Lung diseases are dangerous and fraught with both serious impairments in a person’s condition and death in advanced conditions. At the same time, people often know about pneumonia and bronchitis, but do not remember about other pathologies. But there are a huge number of different diseases of the respiratory system, and they all have their own characteristics.
Article on the topic Lack of air. What diseases make it difficult for a person to breathe?
“During the pandemic, we have all become focused on the symptoms of coronavirus infection, so most people associate cough, shortness of breath and heaviness in the chest only with this new disease. However, I would like to remind you that there is a wide range of diseases with similar symptoms. The doctor and the patient must be very attentive in order to recognize this or that pathology in time,” says the director of the therapeutic clinic and head of the department of therapy, clinical pharmacology and emergency medical care at Moscow State Medical University named after. A. E. Evdokimova, professor, Honored Scientist of the Russian Federation, head of the educational organization for doctors, ROO "Outpatient Doctor" Arkady Vertkin.
Why do doctors say that the patient should also be attentive? Because it is he who must recognize and correctly describe his symptoms to the doctor. “For example, if you have a cough, then you need to pay attention to the following points: the nature of the cough (constant or paroxysmal), its duration, time of appearance during the day, volume and timbre, whether it is dry or wet, what type of sputum is discharged, which brings relief or, on the contrary, what aggravates it,” emphasizes Arkady Vertkin.
To understand what you have to deal with, you need to analyze the characteristic symptoms of certain pathologies, the professor emphasizes.
Will tomography show everything? A doctor on whether COVID can be confused with lung cancer Read more
Lungs' cancer
A terrible disease that can develop silently and unnoticed over years. It's no secret that smokers are often susceptible to it. Therefore, when they start coughing, many o. And so they miss the initial stage of oncology, says Arkady Vertkin.
Symptoms:
- cough that has a long, persistent character;
- hemoptysis;
- hoarseness of voice;
- dyspnea;
- chest pain, often unilateral, aggravated by deep breathing and coughing;
- weight loss and loss of appetite;
- weakness and fatigue.
“In addition, pneumonia of the same localization, occurring repeatedly within a short period of time, may indicate lung cancer,” the specialist emphasizes.
Hidden threat. The tuberculosis epidemic may be worse than the coronavirus Read more
Main symptoms of lung diseases
Main symptoms of lung diseases
Chest pain .
The pain can be of various types. It can be constant or intensify with inspiration. The pain can radiate to the neck, shoulder, and shoulder blade. Chest pain cannot be ignored, since it can be a manifestation not only of the “notorious osteochondrosis” or “intercostal neuralgia”, but of much more serious and dangerous diseases. In addition, chest pain may have a real cause not in the chest at all, but, for example, in the abdomen or retroperitoneum. Chest pain is a reason to see a doctor, and not for self-medication in the form of thoughtless and uncontrolled use of pills and warming ointments. Cough and sputum. The cough can be dry (when sputum is not coughed up) and wet (with sputum discharge). Cough is one of the most constant symptoms of pulmonary pathology, although it is not strictly necessary. Cough can be accompanied not only by lung diseases, but also by heart disease, taking certain medications, diseases of the peripheral nerves, stomach and esophagus, etc. The sputum that the patient coughs up has its own characteristics that can help in diagnosis. For example, the color of sputum is important. Mucous sputum is white and (or) transparent, purulent sputum has a color from light yellow to green. If there is blood in the sputum, it may be scarlet to rusty or brown. The smell of sputum is also important. A fetid, putrid odor indicates destructive processes in the lungs. Unfortunately, patients often neglect to see a doctor, believing that a daily cough is a common occurrence: “I smoke, that means I cough,” “Yes, I have a cough, I’ll have to go to see them.” Unfortunately, if treatment is delayed, it is often difficult to help a patient, and sometimes even impossible.
Shortness of breath and suffocation . Perhaps this is the only complaint that does not allow you to put off a visit to the doctor. Shortness of breath may occur during physical exertion, and may disturb the patient at rest and even during sleep. It happens that shortness of breath intensifies or occurs when in contact with strong odors or pets. Some patients attribute shortness of breath to age, body weight, smoking, and fatigue. There are many reasons for shortness of breath. These may be: lung diseases (asthma, COPD, bronchitis, tuberculosis, cancer, etc.), heart diseases (myocarditis, arrhythmia, coronary artery disease, heart failure, heart defects), blood diseases (anemia, erythremia), vascular diseases ( pulmonary embolism, pulmonary vasculitis, pulmonary arterial hypertension), kidney diseases (glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, polycystic kidney disease), metabolic diseases (obesity) and much, much more. In order to identify the cause of shortness of breath, it is necessary to undergo an in-depth examination, which will make it possible to make the correct diagnosis and begin treatment. Shortness of breath is ALWAYS a DANGEROUS SYMPTOM that requires immediate help.
Snore. Unfortunately, in our country, snoring is paid attention solely as an inconvenience for others, and not as a symptom of a disease. In fact, every fifth inhabitant of the earth after 30 years of age - snoring is a symptom of a serious illness - obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, or OSA for short. This disease increases the risk of death from a heart attack or stroke tenfold and causes a feeling of chronic fatigue and weakness. In order to determine whether snoring threatens you and your health, you need to see a doctor and undergo an examination.
As can be seen from the variety of diseases and symptoms, it is difficult to diagnose respiratory diseases on your own (using the Internet, reference books, friends). If any of the above symptoms occur, you should consult a pulmonologist.
- Pulmonology;
Tuberculosis
Many are still confident that tuberculosis is a thing of the past, in history and in Remarque’s novels, says Arkady Vertkin. Unfortunately, it is not. Russia is in third place in terms of the prevalence of this disease.
Another incorrect belief is that tuberculosis is a disease of people of special social status (people without a fixed place of residence, migrants released from prison, alcohol and drug abusers).
“These are indeed risk groups for infection with this disease, but, unfortunately, due to its widespread prevalence, tuberculosis can be contracted regardless of belonging to any social group - just look at the patients in TB departments,” the professor notes.
Symptoms:
- prolonged dry cough;
- constant low-grade fever (increase in temperature from 37.0 °C to 37.9 °C) or an increase in body temperature in the morning with the evening temperature curve returning to normal;
- sweating, especially at night;
- weight loss with preserved appetite;
- weakness, fatigue;
- generalized or limited enlargement of lymph nodes;
- hemoptysis.
Treatment is required; there should be no self-help, only examination and therapy prescribed by a doctor, so as not to aggravate the situation.
What is COPD and how to cope with chronic bronchitis? More details
Diagnosis and treatment
There are different ways to examine the lungs and adjacent respiratory structures. The most commonly used method is radiographic examination. But in case of severe disease and insufficient data from traditional diagnostic methods, it will be necessary to undergo a targeted tomographic scan using a computer or magnetic resonance imaging unit. Any inflammatory process, abnormal neoplasms at the earliest stages, the extent of the spread of pathology are clearly visible on tomograph images, which helps to establish the most correct diagnosis. Treatment consists of taking antiviral drugs or targeted antibiotics.
You can undergo an MRI examination or in St. Petersburg at any medical center that has the necessary equipment. All diagnostic institutions registered in the city are included in a single list of recording services. Go to the portal, select the desired procedure and make an appointment directly through the website. The centers are located in a differentiated list, which makes it easy to compare prices and ratings, get acquainted with general information and choose a convenient location address. All service users receive special discounts on the selected type of procedure.
COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common disease that often affects smokers or former smokers. This disease develops slowly, so it usually appears only at the age of 40-50.
“If a person has COPD in an advanced stage, then it is difficult for him to do even simple, familiar things, for example, tie his shoelaces, lift a bag or bag of groceries, climb the stairs - such actions will cause shortness of breath,” says Arkady Vertkin.
Symptoms:
- cough daily, often in the first half of the day, rarely at night;
- sputum production of any nature;
- shortness of breath is constant, increasing with physical activity, respiratory infections;
- combination of cough and shortness of breath with prolonged exhalation;
- wheezing.
Hard breath. How to learn to live with bronchial asthma Read more
Bronchial asthma
Literally translated from ancient Greek as “heavy breathing,” the specialist notes. This is a chronic inflammatory disease of the respiratory tract, which is manifested by a narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi due to three components: bronchospasm (involuntary contraction of the smooth muscles of the bronchi), swelling of the bronchial mucosa and viscous bronchial secretions.
“According to WHO statistics, more than 200 million people in the world are diagnosed with bronchial asthma. Many people mistakenly believe that they are not at risk of asthma if there are no asthmatics in their family or if the disease did not manifest itself in childhood. In fact, the prevalence of this disease is gaining momentum every year; people with a burdened allergic history are susceptible to it: allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis and food allergies,” sums up Arkady Vertkin.
Symptoms:
- an attack of suffocation, which is provoked by exposure to triggers (inhalation of strong odors (perfume, tobacco smoke, bleach, gasoline, etc.), cold air, physical activity, emotions (laughter, tears), etc.;
- wheezing, distant wheezing;
- combination of cough and shortness of breath with prolonged exhalation;
- chest congestion;
- paroxysmal cough, mainly at night or in the morning, ending with the separation of transparent (vitreous) viscous, scanty sputum.
Special treatment and observation by a doctor is required.
Vaccination, hardening and vitamins. The doctor talks about how to protect yourself from pneumonia Read more
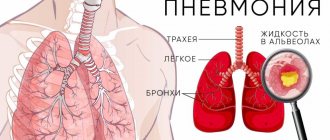
Pneumonia
It is very important to know and remember that pneumonia never occurs just like that: from hypothermia or anything else. “Pneumonia is a sign that the body already has problems associated with the pathology of other organs. Most often these are diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, the presence of cancer, chronic alcohol intoxication, etc., i.e. the patient suffers from comorbid pathology,” notes Arkady Vertkin.
Now, for the most part, pneumonia is associated with the new coronavirus infection COVID-19, but it is worth remembering the symptoms of “classic” pneumonia.
Symptoms:
- increase in body temperature to high numbers - above 38 ° C (not necessary!);
- short-term non-productive cough, followed by productive cough;
- purulent or “rusty” sputum;
- dyspnea;
- chest pain.
It is impossible to delay treatment, because pneumonia is a serious disease that often causes death.
Why is he coughing? Three questions about bronchitis Read more
Bronchitis
Bronchitis is an inflammatory disease of the bronchi. “The symptoms depend on the type of bronchitis: is it acute or chronic, occurs with or without obstruction, etc.,” says Arkady Vertkin. Let us dwell, the specialist notes, on the main clinical symptoms of acute bronchitis lasting less than 3 weeks, which, as a rule, is one of the manifestations of catarrhal respiratory syndrome in acute respiratory viral infection (ARVI)
Symptoms:
- typical symptoms of general intoxication are weakness, malaise, headache;
- fever of varying severity (optional);
- dry cough (boring and paroxysmal), alternating with wet cough;
- greenish and yellowish sputum indicates a bacterial infection, and white or clear mucus indicates its absence;
- possible pain behind the sternum and between the ribs, aggravated by coughing;
- in the presence of bronchial obstruction, shortness of breath with prolonged exhalation and wheezing appears.
We should not forget that symptoms characteristic of pulmonary diseases can also occur with pathologies of other organs and systems, for example, with heart failure and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), the specialist emphasizes.
Flame pump. Why does chronic heart failure develop? More details
Pain when coughing
Fungus
Ulcer
13977 09 December
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Pain when coughing: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Pain when coughing is most often associated with respiratory diseases and is localized in the chest.
The respiratory system consists of the upper respiratory tract (nasal cavity, larynx) and lower respiratory tract (trachea, bronchi and lungs). The air passing through the respiratory tract is cleaned, warmed, and moistened. At the end of the smallest bronchi (bronchioles) there are alveolar ducts and alveolar sacs, in which gas exchange occurs. The respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts and alveolar sacs with alveoli make up the alveolar tree, or respiratory parenchyma of the lung. The listed structures, originating from one terminal bronchiole, form a functional anatomical unit - the acinus. The alveolar ducts and sacs belonging to one respiratory bronchiole constitute the primary lobule (there are about 16 of them in each acini). The number of acini in both lungs reaches 30,000, and the alveoli - 300-350 million. The acini make up lobules, the lobules make up segments, the segments make up lobes, and the lobes make up the whole lung.
Each lung is enclosed in a double membrane - two layers of pleura, between which there is a sealed pleural cavity filled with a very small amount of fluid.
Coughing is the body’s protective reaction to any irritation of the respiratory tract.
Irritants of cough receptors can be sputum, blood in the respiratory tract, mucus from the nose flowing down the back of the throat, various allergens, smoke, dust, foreign bodies, cold air, certain medications, etc. Types of pain when coughing
Pain when coughing can be severe or low intensity, sharp or dull, limited or diffuse. The location of the pain depends on the cause of the cough and the affected organ. It can be felt in the throat, behind the sternum, inside the chest, under the ribs, in the back, stomach, and radiate to the head. Cough and pain can be symptoms of the same disease or independent of each other.
Possible causes of pain when coughing
The following causes of pain when coughing are identified:
- overstrain of the respiratory muscles involved in coughing;
- diseases of the respiratory system;
- heart disease;
- injuries and diseases of the bones, muscles and nerves of the chest;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- kidney diseases, etc.
What diseases cause pain when coughing?
In diseases accompanied by a constant painful cough, the intercostal muscles and diaphragm become overstrained, which manifests itself as dull, diffuse muscle pain.
When the mucous membrane of the trachea is inflamed (tracheitis), a dry, loud, hacking, rough cough occurs, which is characterized by burning and pain in the chest.
The severity of pain decreases when a dry cough turns into a wet one. Tracheitis is most often infectious, caused by viruses or bacteria.
Patients' general health worsens and their body temperature rises.
With inflammation of the lungs (pneumonia), a deep cough with sputum is noted, pain appears in the chest in the projection of the inflamed area of the lung.
The pain increases with coughing and deep inhalation due to the movement of the pleura, and decreases if the patient lies on the side of the affected lung.
Inflammation of the lungs can be primary, in this case the disease begins acutely - with chills, weakness, an increase in body temperature to 38–39 ° C, accompanied by a cough and difficulty breathing, more often occurs as a croupous lesion, that is, the inflammatory process takes over the entire lobe with the involvement a large area of pleura. And it can be secondary, when inflammation moves from the bronchi to the lung tissue. A focus of bronchopneumonia occurs, but even in this case the pleura can become inflamed, with the only difference being that the size of the lesion is much smaller. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
Pleurisy (inflammation of the pleura) can be infectious or non-infectious. Infectious pleurisy
occurs with pneumonia, lung abscess, bronchiectasis (dilation and deformation of the bronchi with the development of chronic purulent inflammation), tuberculosis, abscess under the diaphragm, inflammation of the perirenal adipose tissue, inflammation of the pancreas.
Non-infectious pleurisy
is caused by systemic connective tissue diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc.), spread of tumor cells to the pleura, decreased pumping function of the heart (for example, with myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism), chest injuries (closed rib fractures) and etc. Pleurisy can be dry, in this case the amount of fluid in the pleural cavity decreases, the inflamed layers of the pleura do not slide, but rub against each other when breathing, which provokes a very painful reflex cough, which intensifies with inhalation. Pleurisy is exudative, when due to the inflammatory process fluid is released and accumulates in the pleural cavity. During the period of fluid accumulation, the clinical picture is similar to dry pleurisy, then the fluid pushes the layers of the pleura apart, the pain becomes weaker, but at the same time, due to compression of the lung, shortness of breath occurs.
With gastroesophageal reflux disease, due to the reflux of acidic gastric contents into the esophagus, its mucous membrane becomes inflamed, heartburn, sour belching, pain, burning behind the sternum and coughing are observed, which increases the pain.
Lung tissue does not have pain receptors, therefore, with lung cancer, pain appears when tumor cells grow into the surrounding tissues - pleura, trachea, bronchi, etc. In this case, the patient is bothered by a painful cough, often with blood. General health worsens, weakness, weight loss for no apparent reason bothers you.
A similar situation arises if metastases from other organs enter the lungs; this can happen with cancer of the breast, stomach, esophagus, rectum, skin (melanoma), kidney, liver, etc.
Pericarditis (inflammation of the lining of the heart), similar to pleurisy, can be dry and effusion. It can be caused by heart diseases (myocardial infarction, inflammation of the heart muscle, etc.), various infections, systemic connective tissue diseases, heart injuries, tumors, etc. Dry pericarditis is accompanied by a gradually increasing dull, pressing pain behind the sternum, radiating to the neck and left shoulder blade. In this case, a rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and a dry cough appear, which increases the pain. As fluid accumulates between the layers of the pericardium, the condition worsens due to compression of the heart.
Intercostal neuralgia occurs when the intercostal nerve is compressed at the level of its exit from the spine or along its course. It manifests itself as a sharp, aching pain that intensifies during a deep breath and coughing.
Cough increases pressure in the abdominal cavity and pelvic area, therefore, in case of inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (for example, appendicitis), pelvic organs (for example, inflammation of the ovaries), hernias (linea alba, umbilical, inguinal), cough can provoke or intensify an already existing pain.
The brain and spinal cord are washed by cerebrospinal fluid, its fluctuations during coughing increase intracranial pressure, and headaches occur. This process can be natural, or it can hide serious diseases: space-occupying formations in the cranial cavity, vascular abnormalities that impede the movement of cerebrospinal fluid.
Which doctors should I contact?
First of all, you should contact a general practitioner, and he, if necessary, will refer you to a specialist for consultation (, , etc.).
Diagnosis and examinations in case of pain when coughing
To identify the causes of pain when coughing, the doctor collects anamnesis, conducts a thorough examination of the patient and prescribes additional laboratory and instrumental tests.
- Clinical blood test with a detailed leukocyte formula.
Heart failure
Every minute in Russia one person with chronic heart failure (CHF) dies. This complication is detected in many diseases and vascular accidents, notes Arkady Vertkin. According to statistics, more than 12 million people with this pathology are registered in Russia. 92% of patients in cardiology departments are hospitalized due to decompensation of chronic heart failure. It is important to note, the professor says, that cough and shortness of breath may be the first signs of CHF.
Symptoms:
- dry cough, combined with increasing shortness of breath;
- increased cough during physical activity, in a horizontal position, at night;
- “bubbling” breathing;
- symmetrical swelling of the lower extremities, palpitations, a feeling of interruptions in the functioning of the heart;
- orthopneic position.
A history of diseases of the cardiovascular system, including a previous myocardial infarction, coronary artery stenting, coronary artery bypass grafting, atrial fibrillation, as well as the presence of background pathology (arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus and obesity) will help recognize this complication, the specialist warns .
Gastroesophageal reflux disease: how to prevent exacerbation Read more
Factors that cause pain in the lungs when coughing
When collecting anamnesis, the specialist pays attention to factors such as the patient’s commitment to smoking. Long-term addiction to a bad habit weakens local pulmonary immunity, which facilitates easy penetration of the tuberculosis bacillus. Combustion products contained in cigarette smoke lead to the development of oncology of the respiratory system and the occurrence of asthmatic syndrome. A prolonged cough is also caused by pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, heart and vascular network.
An unfavorable factor is also the systematic use of certain medications necessary to maintain normal heart function. Chronic dry cough often appears among women who have crossed the threshold of menopause. A history of acute respiratory disease serves as the starting point for the appearance of an anomaly that cannot be cured. In this case, only symptomatic treatment is used, taking antitussives.