- Symptoms of intracranial pressure in adults
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting in the absence of gastrointestinal diseases
- Increased fatigue
- Irritability
- Changes in blood pressure, tachycardia, arrhythmia
- Decreased libido
- Meteosensitivity
- What to do if the above symptoms appear?
- Lumbar puncture
- Treatment of intracranial pressure in adults
- Treatment with medications
The condition of increased intracranial (intracranial) pressure is called liquor-hypertension syndrome, intracranial hypertension. This condition differs from the familiar arterial hypertension. The disease can occur for unknown reasons (idiopathic form), and it also appears with head injuries, tumors and inflammatory diseases of the brain.
Symptoms of intracranial pressure in adults
It is not always possible for a person to understand that he has increased intracranial pressure. This is caused by an abundance of symptoms that occur with other diseases.
Headache
Adults often suffer from headaches that arise for various reasons. Even healthy people can get headaches due to overwork during hard work, staying in a stuffy room, or an uncomfortable pillow for sleeping.
Headache due to impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is of a peculiar nature. There is a feeling of fullness, as if something is pressing from within. Such sensations manifest themselves most strongly in the forehead and crown of the head, and there is a feeling of pressure on the eyes from the inside. Because of this, vision becomes blurred, especially when moving the eyeballs. The feeling of a veil before the eyes is due to the fact that the optic nerve swells.
If a headache attack is accompanied by nausea, this may also indicate problems with intracranial pressure. With severe pain, nausea leads to vomiting, but after emptying the stomach, the state of health does not improve. In some patients, the disease provokes fainting and confusion.
The nature of headaches changes with changes in body position and depends on the time of day. The headache is worst in the evening and at night. At such times, activity decreases, the person rests or prepares for sleep. In a lying or reclining position, the pain intensifies. This is caused by increased production of cerebrospinal fluid when its outflow worsens. For this reason, the compression intensifies.
Nausea and vomiting in the absence of gastrointestinal diseases
Almost everyone has experienced nausea and vomiting without gastrointestinal diseases at least once due to poor quality food eaten. If everything is in order with the diet and no pathologies of the digestive system are found during the examination, it is worth suspecting neurological causes of this condition. As a rule, nausea is accompanied by a headache and progresses to vomiting.
Increased fatigue
Any pathology in the body weakens it, so a person quickly gets tired and loses the ability to work productively. Fatigue is a symptom of all diseases without exception, so you should pay attention to other signs.
Irritability
Emotional lability often accompanies neurological diseases. Due to constant poor health and deteriorating quality of life, a person becomes less balanced. Some patients report tearfulness and increased anxiety. This can happen for various reasons, but if there is pain, blurred vision, then irritability can be another sign of intracranial hypertension.
Changes in blood pressure, tachycardia, arrhythmia
Blood pressure and intracranial pressure are different indicators, but they are related. Due to compression of individual brain structures and blood vessels, blood circulation is disrupted. This affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system. A person complains of pressure surges, uneven pulse, and sweating. This is associated with intracranial hypertension and is not an independent disease. The situation may be aggravated if the patient has diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Decreased libido
People with chronic intracranial hypertension almost always feel unwell. Fatigue, irritability and other symptoms of the disease do not contribute to a pronounced desire for physical intimacy. This applies to patients of any gender. At the same time, it cannot be argued that such a condition occurs only when the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted. The reasons may be fatigue, psychological problems, endocrine changes.
Meteosensitivity
If increased meteosensitivity was not characteristic before, but appeared suddenly, the cause may be intracranial hypertension. When the weather changes, a person begins to have headaches, feel dizzy, and have trouble sleeping. In a number of patients, weather sensitivity manifests itself as fluctuations in blood pressure. The whole body or individual muscle groups and joints begin to ache.
Blood pressure norms
In a healthy person, the normal values correspond to 120/80 mm. Hg Art., but sometimes they can differ by 10 units down or up. This factor is influenced by:
- floor;
- age;
- physiological feature.
If the norm indicators deviate by more than 10-15 mm. Hg Art., then this indicates the presence of hypertension or hypotension.
But how can you tell if your blood pressure is high or low if you don’t have a tonometer at hand? The symptoms described below will help you identify them.
What to do if the above symptoms appear?
If there are signs of the disease, you should consult a neurologist. To treat a pathological condition, it is necessary to find out its exact cause. That is why the doctor prescribes a set of diagnostic procedures:
- Fundus examination. Allows you to identify swelling of the optic nerve - one of the main signs of intracranial hypertension.
- Echoencephalography is an ultrasound procedure for examining brain tissue. Such diagnostics will help confirm or refute the presence of a tumor, cyst, hemorrhage, or other pathological changes in tissue structure. This diagnostic method does not require preparation, changes in daily routine or nutrition.
- X-ray of the skull. Prescribed for suspected birth defects, fractures or bone displacement. This method also identifies possible tumors that are causing compression.
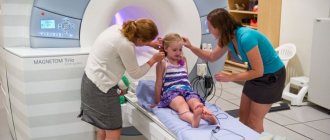
- CT or MRI of the head. The most accurate and informative diagnostic methods. They allow you to thoroughly assess the condition of bones, soft tissues, and blood vessels. As a rule, the doctor prescribes such a diagnosis after echoencephalography, if it shows the presence of a pathological process.
- Ultrasound of the vessels supplying the brain. It is necessary to identify possible anomalies, tortuosities, and thromboses.
- Angiography. Allows you to visualize large and small vessels and detect areas of affected arteries.
The purpose of the above procedures is to determine the cause of the malaise. Based on the examination results, the specialist prescribes additional diagnostics or decides on treatment.
Hypotension
Long-term low blood pressure up to 100/70 mm. Hg Art. and below is called hypotension or arterial hypotension.
Pathology manifests itself in the following cases:
- heredity;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- chronic fatigue;
- lack of sleep;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- hormonal disbalance;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- osteochondrosis;
- diabetes;
- tuberculosis;
- pregnancy.
Hypotonic people often suffer from sleep disturbances. Throughout the day, patients with this diagnosis experience depression, apathy, fatigue, and in the evening they begin a cycle of activity.
The main signs of low blood pressure include:
- drowsiness;
- increased fatigue;
- poor memory;
- increased sweating in the palms and feet;
- rapid heartbeat under any stress;
- digestive problems;
- weather dependence;
- pre-fainting state.
For quite a long time, hypotension, like hypertension, may not manifest itself. When the first of the above signs appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Hypotension is dangerous because it can cause oxygen starvation of the brain and other organs.
Lumbar puncture
If hardware diagnostics do not help identify the cause of the disease, the neurologist prescribes a lumbar puncture - a lumbar puncture. It is an invasive procedure performed to obtain a sample of cerebrospinal fluid. The procedure can be performed for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. During diagnosis, a lumbar puncture helps to more accurately determine the degree of pressure increase. For therapeutic purposes, the procedure is performed for benign intracranial hypertension to improve the patient’s condition.
Symptoms of high blood pressure
Many people have high blood pressure without any symptoms for a long time. However, there are several common signs of hypertension: morning headaches, shortness of breath, nosebleeds, irregular heart rhythms, blurred vision, and ringing in the ears.
Uncontrolled high blood pressure can lead to complications such as heart attack or stroke, aneurysm, heart failure, kidney damage, vision loss, metabolic problems, memory problems and dementia.
You can measure your blood pressure yourself, but to make an accurate diagnosis, we advise you to consult a specialist.
Treatment of intracranial pressure in adults
To improve the patient's well-being, it is necessary to achieve normalization of intracranial pressure. In modern practice, non-surgical and surgical treatment methods are used. Surgery is required if diagnosis reveals a tumor or cystic change. Some patients are diagnosed with a congenital abnormality of the brain structure. Such tumors must be removed. The operation will eliminate the compression and thereby normalize the pressure.
Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition, the procedure is performed immediately, or the patient is given a date for surgery. Urgent surgical treatment is carried out in severe condition of the patient, when the degree of the disease threatens brain dislocation. With dislocation syndrome, compression causes a displacement of brain structures relative to each other. There are eight types of brain dislocation, each of which has its own characteristic manifestations.
In one of them, the cerebellar tonsils penetrate the foramen nagnum - a large oval hole in the occipital part of the skull; due to increasing hypertension, the brain stem, on which vital nerve centers are located, is compressed. They are responsible for the functions of the heart and respiratory system. When these areas are damaged, the disease is most severe. The patient's breathing becomes impaired, the pharyngeal reflex disappears, and the pressure drops. These conditions are directly life-threatening and require immediate surgery.
Hypertension
Persistent elevated blood pressure from 140/90 mm. Hg Art. called arterial hypertension or hypertension.
High blood pressure is most often caused by any pathology:
- thyroid diseases;
- obesity;
- hormonal surges;
- genetic predisposition;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- sick kidneys.
In addition, regular stressful situations, alcohol abuse and smoking can cause hypertension. Hormonal medications and frequent consumption of unhealthy foods - fried, salty, fatty, carbonated and caffeinated drinks - can also be a cause. At the initial stage, arterial hypertension is very difficult to recognize, since it has no obvious manifestations.
When the pathology begins to progress, the following symptoms appear:
- chest pain;
- cardiopalmus;
- pulsation in temples;
- pain in the back of the head or temples;
- feeling of nausea;
- darkening of the eyes;
- weakness;
- dyspnea;
- blood from the nose.
At the first such symptoms, you should immediately seek medical help. If all necessary measures are not taken in time, a person may develop a hypertensive crisis, which can lead to serious complications such as cerebral hemorrhage, pulmonary edema, and heart attack.
Difference between signs of hypertension and hypotension
High blood pressure differs from low blood pressure primarily in its symptoms. Therefore, it is important for people prone to sudden jumps in blood pressure to learn to recognize hypotension from hypertension in order to be able to provide first aid to stop the attack. A comparison table will help you find out whether a person has high or low blood pressure:
| Manifestation | Hypertension | Hypotension |
| Nature of the headache | Sharp, pulsating, concentrated in the temples | Dull, aching, localized in the back of the head |
| Psycho-emotional state | Irritability, aggression | Lethargy, drowsiness |
| Physiological manifestation | Excessive sweating | Cold sweat |
| Fever, redness of the skin | Chills, pale skin, tremors of extremities | |
| Memory impairment | Profound fainting | |
| Problems with the vestibular system | Inability to concentrate on a specific subject |
How to recognize high blood pressure?
High blood pressure or arterial hypertension is considered the most common reason for visiting a cardiologist. According to WHO, it affects 20 to 30% of the world's adult population. With age, the situation only gets worse - more than half of older people over 65 years of age have this disease, and its hemorrhagic complications (stroke, heart attack) often become fatal for a person.
Let's consider the norm and pathological changes, including those that threaten the transition to a hypertensive crisis. Let's touch on the causes, signs and methods of correcting high blood pressure.
WHAT IS HIGH PRESSURE?
High blood pressure (BP) is said to occur when its systolic and diastolic components rise above the physiological threshold.
Normal blood pressure according to WHO:
- systolic (upper) – 120-129 mm Hg. st;
- diastolic (lower) – 80-84 mm Hg. Art.
If, when measuring blood pressure, the upper number is 140 or higher, and the lower number is 90 or higher, then this pressure is considered elevated. It should be understood that systematically recorded high blood pressure is considered a pathology. Episodes of its increase in the morning, during intense physical activity, fear, and stress are natural for the body.
According to medical observations, the following blood pressure levels are considered very dangerous - for the upper 180, for the lower 120. In this case, there is a high probability of developing a hypertensive crisis.
CAUSES OF HIGH PRESSURE
Doctors most often record an increase in blood pressure in people with a hereditary predisposition and/or diseases of other organs and systems (pheochromocytoma, hyperthyroidism, atherosclerosis, diabetes, etc.), leading to the development of hypertension as a symptom.
The mechanism of blood pressure increase is realized in two ways:
- neurogenic – vasoconstriction through the response of the sympathetic nervous system;
- humoral – release of vasopressors (catecholamines, renin-angiotensin, etc.) into the blood.
Also important is the disruption of the depressor system, which is responsible for vasodilation.
At the same time, a number of factors that trigger the process of hemodynamic disturbances have long been identified:
- excess weight;
- little daily activity;
- poor nutrition, including preference for fast food, snacking on carbohydrate foods;
- chronic intoxication caused by smoking, alcohol abuse, drug addiction;
- mental and physical stress;
- lack of sleep;
- hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy, menopause;
- abuse of salt in the diet;
- elderly age;
- harmful working conditions;
- taking medications that can indirectly affect blood pressure (for example, hormonal contraceptives , appetite suppressants, etc.)
With high blood pressure, it is important to monitor the reduction of the influence of these factors in everyday life, which will help reduce the risk of developing the most threatening complications - stroke and heart attack.
SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS OF HIGH PRESSURE
Many people know that hypertension is often asymptomatic, but this is noted only at the beginning. Constantly high blood pressure over time results in a number of clinical symptoms:
- The first signs: rare headaches, dizziness, fatigue, weakness, nervousness, sleep disturbance;
- As it progresses: headaches in the occipital region, “tingling” in the heart area, the appearance of shortness of breath during light physical activity (walking, for example), a feeling of heartbeat, “spots” before the eyes, visual impairment.
External signs of hypertension in men and women are no different. The difference in symptoms mainly depends on the level of pressure and the rate of its increase. Often a sharp increase in blood pressure threatens the development of a hypertensive crisis and rupture of the vessel wall.
HIGH LOWER PRESSURE: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS
By lower or diastolic pressure we mean the force with which the blood flow acts on the vessels during the diastole (relaxation) phase of the heart. Its value depends on the degree of vascular resistance, an increase in which is observed in the following pathological conditions:
- atherosclerosis - the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels decreases, their lumen decreases, which increases tone and resistance to blood flow;
- kidney pathology leads to vasoconstriction due to the implementation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone reaction;
- anatomical and functional changes in the myocardium (dilation of the heart chambers, arrhythmia);
- thyrotoxicosis – a high concentration of thyroid hormones in the blood causes vasospasm;
- diabetes mellitus – vascular patency is impaired;
- tumor of the pituitary gland and adrenal glands - the release of catecholamines into the blood, which constrict blood vessels;
According to statistics, the elderly population and men of any age often suffer from high blood pressure. Signs of its increase are sharp pain in the head, dizziness, tinnitus, and attacks of shortness of breath. Painful discomfort in the cardiac region is possible. Long-term high diastolic pressure threatens the development of a heart attack or stroke.
INCREASED UPPER PRESSURE: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS
Upper (systolic) pressure reflects the contractile activity of the myocardium during systole. Its increase may be due to various reasons:
- congenital defects and acquired cardiac pathology - coarctation of the aorta, PDA, blockade of the atrioventricular node, insufficiency of the valves at the entrance to the aorta;
- ion deviations - accumulation of sodium and calcium in the blood;
- atherosclerosis of large and small vessels;
- renal pathologies of an inflammatory, autoimmune nature;
- diabetes;
- dehydration of the body.
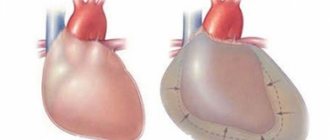
Over time, increased upper pressure first leads to hypertrophy, and then to wear and tear of the myocardium and the formation of heart failure. The aortic wall becomes rigid due to constant trauma by increasing blood pressure. Hemodynamic disturbances of internal organs are also noted due to inadequate distribution of blood through the vessels.
This type of hypertension is more often recorded in women. It manifests itself as regular headaches, discomfort in the heart, fatigue, memory impairment, tinnitus, and decreased vision.
TREATMENT OF HIGH PRESSURE
The main goal of therapy for high blood pressure is to reduce its levels to normal and the maximum possible correction of risk factors (fighting smoking, alcoholism, losing excess weight, doing morning exercises), as well as slowing down the damage to other organs.
Taking into account anamnestic and objective data, various medications are prescribed for hypertension; their main groups are presented below:
- antihypertensive medications to lower blood pressure;
- disaggregants that reduce the risk of hemorrhagic complications;
- statins for correction of lipid metabolism;
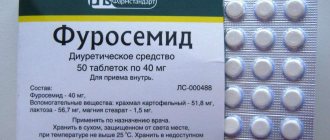
- diuretics that indirectly reduce blood pressure;
- according to strict indications, a and/or β-blockers to correct myocardial contractility.
If high blood pressure is a sign of pathology in another organ, then treatment of the underlying disease will be key.
An important aspect in the treatment of high blood pressure is a balanced diet, in which you need to limit salt intake, eat more vegetables, nuts, fruits, healthy vegetable oils (olive, pumpkin). If possible, replace red meat with fish. Reduce the amount of calcium-rich dairy products in your diet.
WHICH DOCTOR SHOULD I CONSULT WITH HIGH PRESSURE?
At the clinic stage, the first doctor who is contacted with symptoms of high blood pressure is a general practitioner. He can prescribe the necessary examination to make a diagnosis and correct high blood pressure readings. A doctor who has deep knowledge of the problem of high blood pressure in humans is a cardiologist. This specialist not only deals with the correction of hypertension, but also fights its complications, often together with a neurologist, nephrologist, ophthalmologist and resuscitator.
PREVENTION
The coherence of the heart and blood vessels is a key link in the health of the whole organism. Thanks to preventive measures, it is possible to maintain their harmony, thereby preventing the development of hypertension. These include:
- a measured lifestyle with adequate physical activity;
- weight loss to normal levels;
- balanced diet;
- quitting smoking, alcohol, drugs.
If the symptoms described above appear, you should begin to systematically measure blood pressure using a tonometer. Regardless of the reasons for high blood pressure, its long-term retention at high levels is a reason to contact a therapist or cardiologist.
Cardiologist Rudnik N.I.