Fecal incontinence is the most psychologically and socially humiliating symptom that can occur in an otherwise healthy person. This symptom consists of the involuntary passage of hard or liquid stools. The condition is caused by loss of control of the external anal sphincter or its dysfunction.
This symptom should be distinguished from other situations associated with uncontrolled stool. For example, stool leakage may be associated with hemorrhoids, anal warts, fistulas, and rectal prolapse. Insufficient control of stool elimination is also possible due to inflammatory bowel disease, laxative abuse, and infection.
Causes of fecal incontinence
The content of the article
The incidence of fecal incontinence in the general population is estimated at 2-3%. It is greatest in women over 70 years of age. Predisposes to fecal incontinence:
- elderly age;
- severe depression;
- urinary incontinence;
- complicated vaginal birth.
This problem occurs in 13-25% of women within 3-6 months after childbirth, regardless of the type of birth. Six months after giving birth, about 7% of women suffer from fecal incontinence at least once a month.
An increase in the incidence of fecal incontinence in older women has been associated with previous perineal trauma and atrophy of the external anal sphincter and fronto-rectus muscle.
Loss of complete control over bowel movements may be due to:
- sphincter dysfunction;
- impaired ability of the rectum to adapt to the amount and consistency of accumulated stool;
- impaired sensitivity in the rectum.
Loose or loose stools with gas and inflammation of the rectum speed up bowel movements or increase the frequency of the urge to defecate.
Pathogenesis
With constipation, encopresis develops as a result of constant overstretching of the rectum with a subsequent decrease in the tone of the organ wall and anal sphincter, and loss of sensitivity of the receptors responsible for the perception of stretching. In diseases of the anorectal region, the problem is caused by sphincter dysfunction against the background of mechanical obstacles or connective tissue degeneration. In neurological pathologies, incontinence is associated with innervation disorders; in mental pathologies, incontinence is associated with a lack of conscious control.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis
When evaluating a patient with fecal incontinence, a thorough history should be obtained. First, it is necessary to determine whether fecal incontinence is actually present or whether the patient complains of excessive and too frequent urge to defecate.
The gastroenterologist needs to understand how long the symptoms last, whether the patient has diarrhea, how much stool is passed, and whether there is an urgency to it. It is also necessary to determine whether the patient has undergone surgery in the past in the perineal area (in the case of women, we are talking about complicated vaginal births), whether radiation therapy was prescribed in this area, and whether the patient suffers from neurological diseases or diabetes.
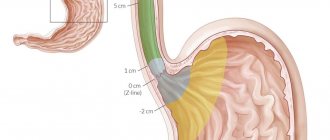
This is followed by a thorough physical examination with perineal and rectal examination, including bilateral rectal reflex examination. The absence of this reflex indicates an interruption of the reflex arc.
Anorectal diseases
Stool incontinence in men occurs with external hemorrhoids, when hemorrhoidal cones begin to fall out. The sphincter muscles no longer completely cover the anus. The result is spontaneous leakage of liquid diarrhea with mucus or at the wrong time before a planned trip to the toilet.
Other diseases of the anorectal area:
Intestinal disorders
- Tumor (malignant, benign) of the rectum, sigmoid colon.
- Paraproctitis in case of formation of a fistula, abscess in the perianal area.
- Coccydynia is a consequence of injury to the sacrococcygeal region, causing severe pain in the gluteal region and perineum. A clear sign of the disease is paroxysmal pain, not associated with the urge to defecate.
- Proctitis is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectal canal, accompanied by pain. Forms of the disease: catarrhal, ulcerative, fibrous, purulent, necrotic.
Infectious diseases caused by sexually transmitted infections can cause stone incontinence, when patients begin to experience particular discomfort in the anorectal area, constipation alternating with diarrhea, or constant difficulties during bowel movements.
Additional Research
Depending on the symptoms accompanying fecal incontinence (diarrhea or constipation), additional tests are performed that are recommended in these situations. Other tests to consider include electromyography and transrectal (endorectal) ultrasound.
- Electromyography.
Electromyography is performed using surface or needle electrodes. Its purpose is to determine the overall myoelectric activity of the external sphincter and frontorectus muscles at rest, conscious sphincter contraction, and the act of pressing on the stool. - Transanal ultrasound.
Transanal ultrasound (TAUS), including three-dimensional ultrasound, evaluates structural abnormalities in the anal sphincters, puborectal muscles, and rectal wall. For the test, endorectal probes with a frequency range of 10-16 MHz are used. This is a simple and relatively minimally invasive test.
TAUS is most useful when the history and anorectal manometry findings suggest occult sphincter injury. The results of transrectal ultrasound have a decisive influence on the choice of treatment.
A morphological defect of the sphincters exceeding 1/3 of their circumference indicates the failure of conservative treatment.
Causes of stool in children
Encocution in children who have not yet turned three years old is considered normal from the point of view of doctors. At this age, children have not fully formed conscious retention of feces. Believes that the skill is instilled during upbringing by parents who teach how to use the toilet or potty.
In the absence of pathology, stool in children over 3 years of age may be associated with relaxation of the stomach, that is, with diarrhea. In only 3% of children older than this age, the disorder may be due to the following reasons:
- psychological;
- physiological;
- psychosomatic.
The cause of the pathology may be:
- punishing a child for stool smearing, which causes fear of the process of defecation and a conscious desire to retain feces;
- eating disorders;
- constipation, including those leading to anal fissures;
- a feeling of shame when a child is not able to perform the toilet outside the usual conditions, for example, at home.
Frequent manifestations require contacting a specialist.
Conservative treatment
- Diet and lifestyle
. With nonspecific conservative treatment, it is important to change eating habits. This will reduce the frequency of bowel movements and improve the consistency of bowel movements. Well-formed stools are easier to control. It is important to understand that hard stool stuck in the rectum increases fecal incontinence, so it is necessary to promptly remove the stool remaining in the rectum. - Pharmacotherapy.
In standard situations, the following are used: loperamide, codeine and diphenoxylate. Patients who tend to pass stool uncontrollably after meals may benefit from anticholinergic medications taken before meals. For idiopathic fecal incontinence, amitriptyline is prescribed. - Sacral nerve stimulation.
This is a relatively new treatment method. Electrical stimulation of the sacral nerve roots can restore bowel retention in patients with intact muscle structure. After a successful 3-week treatment, the stimulation device is implanted subcutaneously.
Classification
Depending on the severity, there are 3 degrees of encopresis:
- First. Uncontrolled excretion of feces during the passage of intestinal gases. Typically a small amount of discharge (staining laundry).
- Second. Periodic involuntary discharge of a large volume of liquid feces.
- Third. The sphincter gapes, and solid fecal matter passes out of the rectum in an unregulated manner.
There are 3 forms of the disease:
- Partial. Incontinence occurs during significant physical exertion, severe fear, and occurs simultaneously with emptying the bladder.
- Uncontrollable. The urge persists, the patient cannot slow down the act of defecation.
- Regular. There are no urges. This type is typical for severely bedridden patients.
Encopresis as a concomitant symptom
Violation of the act of defecation can be an independent disease or a symptom of other pathologies. It is very important to establish this fact; the overall treatment regimen depends on it. People who have suffered an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke often suffer from encopresis. These are not necessarily “bedridden” patients. The patient does not always understand what is happening to him and does not seek medical help, considering what is happening to be a one-time event. Suffering a stroke on your legs is very dangerous; it can lead to deterioration of body functions and even death.
During treatment of encopresis, pathologies of the higher nervous system and disorders of nervous regulation are often identified. Treatment of the underlying disease is given initial attention.
Dysfunction of the pelvic floor organs is observed in encephalitis, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, and dementia. Encopresis also affects people who have been diagnosed with the following diseases:
- abnormalities of the genitourinary system;
- adenoma and prostatitis in men;
- uterine prolapse in women;
- benign or malignant neoplasms.
Clinic for the treatment of encopresis in Moscow
Patients note the individual approach and comfortable accommodation conditions in our clinic. If outpatient treatment does not bring results, the patient is admitted to a hospital. This is necessary for additional diagnostics of the body and search for treatment options.
You can get a preliminary consultation with a gastroenterologist, psychiatrist, or psychotherapist at any time. Specialists with extensive experience will help you understand the true causes of the disease and adjust the course of treatment if necessary.
In adulthood, encopresis can occur as a reaction to severe stress. In this case, individual consultations with a psychotherapist are necessary. During the conversation, the doctor will understand what external irritant or psychological trauma led to the development of the disease. The psychotherapeutic component of encopresis treatment in Moscow involves the formation of a new personality, free from anxiety and depression.
The constant fear that others will see and understand what exactly is happening to the patient’s body pushes him to rash actions and forced isolation. Living always indoors and hiding from loved ones and friends is not an option. Contact Dr. Isaev’s Clinic and you will understand that even with encopresis you can live a full life.
What to do if you have symptoms of pathology
It is important not to self-medicate, but to seek qualified help. You should undergo an examination in the clinic as soon as possible; the following manifestations of pathology make themselves felt:
- blood in stool;
- a person may feel chills and fever;
- pain in the gastrointestinal tract;
- nausea, vomiting.
All this indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the intestines. With these manifestations, you need to get medical help as an emergency.
Encopresis as a consequence of childbirth
Women are at risk for this disease. One of the prerequisites for its occurrence is difficult childbirth. Injury to the anal sphincter can occur both during natural labor and during cesarean section.
Women whose baby was born using obstetric forceps or vacuum fetal extraction are at risk. The causes of encopresis include high weight of the child and the birth of twins. The younger the woman, the less negative consequences there will be for the body. With age, hormone levels decrease, muscles lose elasticity and the anal sphincter can no longer contract with the same force.
Chronic diseases of the rectum and excess weight can provoke illness during labor. Usually the body returns to normal within six months after childbirth, the pathology goes away on its own. If this does not happen, we suggest undergoing a course of treatment for encopresis in Moscow at the Clinic of Dr. Isaev. An attentive approach to each patient is the key to a quick and successful recovery.
Nutrition for encopresis
Once a patient is diagnosed with encopresis, their daily diet should be carefully reviewed. This does not mean that he will not be able to eat his favorite foods, some restrictions will be required.
All dishes that cause flatulence and provoke irritation of the stomach walls must be excluded. These include:
- natural coffee and other drinks that contain it;
- alcohol of any strength, regardless of dosage;
- sugar substitutes;
- smoked, spicy dishes;
- fatty foods, spices;
- cheese, milk and ice cream (in case of poor lactose tolerance).
Meals should be regular and fractional, you need to eat small portions up to 6 times a day. The presence of grains in the diet helps get rid of frequent loose stools. Kefir and yogurt, wholemeal flour, and bran bread are very useful. The menu must include dark rice, pumpkin, nuts, dried fruits, flax seeds, and carrots. Fruits can be eaten by everyone except pears, apples and peaches.
When you urgently need to call an ambulance
An ambulance should be called if intestinal obstruction is suspected. That is, in addition to tenesmus, a person has symptoms such as the inability to empty the intestines for a long time, severe and cramping pain, or slowly increasing pain in the intestines. The symptoms are also dangerous if the patient has vomiting, frequent tenesmus with blood and there is no discharge of gases or feces even after enemas.
Before the ambulance arrives, you should put the person on the bed, apply cold to the stomach and not give any food. In this condition, the patient should not take painkillers and laxatives. You should also not apply a heating pad to your stomach.
Encopresis in the elderly
Relatives of elderly people who suffer from encopresis often come to our clinic. This is a common problem caused by age-related brain disorders. The cortical center, which is responsible for the act of defecation, begins to function incorrectly. This problem is not congenital and develops gradually with age. We are developing an individual treatment program for encopresis, consisting of many components, including the most effective methods and approaches.
Elderly people often experience psychological discomfort due to the inability to control bowel movements. They begin to avoid communication with friends and relatives and become voluntary hermits in their home. If a pensioner previously went to work, he can quit so that no one witnesses his “inconvenient” illness.
Such situations can occur up to 5 times a day. Patients are prescribed medication, as well as consultations with a psychiatrist and psychotherapist. It is important not only to eliminate the problem at the physiological level, but also to remove the consequences of psychological trauma. Often, marasmus is treated in parallel; inability to control bowel movements is a concomitant disease in some cases. In this case, the patient does not understand and does not remember what exactly happened to him.
Questions and answers
How to live with an artificial sphincter, is it a disability?
No, after successful surgery the patient will be able to control every bowel movement. This will return him to a normal life filled with bright colors. Those around him will not know that he has an artificial sphincter; it is invisible from external signs.
Do encopresis have different symptoms in men and women?
Fecal incontinence has the same symptoms, regardless of gender and age. The difference lies in what stage of the disease the patient is at.
Prevention of encopresis in adults
The disease brings considerable discomfort to a person’s life. If its first symptoms are noticed, special attention must be paid to nutrition and lifestyle. By eliminating prohibited foods from the diet and giving up alcohol and smoking, the patient significantly improves his or her prognosis for recovery. If symptoms persist, you do not need to lead an active lifestyle; you should temporarily give up sports and going to the pool. Before leaving the house, you must visit the toilet. You should always take wet wipes and a change of underwear with you. This will help you avoid getting into an awkward situation.