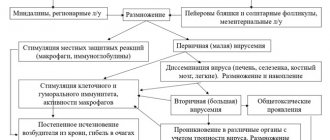
Tuberculosis in Russia is so widespread that by the age of forty, 70-90% of the inhabitants of our country are infected with it. This does not mean that they are sick: after infection, most people's immunity copes with the bacteria. The probability of getting sick is on average 8% in the first two years after infection, then gradually decreases, and acquired cellular immunity is formed. Among adults, people who are weakened and live in poor conditions, with a lack of light and fresh air, are more likely to get sick. However, absolutely each of us can become infected. This is why it is so important to get regular TB screenings and have your children tested.
IMPORTANT! Information from the article cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-medication! Only a doctor can prescribe the necessary examinations, establish a diagnosis and draw up a treatment plan during a consultation!
Why is BCG vaccination necessary?
WHO recommends mass vaccination of newborns against tuberculosis in all countries where the disease is common. Therefore, on days 3-5 after birth, while still in the maternity hospital, all newborns are given a free BCG vaccination. But this vaccine does not protect against tuberculosis infection. Her task is somewhat different. If an unvaccinated child under 2 years of age is infected with tuberculosis, he or she is extremely likely to develop tuberculous meningitis and generalized forms of tuberculosis, which very quickly lead to death. BCG quite reliably protects the child from these forms. It also protects children from pulmonary tuberculosis, but is less effective.
What other vaccinations do children under 2 years old need?
Diagnosis of tuberculosis
Regular examinations have been adopted by law to help identify the disease in a timely manner. The main methods of primary examination are fluorography (in adults) and the Mantoux test (in children).
The Mantoux test is a type of tuberculin diagnostics that is widespread throughout the world and is considered the most reliable method for the early detection of tuberculosis today. In Russia, mass diagnostics using the Mantoux test has been carried out for more than 70 years. Experts believe that it was thanks to her that the Soviet Union managed to achieve a significant reduction in the incidence of tuberculosis.
The Mantoux test is not a vaccination. Unlike vaccines, tuberculin, which is administered during this test, does not contain microorganisms - neither living nor dead, but only components of mycobacteria necessary for “recognition” by the immune system. The Mantoux test does not contribute to the formation of immunity against tuberculosis, since it has a completely different purpose - early diagnosis of tuberculosis. It has a small number of contraindications and is performed on all children starting from 1 year of age.
Targets of the Mantoux test:
- Early diagnosis of tuberculosis allows for timely additional examination and timely initiation of treatment, and this is a necessary condition for achieving a positive outcome in tuberculosis treatment.
- Assessment of the level of infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis among children and adolescents is an indicator characterizing the situation with tuberculosis in society as a whole.
- Timely identification of children in need of repeated BCG vaccination, which will reduce the risk of serious illness in children and adolescents.
Operating principle
If Koch's bacillus is present in the body (it can get there either during infection or as a result of BCG vaccination), then the immune system will react to the administration of tuberculin. In this case, tuberculin will be perceived by the immune system as an allergen, and immune cells containing antibodies will be directed to the injection site. As a result, a so-called allergic skin reaction of the delayed type hypersensitivity develops.
The body begins to respond to the introduction of tuberculin within 5-6 hours after the test. However, in order for the results of this reaction to noticeably manifest themselves at the site of injection of the drug, time is required - at least 48 hours, the most reliable results are observed after 72 hours. That is why the results are assessed no earlier than two or three days after the Mantoux test is performed.
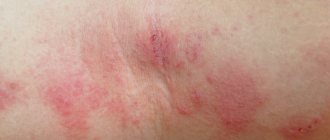
To evaluate the result, a healthcare professional examines the injection site. If mycobacteria are present in the body, then redness will be observed at the site of the test and a papule (solidification) will be detected, which occurs due to the reaction of the immune system to the administration of tuberculin.
The specialist assessing the test results measures the size of the papule with a transparent ruler; the ruler should be applied perpendicular to the axis of the forearm. The dimensions of the papule are estimated in millimeters:
- Papule size 0-1 mm – negative reaction;
- A papule of 2-4 mm and/or redness of any size is a questionable reaction;
- Papule 5 mm or more – positive reaction;
- A papule of 17 mm or more is a sharply positive reaction. Also, a sharply positive reaction is considered to be the situation when an ulcer, suppuration is observed at the site of tuberculin injection, and if inflammation of the lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes occurs.
Normally, if as a result of BCG vaccination, the child has a positive Mantoux test, which becomes less pronounced every year. This is due to the fact that post-vaccination anti-tuberculosis immunity gradually “fades away”, which is why children are revaccinated with BCG at the age of 7 and 14 years.
Deviations from the norm are the following cases:
For BCG vaccinated children:
- If a positive reaction has been observed for four years or more, that is, the size of the papule is 12 mm or more;
- If during the year that has passed since the last tuberculin diagnosis, the size of the papule has increased by 6 mm or more;
- If over the course of several years there has been a gradual increase in the papule, and its size reaches 12 mm or more.
For those who have not received the BCG vaccine:
- If a papule with a diameter of 5 mm or more appears at the injection site for the first time, then a positive reaction may be due, first of all, to the penetration of a tuberculosis infection into the body.
- All these situations may indicate tuberculosis infection, that is, the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the child’s body, which can cause the development of the tuberculosis process.
Interpretation of research results, establishment of a diagnosis, as well as prescription of treatment, in accordance with Federal Law No. 323 “On the fundamentals of protecting the health of citizens in the Russian Federation,” must be carried out by a doctor of the appropriate specialization.
The results of the Mantoux test can be reliably assessed if the study is carried out over time, that is, annually. Let us remind you that the Mantoux test is performed for the first time on a child at the age of 1 year, then every year until the age of 18.
Contraindications for the Mantoux test
There are no absolute contraindications. The Mantoux test can be performed on almost any child, regardless of the presence of certain diseases or disorders. This is due to the fact that the effect caused by the introduction of tuberculin on the body is very gentle.
At the same time, the diagnostic value of this technique is extremely high - children with health problems are more at risk of contracting tuberculosis than their peers who do not have such problems. Therefore, timely detection of the fact of infection with tuberculosis infection, tuberculosis disease in such children is of utmost importance.
At the same time, the Mantoux test has a number of relative contraindications. That is, there are situations when this procedure must be postponed:
- Allergic diseases in the acute stage. The Mantoux test is carried out after preparation - taking antiallergic drugs prescribed by a doctor;
- Acute infectious diseases, including ARI. The Mantoux test is performed no earlier than a month after complete recovery;
- Exacerbations of chronic diseases. The Mantoux test is performed outside of an exacerbation, a month after the symptoms of the disease disappear;
- Neurological diseases (primarily epilepsy). The Mantoux test is performed during non-attack periods against the background of appropriate therapy prescribed by a neurologist;
- The Mantoux test cannot be combined with preventive vaccinations. From the moment of the last preventive vaccination to the Mantoux test, at least a month must pass, and before the next vaccination it is necessary to maintain the same period of time - at least one month.
In order to identify relative contraindications to the Mantoux test, the specialist performing the manipulation must familiarize himself with the child’s medical record and assess his condition during an individual examination. It is also important that parents warn the medical staff of the educational institution where the Mantoux test is planned to be carried out about the problems the child has - this is important to obtain reliable results and exclude any problems with the child’s health.
Possible complications of the Mantoux test
The Mantoux test does not pose a risk of developing complications - this is due to the fact that during its implementation no substances are introduced into the body that can seriously affect the functioning of certain organs and systems. There are cases where an overdose of tuberculin occurred during this test, but these errors did not have any serious consequences. This indicates the highest safety of the Mantoux test for the health of children and adolescents.
A local reaction in children with allergies can be observed at the injection site - an allergic reaction to the components of tuberculin or solvent. The Mantoux test is essentially similar to allergy tests, which are used to identify allergic reactions to a particular substance in children. Then there is bright redness and itching is possible, but these phenomena quickly disappear when antihistamines are prescribed. More serious allergic reactions, such as Quincke's edema, are absolutely not typical for the Mantoux test.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes and blood vessels, possibly an increase in body temperature, is typical only in children or adolescents with an active tuberculosis process in the body. This is due to the fact that the immune system, involved in the fight against tuberculosis infection, actively reacts to the components of mycobacteria that make up tuberculin. However, in this case, such a reaction will be more likely a positive phenomenon, since it will make it possible to identify a dangerous disease and begin treatment.
Alternative to the Mantoux test:
Diaskintest is a type of tuberculin diagnostics that has an allergen composition different from the Mantoux test - artificially synthesized tuberculin (protein ESAT6/CFP10, characteristic only of TB pathogens). Can be used as an independent or clarifying test for the presence of pathogenic mycobacterium tuberculosis in the early stages. The test has similar contraindications to the Mantoux test. Conducted for children from 8 years old.
Quantitative test - blood test for the presence of tuberculous and non-tuberculous mycobacteria (M. kansasii, M. szulgai, M. marinum). Can be used as an independent or clarifying test to detect latent or active forms of tuberculosis in the early stages. Most relevant for people at increased risk of infection, as well as children and adults with skin diseases; tuberculin intolerance; risk of developing allergic reactions; infectious diseases during exacerbation; epilepsy; vasculitis; as well as people at high risk of developing allergic reactions.
Patients with a questionable and positive reaction to an intradermal test or a special blood test for the presence of mycobacteria must be sent to specialized anti-tuberculosis institutions for a consultation with a TB doctor for additional examination for the purpose of early detection of tuberculosis and timely implementation of anti-tuberculosis treatment and preventive measures (order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development RF No. 855 dated October 29, 2009 “On amendments to Appendix No. 4 to the order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated March 21, 2003 No. 109”).
What is needed for a visit to a TB doctor?
Sometimes medical workers who refer a child or adolescent for consultation with a phthisiatrician insist that he first undergo a fluorography or chest x-ray. However, such a requirement is unlawful - the specialist will decide for himself whether the child needs to undergo these examinations.
At the same time, the results of a fluorographic examination of people who are in constant contact with the child - parents, grandparents - must be provided. The doctor will need information about the child or adolescent’s contacts with tuberculosis patients.
If the child has previously consulted a TB specialist, it is necessary to provide the conclusions of this specialist.
The doctor will also require the results of the Mantoux test for all years of tuberculin diagnostics, information on vaccination and revaccination of the child or adolescent with BCG.
It is also necessary to do a general blood and urine test and provide the results to a specialist.
In addition, the doctor needs information about the child’s health status, the presence of chronic, allergic and other diseases, and the results of examinations by relevant specialists. Thus, at the appointment you need to take the child or adolescent’s medical record, as well as all available medical documents and examination results.
What can you expect from a visit to a TB specialist?
During the consultation and further examination, the phthisiatrist will be able to determine whether the reaction to the introduction of tuberculin is caused by mycobacteria tuberculosis in the body, or is associated with the manifestation of post-vaccination immunity after vaccination with BCG, and will eliminate the possibility of a false-positive Mantoux test result.
The specialist’s task is to carefully study the child’s environment and establish the possibility of his contacts with sick people.
A detailed examination aimed at identifying symptoms of the disease, the use of diagnostic equipment and laboratory techniques will allow the doctor to establish the fact of infection or disease and take the necessary preventive and therapeutic measures.
If the fact of infection with tuberculosis is established, the TB doctor can offer preventive therapy aimed at preventing the development of the disease. Typically, such measures are taken if the child has a weakened immune system and there is a high probability that the body will not cope with the infection.
In addition, a child with established tuberculosis infection may be prescribed a repeat Mantoux test after a few months. If the papule decreases, this will indicate that the defenses are coping with the infection and the development of the tuberculosis process is not in danger. The child or adolescent becomes classified as a tubinfected person and is removed from the register.
If, as a result of a repeated Mantoux test, an increase in the papule is observed, this will indicate that the body cannot cope with the infection and tuberculosis may develop into primary tuberculosis. In this case, the TB doctor prescribes preventive treatment for the child, which will help stop the process.
Mantoux test
The Mantoux test is performed annually on all children under 7 years of age. This is not a vaccination (!), but an immunological test that shows whether the tuberculosis pathogen is in the body. In this case, tuberculin, a specific protein containing antigens of human and bovine tuberculosis, is injected intradermally. After 72 hours, the size of the papule is measured. The result of the Mantoux reaction can be affected by visiting a sauna, taking a long bath, swimming in a swimming pool, and scratching the injection site. Temporary contact with water does not in any way affect the results of the Mantoux test, therefore the opinion that Mantoux cannot be wetted is a myth.
How does the procedure work?
Blood sampling takes place under sterile conditions, in compliance with all rules. Sputum is collected on an empty stomach. Biological material must be coughed out so that mucus from the nasopharynx or oral cavity does not get into the container. The sputum should not dry out or become chapped.
No special preparation is required for instrumental and radiation diagnostic methods, with the exception of techniques that require the use of a contrast agent. In this case, kidney function is first assessed to ensure that they can withstand the additional load.
Diaskintest test
It is carried out for children from 8 years old. Also a skin test. But if Mantoux uses antigens of both human and bovine tuberculosis, then Diaskintest uses only human tuberculosis antigens. Diaskintest is much more specific: a reaction to it occurs only if there are active tuberculosis bacteria in the body. Simply put, if the Mantoux test is positive, this does not mean anything: this test often gives false positive reactions. But after the Diaskintest, a reaction appeared - this is a more serious indicator.
The accuracy of Mantoux is 50-70%, Diaskintest - 90%.
Decoding the results
Normally, there should be no mycobacteria in the human body. Their presence is assessed as a positive test result for tuberculosis. Some diagnostic methods are nonspecific and do not have much diagnostic value. They are used to assess the general condition of patients.
Positive results obtained during bacteriological studies can be considered confirmation of the diagnosis. If the patient has clinical signs of the disease, but the test results are negative, then this is a reason to retake the tests.
Quantiferon test
Quantiferon test is one of the new methods for diagnosing tuberculosis using a blood test. It is based on the determination of interferon gamma in the blood, which is produced by cells in response to the introduction of the tuberculosis bacillus. Unlike Mantoux and Diaskintest, the Quantiferon test does not require the introduction of any antigens or bacteria into the body. Blood for research is taken from a vein. The result is ready in a few days and is much more accurate than skin tests. The test will only be positive if the person is truly sick.
Preparation
Before donating blood to a child for tuberculosis, the following recommendations must be followed:
- refrain from eating 8 hours before the test, avoid spicy and fatty foods 24 hours before;
- temporarily limit physical activity;
- 7 days before the study, stop taking antibiotics; if the patient takes any medications on an ongoing basis, then you must inform the specialist who will take the analysis.
T.SPOT.TB (“tee-spot”)
This method of diagnosing tuberculosis by blood is similar to the quantiferon test. The difference is that the quantiferon test detects interferon gamma in the blood, produced in response to the introduction of the tuberculosis bacillus, and T-SPOT detects the T cells themselves, which produce interferon gamma in response to the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Both tests are equally sensitive and informative (up to 97%), they are more sensitive than Diaskintest and much more sensitive than the Mantoux reaction. “T-spot” practically eliminates false-positive and false-negative reactions, while the quantiferon test can still give a false-positive reaction if, for example, the person was sick with ARVI at the time of donating blood.
What else is prescribed with this study?
Sputum analysis for Mycobacterium tuberculosis
16.15. Sputum 1 day
780 ₽ Add to cart
Diagnosis of tuberculosis infection using the T-SPOT method
20.136. Ven. blood 5 days
7,990 ₽ Add to cart
Mycobacteria, DNA (Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex, PCR) scraping, quality.
19.32.2. Scraping 1 day
450 ₽ Add to cart
Culture for tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis)
148.0. Sputum, Urine 45 days
720 ₽ Add to cart
Comparative characteristics of four tests for tuberculosis
| Mantoux | Diaskintest | Quantiferon test | T.SPOT.TB | |
| Accuracy | 50,00% | 90,00% | 97,00% | 97,00% |
| Data evaluation | Subjective | Subjective | Objective | Objective |
| False Positives | Often | Rarely | Rarely | No |
| With latent form of tuberculosis | Not reliable | Not reliable | Reliable | Reliable |
| Contraindications | A lot of | Eat | No | No |
| Adverse reactions | Eat | Rarely | No | No |
| For HIV and other immunodeficiencies | Not informative | Not informative | Informative | Informative |
| Research method | Skin test | Skin test | Blood analysis | Blood analysis |
Fluorography
All adults over 15 years of age in Russia are recommended to undergo fluorography once a year. Children from 15 to 17 years old are allowed to undergo Fluorography, but this does not cancel the Diaskintest. A certificate with a recent photograph is required everywhere - even when visiting a child in the hospital. Fluorography is more of a “collective barrier” to tuberculosis than a method of choice for individual testing. Fluorography reveals only pulmonary forms of tuberculosis.
If you still have questions about tuberculosis diagnostic methods, call us: +7 812 331 00 00, we will answer them!
References
- Chernousova, L.N., Sevastyanova, E.V., Larionova, E.E. and others. Federal clinical recommendations for the organization and conduct of microbiological and molecular genetic diagnostics of tuberculosis, 2014. - 56 p.
- Yablonsky, P.K., Vasilyeva, I.A., Ergeshov, A.E. and others. Clinical recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory tuberculosis in adults, 2013. - 51 p.
- WHO : The Stop TB Strategy : website / WHO - 2021, - URL: https://www.who.int/tb/strategy/stop_tb_strategy/en/.National