10 minutes
A stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation, leading to the destruction of brain tissue. Every year in Russia there are 450,000 cases of stroke - one every 1.5 minutes.
The causes of ischemic stroke can be atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, coronary heart disease with cardiac arrhythmias, heart defects, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, and arterial hypertension. With these diseases, obstruction or blockage of brain vessels develops, the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, which leads to bleeding of the brain - ischemia. If blood circulation in the ischemic area is not quickly restored, the brain tissue in it dies. The dead tissue then gradually dissolves to form cysts (holes) in the medulla.
The consequences of ischemic stroke are determined 90% by its severity and only 10% depend on treatment. Therefore, preventing stroke is many times more effective than treatment; Hippocrates said: “It is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it.”
Stroke prevention: simple rules for preventing stroke
What is a stroke
The essence of a stroke is the cessation of blood supply and functioning of a part of the brain as a result of damage to a vessel.
The larger the affected area, the more severe the stroke. Necrosis of a portion of the brain substance is called an infarction [3]. There is a high risk of death in the first few hours, and then in the period up to 28 days after a vascular accident. The annual mortality rate from stroke in the Russian Federation is 374 cases per 100,000 [10]. In 2018, 35% of patients died in the acute period of stroke; by the end of the first year, this figure increases by 15%, and in general, in the first 5 years, the mortality rate of strokes is 44% [11]. The mortality rate from stroke was 92.9 per 100,000 population, and the hospital mortality rate was 19.1% [5].
Long-term disability is most likely for patients who have suffered a stroke. The prevalence of primary disability due to stroke in 2018 was 3.2 per 10 thousand population [2]. Of these, 31% need constant care, 20% have severe mobility limitations, and only 8% return to work [3]. The prevalence of recurrent strokes in 2014 was 0.79%, of which ischemic
strokes account for 87.5% [9].
Consequences (complications)
The sooner therapy is started, the greater the patient’s chances for the most complete restoration of body functions.
Consequences of a major stroke:
- hemiplegia (paralysis of half the body);
- complete paralysis (if both hemispheres are affected);
- problems with speech (with an extensive lesion in the left hemisphere);
- cognitive impairment (difficulty perceiving and processing information);
- amnesia (partial memory loss);
- hearing and (or) vision impairment;
- decreased tactile and pain sensitivity;
- loss of ability to concentrate.
Often the possibility of full rehabilitation is excluded, and severe consequences persist for the rest of your life.
Coma as a consequence of a stroke. Principles of treatment
A comatose state is characterized by a complete lack of consciousness and lack of reactions. It can develop rapidly, but often (in approximately every fourth case) the cause is untimely provision of assistance.
Coma with a major stroke, as a rule, lasts from several hours to 1-1.5 weeks, but can drag on for months and even years. According to statistics, the chances of partial recovery after several months in this condition are less than 15%. The mortality rate for this complication is very high. Even if the patient manages to emerge from a long coma, there can be no talk of complete rehabilitation.
The danger of this condition is that not only brain functions are affected; there is often no control of breathing and cardiac activity, and therefore the patient must be connected to a life support system. In this condition, the likelihood of repeated acute cerebral circulation disorders remains high.
The first signs of coma:
- incoherent, quiet speech;
- rave;
- lethargy;
- confusion;
- body lethargy;
- weak pulse filling;
- tachypnea (rapid breathing).
Falling into a coma is accompanied by a lack of control over the functions of the pelvic organs (involuntary urination and defecation are noted).
In the first degree, reflexes are generally preserved (skin ones are weakened), and muscle tone is increased. In the second case, there is no reaction to external stimuli; the victim is in a state of deep sleep. The third degree is characteristic of extensive hemorrhage and is characterized by the absence of basic reflexes and the reaction of the pupils to light. In the fourth, against the background of suppressed reflexes, there is a sharp decrease in pressure and depression of respiratory function.
The prognosis for life in a coma after a second stroke is disappointing, especially when it comes to the hemorrhagic type. After ischemia, the chances of recovery from this condition and partial recovery are significantly higher.
Measures must be taken to combat brain swelling, seizures and the risk of infections. The victim requires constant care. Prevention of bedsores is of great importance. Treatment also includes vitamin therapy and general massage.
Causes of stroke
Depending on the cause of cerebrovascular accident, ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes are distinguished.
Ischemic stroke occurs as a result of blockage of cerebral vessels by a blood clot, when gradually less and less blood flows to an area of the brain. Hemorrhagic stroke develops as a result of rupture of a vessel and hemorrhage in the brain tissue, as a result of which the blood supply to its area abruptly stops. Hemorrhage can be into the subarachnoid space (SAS) or directly into the cerebral substance (ICH). The ratio of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes is 4-5:1 [4].
Pathologically, a stroke can be cardioembolic, lacunar, atherothrombotic, or another, including unknown, etiology (TOAST classification) [10].
Predisposing factors:
- men from 45 to 59 years old;
- age 70 years and older (for both sexes) [4];
- arterial hypertension;
- atrial fibrillation;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- coagulopathy, thrombophilia, anemia;
- arteriovenous malformations;
- osteochondrosis with damage to the vertebral artery;
- brain tumors;
- dyslipoproteinemia;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- intermittent claudication;
- mechanical prostheses of heart valves and blood vessels;
- IHD, myocardial infarction less than 6 months before the stroke;
- other cardiac diseases;
- smoking, alcoholism;
- family history of stroke;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- stress [1, 3].
Consequences of ischemia
{banner_banstat2}
With a small area of necrosis of brain tissue or a micro-stroke on the right, the prognosis for the patient’s life is favorable: neurological changes are minimal and do not criminally impair brain function. An exception is trunk ischemia, since vital centers - respiratory and cardiovascular - are concentrated here. Therefore, even a microstroke of the brain stem almost 100% ends in death in the first hours.
The remaining patients will experience disability because, although they are not completely bedridden, they lose even a small ability to adequately, fully perceive the surrounding reality, understand what is happening to them, and the ability to think logically. For left-handed people it’s the other way around. For them, the consequences of a right-sided stroke are similar to ischemia of the left hemisphere in right-handed people.
The main consequences are presented in the table. We must understand that the consequences of ischemic stroke decrease over time with proper treatment. About a quarter of patients under 55 years of age recover fully from a microstroke without visible signs of any neurological impairment.
At the same time, no matter how many functions are rehabilitated in the first two years after a micro-stroke, so many will remain until the end of days. Nerve cells are practically not restored.
| Outcome of stroke on the right | Consequences of micro and macro ischemic stroke |
| Complete paralysis of the left side of the body | The movements of the left limbs are minimized, the position is half-bent, the patient is able to sit, but without assistance he is not able to walk or grasp objects with his hand (hemiplegia) |
| Imbalance of sensitivity on the left | Pain and temperature threshold increases (hypoesthesia) |
| Loss of sense of spatial arrangement of arms and legs | |
| Mental disorders | Criticism decreases, foolish behavior arises, speech becomes inadequate, the person becomes aggressive |
| Memory loss | Patients remember the past, but forget what they did an hour ago; temporary complete amnesia and disorientation in space and time are possible |
| Left vision disorders | Decreased vision up to blindness, double vision, turning the head and left eye to the left |
If the area of brain necrosis is large (massive stroke), the prognosis is disappointing: up to 70% of patients die in the first few days, others become deeply disabled. The consequences are:
- persistent paralysis: patients cannot even sit;
- cerebral coma;
- complete lack of criticism and thinking;
- swallowing disorders.
Signs of an incipient stroke
The onset of a hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by the following symptoms:
- severe headache;
- increased blood pressure;
- vomit;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- weakness in the limbs;
- visual impairment;
- seizures [1].
The onset of ischemic stroke is gradual; within an hour, some of the following symptoms appear:
- facial asymmetry, numbness;
- difficulty speaking – incoherent, impaired understanding;
- double vision, visual disturbances;
- headache;
- numbness, limited mobility in the limbs, often on one side;
- dizziness, imbalance, staggering, staggering gait;
- confusion with disorientation, subsequently there may be loss of consciousness [3].
If one or more of these signs appear, you should:
- Sit the patient down, providing access to fresh air.
- Call emergency medical help immediately.
- If the patient is conscious and able to chew and swallow, give him one aspirin tablet.
The patient must be hospitalized in a neurological or neurosurgical department, where stroke treatment will be carried out. The sooner the patient is in the hospital, the more effective the therapy.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke in older people
Most often, ischemic cerebral infarction occurs at rest or even during sleep. The process develops gradually, more slowly than with the hemorrhagic form, but it still begins unexpectedly, and the manifestations progress quickly.
Since cell damage occurs in separate areas of the cerebral cortex, symptoms arise in the form of focal disorders.
Clinical manifestations of blockage or spasm of the carotid arteries:
- reduction (paresis) or complete loss (paralysis) of the ability to move limbs on one side of the body;
- pathological muscle tone and reflexes;
- paresis of facial muscles - impaired facial expressions, immobilization of half the face, distortion, inability to smile evenly, raise eyebrows, smoothness of the nasolabial fold, drooping of the corner of the eye, lips;
- loss of sensitivity in the affected limbs;
- blurred vision, flashes of light, visual hallucinations;
- slurred speech;
- inability to act purposefully (apraxia);
- violation of the eye, difficulty determining the distance to objects, their relative position;
- emotional and mental disorders.
Signs of ischemic stroke in older people that cause reasonable concern:
- sudden numbness of the limbs or any other part of the body;
- loss of control over one’s body – it is difficult for an elderly person to understand what is happening to him or where he is;
- speech disorders (incoherent words, the victim does not understand what others are saying to him);
- blurred vision, the image in the eyes is double, the field of view is partially lost;
- a distorted face, the corners of the mouth droop; if you ask the victim to smile, he will not be able to do so;
- paralysis of any limb - it is impossible to raise an arm or leg, or move them;
- when the tongue sticks out of the mouth, it deviates from the middle to the side;
- general cerebral disorders - loss of consciousness, convulsions, nausea, vomiting, headache.
The consequences of the disease, which will subsequently affect a person’s standard of living, ability to work, and do without outside help, depend on the timely start of treatment. In most cases, older people who have suffered a stroke can no longer return to their normal lives; they develop vestibular disorders, paralysis, and speech changes.
Symptoms of a stroke
Stroke leads to various brain injuries, depending on the location of the lesion and the pathological type of cerebrovascular accident:
- disturbances of movement in the limbs: from restrictions (paresis) to complete paralysis. When the lesion is localized on the right, the left limbs suffer; with a left-sided lesion, right hemiparesis is formed; in some cases, movements in all limbs may stop (tetraparesis or double hemiparesis);
- sensory disturbances on one or both sides;
- speech disorders (dysarthria - poor articulation; aphasia - inability to pronounce and understand words, write and read);
- ataxia (impaired coordination of movements, “overshooting”, unsteadiness, imbalance, tremor);
- visual impairment: from blindness to double vision and gaze paresis;
- hearing impairment and dizziness;
- violation of mental functions (consciousness, thinking, attention, memory, will, behavior);
- paresis of the soft palate and pharynx, swallowing disorders;
- disorders of urination and defecation;
- depression of respiration and vascular tone;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- patients complain of headaches, vomiting, hiccups, yawning, shoulder pain;
- consciousness is gradually depressed to the point of coma [1, 3].
Causes of death may include cerebral edema, pneumonia, heart failure, and recurrent stroke. In severe cases, “locked-in syndrome” may develop: the patient is conscious, but cannot move, swallow or speak [3].
What happens after a hemorrhage?
{banner_banstat3}
It makes sense to talk about the consequences of a hemorrhagic stroke only if we are talking about small hemorrhages on the right. Stroke-hematoma or large hemorrhage of the right hemisphere is almost 100% fatal.
No more than 10% of such patients can be saved by emergency removal of blood clots with drainage of the cranial cavity, but those who survive will remain deeply disabled for the rest of their days. Life expectancy is very short - from several days to several months.
With a small hemorrhage on the right, the prognosis is ambiguous: 75% survive, but become disabled, and the degree of disability is higher than with ischemia. Patients in 10% can fully recover, in 70% they are able to walk with difficulty, care for themselves, and are immobilized - up to 20%.
Differences in the consequences of hemorrhagic stroke of the right hemisphere:
- intolerance to loud sounds and bright light;
- increased irritability;
- cephalgia;
- lack of coordination;
- insomnia;
- swallowing disorder;
- hematoma in the ventricles of the brain.
In seriously ill patients after a stroke on the right side, regardless of the form, delayed complications occur: congestive pneumonia, bedsores, exhaustion due to great difficulties in caring for such patients. It is complications of this nature that cause the death of patients in the first two years of post-stroke life. About 15% live 10 years or more.
Consequences of a stroke
There are transient ischemic attack (less than a day), minor stroke (from 1 day to 3 weeks) and stroke with persistent residual effects. The consequences of a stroke are expressed mainly in motor and sensory disorders, the formation of muscle contractures (pronounced constant restriction of movements in the joints), speech and swallowing disorders. General symptoms may also remain, including confusion, disturbances in thinking, will, and emotional regulation. Complications can develop: from epilepsy to bedsores, encephalopathy and anxiety-depressive syndrome [1, 3].
Diagnostics
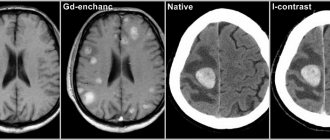
When a patient with signs of a stroke comes to the Yusupov Hospital, specialists strive to accurately determine the state of blood flow in the brain vessels of the right hemisphere. The first priority in complex diagnostics are visualization methods: CT and MRI, which make it possible to establish the localization of the lesion, the type and subtype of stroke, and also determine which vessel pathology led to disruption of brain nutrition.
With ischemic stroke, a “mismatch” phenomenon occurs, which can be detected during perfusion CT. A feature of this condition is that with a decrease in blood volume and the speed of its movement, an ischemic penumbra zone appears. This area of the brain contains cells whose death can be prevented.
Comprehensive diagnosis of ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out using high-precision methods:
- cerebral angiography is prescribed to patients if surgical intervention is necessary;
- transcranial Doppler sonography is carried out to study the state of blood flow in the brain;
- electroencephalography is used to establish areas of subcortical and cortical damage;
- Positron emission tomography and scintigraphy are performed to assess the nature of brain metabolism.
Diagnosis of strokes
First of all, it is necessary to conduct a detailed neurological examination. Instrumental diagnostic studies and laboratory tests are also prescribed. In case of a stroke, in the first hours, an MRI or CT scan of the brain is performed, if necessary, CT or MR angiography, color Doppler mapping of blood flow, ECG or Holter monitoring, echocardiography as indicated, monitoring of blood pressure, saturation, assessment of the risk of developing bedsores, assessment of swallowing function [ 1, 3, 6].
Tests for stroke
- Complete clinical blood test, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
- Biochemical blood test with determination of C-reactive protein and homocysteine, glucose level, platelet count, activated partial thromboplastin time, INR.
- Interleukin 10.
- Extended coagulogram.
- Determination of acid-base status.
- General urine analysis.
To prepare for neurosurgical intervention, a blood test is additionally performed for hepatitis, syphilis, HIV, blood group and Rh factor determination.
First aid
Irreversible changes in the brain begin within a few hours after the first signs of a major stroke appear. There is the concept of a “therapeutic window” - a period of 4.5 hours, during which it is still possible to prevent the death of a critical number of nerve cells. In practice, doctors have significantly less time to carry out a set of measures - on average, about one and a half hours.
If symptoms appear that indicate an acute circulatory disorder, you need to call a medical team without wasting a minute. Before their arrival, it is necessary to calm the victim and help him take a semi-lying or horizontal position with his head raised. If the patient is unconscious, the head should be turned to the side to prevent aspiration of vomit. The shirt collar should be unbuttoned, the trouser belt should be loosened, and other clothing that may restrict breathing should be removed. To ensure the flow of fresh air, it is recommended to open a window or vent.
If the attack began against the background of a hypertensive crisis, to improve the outflow of blood from the brain, you can lower the patient’s legs into a basin of hot water.
Important: It is strictly forbidden to give vasodilators, as well as give water and food to the patient! You should not take him to the hospital on your own, especially by public transport!
Relatives or friends need to accompany him to the hospital by ambulance, so that they can then describe the symptoms in detail to the doctors. This will help specialists objectively assess the situation and quickly make the correct diagnosis.
If necessary, the ambulance team can perform mechanical ventilation and tracheal intubation, as well as administer drugs to lower blood pressure and begin correcting the water and electrolyte balance by placing a drip with saline solution. The basic principle that guides transportation is “delivery with the least possible deterioration in condition.”
Stroke treatment
Treatment of stroke is regulated by relevant clinical guidelines and the Procedure for providing medical care to patients with acute cerebrovascular accident. In the first hours, thrombolytic therapy is carried out and subsequently - prevention of thrombus formation. For hemorrhagic stroke, neurosurgery may be performed. They normalize blood pressure, water-electrolyte balance, glucose levels in peripheral blood and urine, support the basic vital functions of the body and prevent complications. Drug therapy is also aimed at improving the affected functions of the nervous system [1, 3, 6].
Treatment and rehabilitation
First aid
If you detect the first signs of a stroke, you should immediately call an ambulance (112 - from a mobile phone, 03 - from a landline).
Next, do the following:
1. The patient's head should be elevated. Lay him on the bed and place pillows under his head, shoulders, and upper back; 2. Open the window to allow fresh air; 3. Unbutton all tight clothing: shirt, belt, tie; 4. Measure your blood pressure; 5. If the patient is vomiting, turn your head to the side - the vomit should not enter the respiratory tract.
No medications should be given until doctors arrive. If the patient has lost consciousness and fallen into a coma, artificial respiration and chest compressions must be performed. In a difficult situation, continue to fight for the life of the victim until the end - there is a chance of salvation. People who suffered severe attacks were saved even in the most difficult cases. Remember that only medical professionals can confirm death. Help the patient and wait for the ambulance.
Treatment in hospital
After arriving at the hospital, the patient is sent to the neurovascular department of the hospital, where he undergoes therapy. The patient must normalize blood pressure, prevent swelling and hypoxia of the brain, restore healthy brain function, normalize blood counts and prevent disability.
An elderly person who has survived a stroke needs constant medical care and care from loved ones. Measures are taken depending on the type of stroke:
• Ischemic: reperfusion treatment. Medications are used along with mechanical treatments to restore healthy blood flow in the blocked vessel. • Hemorrhagic: treated with hemostatic agents that lower blood pressure. In case of major hemorrhage, surgery is performed. Surgery can remove blood clots and reduce hematoma.
In the treatment of stroke in the elderly, drugs are used to lower blood pressure, normalize cholesterol, fight blood clots, improve heart function and circulation, antidepressants and sedatives. Medicines are prescribed depending on the individual situation of the patient.
An elderly patient may be prescribed intra-arterial thrombolysis, and endovascular treatment methods are also used. At the beginning of therapy, antiplatelet agents are used. In the first hours after the onset of a stroke, the patient is given aspirin.
After the first treatment, the patient expects long-term rehabilitation and care. Care for the patient depends on his condition. Bed rest and regular skin hygiene by wiping are recommended to everyone. The bed in the head area should be higher, and you should also change your body position regularly (every 2-3 hours) - this is the prevention of bedsores.
A neurologist treats strokes. It helps restore lost physical and mental functions, and also prevents recurrent attacks.
During rehabilitation, various exercises and techniques are used to restore a person’s speech and motor activity. Teachers and psychologists work with the patient to help him return to the social environment. The person is prescribed medication, nutritional therapy, and physical procedures. It is important to follow a healthy diet: eat boiled or steamed food, limit yourself to sweets, salty, fatty foods. You need to give up alcohol and tobacco.
The effectiveness of restoring lost functions will depend on the size and location of the affected area, the general health of the patient, the participation and assistance of loved ones, and the quality of rehabilitation. It is better to begin recovery a week after the stroke, when the patient’s condition becomes stable.
Rehabilitation lasts from several months to several years. Much depends on the patient’s condition and the quality of rehabilitation. Motor activity may return within six months, speech within 2-3 years. With a high-quality integrated approach, the patient will recover faster.
Rehabilitation: highlights
Rehabilitation after a stroke can be divided into several areas of recovery: speech, motor functions, swallowing and bowel function, memory, vision and facial symmetry.
Speech restoration occurs with the help of special exercises that must be performed regularly. A speech therapist works with the patient. A person is taught to pronounce simple words and phrases, communicate with him by asking easy questions, and learn to understand speech. It is also important to train the muscles of the face and tongue, and develop facial expressions. Next, a person is taught reading and writing. If speech cannot be restored, a person learns to communicate using facial expressions and gestures.
To restore memory, they use short texts to memorize, recall incidents from life, communicate on light topics, use finger games and mental games (for associations, invention, logical connections).
Physical therapy is used to restore movement. Use exercises to flex, rotate and move the limbs. They should be done slowly, gradually increasing the load. There should be no pain or discomfort. They also do exercises for the eyes.
In order for the face to become symmetrical again, it is necessary to restore healthy muscle tone and normal shape. To do this, use special exercises for the facial muscles: smiling, winking, jaw movements.
To restore swallowing, the patient is fed light and tasty foods that are easy to chew and swallow. He also does gymnastics for the tongue and lips.
After a stroke, a person spends a long time in a lying position, and this negatively affects the condition of his intestines. To maintain or restore healthy bowel function, he is prescribed laxatives and enemas, as well as a diet rich in fiber.
After an attack, a person may partially or completely lose vision. To prevent blindness, they do special eye exercises, use medications, or perform surgery.
For recovery, a therapeutic massage may be prescribed: it will help to quickly establish healthy physical activity.
Additional Treatments
In addition to the main methods of treatment and rehabilitation, additional methods are used. Let's take a closer look at them.
• Botox therapy. The muscles of people who have suffered a stroke are in tense tone. To relax them, various techniques are used, including Botox therapy. Botox injections help relieve muscle tension. • Exercise therapy – helps restore limb mobility. • Therapeutic massage will improve blood circulation, help cope with spasms, and improve the functioning of the nervous system. • Physiotherapeutic methods relieve pain, restore healthy blood flow, and improve organ function. They use different techniques – both individually and in combination. Vibromassage, electrical stimulation of muscles, electrophoresis, and laser therapy are popular. • Kinesthetics. The patient gradually learns to make movements that do not cause pain. This allows him to move without an assistant - for example, to turn independently in bed. • Reflexotherapy – impact on biologically active points using needles. Acupuncture helps relieve muscle tension, improve the condition of the musculoskeletal system, and establish healthy functioning of the nervous system. • Bobath therapy – teaches healthy areas of the brain to perform duties instead of damaged ones. The entire therapeutic process is under the supervision of a doctor. • Psychotherapy. A person who has experienced a stroke needs psychotherapeutic help and support. It will help cope with depression and psychological problems. This will support the patient's mental health and brain health, which is very important for successful recovery. • Occupational therapy – helps a person return to normal life and restore ability to work.
Folk remedies for recovery
Folk remedies are good helpers during the rehabilitation period. They cannot replace traditional medications, nor can they be self-prescribed. A suitable folk recipe, agreed upon with the attending physician and used as an addition to the main methods of treatment, will help the elderly patient in recovery.
For people who have suffered a stroke, recipes based on black radish, aloe juice, bay leaf, horse chestnut, hawthorn, rose hips and other herbs are suitable. Herbal infusions are popular.
Stroke rehabilitation
Stroke is a disease in which rehabilitation and care are of the utmost importance.
Recovery from a stroke begins in intensive care, from the moment vital functions are stabilized. A multidisciplinary rehabilitation team works with the patient, which includes a rehabilitation doctor, physical therapist or exercise therapy instructor, speech therapist, massage nurse, physiotherapist and physical therapy nurse, psychologist, occupational therapist, guard and rehabilitation nurse. Diagnosis is carried out using special scales that reflect the degree of dysfunction and limitations in the patient’s activity, the influence of environmental factors on the rehabilitation potential. The rehabilitation process continues throughout the entire period of hospitalization. At the second stage, patients with serious disabilities who are unable to move independently are sent to rehabilitation departments or specialized hospitals. Those who can walk independently or with support are rehabilitated in outpatient centers based in clinics and sanatoriums.
The rehabilitation process should not be interrupted, so classes must be continued at home. Of course, there are no high-tech robotic complexes or physiotherapeutic equipment at home, but exercise therapy, massage, and work with a psychologist, speech therapist and occupational therapist are possible. For this purpose, telemedicine technologies are used and visits to rehabilitation specialists are organized.
The individual rehabilitation program includes not only a referral for rehabilitation treatment, but also technical means of rehabilitation. However, usually relatives also have to devote significant physical and financial resources to achieve the best effect [7].
Rehabilitation after a stroke at home
After overcoming the acute period in the hospital, a rehabilitation period begins for a pensioner with a stroke. Relatives need to decide where it is better for an elderly person to undergo a recovery course: at home or in a rehabilitation center.
You may also be interested in the article: How to obtain patronage for an elderly person
If the family has decided to independently care for the patient after a stroke, they need to follow the recommendations of the attending physician and maintain constant contact with specialized specialists: a psychologist, a neurologist, a speech therapist.
At home, a separate place is assigned to a bedridden patient after a stroke. The bed is equipped with an anti-decubitus mattress. A small table is placed nearby, on which essential items are placed: a bottle of water, care products, a table lamp.
Specialists can come to the home 1-2 times a week, work with the patient and teach home methods of conducting developmental activities. The rest of the time, family members carry out the recommended exercises with the pensioner for 10-20 minutes several times a day. During weekly visits, specialists monitor the dynamics of changes, make additions and adjustments.
Motor abilities are restored using a complex of therapeutic exercises. Before performing the exercises, it is advisable for the patient to take a shower or bath to warm up the body. If there are contraindications to taking a bath or other difficulties, the affected areas are warmed with a heating pad. The muscles will be more flexible and there will be no pain.
Examples of gymnastic exercises:
- pulling up while lying on your back, holding the headboard of the bed;
- eye movements left and right, up and down with closed and open eyelids;
- alternately raising the right and left arms and legs;
- bending the knee and grabbing the shin with the hand;
- joint movements of healthy and motionless limbs to the right and left with a rubber ring put on them.
When carrying out therapeutic exercises, the pensioner’s condition is closely monitored. He shouldn't get tired. If such signs are observed, it means that the amount of stress does not correspond to the physical strength of the patient. We need to make an adjustment: reduce the pace and number of exercises.
Speech is restored by memorizing poetry and tongue twisters. At the initial stage, simple children's poems are chosen, which are easier for a pensioner to recite after a stroke. Gradually more complex material is selected.
Looking at family photographs can activate the process of remembering, since it is easier for the patient to recall the past in his memory. An elderly person remembers acquaintances and friends in the images, then the events associated with them. He tries to pronounce the names of the places he has visited, the objects he sees in the images.
Scientists believe that singing has a beneficial effect on people who have suffered a stroke. If they hear singing, sing together with loved ones, speech activity will be restored faster.
For rehabilitation to be successful, an elderly person should not be in a social “vacuum”: you constantly need to communicate with him, talk, ask questions, even if at first he cannot answer them. In this way, the patient’s desire to speak is stimulated, he remembers words and their meaning.
Chess, checkers, and dominoes are used to develop thinking abilities. In a family, even a small child can take part in restoring the health of a grandfather or grandmother by putting together puzzles, mosaics, or playing a board game.
A separate issue is the organization of nutrition for an elderly person after a stroke.
Excluded from use:
- alcoholic drinks;
- fatty and spicy foods;
- coffee, strong tea;
- sweets.
It is advisable to add to the diet:
- drink liquid of at least 1.5 liters. per day;
- increase consumption of fruits and vegetables;
- eat whole grains;
- replace sweets with dried fruits.
Food should consist of useful substances and be easily digestible so that the body is not overloaded.
It is useful to cook boiled vegetables, dishes from lean fish and meat, and porridge with low-fat milk. If there are paresis and problems with swallowing, the patient is fed through a tube with ready-made nutritional mixtures. As soon as the opportunity arises, you need to take the patient for a walk. Staying in the fresh air is good for brain activity, the body receives oxygen and vitamin D, and appetite appears.
You may also be interested in the article: How to choose a private facility for the elderly
The moral atmosphere in the house is of great importance. Patients who receive family support recover faster. If they experience hostility from others or rudeness, the healing process is slowed down. There is no need to criticize and laugh at clumsiness and awkwardness. Only with encouragement will an elderly person develop a strong desire to overcome the disease.
Prevention of strokes
Hereditary predisposition to stroke, the presence of cardiac diseases, pathology of blood vessels and blood composition, age over 40 years, obesity and diabetes require a number of preventive measures:
- Maintaining normal blood pressure, taking antihypertensive drugs as prescribed by a doctor, monitoring blood pressure.
- Maintaining a normal level of physical activity, exercise, walking 30-40 minutes a day (for example, walking the dog).
- Conducting preventive examinations, including a standard set of laboratory parameters. During a preventive examination, the following tests are additionally required: gene diagnosis of CADASIL syndrome using the PCR method, plasma factors of the blood coagulation system, antibodies to prothrombin of the IgG and IgM classes to determine the risk of thrombosis, determination of polymorphisms associated with the risk of arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, lipid disorders exchange, in order to identify a predisposition to diseases that increase the risk of stroke, von Willebrand factor (a glycoprotein that ensures the formation of blood clots), complex laboratory tests for preclinical diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases are offered (“ELI-ANKOR-Test-12”, “Cardiorisk”).
- Avoiding chronic and acute stress, maintaining mental hygiene.
- Normalization of weight (BMI <25 kg/m2).
- Healthy eating (for example, Mediterranean diet, limiting salt to 5 5 g/day).
- Quitting smoking and taking psychoactive substances.
- Treatment of diseases that are a risk factor for stroke [8, 11].
Causes of ischemic stroke in older people
The main blood vessels that provide blood flow to brain cells (carotid, vertebral arteries) are called cerebral. If their patency is impaired, a cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke) develops. The cause may be a detachment of a blood clot, an increase in atherosclerotic plaque, or persistent vasospasm. When a blockage occurs, brain cells no longer receive enough oxygen and nutrients, causing irreversible tissue changes in that area.
The frequent manifestation of ischemic stroke in older people is associated with age-related organic changes in the walls of blood vessels, their compaction, and the deposition of cholesterol on them. Regular circulatory disorders in the body associated with other diseases and pathologies also have an effect:
- atherosclerosis of coronary vessels, peripheral arteries;
- obesity;
- hypertension and secondary hypertension;
- hereditary predisposition;
- metabolic syndrome;
- diabetes;
- lipid metabolism disorder (dyslipidemia);
- nicotine addiction;
- chronic alcoholism.
Disorders of cerebral hemodynamics can be provoked by a sedentary lifestyle, consumption of large amounts of fatty meat products and sweets, and frequent stressful situations.
We recommend
“Stroke in an old person: causes and consequences” More details
With age, the risk of ischemic stroke in older people increases; after 55 years, it is more common than hemorrhagic. Rupture of cerebral vessels and hemorrhage occur mainly in persons suffering from prolonged arterial hypertension, atherosclerotic artery disease, and amyloidosis. Uncontrolled use of drugs that prevent blood clotting can also cause hemorrhagic stroke.
Among the potential victims of vascular pathology of the brain, most of them are those who suffer from diabetes. This connection has its own explanations. :
- angiopathy (changes in the thickness of the walls of blood vessels) develops against the background of increased glucose levels in the blood;
- due to constant efforts aimed at removing glucose and fluid from the body, dehydration occurs and the blood thickens;
- tissues chronically lack nutrients, because due to a lack of insulin, glucose does not enter the cells;
- Against the background of diabetes, it is difficult for the body to form bypass pathways to restore blood supply to the affected area.
The excessive obesity of many diabetics is associated with a violation of not only carbohydrate but also fat metabolism. Insulin deficiency leads to increased cholesterol levels in the blood, which, in turn, causes the early manifestation of atherosclerosis, which is quite severe.
Hence the prevalence of extensive forms of ischemic cerebral infarction in older people, accompanied by complications and frequent death.
Bibliography
- Hemorrhagic stroke in adults: clinical recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2021. Developers: Association of Neurosurgeons of Russia. - Electronic text. - URB: (access date 08/18/2020).
- Efremova M.D. Stroke as an urgent socio-psychological problem / M.D. Efremova – electronic text//Skif. Questions of student science.- 2021 - No. 2(24) URB: (date of access 08/17/2021) Access mode: Cyberleninka electronic library system. — Text: electronic.
- Ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack in adults: clinical recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2021 developers: All-Russian Society of Neurologists, National Association against Stroke, Association of Neurosurgeons of Russia, Association of Neuroanesthesiologists and Neuroreanimatologists, Union of Rehabilitologists of Russia. - Electronic text. - URB: ( access date 08/18/2020).
- Machinsky P.A. Comparative characteristics of incidence rates of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in Russia / P.A. Machinsky, N.A. Plotnikova, V.E. Ulyankin [and others] – Direct text.// News of higher educational institutions. Volga region. Medical Sciences.- 2021.- “2(50)-P.112 – 132 DOI 10.21685/2072-3032-2019-2-11.
- Monitoring the implementation of the federal project “Combating Cardiovascular Diseases” - Presentation Department of Organization of Medical Care and Sanatorium Affairs of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation URB: (date of access 08/17/2021).
- Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 15, 2012 N 928n “On approval of the Procedure for providing medical care to patients with acute cerebrovascular accidents.” — URB: (access date 08/17/2021) Access mode: Electronic library system “Garant”. — Text: electronic.
- Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated July 31, 2021 No. 788n “On approval of the Procedure for organizing medical rehabilitation of adults.” – URB: (date of access 08.17.2021).- Access mode: Electronic library system “Garant”. — Text: electronic.
- Prevention of cerebrovascular accidents: textbook. manual / Compiled by: L.B. Novikova, A.P. Akopyan. – Ufa: Publishing house of the State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education BSMU of the Ministry of Health of Russia, 2015.-58 p.
- Stakhovskaya L.V. Analysis of epidemiological indicators of recurrent strokes in the regions of the Russian Federation (based on the results of the territorial-population register 2009-2014) / L.V. Stakhovskaya, O.A. Klochikhina, M.D., Bogatyreva, etc.]. CONSILIUM MEDICUM, 2021, vol. 5, no. 9, p. 8-11.
- Shamalov N. A. Analysis of the dynamics of the main types of stroke and pathogenetic variants of ischemic stroke / N. A Shamalov, L. V Stakhovskaya, O. A Klochikhina [and others]. Direct text. // Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry named after. S.S. Korsakov. Special issues. 2019;119(3-2):5-10. doi.org/10.17116/jnevro20191190325.
- 1RRE Electronic edition. Updated daily Stroke Day is celebrated on October 29, 2021 URB: (accessed 08/17/2021).
Author:
Pugonina Tatyana Alekseevna, Therapist
Diagnosis of ischemic stroke in the elderly
Data from objective and instrumental research methods and their comprehensive competent assessment will help diagnose ischemic stroke in older people:
- neurological examination;
- Ultrasound examination of the arteries of the head and neck;
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging;
- angiography;
- transcranial Doppler ultrasound;
- electroencephalographic study.
Proper diagnosis will help distinguish ischemic stroke from hemorrhagic stroke. Neuroimaging techniques for studying the disease play an important role here. It is necessary to identify and differentiate between ischemic stroke and other brain diseases, for example, acute hypertensive encephalopathy. It is important to distinguish impaired brain activity due to blockage or spasm of blood vessels from toxic or metabolic types of encephalopathy, from brain tumors, abscesses, encephalitis and other brain lesions of an infectious nature.
What are the features of a left hemisphere stroke?
As we said above, the left hemisphere of the brain controls the right half of the human body. If the left hemisphere of the brain is damaged, paresis (paralysis) of the right limbs will be noted.
The left hemisphere also controls speech (for all right-handers and half of left-handers, and for the other half of left-handers, the center of speech is located in the right hemisphere of the brain), memory and cognitive functions, so during a stroke the patient may have problems with speech, he will lose memory, and mood swings, behavior will change - he will become slow and cautious.
Treatment
A patient who has suffered a stroke requires emergency care and hospitalization. Numerous studies of this disease confirm that treatment carried out in the first three days is most effective, since the activity of nerve cells surrounding the lesion is high.
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital begin treating the consequences of a stroke after a comprehensive examination of the patient. The treatment and rehabilitation programs developed by our specialists are based on the principle of the individuality of each patient, however, if the blood supply to the brain is impaired, the following measures are mandatory:
- monitoring of cardiac activity and blood pressure;
- prevention of early contractures, pneumonia;
- ensuring the required level of blood oxygen saturation and removing excess carbon dioxide;
- maintaining homeostasis - equilibrium of the internal environment;
- monitoring the condition of the intestines and bladder;
- swallowing control;
- skin care and prevention of bedsores.
Treatment of patients after pneumonia involves the use of drugs and non-drug methods. To take into account contraindications, cardiologists, neurosurgeons and resuscitators take part in drawing up the treatment program.
Drug therapy after a stroke involves the use of the following drugs:
- antihypertensive drugs for high blood pressure;
- osmotic diuretics and dexazone are used for cerebral edema, as well as to prevent increased intracranial pressure;
- anticoagulants, which include heparin, help control blood clotting;
- antiplatelet agents (trental, beta blockers, calcium antagonists) are used to identify signs of insufficient blood supply;
- drugs with a neuroprotective effect are used to restore neurons.
The Yusupov Hospital creates comfortable conditions for every patient. After a stroke, patients need professional care, which is provided by the staff of the neurology clinic:
- introducing fluids and nutrients into the body;
- turning the patient from one side to the other every 2 hours;
- performing cleansing enemas once every two days;
- wiping the skin every 8 hours with camphor alcohol;
- cleaning the nasopharynx and oropharynx using suction and then rinsing them.
Rehabilitation
The implementation of the rehabilitation program begins after the patient’s condition improves. In the rehabilitation clinic, patients interact with speech therapists who offer exercises to gradually restore written and spoken language skills. Physiotherapeutic procedures and massages are carried out by professional rehabilitation therapists. Exercise therapy instructors at the Yusupov Hospital restore motor function through therapeutic exercises, physical education and kinesitherapy.
Stroke rehabilitation programs may include the following:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- acupuncture;
- kinesio taping;
- Voita therapy;
- massage sessions;
- treatment by position and movement.
The rehabilitation clinic of the Yusupov Hospital has modern technical equipment, which, combined with the knowledge of specialists, ensures effective restoration of functions after an ischemic stroke on the right side of the brain.
Forecast
Right hemisphere ischemic stroke is a disease associated with high mortality. However, the achievements of modern medicine allow neurologists to fight for the life of each patient and improve its quality. The prognosis for ischemic right-sided stroke depends on factors such as the timeliness and correctness of first aid, the age of the patient, treatment and rehabilitation tactics, and the patient’s readiness.
Restoring functions lost due to a stroke lasts up to a year. However, activities carried out in the first trimester are most effective. There are cases where specialists are unable to restore speech in left-handed people with a right-sided stroke, while other functions are completely restored.
The patient and his loved ones must be prepared for the fact that rehabilitation measures are delayed for several years. During this period, it is important to follow your doctor’s orders, do home exercises, and attend procedures. At the Yusupov Hospital, relatives are trained in the basics of care and interaction with the patient.
The rehabilitation programs implemented at the Yusupov Hospital are highly effective, this conclusion can be drawn from research conducted by neurologists. Some patients who underwent treatment and rehabilitation were able not only to return to a full life, but also to continue working. The achievement of other people after rehabilitation was that they were able to take care of themselves and communicate with others.
Treatment and rehabilitation after ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere is carried out in accordance with international standards. The medical staff provides a wide range of services and creates conditions for the recovery of patients. To schedule a consultation or get answers to your questions, you can contact the Yusupov Hospital by phone.