosis and treatment of stenotic lesions of the visceral branches of the aorta.
- Surgical interventions (including endovascular) for renal (renovascular) hypertension.
- Comprehensive examination and treatment of patients with nonspecific aortoarteritis (Takayasu disease).
- Diagnostics and surgical interventions (including endovascular) for atherosclerotic lesions of the iliac and femoral arteries.
- Surgical interventions for aneurysms of the great vessels.
- Treatment of patients with critical limb ischemia, operations of arterialization of the venous blood flow of the foot.
- Varicose veins – diagnosis, minimally invasive surgery, sclerotherapy.
- Diagnosis and treatment (operative, surgical) of lymphedema of the extremities.
- Formation of vascular access for hemodialysis.
Emergency assistance is provided for the following conditions:
- Acute limb ischemia;
- Pulmonary embolism
- Deep vein thrombosis of the extremities;
- Thrombophlebitis of the superficial veins of the lower extremities.
Diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases is carried out using the following methods:
- Laboratory diagnostics;
- ECG;
- Echocardiography (a safe, non-invasive method of ultrasound examination of the heart, which can be used to determine the thickness of the walls of the heart, the condition of the valve apparatus, the volume of the cavities of the heart, and the contractile activity of the myocardium);
- Duplex scanning of vessels: brachiocephalic arteries, aorta, arteries and veins of the lower extremities;
- Load tests (bicycle ergometry, stress echocardiography);
- Holter ECG monitoring (for diagnosing cardiac arrhythmias and myocardial ischemia);
- Multislice computed tomography (arteries of the neck and head, renal arteries, thoracic and abdominal aorta, arteries of the lower extremities);
- Aorto-arteriography, coronary angiography (x-ray contrast method for studying the heart and blood vessels, allowing the most accurate and reliable determination of the nature, location and extent of the lesion. Today it is recognized as the “gold standard” of diagnosis
- Doppler ultrasound (measurement of the ankle-brachial index to assess the blood circulation of the limb).
Signs and symptoms of acute cerebrovascular accidents depending on the area of brain damage
- The basin of the internal carotid artery – paresthesia, paresis, paralysis on the opposite side of the face and body. Pathology of speech and vision in one eye.
- Vertebrobasilar basin - systemic dizziness, pain in the back of the head, unsteady gait, loss of visual fields, double vision, inability to swallow and speak.
- Brain stem - eye paralysis, hearing loss, swallowing and speech disorders, paresthesia of the facial skin.
- Medulla oblongata – bilateral paralysis.
- Temporal lobe – loss of spatial and temporal orientation, memory impairment.
Symptoms of brain diseases
The most common brain diseases include atherosclerosis, stroke, tumor, vascular aneurysm, and Alzheimer's disease. According to statistics, up to 85% of people are predisposed to developing diseases related to the blood supply to the brain. Such data are a consequence of the unhealthy lifestyle of modern man. The danger of brain diseases lies in their asymptomatic nature. That is, for a long time they do not make themselves felt.
Common symptoms of brain diseases include:
- Frequent headaches that do not go away even after taking medications.
- Memory impairment.
- Constant fatigue.
- Fainting.
- Cramps.
- Fever. Body temperature can reach up to 40 degrees.
- Weight loss to the point of exhaustion.
Specific symptoms of atherosclerosis:
- Noise in ears. It occurs when a cholesterol plaque has blocked 60% of the blood flow in an artery.
- Decreased erection. If a man under 50 years of age has decreased erection, then such a patient's risk of dying from a myocardial infarction is many times higher than that of the same person with normal erectile function.
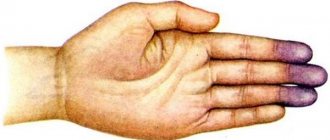
- Coldness in the extremities. The vessels become stiffer and blood flows through them worse.
Specific symptoms of stroke:
- Numbness of the face and limbs.
- Double vision.
- Difficulty moving.
Every third death in Russia is associated with this pathology.
Stroke happens:
- Ischemic. Associated with blockage of arteries, cessation of blood flow to the brain and necrosis of its tissue. The cause of the appearance is blockage of blood vessels leading to the brain due to atherosclerotic plaque. The second reason is the occurrence of a blood clot in the heart when it is not working properly (for example, during an arrhythmia). As a result, the blood clot “runs” into the brain vessels, causing thrombosis.
- Neurological. Associated with hemorrhage and hematoma formation inside the skull. It occurs due to high blood pressure when, at its peak, a small vessel inside the brain ruptures and a hematoma appears.
There are signs of a stroke that, if recognized in time, can save a life. To make it easier to memorize, they can be combined into the word “IMPACT”:
- Smile. If a person cannot smile and one of the corners of his mouth is drooping.
- Movement. A person cannot move both arms or legs at once.
- Articulation. A person cannot say anything clearly, not even his name.
- Solution. To save a person, you should take him to the hospital and carry out the necessary examinations within 1-2 hours.
Specific symptoms of Alzheimer's disease:
- Avoiding contact with people.
- Lost in space.
- Decreased emotionality and interest in life.
- Hallucinations.
Alzheimer's disease is a form of dementia that occurs in older people. It is most often found in patients who have crossed the threshold of 65 years. At the moment it is incurable.
Specific symptoms of a brain tumor:
- The headache does not go away within two weeks to a month.
- Headache is accompanied by vomiting, hearing loss and coordination.
- Motor perseverations (inability to stop performing an action).
- Inattentiveness and forgetfulness progresses.
Brain tumors are divided into benign, malignant and metastases. In the case of benign, the disease develops gradually, slowly and gently over several years.
Types of brain tumors:
- Intracerebral. The most common and aggressive form is glioblastoma. It is almost impossible to defeat her. The tumor grows through healthy tissue and cannot be localized.
- Extracerebral. They grow on the base or surface of the skull.
- Metastases are secondary brain tumors. The main cancer cells penetrate the bloodstream into the brain and cause the growth of metastases.
Sign up for a consultation
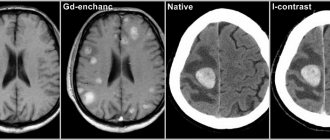
Diagnostics of NMC
- Duplex ultrasound examination of blood vessels.
- Contrast venography, angiography.
- CT, MRI.
- Transcranial Doppler.
- Laboratory tests - clinical, biochemical blood tests with determination of lipid profile, hematocrit.
- Fundus examination.
- Detection of hearing loss, smell, taste, and pathology of the vestibular apparatus.
Treatment
In case of acute cerebrovascular accident, treatment should be started immediately. The minutes count down.
For chronic pathology, the course of therapy is drawn up individually after diagnosis. The doctor takes into account age, concomitant diseases, and stage of the process.
Basic treatment includes, among other things, 3 mandatory recommendations.
- Nutrition correction. It should help normalize lipid metabolism and reduce blood cholesterol. Usually the consumption of meat, deli meats, and animal fats is limited. It is recommended to eat more vegetables, herbs, and dairy products.
- Increased physical activity. Helps normalize blood flow and increase vascular tone.
- Weight loss. Correcting your diet and increasing physical activity usually helps you lose extra pounds and be in good physical shape. If this is not enough, seek the help of an endocrinologist.
In case of cerebrovascular accident, with various symptoms, treatment is prescribed:
- physiotherapy;
- physical therapy;
- medicines;
- surgical treatment.
Diseases associated with cerebrovascular accidents
Acute or chronic damage to cerebral vessels leads to numerous cerebrovascular diseases.
Acute cerebrovascular accidents (ACVA) include various types of strokes (ischemic or hemorrhagic), transient ischemic attacks and subarachnoid hemorrhages. In ischemic types of stroke (ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack), there is a sudden obstacle to the flow of blood through the vessels, for example, a blood clot or an atherosclerotic plaque. As a result, a certain area of the brain becomes deprived of oxygen, and neurons begin to die. If during a transient ischemic attack the blockage to blood flow quickly regresses, then during an ischemic stroke it remains and a cerebral infarction is formed.
Hemorrhagic circulatory disorders arise as a result of a violation of the integrity of the blood vessels of the brain, which is manifested by hemorrhage into the substance of the brain (hemorrhagic stroke) or into the space between the brain and its membranes (subarachnoid hemorrhage).
The problem of stroke is colossal! Every day, stroke kills at least 400 people worldwide, that is, every 3.7 minutes someone dies from a stroke.
Chronic cerebrovascular accident is an equally dangerous condition. It is believed that today there are more than 35 million people living with dementia in the world. More than 40% of cases of this disease are caused by chronic cerebrovascular accidents or their combination with Alzheimer's disease. It should be said that this condition has nothing in common with “osteochondrosis of the cervical spine” and “pinched muscles in the neck.” Recently, a more precise term has been used - cerebral small vessel disease. This condition is characterized by a change in the structure of small-diameter vessels against a background of, for example, high blood pressure and, consequently, a long-term inadequate blood supply to the brain. Clinically, such conditions are characterized mainly by cognitive impairment - up to the development of vascular dementia, as well as disturbances in gait, speech, and urination.
Prevention
To avoid the sudden appearance of cerebrovascular accidents, you need to lead an active lifestyle. Do as much physical activity as possible, morning exercises. Walk more, swim, take a contrast shower. Be sure to monitor blood pressure.
You should stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
It is recommended to consume more foods rich in vitamins C, D, E, and fiber. Minimize the intake of fried, fatty, spicy, salty foods. If you have chronic diseases, they must be treated. If you have hypertension, monitor your blood pressure.
Unique methods for treating deep vein pathology
The interests of the doctors at our center were not limited solely to the treatment of varicose veins and spider veins. We have been actively involved in the problems of the main veins - the treatment of venous thrombosis and post-thrombotic disease, restoration of venous valves and bypass surgery on veins.
The leading vascular surgeon of our center, Igor Mikhailovich Kalitko, deals with the treatment of pathology of the main veins and microsurgical operations on venous valves. He was one of the first in Russia to begin using endovenous laser coagulation methods for varicose veins.
The hospital performs unique operations to restore venous valves in post-thrombotic disease, and stenting of deep veins in case of obstruction. For patients with acute venous thrombosis, we successfully dissolve blood clots - thrombolysis and perform rare operations to eliminate venous compression in thoracic outlet syndrome.
In our inpatient department, a topic is being developed at the intersection of phlebology and cardiology - the treatment of one of the most dangerous complications of venous thrombosis - pulmonary embolism. This is the highest level of treatment in vascular surgery today.
Our center does not stand still and strives to introduce all the newest and most advanced in vein treatment for the benefit of our patients. Excellent conditions have been created for them to diagnose diseases of the veins of the lower extremities; unique modern phlebology technologies are used, but the prices for our services are affordable for most patients.