- What are the benefits of fluoride?
- Why is fluoride deficiency dangerous?
- If there is too much fluoride in the body
- Fluoride products for teeth
- Water fluoridation
- Fluoride in toothpastes
- Can children have toothpaste with fluoride?
- Is there an alternative?
Most dental and oral care products contain fluoride. This is an important substance that helps strengthen enamel and prevents the spread of pathogenic microflora.
In the body, fluoride is contained in tooth enamel and bones in an amount of about 2.5–3 g. Our daily need for it is 1.5–5 mg. With a lack of this element, caries forms on the teeth. Therefore, in the USA and some European countries, fluoride is recommended for addition to drinking water and toothpastes.
Recently, articles have increasingly appeared that fluoride in toothpaste is harmful. Is it true? Let's try to figure it out.
Foods rich in fluoride
Among food sources, you can primarily consume sea fish and kelp (seaweed) as sources of fluoride, as well as eat shrimp and shellfish.
Meat, liver, milk and its derivatives, as well as eggs have an average fluoride content. Fluoride is present in apples and other fruits, nuts, some vegetables and cereals.
In order to supply your body with fluoride, you need to not only eat, but also drink. Thus, it is known that fluoride is contained in drinking water. In different regions of the country, the concentration of the mineral in water is different.
Acute poisoning[edit | edit code]
Sources F
Such poisoning is not uncommon. It usually occurs due to accidental ingestion of fluoride-containing insecticides or rodent control agents.
The first symptoms (salivation, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea) are associated with the local effect of fluoride compounds on the gastrointestinal mucosa. Systemic symptoms are varied and severe: nervous excitement (apparently caused by the calcium-binding effect of fluoride ions), hypocalcemia and hypoglycemia. Blood pressure decreases, which can be explained both by inhibition of the vasomotor center and by direct cardiotoxic effects. Breathing initially quickens, but then becomes depressed. Death usually occurs from respiratory arrest or heart failure. The lethal dose of sodium fluoride for humans is approximately 5 g, although it varies widely. Treatment boils down to intravenous administration of saline with glucose and gastric lavage with lime water (0.15% calcium hydroxide solution) or solutions of other calcium salts to bind fluoride ions. For tetany, calcium gluconate is administered intravenously. With the help of intensive infusion therapy, high diuresis is maintained.
Biological role of fluoride
Functions of fluoride:
• Improves the condition of tooth enamel, makes it stronger, reduces tooth sensitivity, reduces the risk of developing caries • Strengthens skeletal bones, helps bones maintain strength, improves recovery after fractures, slows down the development of osteoporosis in older people • Takes part in the formation of red blood cells • Participates in carbohydrate metabolism, regulating the storage of glycogen by the liver • Prevents the accumulation of heavy metal salts and radionuclides in the body, reduces the harmful effects of radiation exposure on the human body • Interacting with phosphorus and calcium, enhances their effects in mineral metabolism • Important for pregnant women for the full formation of the skeleton in the fetus • Increases the absorption of iron by the body.
CHLORINE
A constant companion of sodium in the body.
Daily requirement
Toxicity occurs at a dose of more than 15 g per day.
Significance in the body
Regulates the intake, expenditure and distribution of water in the body. Promotes the removal of toxins, helps digestion, improves liver function.
Role in vitamin metabolism
Chlorinated water destroys vitamin E.
Relationship with other microelements
Chlorinated water disrupts calcium metabolism.
Use in medicine
Chlorine ions in table salt neutralize the calming effect of bromine preparations.
Causes of deficiency
His need is fully satisfied by ordinary food, since it always contains an excess of table salt.
Causes and effects of excess
Disinfection with chlorine inevitably causes the formation of organochlorine compounds in tap water, which are the most dangerous and harmful, contributing to the occurrence of many diseases and having a carcinogenic effect.
Signs of excess fluoride
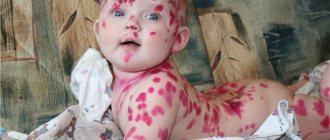
In areas where there is too much fluoride in the water and soil and where people are exposed to excess amounts of fluoride in food and liquids, a disease called fluorosis often occurs. Gray and black spots appear on the enamel of patients, and their teeth rapidly deteriorate. Joint pain is also observed, bone tissue is subject to destruction, and fractures often occur. According to a number of studies, with an excessive intake of fluoride into the body, the risk of developing malignant bone tumors in humans increases.
Excess fluoride can be not only chronic, but also acute. Poisoning occurs upon contact or ingestion of fluorine-containing substances into the gastrointestinal tract or respiratory system. If a fluoride dosage of more than 5-7 mg enters the body, it can worsen your health. Ingestion of 20 mg or more can cause severe symptoms. The patient experiences nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, blood pressure drops sharply, hemorrhages, itchy skin, and coma may even occur. The condition requires immediate hospitalization and emergency medical care.
Benefits of Fluoride in Toothpaste and Other Oral Care Products
Today, experts consider fluoride-containing dental products to be the first line of defense against dental caries [15]. The range of such products is wide. These include:
- toothpastes and mouth rinses;
- specialized and professional fluoride-containing dental preparations - varnishes, filling materials, special solutions.
It has been established that caries in the initial spot stage is amenable to remineralizing therapy, in which the surface layer of the affected enamel is restored [4]. It uses professional preparations containing a high concentration of fluoride, which are applied only in the dentist’s office, in combination with fluoride toothpastes and rinses for home use [4]. To prevent caries, experts recommend that adult toothpaste contain at least 1450 ppm of fluoride [16]. Daily use of such toothpaste increases the mineralizing potential of saliva and promotes the incorporation of minerals into weakened tooth enamel. At the same time, it is important to exclude the ingestion of any fluoride-containing products due to the risk of excess fluoride entering the body and the development of fluorosis [17].
Despite the high effectiveness of such products, the fluoride content in toothpaste for young children carries a certain amount of risk. This is due to the fact that a child may swallow the toothpaste when brushing his teeth, which may result in exceeding the daily fluoride intake. Therefore, it is very important to teach children proper oral hygiene and explain that toothpaste should be spat and not swallowed. It is necessary that young children have an adult with them while brushing their teeth to help the child and monitor the correctness of his actions. This way, parents can be sure that the paste is being spat out. If the risk of ingestion is still high, for example, the child is unwell, it is better to use specially formulated children's toothpastes that do not contain fluoride.
List of sources
- Kono K. Health effects of fluorine and its compounds. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 1994 Dec;49(5):852-60. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7830341 (access date: 02.22.2020).
- Medjedovic E, Medjedovic S, Deljo D, Sukalo A. IMPACT OF FLUORIDE ON DENTAL HEALTH QUALITY. Mater Sociomed. 2015;27(6):395–398. doi:10.5455/msm.2015.27.395-398. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4733546/ (accessed 02/22/2020).
- Sananda Dey,Biplab Giri,Fluoride Fact on Human Health and Health Problems: A Review.Med Clin Rev. 2015, 2:2. doi: 10.21767/2471-299X.100011 https://medical-clinical-reviews.imedpub.com/fluoride-fact-on-human-health-and-health-problems-a-review.php?aid=7968 (date access: 02/22/2020).
- Dentistry. Textbook Aleksandrov M.T., Bazhanov N.N., Medvedev Yu.A., Platonova V.V., Sergeev Yu.N. / Ed. N.N. Bazhanova. - M.: GEOTAR, 2008.
- Krylova L.V. Health status and level of fluoride provision for young children: dissertation... Candidate of Medical Sciences: 01/14/08 / Krylova Lidiya Valerevna [Place of defense: State Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Ural State Medical Academy"]. Ekaterinburg, 2012. https://elib.usma.ru/bitstream/usma/688/1/USMU_Thesis_2012_011.pdf (access date: 02/22/2020).
- Iordanishvili A.K. Fluorides: their importance for human health in modern conditions and prospects for use // Kursk scientific and practical bulletin “Man and his health”. 2021. No. 2. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/ftoridy-ih-znachenie-dlya-zdorovya-cheloveka-v-sovremennyh-usloviyah-i-perspektivy-ispolzovaniya (date of access: 02.23.2020).
- International Program on Chemical Safety. WHO. https://www.who.int/ipcs/assessment/public_health/fluoride/en/ (accessed 23.02.2020).
- Fluoride and healthy teeth. Paediatric Child Health. 2002;7(8):575–584. doi:10.1093/pch/7.8.575. https://academic.oup.com/pch/article/7/8/575/2654220 (access date: 02/23/2020).
- Water, sanitation and hygiene. Water-related diseases: fluorosis. WHO. https://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/diseases/fluorosis/ru/ (access date: 02/23/2020).
- Donskikh I.V. The influence of fluorine and its compounds on public health (review of literature data) // Acta Biomedica Scientifica. 2013. No. 3-2 (91). URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/vliyanie-ftora-i-ego-soedineniy-na-zdorovie-naseleniya-obzor-dannyh-literatury (date of access: 02/23/2020).
- Everett ET. Fluoride's effects on the formation of teeth and bones, and the influence of genetics. J Dent Res. 2011;90(5):552–560. doi:10.1177/0022034510384626 (access date: 02/23/2020).
- Knappvost A. Indications for use and mechanisms of caries-preventive action of deep fluoridation preparations - enamel-sealing and dentin-sealing liquids // Problems of Dentistry. 2005. No. 3. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/pokazaniya-k-primeneniyu-i-mehanizmy-kariesprofilakticheskogo-deystviya-preparatov-glubokogo-ftorirovaniya-emal-germetiziruyuschego (date of access: 02.23.2020).
- Fernández CE, Fontana M, Samarian D, Cury JA, Rickard AH, González-Cabezas C. Effect of Fluoride-Containing Toothpastes on Enamel Demineralization and Streptococcus mutans Biofilm Architecture. Caries Res. 2016;50(2):151-8. doi: 10.1159/000444888. Epub 2021 Apr 14. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27073873 (accessed 02/23/2020).
- Thurnheer T, Belibasakis GN. Effect of sodium fluoride on oral biofilm microbiota and enamel demineralization. Arch Oral Biol. 2018 May;89:77-83. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.02.010. Epub 2018 Feb 20. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29482049 (access date: 02.23.2020).
- Carey C.M. Focus on fluorides: update on the use of fluoride for the prevention of dental caries. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2014;14 Suppl:95–102. doi:10.1016/j.jebdp.2014.02.004. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4058575/ (accessed 02/23/2020).
- Novikova Zh.A. fluoride content in oral fluid in individuals with high caries intensity after using toothpastes with different fluoride concentrations // Bulletin of Dentistry. 2010. No. 2 (71). URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/soderzhanie-ftora-v-rotovoy-zhidkosti-u-lits-s-vysokoy-intensivnostyu-kariesa-posle-primeneniya-zubnyh-past-s-raznoy-kontsentratsiey- ftora (date of access: 01/29/2020).
- Walsh T, Worthington HV, Glenny AM, Marinho VCC, Jeroncic A. Fluoride toothpastes of different concentrations for preventing dental caries. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2021, Issue 3. Art. No.: CD007868. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007868.pub3. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30829399 (access date: 01/29/2020).
Why does fluoride deficiency occur?
The main reason for fluoride deficiency is the characteristics of the area in which a person lives, that is, a lack of fluoride in water and soil. However, now few people consume only local products; many types of food “come” to us from other regions of the country and even from abroad. Therefore, fluoride deficiency is rare.
Interestingly, fluoride deficiency can be caused not only by poor nutrition, but also by the use of ultra-modern water purification systems. They work so well that they strip most of the minerals from the water, and some of them are very beneficial to health and are important for maintaining health.
Forewarned is forearmed!
Let's summarize: the harm to human health from using toothpaste with fluoride today cannot be considered a scientifically proven fact. Research in this direction is carried out regularly around the world, and its results can be found from open sources. It’s up to you to decide which product to choose for daily oral care for yourself and your loved ones. But when making such a serious choice, remember two important nuances.
- Fluoride is poison, and fluoride is medicine.
- Excess fluoride leads to fluorosis, while its deficiency makes the way for caries easier.
Fluorine: price and sale
Is there low fluoride in the area where you live? Are you a vegetarian or on a strict diet? It is unlikely that you need fluoride exclusively; rather, you can be recommended complex vitamin and mineral supplements containing this and other elements.
Check out our assortment, you can buy any useful dietary supplement at great prices! Add the selected drug to your cart or call.
Also on our website you can get a free consultation with a nutritionist on taking dietary supplements and vitamins.
There is a toll-free number for regions
8 800 550-52-96.
History of discovery
The first fluorine compound was described even before the discovery of the element itself. This compound is the mineral fluorite, also known as fluorspar, calcium fluoride, CaF2. The properties of fluorite were described back in the 16th century. German scientist Agricola. In those days, fluorspar was used in metallurgy.
The mineral increased the fluidity and reduced the temperature of metal slag. As a result, slags in melts were more easily separated from metals during their smelting.
The name fluorite comes from lat. fluo – flowing.
A remarkable property of fluorite: when heated after irradiation with ultraviolet light, it emits a glow. This is where the term “fluorescence” comes from.
In 1771, the Swedish chemist Scheele reacted fluorite with sulfuric acid. In this case, hydrofluoric acid was obtained - an aqueous solution of hydrogen fluoride, HF.
Some mistakenly considered it to be the oxide of an unknown substance fluorium or fluorine. Later, in 1810, the English chemist Davy isolated chlorine by electrolysis of hydrochloric acid, HCl. And then he logically assumed that hydrofluoric acid is a compound of hydrogen and fluorium.
And if so, then this substance can also be isolated in much the same way as chlorine. The famous French scientist Ampere, having familiarized himself with the properties of hydrofluoric acid, proposed replacing the name “fluor” with “fluorine” (from the other Greek phtoros - death, destruction). However, it was not possible to obtain it for a long time.
The reason is the high chemical activity of this substance. Only in 1886 did the French chemist Moissan manage to isolate pure F by electrolysis of hydrogen fluoride. Due to the difficulty of obtaining and storing it, it did not find practical use for a long time. In the second half of the 20th century. it began to be used for industrial purposes, as well as for the separation of uranium isotopes in the production of nuclear weapons.
The fight against fluoride: complete victory is still far away
Today, fluoride toothpastes are under attack by activists and some dentists. But how did fluoride become the object of criticism, if just yesterday it was considered the main fighter against caries? Here is a brief chronology of events.
The leader of the fight against fluoride was the former head of the department of cellular biochemistry at the National American Cancer Institute, Dean Berg. In 1977, he spoke in the press with accusations against companies using fluoride.
Together with the Water Safety Foundation, Berg conducted a study and came to the conclusion that an excess of this substance in the body provokes cancer. Japanese scientists from the College of Dentistry in Nippon share the same opinion.
Articles appeared in the press accusing the American government of using fluorides to purify water to get rid of fluoride reserves accumulated during the Cold War. Companies producing hygiene products containing sodium fluoride were also ostracized.
In 1991, the U.S. Public Health Service released a report indicating that the average American's fluoride intake exceeded 6.5 mg per day, well above safe levels. The main sources of the substance entering the body: fluoridated water, toothpastes, drinks, food. How does fluoride get into food? The fact is that this is a component of fertilizers that are used in the States.
Under pressure from public organizations, the US government has required manufacturers to place warnings on fluoride toothpastes. In particular, companies must indicate that ingestion of this product can cause poisoning. Since 1997, such a warning has been included on all tubes of toothpaste containing fluoride. Also, as a result of the publication of these facts, many countries have abandoned water fluoridation.
However, all this hype in the press for corporations producing toothpastes means little so far. If we compare the anti-fluoride fight with a war, the enemy is defeated, but has not yet laid down his arms.
The perfumery and cosmetics industry is not going to give up such a profitable business. In addition, scientific research is being conducted in order to obtain a compound that will be completely safe. Today, tin fluorides are increasingly used in hygiene products, which are supposedly less dangerous compared to sodium fluoride.
Clinical researches
Clinical studies have proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66% after just 4 weeks.
Sources:
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
How to strengthen teeth effectively and without harm to health?
In the prevention of tooth decay and gum disease, hygiene is of paramount importance. At the same time, it is not only toothpastes that protect against pathogenic bacteria. The main thing to remember is that microbes multiply when the acid-base balance is disturbed. And you can restore this balance if you simply rinse your mouth thoroughly after eating.
Diet is also very important. Don't forget to eat solid plant foods: carrots, apples, cabbage. This will strengthen your teeth and gums and help cleanse your mouth naturally.
To prevent periodontitis, it is recommended to take a supplement such as Osteomed. It contains calcium citrate, which is perfectly absorbed, and another component of the drug is drone homogenate. It is the source of all the amino acids, vitamins and minerals needed for our health. Calcium citrate supplies the mineral to teeth and bone tissue, and drone homogenate normalizes hormonal levels and improves metabolic processes. The action of these two components gives a synergistic effect, which perfectly protects teeth and gums from diseases.
Category Hygiene Published by Mister stomatolog
Echoes of the arms race
Until the mid-20th century, only specialists knew about fluoride. Everything changed in the 1940s, when the United States turned to it during the development of atomic weapons - the chemical was needed to process uranium ores. Then they tried to use it as a component of rocket fuel, but abandoned this idea due to the high toxicity of the substance.
Fluorides are still used in industry today, so industrial emissions contain these substances. These are components of freons, which today are considered the main destroyers of the ozone layer. Fluorides are present in some medications; for example, fluorouracil is a well-known antitumor agent.
Few people know that fluorine is used to produce Teflon-coated cookware. The real name of Teflon speaks for itself - polytetrafluoroethylene. This material is also called fluoroplastic.
Fluorides are still used in the United States for antibacterial water purification. This method began to be used in the 1940s, when there was an urgent need to find a means for disinfection and there was little concern for safety. In countries such as Finland, Canada, and Israel, water fluoridation was abandoned.
Which toothpastes are better?
The question arises: “If fluorides are so dangerous, wouldn’t the solution be to abandon them altogether?” Dentists do not have a clear opinion on this matter. On the one hand, fluoride compounds are toxic, and on the other, they protect tooth enamel. However, given their ability to accumulate in the body, it is better to opt for products that do not contain fluoride.
You also need to take into account that toothpastes are filled with other, no less dangerous chemicals. Among the main anti-heroes is sodium lauryl sulfate, which manufacturers designate with the abbreviations SLS and SLES. This substance was previously used to wash engines, and is now a component of hygiene products. It is contained not only in toothpastes, but also in shampoos, shower gels, and shaving foams.
Scientists from Oslo believe that SLS provokes ulcerative lesions of the oral cavity, causing a disease such as aphthous stomatitis. They also suggest that this component dries out the oral mucosa.
If you want to protect yourself from the harmful effects of fluoride, then today there are every opportunity for this. The market is replete with toothpastes that do not contain this “suspicious subject” at all. They contain other active ingredients to destroy harmful bacteria, such as zinc. It slows down the formation of plaque and tartar well.
Calcium compounds are also used as an alternative to fluorides: calcium citrate, calcium pantothenate, calcium lactate, calcium glycerophosphate, synthetic hydroxyapatite. When the composition contains such compounds, you will not find fluorides there. Also, natural ingredients are included in toothpastes, for example, calendula, eleutherococcus. This is understandable, since calendula is one of the most powerful plants in terms of anti-inflammatory effects. Here is just a short list of fluoride-free toothpastes: PresidentUnique, Rocs, Biocalcium, Maximum, Asepta.
Application
Fluorine is used to obtain:
- freons - widely used refrigerants;
- fluoroplastic - chemically inert polymers;
- SF6 gas - a gaseous insulator used in high-voltage electrical engineering;
- uranium hexafluoride UF6, used for separating uranium isotopes in the nuclear industry;
- sodium hexafluoroaluminate - an electrolyte for producing aluminum by electrolysis;
- metal fluorides (eg W and V), which have some beneficial properties;