Why is opisthorchiasis dangerous?
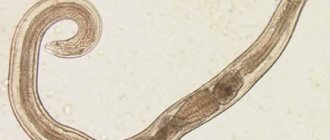
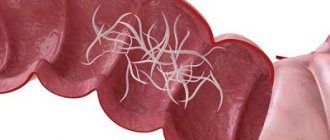
The causative agent of the disease, the cat fluke, parasitizes the gallbladder and bile ducts and devours the mucous membrane of organs. The normal digestive process gradually deteriorates. Dysbacteriosis occurs, an allergic reaction of unknown origin appears, the internal organs closest to the gallbladder become inflamed, and stones form.
If the pathology appears during pregnancy, the parasite has a depressing effect on the development of the fetus, physical and mental development. One of the most terrible consequences is cancer of the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas.
In addition to the gastrointestinal tract, the patient’s heart and blood vessels, metabolism, and nervous system suffer. As a result, vegetative-vascular dystonia, insomnia, nervousness may occur, tremors of the limbs appear, appetite decreases, and the menstrual cycle changes.
Pathological anatomy
With intense invasion, the liver is enlarged and thickened; under its capsule, dilated bile ducts appear in the form of cords and cysts. Sometimes deep scar retractions are visible. The walls of the ducts are thickened due to the development of connective tissue; their epithelium is in a state of glandular hyperplasia, infiltrates from lymphoid elements are observed; In some places there are accumulations of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, among which there are many eosinophilic granulocytes. In the lumen of the ducts there are helminths, desquamated epithelium, leukocytes, including eosinophilic granulocytes, mucus, dark grains thrown out of the intestines of parasites. In the circumference of the ducts there are strands of connective tissue with lymphoid infiltrates and newly formed bile canaliculi. There are sometimes micronecrosis in the liver parenchyma. With a large number of parasites and long-term existence of the invasion, liver cirrhosis develops, which is characterized by focal changes associated with the localization of helminths. The gallbladder is often atonic. In the pancreas - dilation of the ducts, thickening of the walls, glandular hyperplasia of the epithelium; in the parenchyma of the organ there is sometimes necrosis and sclerosis.
The first symptoms of opisthorchiasis
The first signs appear when the protective function of the immune system decreases. In the early stages, the patient experiences the appearance of general weakness and sweating increases. The acute form of opisthorchiasis manifests itself as follows:
- the appearance of insomnia and nervousness;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- pain in the back and abdomen;
- presence of asthmatic bronchitis;
- feeling of body aches and fever;
- the appearance of allergic rashes on the skin;
- the presence of flatulence, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, general discomfort;
- a sharp decrease in appetite, too liquid stool consistency.
When examining the body, the doctor may detect an enlarged liver and an increased number of eosinophils in a general blood test.
Symptoms of opisthorchiasis in adults are somewhat different from the first signs of children. In little fidgets, the disease is expressed in the manifestation of persistent allergosis, intoxication of the whole body and an immunosuppressive state. The temperature may also rise and last up to 2-3 weeks.
Symptoms in women are most pronounced during the menstrual cycle. If a woman has a parasite in her liver, her periods become very painful and her cycle becomes unstable.
Prevention of opisthorchiasis - routes of infection
Wednesday, August 16, 2017
Infection with opisthorchiasis by eating raw, insufficiently heat-treated, lightly salted and dried fish of the carp family
Infection with opisthorchiasis occurs only when eating carp fish with undisinfected larvae of the parasite. In this regard, ide and Siberian dace are especially dangerous. Their infestation with metacercariae of the parasite in some years can reach up to 90-100% with a very high intensity of invasion. It is almost impossible to see the opisthorchid larva in tissues with the naked eye - its diameter is only about 0.3 mm.
In many areas of our country, the custom of salting fish is widespread. In this case, the so-called “stock” salting is usually used - the fish is covered with salt in layers and is not filled with water, but is salted in its own juice. It has been established that with such salting at room temperature in small fish (weight 10-15 g), the larvae die only on the 4-5th day, and in ides weighing up to 1 kg they remain viable for up to 8-10 days. Meanwhile, very often fish salted in this way is used for food already on the 2-3rd day after salting, which, of course, leads to infection, since during this time most of the larvae do not yet lose their invasiveness. Therefore, to prevent opisthorchiasis, poorly salted fish should be excluded from the diet.
Hot smoking of fish practically kills the metacercariae present in it, but with cold smoking and drying with short salting, many larvae can remain alive for several days. Therefore, to prevent opisthorchiasis, poorly dried or poorly smoked fish should be excluded from the diet.
In the northern regions, there is a widespread custom of eating thinly sliced fresh frozen fish - “stroganina”. This is one of the undoubted and important factors in opisthorchiasis infection. No less dangerous in this regard are dishes prepared from fresh or frozen fish, when, cut into small pieces, it is poured with vinegar, seasoned with spices and eaten without heat treatment. Therefore, to prevent opisthorchiasis, you should categorically avoid eating raw or half-raw fish.
Freezing fish does not immediately kill the larvae. So, for example, in small fish (weight 10-15 g) at a storage temperature of 8-12 ° C below zero, metacercariae die only after 4 days, and in large ides under the same conditions they persist for up to 17-20 days. Very low temperatures (minus 26-32°C) kill metacercariae in 2-3 days.
Even boiling and frying fish does not always kill metacercariae. It is recommended to cut large fish into pieces and keep them in boiling water for at least 15-20 minutes, and cover them with a lid when frying, which significantly increases the likelihood of death of the larvae. This is especially recommended when frying with breadcrumbs or flour.
The best prevention of opisthorchiasis is thorough heat treatment of fish during its preparation.
Infection with opisthorchiasis when using undisinfected equipment (knives, dishes, equipment) for preparing other dishes
It should be remembered that when cleaning and cutting fish, metacercariae may end up on a knife, dishes and other objects that come into contact with fresh fish. Therefore, to prevent opisthorchiasis, they must be thoroughly washed immediately after finishing work.
Infection with opisthorchiasis due to non-compliance with personal hygiene rules during cutting (processing) of raw fish or after finishing it (poorly washed hands)
It must be remembered that when cleaning and cutting fish, metacercariae may appear on the skin of hands in contact with fresh fish. Therefore, to prevent opisthorchiasis, immediately after finishing work, hands should be thoroughly washed with soap and hot water.
Infection with opisthorchiasis when taking a sample during the preparation of fish dishes
Very often, opisthorchiasis infection occurs when fish is sampled during cooking. Therefore, to prevent opisthorchiasis, you should not try fish and fish dishes that have not yet been cooked.
Prevention of opisthorchiasis - precautions
Measures to prevent opisthorchiasis are simple:
- To prevent opisthorchiasis, you should not eat raw or undisinfected fish;
- To prevent opisthorchiasis, it is necessary to strictly follow the rules of heat treatment of fish
- fry the fish in a sheet form for at least 20 minutes in a well-heated frying pan in boiling fat. The same time is required for frying fish cutlets. Cook the fish for at least 15 minutes from the moment the water boils, after cutting it into pieces. Salt in a warm solution at a temperature not lower than 15°C for at least two weeks, with a salt consumption of 270-290 g per kilogram of fish. Dry the fish (25 cm in size) for at least 3 weeks after 2-3 days of salting at the rate of 12-14% salt to the weight of the fish. Opisthorchids die when fish are frozen at -40°C for 7 hours, at -35°C for 14 hours, at -28°C for 32 hours; - to prevent opisthorchiasis, it is necessary to thoroughly treat kitchen utensils after cutting fish;
- To prevent opisthorchiasis, you must wash your hands thoroughly after cutting and preparing fish.
.
Strict adherence to preventive measures will protect you and your loved ones from infection and the need for treatment for opisthorchiasis!
How quickly does pathology manifest itself?
When parasites enter the human body, the protective functions of the immune system begin to decline. After this, the first signs may appear within 20 days. A person experiences general weakness, malaise, rapid heartbeat, increased body temperature, and severe sweating.
After about 30 days, the disease enters the chronic stage and its symptoms become similar to chronic cholecystitis, gastroduodenitis, pancreatitis, and hepatitis. I am worried about attacks of pain in the right hypochondrium, similar to biliary colic. Nervousness, sleep disturbances, chronic fatigue, frequent allergic skin rashes, trembling hands and eyelids appear.
The period of the acute stage of the disease ranges from several days to 3 months, sometimes longer. Symptoms are accompanied by signs of pulmonary diseases, the liver is enlarged, erosions and ulcers of the mucous membranes and tissues of the stomach and duodenum may be revealed during the study.
Diphyllobothriasis
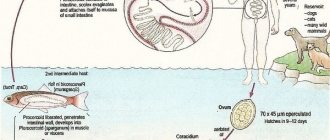
Diphyllobothriasis is a helminthic disease affecting the digestive organs. The causative agent is the broad tapeworm. This is the largest of the human helminths, its length can reach 10 and sometimes 20 meters. The parasite consists of a head, neck and body. The head is oblong oval in shape, flattened on the sides and has on its narrow sides two longitudinal suction slits (bothria), with which the tapeworm is attached to the intestinal wall. The body consists of many segments, and the width is much greater than the length, which is due to the name of the parasite (wide tapeworm). The number of segments can reach 3000-4000 pieces. The tapeworm lives in the upper parts of the small intestines, feeds on the entire surface of the body, while absorbing various nutrients, including vitamins Bi2 and folic acid. The wide tapeworm is hermaphrodite. During the day, up to 2 million eggs are released into the external environment with feces. The number of parasites can reach up to 100 copies. The lifespan of parasites in the human body reaches 28 years.
For the development of a wide tapeworm, like opisthorchiasis, the presence of three hosts is necessary.
The definitive host is humans, domestic and wild animals. All of them secrete eggs, which end up in water bodies with meltwater. Diphyllobothriasis cannot be contracted through water.
The intermediate host is Cyclops (crustaceans). The eggs are swallowed by crustaceans (cyclops) and larvae develop in their bodies. Cyclops are swallowed as food by freshwater predatory fish.
Additional hosts are fish of predatory species: pike, burbot, perch, ruff; pike caviar is especially dangerous.
Having attached themselves to the wall of the intestines, the parasites injure the intestinal mucosa with bothria and can be one of the reasons for its necrosis. Sometimes intestinal blockage occurs.
Diphyllobothriasis occurs in mild or severe form, which is associated with the intensity of invasion, the presence of concomitant diseases and the general condition of the body. Sometimes the disease is asymptomatic.
In mild cases, patients complain of general weakness, poor appetite, nausea, pain and rumbling in the abdomen, intestinal disorders, and decreased ability to work.
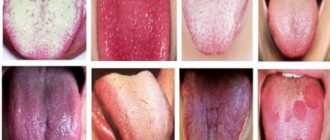
In severe cases, intestinal obstruction occurs. In 2-3% of patients, a severe form of anemia (anemia) occurs. Patients complain of weakness, drowsiness, dizziness. Bright red spots and cracks appear on the tongue. The skin becomes pale with a yellowish tint; The liver and spleen may enlarge. Body temperature reaches 36-38 degrees.
The diagnosis of these diseases is established based on the detection of tapeworm and opisthorchid eggs in the feces.
Stages of acute opisthorchiasis
When it comes to acute opisthorchiasis, it is divided into 4 classes.
- Typhoid-like course - there are symptoms of pancreatitis, jaundice and hepatitis, an enlarged liver, gastritis, eosinophils in the blood up to 90%.
- Hepatocholangetic type - pancreatitis, aching abdominal pain, the liver is affected, the function of the pancreas is impaired.
- Gastroenterological – the presence of enterocolitis, stomach ulcers, erosive gastritis, stool disorders are observed.
- Damage to the respiratory tract - the presence of asthmatic-type bronchitis, pleurisy and pneumonia.
Complications
If opisthorchiasis occurs in a severe form, then experts talk about a difficult prognosis and the possibility of complications. Thus, cirrhosis of the liver, primary cancer of the liver and pancreas, and biliary peritonitis can develop as complications of this disease. Serious damage to the nervous system is also possible, as evidenced by headaches, insomnia, irritability, and depression.
In addition, infection with opisthorchiasis can aggravate the condition of patients with other diseases, can adversely affect the development of pregnancy, and contribute to the formation of typhoid-paratyphoid carriage. If a person is repeatedly infected with opisthorchiasis, the course of the disease is progressive.
How is the disease diagnosed?
The first thing you need to do if you find signs of opisthorchiasis is not to self-medicate, but to seek the advice of a gastroenterologist. The doctor will conduct a visual examination, collect anamnesis and refer for tests and duodenal intubation. This is a method of examining a patient, which is carried out for diseases of the biliary tract and gallbladder to collect bile for laboratory testing.
Other types of diagnostics:
- general blood analysis;
- examination of internal organs using ultrasound;
- stool analysis for worm eggs;
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
After the diagnosis, the doctor examines the results of all tests and studies and gives the patient an accurate diagnosis. After an accurate diagnosis is made, the patient is prescribed treatment. It is carried out under strict supervision.
Story
Opisthorchiasis, caused by O. felineus (Vinogradov's disease), in humans was first described by K. N. Vinogradov in 1891. Askanazi (M. Askanazy) in 1904 proved that opisthorchiasis infection of humans and mammals occurs through fish. Vogel (N. Vogel) in 1932 identified a mollusk as an intermediate host of O. felineus. The first description of the clinic of Opisthorchiasis belongs to E. A. Pastor (1898). Helminthicidal properties in Opisthorchiasis were discovered in fuadin by Sidat and Erhardt (L. Szidat, A. Erhardt, 1931), in tartar emetic and carbon tetrachloride by H.N. Plotnikov and L.K. Zerchaninov (1932), in hexachloroethane by H.N. Plotnikov.
Treatment of opisthorchiasis
Treatment of the pathology should be carried out regardless of the stage and type of opisthorchiasis. The sooner treatment is started, the less likely it is that the parasite will cause severe damage to your body.
In order to start treatment, it is necessary to have the latest results of a general blood and urine test, a biochemical blood test, FGDS, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, and for patients over 40 years old, also an ECG.
The use of medications relieves inflammation. If there are allergic reactions or intoxication, then this problem is eliminated through the use of antihistamines. Choleretic drugs are prescribed, which are taken at the time prescribed by the doctor, and antibiotics are prescribed. The drugs are most often taken for up to 14 days. A special diet is established for the patient, which he must follow.
After the course of treatment, a control duodenal intubation will be done, you will receive a full medical report and doctor’s recommendations, which you must adhere to throughout your life.
After antiparasitic therapy, a rehabilitation period begins. It can last for 3-4 months, its main tasks are:
- restoration of normal functioning of the digestive system;
- complete disposal of dead helminths that remain in the body;
- elimination of the consequences of helminth activity in the human body.
Medicines
Photo: expertdent.net
To eliminate the allergic reaction, drugs from the group of H1-histamine receptor blockers (Loratadine, Cytherizine, Clemastine, Chloroperamine) are used.
To eliminate spasm of the biliary tract and the associated pain syndrome, antispasmodic (Drotaverine, Papaverine, Metamizole, Mebeverine) and choleretic drugs (Ursodeoxycholic acid, Ademethionine) are used. Such drugs are prescribed from the beginning of treatment and used for at least three months.
If indicated, it is possible to prescribe drugs that enhance intestinal motility (Metoclopramide, Domperidone), as well as pancreatic enzymes (Creon, Pancreatin), probiotic drugs (Linex, Bifiform, Hilak) and drugs for eradication therapy.
For chemotherapy, the anthelmintic drug Proziquantel is used. The drug has a wide spectrum of action and is used not only for opisthorchiasis, but also for other helminthic infestations. Affects the muscles of parasites, causing paralysis. The course of treatment is 2 days, during which the patient takes 6 doses of the drug. Contraindications for use are pregnancy and acute complications of opisthorchiasis.
During the rehabilitation period, probiotics, hepatoprotectors (Phospholipids, Thioctic acid, Ademethionine), and mineral medicinal table waters are prescribed. The rehabilitation period is aimed at the complete restoration of the body.
Treatment of opisthorchiasis in Krasnoyarsk
Diagnosis and treatment of parasites can be done at the Medunion private medical clinic. During the pandemic, we provide all medical services in accordance with the mask regime. A distance is maintained between patients and clinic staff, and all work surfaces are sanitized every hour. Our patients can use masks and hand sanitizers.
The cost of diagnosis and treatment will depend on the procedures performed. To find out more information, make an appointment with a gastroenterologist who will conduct an examination, prescribe tests and treatment. To sign up, call or fill out the online form. Indicate the procedure you need and leave your details - our specialist will call you back and discuss a convenient time for the procedure.
In addition, the clinic operates a comprehensive diagnostic program “Gold Standard”. It includes all types of tests, including tests for parasites.