The liver is the “laboratory” of the human body. Complex reactions of splitting and neutralizing compounds coming from inside and outside take place in this gland. Constant toxic or infectious exposure leads to a malfunction of the organ and the gradual destruction of its structure. Healthy tissue is gradually displaced and the gland ceases to function normally.
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic disease in which hepatocytes die and the affected areas of parenchyma are replaced by connective tissue. The surface becomes scarred and wrinkled. The changes are irreversible, especially in the last phase.
Treatment of liver cirrhosis in the early stages can stop the damage and prolong a person’s life for decades. At the same time, the liver remains active, which allows you to live a full life. Delaying contact with a doctor is fraught with serious irreversible consequences. How does pathology develop? Let's take a closer look.
If you need emergency help, contact Alco-Center
Call the hotline +7 (495) 773-03-43 and our doctors will provide emergency care for intoxication of the body with breakdown products of alcohol and narcotic substances.
from 3,200 rub.
Withdrawal from binge drinking
Emergency body detoxification procedure
from 4,000 rub.
Coding
Urgent blocking of cravings for alcoholic beverages
from 68,000 rub.
Rehabilitation
Comprehensive rehabilitation giving 100% results
Fatty liver on ultrasound
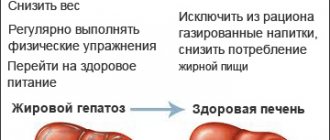
Fatty hepatosis is extremely rare in completely healthy people. It develops as a consequence of existing diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, pancreatitis, gastric ulcer, alcoholism, etc. Hepatosis is characterized by extremely rapid development of the disease. Thus, after toxic damage to the liver as a result of poisoning (mushrooms, chemicals), fatty infiltration occurs within a week. Fatty liver disease can be easily detected using ultrasound. Depending on the location of fat deposits, the disease is of three types:
- Diffuse hepatosis . Fat cells are evenly distributed throughout the organ. This type also develops in completely healthy people who violate their diet. For example, in vegetarians, a lack of protein due to the refusal of animal foods disrupts the production of lipids, which also occurs after a long-term strict diet, after eating fatty and carbohydrate foods. Metabolic disorders also occur after a course of antibiotics.
Unlike a healthy organ, with diffuse hepatosis, the freedom to conduct ultrasound is reduced, which is displayed as white spots on the screen. The deep parts of the liver are poorly visualized, and the small venous pattern is not visible. The contours of the liver remain clear, but the size of the organ increases slightly.
- Local hepatosis . Fatty formations are found only in certain areas of the liver. On ultrasound, this is reflected by hypoechoic areas against the background of healthy parenchyma. focal hepatosis. Foci affected by fatty deposits are visualized as voluminous hyperechoic areas.
Common signs of hepatosis are a “light” liver - a predominance of low-echoic tissue areas that do not conduct ultrasound well. Areas affected by fat cells prevent the organ from functioning normally, which leads to serious consequences: stagnation of bile, intoxication of the body, decreased immunity. bile does not arrive in full, food is digested worse, enters the intestines not completely digested, provoking dysbacteriosis and intestinal infections.
The liver is less able to cleanse the body of toxins, reducing the supply of nutrients and vitamins. With fatty hepatosis, the cardiovascular system suffers, hypertension, myopia, and cardiac dysfunction develop. General intoxication reduces immunity, creating favorable conditions for ARVI, influenza and other infections.
Causes of liver cirrhosis
It has been scientifically proven that regular consumption of alcohol over several years (10 or more) causes 60-70% of diagnosed cases of liver cirrhosis. Fibrosis originates from progressive alcoholic hepatosis. It is not without reason that those suffering from alcoholism are at risk of developing cirrhosis.
The prerequisites for the pathological process and the development of liver cirrhosis include:
- Chronic viral hepatitis C, B, D, G. More aggressive - type C. Virus carriage may not manifest itself for a long time, which is why in 97% it leads to massive death of hepatocytes.
- Autoimmune aggression provoked by a disorder in the immune system. Appears against the background of exposure to a virus or occurs independently.
- A parasitic infection that lasts for a considerable period of time.
- Long-term use of hepatotoxic drugs.
- The influence of toxic elements - work in hazardous industries, with reagents, chemicals.
- Development of bile duct obstruction.
- Chronic diseases of the heart and blood vessels cause venous stagnation and the formation of foci of necrosis.
The disease is asymptomatic and people are unaware of the existing threat. Progression is accelerated by a combination of several damaging factors. For example, alcohol addiction together with hepatitis C will quickly lead to a complicated course. Knowing the first signs and thinking about liver treatment is important. And yet, cirrhosis of the liver is not a death sentence and this disease is treatable and preventable.
Content:
- How does alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver develop?
- Classification
- Symptoms of the disease
- Diagnostic features
- How to treat alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver
- How long do people live with cirrhosis of the liver?
The human liver is the main organ that protects the body from the effects of poisons. It takes the brunt of alcohol and neutralizes toxins. In this difficult and sometimes unequal struggle, it itself is gradually being destroyed. As a result, inflammation develops - hepatitis, which, with continued alcoholization and the destructive influence of alcohol, turns into alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver. This complication is life-threatening and, in the absence of sobriety and adequate treatment, leads to disastrous consequences. Therefore, the sooner the patient begins to get rid of this disease, the greater his chances of regaining health. Healing pathology is included in the tasks of the main course of anti-alcohol treatment. Hepatologists deal with advanced stages.
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis
According to statistics, up to 80% of people who fall ill do not experience any significant changes in their health. A decrease in detoxification function provokes weakness, muscle pain and heaviness on the right side, under the lower rib after fried and fatty foods.
Undamaged cells are able to compensate for the work of dead cells up to a certain point. This condition lasts up to several years. Some patients experience dyspeptic disorders after drinking alcohol, even in small doses. Possible nausea, vomiting, pain in the epigastrium, flatulence, diarrhea. Once the symptoms are eliminated, everything stops.
Doctors distinguish three stages of liver cirrhosis with characteristic signs:
Compensated
- moderate pain in the right hypochondrium;
- feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- disturbance of sleep and concentration;
- external phenomena - spider veins on the skin in the upper part of the body.
Subcompensated
- an increase in neurological symptoms - drowsiness, forgetfulness, handwriting changes, fingers trembling;
- skin manifestations - spider veins in the shoulder girdle area, itching, redness of the palms, pale nails, crimson tongue;
- baldness of the armpits and pubis;
- passing episodes of water retention, flatulence, diarrhea;
- increased bleeding;
- hormonal disorders - gynecomastia in men, menstrual irregularities in women.
Decompensated
- weight loss and loss of appetite;
- osteoporosis;
- muscle weakness;
- ascites that cannot be cured;
- darkening of urine and discoloration of feces;
- yellowing of the skin and sclera;
- increased body temperature;
- hepatic encephalopathy - dizziness, heaviness in the head, confusion, possible coma;
- the addition of infection and the occurrence of pneumonia, sepsis;
- varicose veins of the digestive tract.
External signs of liver cirrhosis - “stars, red palms, a bright shade of the tongue - are associated with an excess of female sex hormones. An imbalance that occurs during the breakdown of hormones is to blame for this. Therefore, they accumulate and expand the capillaries.
When palpated in the area of the right hypochondrium, in 30% of patients, an uneven, knotty surface of the deformed gland is revealed. In 70% it is enlarged, and in 50% an enlarged spleen is added. At the stage of decompensation, a decrease in size below normal is noted. This is due to the greater coverage of fibrosis.
There are active and inactive forms. The first is characterized by slow growth of connective fibers, which lasts up to several years. Sometimes - decades. The second is characterized by progression. In the presence of provoking factors - drinking alcohol, smoking, etc., it quickly passes into the decompensated phase. Concomitant HIV infection also contributes to rapid progression.
Special methods are used to detect dangerous violations.
Compensatory stage
The onset of the disease is characterized by a slight intensity of manifestations. The patient periodically feels heaviness or discomfort on the right side in the hypochondrium - usually these sensations occur after eating or physical activity. Flatulence develops, performance decreases, periodic nausea and a bitter taste in the mouth are possible. The liver and spleen increase slightly in size. When you consult a doctor, it is quite easy to stop the development of the disease, preserving liver function.
Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis
Liver cirrhosis is often discovered unexpectedly during examination for another reason. Specific diagnostics include assessment of complaints, examination of the skin and oral mucosa. In addition, laboratory techniques are used.
The main indicator is a biochemical blood test. An increase in the values of ALT and AST, bilirubin and globulin fractions, as well as a decrease in the number of albumin fractions indicates persistent dysfunction. Deviations in creatinine and urea indicate abnormalities in kidney function.
General expanded shows reduced hemoglobin, elevated leukocyte levels and decreased platelets.
Specific markers of viral hepatitis using qualitative PCR.
Ammonia test. It does not break down and accumulates, causing intoxication.
Detection of oncology - alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) test.
Determining the concentration of immunoglobulins A and G, as well as T-lymphocytes, reveals autoimmune aggression towards its own components.
Fecal occult blood testing reveals signs of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
In addition to laboratory tests, accurate information is obtained through hardware testing.
- MRI and computed tomography can detect necrosis at the beginning of development. They detect tumor neoplasms and fibrotic foci.
- Ultrasound detects fibrous areas, determines dimensions and changes in structure. Examination of the abdominal organs, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, shows an enlargement of the gland - hepatomegaly and spleen - splenomegaly, the size of the portal vein. The conclusion is used to select the correct therapeutic tactics.
- Elastometry determines the degree of fibrosis.
- Biopsy - collection of biomaterial by puncture is done in a hospital. An informative method allows you to determine the type, root cause and degree of damage.
- FEGDS reveals varicose veins in the stomach and esophagus and the presence of nodes.
- Scintigraphy is a radionuclide examination that helps evaluate functioning. A chemical radiopharmaceutical compound is administered. By its further distribution in the body, the ability to capture and neutralize toxins is judged. In such a situation, this function is reduced. The settling of the element in the bones of the spine and pelvis indicates a critical situation.
In the compensated phase, destruction can be stopped. It will not be possible to recover completely. It is important to detect changes in time and take action. To do this, you need to consult a specialist - a hepatologist or gastroenterologist.
Classification
The disease is divided according to changes in the organ and severity. The following types of cirrhosis are distinguished:
- Small-knot.
- Large-knot.
- Mixed.
Stages of alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver:
- Compensated – without pronounced symptoms.
- Subcompensated – with initial manifestations, but with preservation of functions.
- Decompensated – accompanied by partial and then complete failure of functioning.
Treatment of liver cirrhosis
The main condition for successful therapy is the elimination of the causes that led to the pathological condition. This includes giving up alcohol, stopping hepatotoxic drugs, compensating for heart failure, eliminating infection, and following a diet.
If you start the fight when there are no obvious manifestations, you can achieve lasting improvement. Tactics are selected by the doctor individually. But there are unifying principles.
Nutrition and daily routine
For the fastest recovery, you need to eat right. Diet No.5 is prescribed. It excludes fried, spicy and smoked foods. Fatty foods - meat, fish and animal fats in any form remain prohibited. Low-fat protein foods are limited. Industrial canned food, offal and meat, fish, and mushroom broths will have to be put aside. Dishes made from legumes and high in spices are not allowed.
The doctor will recommend a decoction of rose hips or dried fruits to normalize digestion and reduce swelling. Salt is also limited. You need to eat up to 6 times a day in small portions, preferably at the same time. The daily routine includes naps and walks in the fresh air. Physical activity is limited. Lifting heavy objects and walking long distances is avoided.
Medicines
Therapy is prescribed by a specialist. Self-medication will lead to delaying time and worsening the situation. The doctor will draw up a suitable rehabilitation program, taking into account the information received. The treatment complex includes:
- Hepatoprotectors restore damaged hepatocytes and protect against damage. Preparations of ursodeoxycholic acid, essential phospholipids, and milk thistle are mainly prescribed. They stimulate the secretion of bile and reduce intoxication. This improves well-being, eliminates cramps and nausea, and improves digestion.
- Diuretics reduce swelling and remove fluid accumulated inside the peritoneum. If there is no effect, then the contents are pumped out through a puncture in the abdominal wall.
- Antibiotics are prescribed to prevent peritonitis and bacterial infection.
- Beta blockers - Atenolol, Propranolol, reduce pressure in the portal vein.
- Containing lactuose - Duphalac, Normaze, Prelaxan. Neutralizes amino acids in the intestines that cause encephalopathy.
- Complexes of vitamins B, A, C, E, P, cocarboxylase and alpha-lipoic acid improve metabolism and exhibit an antioxidant effect.
- Reducing ammonia levels - Ornilatex, Hepa-Merz, zinc preparations.
- Lipotropic agents - Heptral, Lecithin, Betargin stimulate lipid metabolism, reduce “bad” cholesterol, stimulate lipid oxidation and prevent their deposition in the cell.
- Enzymes – Mezim, Pancreatin, Creon, Micrasim, etc.
- Plant-based soothing tablets – Novopassit, Persen, Valerian and Motherwort extract. Tinctures are contraindicated here, but water infusions of medicinal herbs will be beneficial. But, before use, you will need to consult a doctor.
The result depends on the psychological mood and the efforts made. It is necessary to strictly adhere to the recommendations and medication regimen, and monitor body weight daily.
Surgical
Surgery is performed for varicose veins of the esophagus. During the manipulation, vascular anastomoses are performed and the affected areas are removed.
If the results of MRI and CT scans reveal oncological tumors, they are removed surgically. But, intervention is allowed only at the compensation stage.
Transplantation
In advanced situations, with severe damage, a liver transplant is performed. Sometimes, this is the only chance to save the patient. Unfortunately, the operation does not always end successfully.
According to the Russian Transplantation Center, Research Institute of Emergency Medicine named after. Sklifosovsky, survival rate in the postoperative year is 91%, in the next year - up to 82%. The disadvantages of this method include a large list of contraindications and high cost.
Literature:
- Gastroenterology: National Guide / Ed. V.T. Ivashkina, T.L. Lapina. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2008. - 704 p.
- Mukhin N.A., Lopatkina T.N., Abdurakhmanov D.T. Etiotropic therapy of liver cirrhosis. Clinical pharmacology, therapy. 2006, no. 1.
- Alcohol disease. Damage to internal organs / Ed. V.S. Moiseeva. — 2nd ed. reworked and additional - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2014. - 480 pp.: ill.
- Grigoriev P.Ya., Yakovenko A.V. Clinical gastroenterology: Textbook for medical students. — 3rd ed. reworked and additional - M.: Medical Information Agency, 2004. - 768 p.
Complications of liver cirrhosis
They are the result of carelessness or lack of awareness of the seriousness of the consequences. Severe complications cannot be cured and cause death. These include:
Ascites is an accumulation of liquid substance in the peritoneum. The abdomen increases, which is noticeable even in a lying position. There is weight gain and swelling of the legs. Swelling does not go away after rest and makes movement difficult.
Bacterial peritonitis occurs when fluid in the abdominal cavity becomes infected. Body temperature rises - up to 40C, severe pain and malaise appear. In the absence of emergency assistance, death occurs.
Hepatic encephalopathy is a neurological symptom complex. Headache, dizziness, and unsteady gait are observed. Often progresses into a coma.
Acute renal failure due to dysfunction of the hepatobiliary system. In the absence of timely resuscitation, it ends in death.
Portal hypertension is accompanied by varicose veins of the gastrointestinal tract. Because of this, bleeding begins, during which the pressure drops, and vomiting with bloody elements appears. The condition often ends in death. Resuscitation does not always help save the patient.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the formation of a cancerous tumor. Occurs when the disease lasts for a long time. Provoking factors are considered to be heredity and bad habits - smoking, alcoholism. In case of single tumors and the absence of metastases, it is removed surgically. In case of extensive degeneration, transplantation will help solve the problem.
The likelihood of complications of liver cirrhosis increases significantly with an inadequate approach or late detection of problems. To protect yourself, you need to undergo a preventive examination once a year, take general and biochemical tests, and do an ultrasound scan of the body. At the slightest suspicion, it is better to consult a doctor.
To prevent liver cirrhosis, play sports or engage in other adequate physical activities. Classes should be regular, preferably in the fresh air. This will help avoid stagnation. The psycho-emotional background is of great importance. Stress causes spasm of internal organs, which affects their functioning. It is better to avoid negative emotions as much as possible.
You should not ignore problems with bile discharge and excess weight. It is important to follow healthy eating rules. Doctors advise keeping a food diary. More movement, less negative emotions - the rule for restoring strength. An active lifestyle and giving up bad habits - drinking alcohol and smoking - will help avoid serious health misunderstandings and eliminate the causes of liver cirrhosis.
Author of the article: Yakovlev Evgeniy Anatolyevich
Narcologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences.
conclusions
Our ultrasound clinic offers a complete liver examination, including consultation with a highly qualified doctor, a full range of blood and urine tests, as well as ultrasound diagnostics.
It is recommended to undergo a liver examination for men over 40 years of age and women over 50, as well as younger people working in heavy industry, residents of megacities, as well as patients with a family history of liver pathologies.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Some historical data
Since ancient times, the liver has been considered as important an organ as the heart. According to the inhabitants of Mesopotamia, the liver produces blood and the soul lives. Hippocrates also described the connection between liver diseases and jaundice, as well as ascites. He argued that jaundice and hard liver were a bad combination of symptoms. This was the first judgment about liver cirrhosis and its symptoms.
Cirrhosis of the liver and its causes were described in 1793 by Matthew Baillie in his treatise Morbid Anatomy. In his work, he clearly linked the consumption of alcoholic beverages with the occurrence of symptoms of liver cirrhosis. In his opinion, middle-aged and older men were more likely to get sick. The British dubbed cirrhosis the “gin plague” or “gin liver.”
The term cirrhosis comes from the Greek “kirrhos”, which means yellow and belongs to René Théophile Hyacinthe Laennec, a French physician and anatomist. Many scientists have worked and continue to work on the study of liver cirrhosis to this day. Virchow, Kuehne, Botkin, Tatarinov, Abelov and others proposed many theories about what liver cirrhosis is, its symptoms, causes, methods of diagnosis and treatment.
First signs
Early symptoms indicating cirrhosis include the following:
- A feeling of bitterness and dryness appears in the mouth, especially often in the morning;
- The patient loses some weight, becomes irritable, and gets tired faster;
- A person may be bothered by periodic stool disorders, increased flatulence;
- Periodically occurring pain localized in the right hypochondrium. They tend to increase after intense physical activity or after taking fatty and fried foods, alcoholic beverages;
- Some forms of the disease, for example, postnecrotic cirrhosis, manifest themselves in the form of jaundice already in the early stages of development.
In some cases, the disease manifests itself acutely and there are no early signs.