Why is it important to take care of your liver?
Despite the fact that the liver is quite hardy and capable of self-regeneration, it still requires careful handling. Since regular destruction of organ cells leads to an inflammatory process, tissue scarring and even cirrhosis.
In turn, such conditions reduce the size of the liver, make it dense and change the normal structure. All this leads to disruption of the functioning of the organ, as a result of which the formation of bile worsens, the blood is poorly cleared of toxins and drug residues, and poor digestion of fats is observed.
The destruction of the liver is caused by the consumption of alcoholic beverages, unhealthy diet, viral pathologies and other conditions that provoke damage to its cells. As a rule, various diseases do not cause characteristic symptoms until serious damage to the organ occurs.
Treatment
To temporarily relieve pain in the liver, patients take painkillers and antispasmodics on their own. Always remember that they can only be used after examination and recommendations from a specialist. Treatment is prescribed only after thorough diagnostic studies. Since many liver diseases have a similar course, it is necessary to make a correct diagnosis.
Before visiting a doctor, do not take painkillers or antispasmodics. They will mask important symptoms and make it difficult to make a diagnosis during examination.
Under no circumstances should you select medications yourself. And especially do not take medications prescribed to your friends in similar situations. There is no guarantee that the drugs that help them won't make things worse for you. Treatment is selected strictly individually.
To deal with this situation, consult a doctor as soon as possible. Our center is equipped with modern research equipment. This helps specialists make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment as soon as possible.
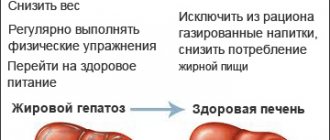
Before visiting a doctor to relieve pain symptoms (instead of taking medications), pay attention to your diet. You can independently reduce the load on the organ.
The diet to eliminate pain in the liver should be gentle and low in fat.
- It is recommended to eat: black bread, low-fat dairy products, various cereals, vegetables and fruits, boiled meat and poultry (beef, chicken).
- it is necessary to completely exclude: fried, spicy smoked, and fatty foods, baked goods, mushrooms, pork, duck, canned food, confectionery, coffee.
In some cases, diet helps much more effectively than drug therapy.
The best diagnosis of pain in the liver is MRI of the liver and MRI of the gallbladder. To identify health problems in the early stages, doctors recommend periodically undergoing a full comprehensive examination of the body.
The contents of this article have been checked and confirmed for compliance with medical standards by a gastroenterologist of the highest qualification. category Grankova Tatyana Mikhailovna.
Main signs of liver disease
There are a number of clinical symptoms that confirm organ damage and indicate that it is time to take special measures. The main signs of liver dysfunction include:
- Constant malaise and fatigue. They are consequences of intoxication of the body.
- Feeling of nausea. It develops due to insufficient quality work of the organ to cleanse the bloodstream of toxic substances.
- Discolored, often loose stools. This is a clear sign of a liver problem. Indicates the absence of bile elements in the feces, which are normally produced by a healthy organ.
- Rich dark stools. It is considered a dangerous symptom that occurs in the later stages of liver disease. It is characterized by the presence of blood in the gastrointestinal tract. This condition requires immediate medical attention.
- Jaundice syndrome. It includes a number of signs, this is the yellowing of the whites of the eyes, skin and mucous surfaces as a result of the formation of high levels of belirubin in the body. It also irritates the skin, causing severe itching.
- Vascular networks. Accompanying many diseases. They are present in everyone - men and women in small quantities. However, if they appear all over the body, this is a signal of liver cell damage.
- The appearance of bruises on the body. They form easily and appear everywhere. This is due to the fact that the liver is not able to synthesize the required amount of proteins for blood clotting.
- Hyperemia or erythema of the palms. Often observed in patients with liver pathologies.
- Dark color of urine. It acquires a rich brown, woody color due to the accumulation of bile pigment in the body.
- Ascites. Characterized by extensive stagnation. There is bloating, swelling of the legs, feet and hands.
Liver function can be impaired due to many pathologies. In total, more than a hundred liver diseases are known, caused by different reasons and having different mechanisms of development, different course and prognosis. They occur in people of any age and can be congenital, hereditary, or acquired.
Some liver diseases have a short duration and end in complete recovery, others can bother a person for years and lead to irreversible changes in the liver tissue and serious, life-threatening complications.
English synonyms
Liver disease, hepatic disease.
Symptoms
In the initial stages, symptoms of liver disease may be nonspecific. Some diseases are asymptomatic. Characteristic signs of liver dysfunction appear when a significant part of the liver tissue is damaged. Main symptoms of liver diseases:
- nausea, vomiting;
- heaviness, pain in the right hypochondrium;
- yellowness of the skin, mucous membranes and sclera.
There are also a large number of additional symptoms, the presence and intensity of which depend on the form of liver pathology, the activity of the disease and the degree of damage to the liver tissue.
General information about the disease
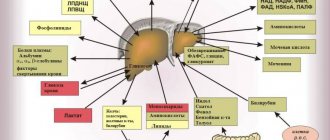
The liver is the largest gland in the human body. It is located in the right hypochondrium under the diaphragm, borders the stomach, right kidney and intestinal loops and consists of two main lobes and many lobules. Blood enters it through the hepatic artery and portal vein (from the gastrointestinal tract), and flows out from it through the hepatic vein. The liver also has a system of bile ducts, through which bile enters the gallbladder and intestines.
The liver performs a number of vital functions necessary for the normal functioning of the body:
- cleansing – cleansing the blood of microorganisms, toxins, allergens, poisons that enter the liver through the portal vein from the gastrointestinal tract, removing excess hormones and toxic metabolic products;
- synthetic – the formation of blood proteins (components of the blood coagulation and anticoagulation systems), hormones, enzymes, cholesterol, fats and their derivatives;
- digestive - synthesis of bile, which accumulates in the gallbladder, enters the intestine through the bile ducts and is involved in the digestion of fats;
- depositing - storage of blood, glycogen (a polysaccharide formed by glucose molecules), fat-soluble hormones, vitamins and microelements.
With liver disease, it can increase in size, which causes a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen. The outflow of bile, necessary for the digestion of fats, is disrupted, resulting in nausea, vomiting, increased gas formation, bloating, and bowel problems (diarrhea or constipation). The liver does not cope with the cleansing function, which leads to the penetration of poisons and toxins into the blood and causes malaise and weakness. When bile acids enter the bloodstream when liver cells are destroyed, it can cause itching. Yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes is caused by an increase in bilirubin levels. It is formed during the destruction of red blood cells, binds to glucuronic acid in the liver (direct, bound bilirubin is formed) and is excreted in the bile. In liver disease, this process is disrupted, and direct bilirubin enters the blood. Violation of protein (albumin) synthesis leads to a decrease in the osmotic pressure of the blood and the release of fluid into the tissue, as a result, edema occurs. Due to a decrease in the number of clotting factors, bleeding increases.
The following factors can cause liver damage:
- inflammation of the liver tissue, for example, with viral hepatitis;
- direct destruction of liver cells by poisons, toxins or malignant tumor cells;
- impaired blood flow in the liver, for example, with cardiovascular failure, hepatic vein thrombosis (Budd-Chiari syndrome);
- disruption of the outflow of bile, for example, when the bile duct is blocked by a stone;
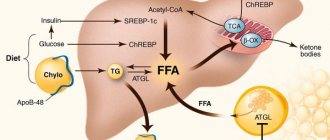
- accumulation of fats and cholesterol in the liver, that is, steatosis.
Among the many liver diseases, the most common are:
- alcoholic hepatitis - inflammation of the liver as a result of many years of alcohol abuse, which has a toxic effect on liver tissue;
- cholelithiasis - the formation of stones in the gall bladder and bile duct;
- viral hepatitis A, B, C is an inflammation of the liver tissue that is caused by hepatitis viruses;
- non-alcoholic steatohepatitis - a disease that is accompanied by the accumulation of fats in the liver and can be combined with diabetes, obesity and other metabolic diseases;
- Liver cirrhosis is a serious disease in which irreversible changes occur in the liver tissue with the replacement of normal cells by fibrous connective tissue;
- liver cancer – it can also cause damage to the liver tissue by metastases from cancer of another location;
- toxic hepatitis - caused by a direct toxic effect on the liver of poisonous mushrooms, alcohol substitutes, arsenic compounds, toluene, benzene, lead and other substances.
Less common are hereditary and autoimmune liver diseases, tumors, as well as liver pathologies associated with diseases of other organs and systems of the body. The reasons for some of them are not fully understood.
Liver disease associated with other diseases and conditions
- Jaundice in pregnancy is a manifestation of severe pregnancy pathology, in which the liver can no longer cope with the increasing load.
- Sarcoidosis is a disease that affects the liver, lymph nodes, spleen, lungs and other organs with the formation of limited areas of inflammation in them - granulomas. The cause of the disease is not fully understood.
- Neonatal hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that occurs in children in the first months of life. The most common cause is intrauterine infection with hepatitis A or B viruses. In some cases, the cause of liver damage remains unclear.
- Reye's syndrome is a severe damage to the liver and brain in children after viral infections, which is based on a disruption in the functioning of liver cell enzymes. Often associated with taking medications containing acetylsalicylic acid.
- Amoebic liver abscess is the formation of a purulent focus in the liver, which is caused by a parasite - dysenteric amoeba, which enters the liver from the intestines.
- Autoimmune diseases: autoimmune hepatitis is a disease in which cells of the immune system destroy normal liver cells; the reason for the formation of a pathological immune reaction is not fully known;
- primary sclerosing cholangitis - destruction of the bile ducts by cells of the person’s own immune system; as a result, inflammation and obstruction of the bile ducts develop.
- Hereditary diseases:
- Wilson-Konovalov disease - a disorder of copper metabolism, in which it is deposited in the liver and other organs;
- deficiency of alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT), a protein that protects the lungs from damage, while a defective AAT enzyme accumulates in the liver, resulting in impaired lung and liver function;
- Alagille syndrome is a hereditary disease characterized by congenital heart defects, pathologies of the spine, eyes, liver and kidneys;
- Glycogen storage diseases - a violation of the synthesis and breakdown of glycogen; defective glycogen can accumulate in the liver, kidneys, intestinal walls and other organs, disrupting their function;
- galactosemia - a violation of the metabolism of galactose (sugar) and its conversion into glucose with the accumulation of its breakdown products, toxic to the liver and other organs;
- hemochromatosis is a disease in which the absorption of iron in the intestine increases and it is deposited in the tissues of the body.
Who is at risk?
- People who require long-term use of medications that are toxic to the liver.
- Drug users.
- Alcohol abusers.
- Not vaccinated against hepatitis A and B.
- Frequently in contact with high doses of toxic chemicals - pesticides, insecticides, household chemicals - without appropriate protective equipment (masks, gloves).
- Pregnant women.
- Obese people.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of liver diseases is aimed at determining the immediate cause of the pathological process and the degree of damage to the liver tissue. A number of studies are also necessary to monitor the effectiveness of the therapy. Some diagnostic methods can detect the disease in the initial stages, when symptoms are absent or mild.
Laboratory diagnostics
- General blood analysis. The level of leukocytes may be increased, which is caused by insufficient purification of the blood from microorganisms or an infectious cause of liver damage. A lack of platelets may also be detected due to a decrease in the concentration of thrombopoietin, an active substance that is synthesized by the liver and stimulates the formation of platelets.
- AST (aspartate aminotransferase), ALT (alanine aminotransferase). Liver enzymes that enter the bloodstream when liver tissue is damaged. With liver disease, their increase is likely.
- Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (gamma-GT). A liver enzyme, the amount of which increases with damage to the liver and bile ducts. This is especially true for alcoholic hepatitis.
- Prothrombin index. Prothrombin is a precursor of thrombin and is involved in blood clotting. The test is used to assess the rate of blood clotting. In liver diseases, the prothrombin index may be reduced.
- Fibrinogen is a blood clotting factor that is synthesized by liver cells. When liver tissue is damaged, it may be reduced.
- Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme that is found in all tissues of the body, but mainly in the bones, kidneys and liver. In case of liver diseases, it may be increased.
- Total bilirubin. In liver cirrhosis, it is increased mainly due to the direct (bound) fraction.
- Total whey protein. In liver disease, the level of total protein can be reduced by reducing the amount of albumin. Albumins are the main proteins in blood plasma that are synthesized in the liver.
- Total cholesterol is a substance that is synthesized in the liver and is an element of cell membranes, a precursor of bile acids and some hormones. In case of liver diseases, it may be lowered.
- Tests for hepatitis B, C, D. The presence of hepatitis viruses and antibodies to them in the body is determined.
- Ferritin, transferrin. Ferritin is a protein that binds iron in the liver, and transferrin is a protein that transports iron from the intestines to the liver. Their levels may also be elevated in hemochromatosis.
- Copper, ceruloplasmin. The level of these substances is examined if Wilson's disease is suspected, in which there is a decrease in the level of ceruloplasmin and an increase in the amount of copper in the body.
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin. A decrease in the level of this enzyme may indicate congenital alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
- Alpha fetoprotein. This is a protein that is produced in the liver and gastrointestinal tract of the fetus. The maximum level of alpha-fetoprotein is observed in the fetal blood at the 13th week of pregnancy, which causes an increase in the amount of this protein in the mother's blood. Normally, men and non-pregnant women have very low levels of alpha-fetoprotein - less than 1% of the level of alpha-fetoprotein in the fetal blood. However, in diseases that are accompanied by active cell division (proliferation), its amount may increase. In particular, an increase in alpha-fetoprotein levels is a marker for testicular cancer in men or liver cancer.
- Antimitochondrial antibodies are proteins that destroy the membranes of mitochondria (cell components necessary for energy production). Their level may increase in primary sclerosing cholangitis.
- Screening study for the presence of narcotic, psychotropic and potent substances. Determination of compounds that could cause liver cell destruction.
Additional research:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Used to determine the size and structure of the liver. It also allows you to identify abscesses, granulomas and other pathological elements in the liver tissue.
- Radiography. Used to determine the size and structure of the liver, and to exclude other liver diseases. With cirrhosis, the liver can be enlarged or reduced, the liver tissue is heterogeneous, with areas of compaction.
- Angiography is of great importance in diagnosis - an x-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast agent into the liver vessels, which is clearly visible in the pictures. Used to assess hepatic blood flow.
- Cholangiography. X-ray examination, which is carried out after the injection of a contrast agent into the bile ducts. Allows you to assess the patency of the bile ducts.
- CT, MRI. Methods that resemble radiography, but provide more detailed and clear information about the structure of the liver.
- Radionuclide scintigraphy. This test involves injecting a special short-lived radioactive substance into the body, which is absorbed by liver cells, and then obtaining an image by recording the radiation it emits. Allows you to assess the condition of liver cells and the patency of the bile ducts.
- Fibroelastometry. A method reminiscent of ultrasound. A sensor is used that generates oscillations of a certain frequency. Used for liver cirrhosis to determine the percentage of connective tissue in the liver.
- Liver biopsy. The procedure for taking a sample of liver tissue is carried out using a thin hollow needle, which is inserted through the skin of the abdominal wall after preliminary anesthesia.
Treatment
Treatment of liver diseases is directly determined by the cause of the development of the pathological process. For example, antiviral and antibacterial drugs can be used to treat infectious liver lesions. The treatment regimen also depends on the stage of the disease and the degree of damage to the liver tissue.
Many liver diseases require long-term, complex treatment, which, in addition to treating the immediate cause of the disease, includes monitoring the main symptoms of liver pathology, diet, and general health procedures. In Russia, so-called hepatoprotectors are also used, that is, medications that protect liver tissue. However, there is still no reliable evidence of the effectiveness of these drugs, and they are not used in other countries.
In certain cases, surgical treatment is effective, for example, for cholelithiasis, portal hypertension. Some patients with severe liver disease that cannot be treated with medication may require a liver transplant.
Prevention
- Timely vaccination against hepatitis A and B
- Use of personal hygiene products
- Quitting alcohol and drugs
Recommended tests
- General blood analysis
- Coagulogram No. 2 (PI, INR, fibrinogen)
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- Alkaline total phosphatase
- Total bilirubin
- Direct bilirubin
- Total protein in whey
- Serum albumin
- Total cholesterol
- Transferrin
- Ferritin
- Ceruloplasmin
- Copper in the blood
- Alpha 1-antitrypsin
- α-fetoprotein (alpha-FP)
- HBsAg
- Anti-HCV
- Anti-mitochondrial antibodies (AMA)
- Screening study for the presence of narcotic, psychotropic and potent substances
- Cytological examination of punctates, scrapings of other organs and tissues
The most obvious signs of liver disease and their causes
Persons suffering from liver pathologies experience a number of characteristic symptoms that unmistakably indicate severe diseases of the organ. These include:
- Jaundice.
- Bleeding.
- Ascites.
- Encephalopathy.
- Liver fibrosis.
Jaundice
This is a clear sign of liver damage. It is expressed by yellowing of the entire body, also mucous membranes and eyes. There is skin itching and malaise. The condition is associated with liver dysfunction, when a lot of bile pigment accumulates in the body due to the inability to fully filter the blood.
Bleeding
As a rule, bleeding develops from nearby organs - the esophagus or stomach due to high pressure in the liver. The main symptoms of blood loss are severe nausea with bloody vomiting and black, sticky stools. The condition requires urgent medical attention.
Ascites
It represents extensive congestion throughout the body due to increased pressure in the liver. The abdomen increases in size, appetite and general well-being worsen. There are breathing problems, especially when lying down.
As a result of malnutrition, the body does not receive enough vitamins and nutrients it needs.
This condition is dangerous because the fluid in the body can become infected, causing extremely serious consequences.
Characteristic signs of ascites: acute and severe abdominal pain, fever. Medical intervention required.
Encephalopathy
It occurs due to severe intoxication of the body, as a result of which the brain suffers. The initial symptoms of encephalopathy are sudden changes in mood, sleep and memory disturbances. Late symptoms include confusion, drowsiness, chronic fatigue and unusual behavior.
All of these symptoms appear differently, depending on the degree of liver damage.
Contributing factors are:
- Causative agents of hepatitis.
- Overweight.
- Genetic disorders.
- Improper nutrition.
- Autoimmune diseases.
How does the disease manifest itself?
This organ is located in the abdominal cavity under the diaphragm, in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. Many people who suspect they have certain diseases are interested in three questions: “How does the liver hurt and where?”, “What does pain and discomfort in the right hypochondrium indicate?” It should be noted here that there are no nerve endings in the organ itself, so the sensation of pain in the liver is impossible. However, there are a lot of nerve endings in the outer shell (capsule) of the liver. Therefore, if the liver enlarges and begins to put pressure on the capsule, the person experiences discomfort. There is never any acute pain. As a rule, she is stupid and persistent, and does not let go for a long time. As problems increase, the pain intensifies, becomes constant, and is especially evident when moving. In some cases, discomfort occurs in the right shoulder blade and back. If the pain is severe and cramping, then, as a rule, it speaks not of diseases of the liver, but of the gallbladder and biliary tract.
Consequences of hepatic colic
The interval between relapses of painful attacks is often calculated in months, or even years. Because of this, many patients do not attach due importance to this pathology and do not seek medical help. As a result, this results in a whole bunch of diseases:
- Non-calculous, acute or emphysematous cholecystitis.
- Reactive pancreatitis.
- Hydrocele of the gallbladder.
- Cholangitis.
- Empyema (excessive purulent accumulation inside the affected organ).
- Perforation of the gallbladder.
- Gastric fistulas.
- Intestinal obstruction caused by the formation of gallstones.
What to do if you suspect liver problems?
Without delay, go to a doctor - first to a therapist, who will give you a referral for tests and, based on their results, will advise you to consult a gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, or hepatologist.
The so-called liver tests (tests) will help to assess how the liver functions:
- AST level;
- ALT level;
- GGT level;
- total bilirubin;
- alkaline phosphatase.
These are biochemical tests of blood taken from a vein.
In general, doctors recommend checking your liver function regularly, for preventive purposes, especially for people who are obese, have diabetes, or are addicted to alcoholic beverages.
Causes of the disease
Although biliary colic is closely related to cholelithiasis, other diseases can also provoke its appearance. So:
- In children and adolescents, this pathology often occurs against the background of functional disorders. Mainly - with biliary dyskinesia of the hypertensive type. In such cases, the pain attack is minor and does not last long. As a rule, it goes away on its own, without medication.
- Giardia is considered another cause of hepatic colic. These single-celled parasites enter the intestines along with food, causing inflammation of the bile ducts and their blockage. The effectiveness of treatment depends on how quickly giardiasis is detected. Duodenal intubation and bile culture are used to detect parasites.
- In adult patients, the cause of the development of pathology is often a stone in the gallbladder or common bile duct (choledochus). Driven by bile flows, it clogs the lumen, causing the smooth muscles to begin spasmodic contraction, and the patient experiences pain.
- Today, hepatic colic is increasingly developing against the background of congenital narrowing or deformation of the ducts. In such a situation, only surgical intervention (preferably) or prolonged treatment of the pathology with conservative methods can help. Ultrasound examination helps diagnose the presence of deformities.
Diagnosis and treatment
The symptoms of hepatic colic are similar to those of a number of other diseases. Therefore, an accurate diagnosis can be made only after the patient undergoes radiography and ultrasound examination of the liver and gallbladder.
Pain relief is achieved by taking antispasmodics and analgesics. Patients often combine it with the application of heat to the painful area of the body. And sometimes they try to get rid of pain with the help of choleretic drugs. If all this happens without the supervision of a doctor, the result is usually disastrous. Ordinary people do not have sufficient knowledge and experience to accurately diagnose the disease. And by self-medicating, they only put their body at risk.
It is necessary to combat hepatic colic and related diseases in a comprehensive manner. Medical gastroenterologists are ready to help you. Our specialists are leading practicing doctors in the Moscow region. They will quickly identify the disease and help neutralize it. For the convenience of patients, online registration is used. A flexible system of discounts is provided for regular clients of the clinic and patients from various social groups.
Signs of liver disease in women: how do you know when it’s time to see a doctor?
So, the main signs of liver disease in women are listed. But how do you know when it’s time to get tested for hepatitis and contact a specialist? Try answering the following questions:
- Do you feel discomfort or pain in the right hypochondrium?
- Do you have an aversion to food or have you lost your appetite?
- Do you sleep poorly and often suffer from nightmares?
- Do you feel like doing nothing and are often overcome by sadness?
- Have you noticed that your urine has become unusually dark and your stool has become colorless?
- Do you sometimes feel sick in the morning?
- Have you lost a lot of weight, but your belly hasn't gotten smaller?
- Do you have cold-like symptoms that cannot be stopped?
- Do red dots, networks of blood vessels, and bruises appear on the skin?
- Have your skin and eye whites turned yellow?
If you answered yes to at least 5 of the questions above, you need to get tested for viral hepatitis and see a doctor. It is recommended to make an appointment with a hepatologist - a highly specialized specialist who deals with liver diseases. Get a free online consultation with a hepatologist→
Rate this article:
| Total votes: 1 Average rating: 5
The first signs of liver disease in women: symptoms and treatment