If you know exactly the signs of stroke in men, you can avoid serious complications leading to disability and death. A cerebral stroke (CBI) occurs due to impaired blood supply. The attack is facilitated by narrowing of the lumen in the arteries or rupture of blood vessels, resulting in hemorrhage.
What is a stroke, its types
A stroke is a disorder of cerebral circulation leading to brain damage.
The pathology is widespread. In the Russian Federation alone, there are 3 cases of stroke per 1000 inhabitants. In the post-mortem extract, it is listed as the cause of death in 23.5% of people.
Even if patients do not die after suffering a vascular accident, more than 80% of them remain disabled. Often neurological disorders are so severe that the patient is unable to care for himself. Stroke is the third leading cause of death.
There are 2 types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic. The mechanism of their development and the features of treatment have nothing to do with each other. There is also a special type of hemorrhagic vascular damage - subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Ischemic
Ischemic stroke is a cerebral circulatory disorder accompanied by an acute onset. Pathology develops due to disruption or complete cessation of blood supply to the brain. This leads to softening of its tissues and infarction of the affected area. It is cerebral vascular ischemia that is one of the main causes of death worldwide. Such a stroke occurs 6 times more often than hemorrhagic lesions.
It can be of 2 types:
- Thrombotic . Develops due to blockage of blood vessels in the brain by a blood clot.
- Embolic . Occurs when blood vessels located far from the brain become blocked. The most common source of embolism is the heart muscle (cardioembolic stroke).
In 80% of cases, the pathological focus is localized in the middle cerebral artery. Other vessels account for the remaining 20%.
Reasons that can provoke ischemic damage to cerebral arteries and veins:
- Myocardial infarction.
- High or low blood pressure.
- Atrial fibrillation.
- Diabetes.
- Lipid metabolism disorders.
Risk factors include: old age, hereditary predisposition to vascular accidents, as well as lifestyle features.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke do not increase as quickly as symptoms of hemorrhagic brain damage.
Its manifestations:
- Drowsiness, dazedness.
- Brief fainting.
- Headache, dizziness.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Pain in the eyes that gets worse with movement.
- Cramps.
- Sweating, hot flashes, dry mouth.
Depending on which part of the brain is affected, the neurological manifestations of ischemia differ. The lower and upper extremities are affected to a greater or lesser extent, paresis of the tongue and face is observed, and visual and/or auditory function deteriorates.
Hemorrhagic
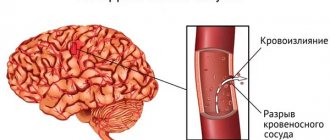
Hemorrhagic stroke is bleeding into the cranial cavity. The most common cause of blood vessel rupture is high blood pressure.
Other provoking factors include:
- Aneurysm.
- Malformation of cerebral vessels.
- Vasculitis.
- Systemic connective tissue diseases.
- Taking certain medications.
- Amyloid angiopathy.
The onset of the pathology is acute; most often the manifestation occurs against the background of high blood pressure. A person experiences severe headaches, dizziness, accompanied by vomiting or nausea. This state is quickly replaced by stupor, loss of consciousness, and even the development of coma. Convulsions are possible.
Neurological symptoms manifest themselves in the form of memory loss, deterioration of sensitivity and speech function. One side of the body, which is on the opposite side of the lesion, loses the ability to function normally. This applies not only to the muscles of the torso, but also to the face.
A stroke with blood escaping into the ventricles of the brain is difficult to endure. The victim develops symptoms of meningitis and has seizures. He quickly loses consciousness.
The next 3 weeks after a stroke are considered the most difficult. At this time, cerebral edema progresses. It is he who is the main cause of death of patients. Starting from the fourth week, in surviving people, the symptoms of the lesion begin to reverse. From this time on, the severity of brain damage can be assessed. They are used to determine what degree of disability to assign to the victim.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is understood as a condition that develops as a result of a breakthrough of blood vessels into the subarachnoid space of the brain. This pathology is a type of hemorrhagic stroke.
The subarachnoid space contains cerebrospinal fluid, the volume of which increases due to blood flow. The patient's intracranial pressure increases and meningitis of aseptic nature develops. The situation is aggravated by the reaction of cerebral vessels. They spasm, which leads to ischemia of the affected areas. The patient develops an ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack.
The following reasons lead to hemorrhage into the subarachnoid space::
- Traumatic brain injuries with damage to the integrity of blood vessels.
- Aneurysm rupture.
- Dissection of the carotid or vertebral artery.
- Myxoma of the heart.
- A brain tumor.
- Amyloidosis.
- Diseases associated with blood clotting disorders.
- Uncontrolled use of anticoagulants.
The pathology manifests itself as a severe headache. Possible loss of consciousness. In parallel, symptoms of meningitis develop, with neck stiffness, vomiting, and photophobia. A distinctive sign is an increase in body temperature. In severe cases, there is a disorder of respiratory function and cardiac activity. With prolonged fainting and coma, one may suspect that blood has entered the ventricles of the brain. This occurs during its massive outpouring and threatens with serious consequences.
The first signs of stroke in men
The general symptoms and first signs of stroke in men are practically no different from the warning signs in women, but the stronger sex is more likely to exhibit motor activity disorders, which is typical for brain diseases.
What to pay attention to:
- Feeling of weakness in the upper and lower extremities, often unilateral. For example, when raising hands, one of the parties “doesn’t listen well.”
- Migraine-like pain syndrome. It is impossible to get rid of pain with painkillers.
- Vomiting is cerebral, with no feeling of relief.
- Increased salivation.
- Difficulty in speech pronunciation due to decreased sensitivity of the tongue.
- Discomfort when swallowing, as contractility in the muscular system of the oropharynx and throat weakens.
- Impaired coordination of movements - it is impossible to perform precise movements, especially when walking (the gait becomes unsteady).
- Disorientation in space and time - the patient does not recognize familiar objects, people, etc.
- Double vision is the inability to focus your gaze. The mobility of one of the eyeballs is difficult, so from the outside the gaze seems lifeless.
- Involuntary urination and cramps - in severe cases of the disease.
- Fear of light and loud noises. A person reacts inappropriately to a switched-on lamp and music (knock, thunder, etc.).
- Loss of strength, drowsiness, general weakness. The patient gets tired quickly, sleeps restlessly, and feels constantly tired.
Symptoms of stroke in men are divided into 2 groups:
- General cerebral: intense localized pain that occurs suddenly. Drowsiness and convulsions, nausea and gag reflexes, pale face and fainting, cyanosis of the skin.
- Focal: occur after general cerebral ones in 15-20 hours. They manifest themselves as numbness of the extremities, decreased sensitivity of the skin in areas of the body that are under the control of the affected part of the brain (BM). Further, visual and hearing acuity is impaired, pupils dilate, eyelids droop, memory is partially lost, and sweating increases. Feature: if hypotension is present, blood pressure drops, if hypertension is present, it increases.
Expert opinion
Author: Daria Olegovna Gromova
Neurologist
The danger of a stroke is the high risk of death. In addition, impaired cerebral circulation leads to serious complications. According to the Federal State Statistics Service, stroke ranks second in the structure of mortality. The disease causes disability. Depending on the severity of the lesion, in 60-70% of cases patients are assigned a disability group. The ability to self-service is lost in 10-15%. Stroke occurs at the same rate in men as in women. Cerebrovascular accidents are most often recorded between the ages of 40 and 65 years. However, recently doctors have been identifying the onset of the disease at an earlier age.
Diagnosis of stroke at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out using modern medical equipment. With the help of CT and MRI, it is possible to determine the type of disorder, its location and extent of prevalence. In accordance with the data obtained, the correct therapy is selected. With timely initiation of treatment, complete restoration of lost functions is possible. An individual rehabilitation complex is developed for each patient at the Yusupov Hospital. It includes not only medications, but also exercise therapy and physiotherapy.
Signs and symptoms of stroke
A stroke manifests unexpectedly for a person, although sometimes it is preceded by certain symptoms. If you interpret them correctly, you can avoid a terrible vascular catastrophe.
Warning signs of an impending stroke include:
- Prolonged headaches. They do not have a clear localization. It is not possible to cope with them with the help of analgesics.
- Dizziness. It occurs at rest and can intensify when performing any actions.
- Ringing in the ears.
- Sudden attack of atrial fibrillation.
- Difficulty swallowing food.
- Memory impairment.
- Numbness of arms and legs.
- Loss of coordination.
- Insomnia.
- Increased fatigue.
- Decreased overall performance.
- Rapid heartbeat and constant thirst.
The listed signs may have varying intensities. You should not ignore them; you should consult a doctor.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke increase slowly. With hemorrhagic brain damage, the clinical picture unfolds rapidly.
You can suspect a brain catastrophe based on the following symptoms::
- General cerebral symptoms . The patient experiences unbearable headaches. Nausea ends with vomiting. Consciousness is impaired, and both stupefaction and coma may occur.
- Focal symptoms . They directly depend on where exactly the lesion is localized. The patient may have decreased or completely lost muscle strength on one side of the body. Half of the face is paralyzed, causing it to become distorted. The corner of the mouth lowers, the nasolabial fold smoothes out. On the same side, the sensitivity of the arms and legs decreases. The victim’s speech deteriorates and he has difficulty oriented in space.
- Epileptiform symptoms . Sometimes a stroke provokes an epileptic attack. The patient loses consciousness, has convulsions, and foam appears at the mouth. The pupil does not react to the light beam; on the side of the lesion it is dilated. The eyes move right and left.
- Other symptoms . The patient's breathing quickens and the depth of inspiration decreases. A significant decrease in blood pressure and increased heart rate are possible. Often a stroke is accompanied by uncontrolled urination and defecation.
When the first signs of a stroke appear, you should not hesitate to call an ambulance.
Precursors of stroke in men
The first symptoms of a stroke in men may be mild, so the patient does not always realize the danger of the condition. The appearance of alarm bells does not last long, but between exacerbations the period of remission is also short-lived. To recognize the approach of an attack, it is necessary to pay attention to the precursors of the disease, which have characteristic differences:
- frequent dizziness and pain at the site of the outbreak;
- squeezing sensation in the chest area;
- nausea, gag reflexes;
- sudden mood swings, causeless psycho-emotional disorders;
- facial redness due to hot flashes;
- tinnitus;
- rapid breathing;
- sharp pain in the back of the head;
- insomnia;
- fast fatiguability;
- shortness of breath during movement and at rest;
- absent-mindedness.
If such signals persist for several days, you should seek help from the hospital. You can undergo an examination in Moscow at the Yusupov Clinic, where neurologists will carry out diagnostics using modern equipment and establish an accurate diagnosis even at the initial stage of development of a stroke condition.
Depending on the location of the damage to the cerebral arteries, characteristic symptoms of a stroke appear in a man:
- In the brain stem there is a sudden loss of consciousness, paralysis on both sides, after which the person falls into a coma.
- In the subarachnoid space there are pronounced general cerebral signals.
- In the cerebellum - intense pain in the back of the head, severe nausea and vomiting. Feature: the patient cannot take a vertical position.
- In the ventricles - the disease is accompanied by fainting.
- In the parietal lobe, acquired skills are lost, tactile sensations are disrupted, and spatial disorientation occurs.
- In the temporal lobe - the patient does not recognize familiar sounds and does not understand native speech. The pathology is accompanied by hallucinations.
- In the frontal lobe, causeless aggression or, conversely, depression and convulsions appear.
Diagnostic methods
It is important to quickly distinguish a stroke from other diseases that can lead to the development of similar symptoms. It is almost impossible to do this on your own, as well as to determine the type of vascular accident.
The main difference between an ischemic stroke is a gradual increase in symptoms that do not lead to loss of consciousness. With hemorrhagic hemorrhage, the patient passes out quickly. However, stroke does not always have a classic course. The disease may begin and progress atypically.
Diagnosis begins with examination of the patient. The doctor collects anamnesis and determines the presence of chronic diseases. Most often, you can get information not from the victim himself, but from his relatives. The doctor performs an ECG, determines the heart rate, takes a blood test, and measures blood pressure.
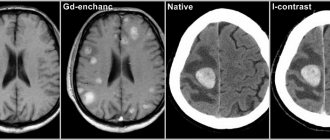
It is possible to make the correct diagnosis and obtain maximum information about the patient’s condition thanks to instrumental diagnostic methods. The best option is a CT scan of the brain. Performing an MRI is difficult because the procedure takes a long time. It takes about an hour. It is impossible to spend this amount of time diagnosing an acute stroke.
Computed tomography allows you to clarify the type of pathology, where it is concentrated, to understand how badly the brain is damaged, whether the ventricles are affected, etc. The main problem is that it is not always possible to perform a CT scan in the shortest possible time. In this case, doctors have to focus on the symptoms of the disease.
To determine the source of the stroke, the method of diffusion-weighted tomography (DWI) is used. The information will be received within a few minutes.
Other examination methods include:
- Lumbar puncture.
- Cerebral angiography.
- Magnetic resonance angiography. It is performed without the introduction of a contrast agent.
- Doppler ultrasound.
Once the diagnosis is made, the doctor will immediately begin treatment.
Who is at risk
There are people who need to be especially wary of developing a stroke, as they are at risk.
Among them:
- Persons with hypertension.
- Patients with diabetes.
- Men and women over 65 years of age.
- People with abdominal obesity.
- Persons with a hereditary predisposition to vascular pathologies.
- Patients who have previously had a stroke or heart attack.
- Patients with diagnosed atherosclerosis.
- Women over 35 years of age taking oral contraceptives.
- Smokers.
- People suffering from heart rhythm disturbances.
- People with high cholesterol levels.
Most often, patients with the listed diagnoses are registered at the dispensary. Special mention should be made of people living in a state of chronic stress. Emotional stress negatively affects all systems of the body and can cause a stroke.
Risk factors for stroke in men
Blood circulation in the brain is disrupted due to negative factors. The causes of stroke in men do not differ from the etiology of the disease in women, but the most common factors are bad habits. What can cause brain damage in the stronger sex:
- frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- long-term smoking;
- taking narcotic drugs;
- obesity due to diabetes and poor nutrition;
- physical inactivity - a sedentary lifestyle;
- doing strenuous sports;
- backbreaking physical labor;
- taking certain groups of drugs;
- constant overheating of the body (in the sun, in a hot workshop, etc.);
- pathological changes due to age;
- genetic predisposition;
- frequent stress, nervous strain;
- blockage of blood vessels due to diseases of the cardiovascular system (atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, arrhythmia, ischemia, heart failure, vasculitis, etc.);
- hormonal imbalance due to thyroid diseases, diabetes;
- migraine;
- intoxication of the body;
- infectious diseases.
Representatives of the stronger half of humanity tolerate the pathological condition more easily than women. It takes less time for the body to recover. This is due to physical fitness and the lack of a tendency to frequent psycho-emotional disorders. The consequences of a stroke in men can be severe, depending on the course of the disease and the timeliness of contacting the clinic.
How to provide first aid for a stroke
There is a clear algorithm for providing first aid to a person suffering from a stroke :
- Call a medical team . To do this, you need to dial 103 from a landline phone. If you happen to have a smartphone at hand, then the call is made to the single number 112. The doctor must immediately be informed that the person is unwell and there is a suspicion of a stroke.
- The victim must be laid on a flat surface so that his head is higher than his body. They take off his glasses and remove his lenses. If possible, you need to help him get removable dentures.
- If there is no consciousness, then you need to open the patient’s mouth slightly and turn his head to the side . This is done to prevent aspiration of vomit. It is imperative to listen to the patient’s breathing.
- For better access to fresh air, it is recommended to open a window or vent..
- Before the arrival of the medical team, it is necessary to prepare documents, if any..
Doctors need to be informed about the person’s illnesses, as well as what medications he is taking. It is prohibited to give the victim any medications. Medication correction should be carried out by emergency physicians. You should not try to give water or food to a person. This may make the situation worse.
If the patient falls and has an epileptic attack, there is no need to unclench his teeth or try to hold him. It is necessary to protect the victim from injury. To do this, place a soft object, such as a pillow, under his head. If a stroke with an epileptic attack happened on the street, then you can use a jacket or other suitable thing. Foam flowing from the mouth is wiped away with a cloth. The head should be elevated at all times.
There is no need to try to bring a person to his senses with ammonia. Until the end of the attack, it should not be moved from place to place.
If breathing stops, resuscitation measures must be started immediately. To do this, perform a heart massage and breathe mouth to mouth or mouth to nose.
What to do if you have a stroke
There are techniques that allow you to identify signs of a stroke yourself. For example, they can be used if someone becomes ill on the street and you suspect a stroke. You need to ask the person to smile, speak, raise both hands. If the victim cannot comply with your request or there is asymmetry, you should immediately call for help and list all the symptoms.
At the same time, you need to provide first aid: lay the victim down, placing a small support under his head, and free him from clothes that are preventing him from breathing. He should not eat or drink or make sudden movements. When vomiting, turn your head to the side.
Further treatment is carried out in a hospital. First, diagnostics are carried out to clarify the diagnosis; computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, lumbar puncture and EEG (echoencephalography), angiography are prescribed. Then conservative (basic therapy, treatment of neurological complications) or surgical treatment is prescribed.
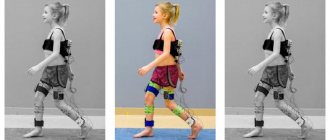
After the end of the acute period, rehabilitation is prescribed: massage, physical therapy and other activities, depending on the degree and type of disorder. The patient is observed by a neurologist, physiotherapist, speech therapist, and psychotherapist.
The brain has neuroplasticity: with the right approach, you can recover from a stroke, restore brain function and prevent stroke complications. The key factor is timely initiation of treatment, proper rehabilitation and regular exercise.
According to WHO, about 60% of patients do not require assistance by the end of the first year, and 30% of patients of working age can return to work.
Treatment and rehabilitation
The patient receives treatment in a hospital. All patients with suspected stroke are hospitalized on an emergency basis. The optimal period for providing medical care is the first 3 hours after a brain accident has occurred. The person is placed in the intensive care unit of a neurological hospital. After the acute period has been overcome, he is transferred to the early rehabilitation unit.
Until the diagnosis is established, basic therapy is carried out. The patient’s blood pressure is adjusted, the heart rate is normalized, and the required blood pH level is maintained. To reduce cerebral edema, diuretics and corticosteroids are prescribed. Craniotomy is possible to reduce the degree of compression. If necessary, the patient is connected to an artificial respiration apparatus.
Be sure to direct efforts to eliminate the symptoms of stroke and alleviate the patient’s condition. He is prescribed medications to lower body temperature, anticonvulsants, and antiemetics. Medicines that have a neuroprotective effect are used.
Pathogenetic therapy is based on the type of stroke. In case of ischemic brain damage, it is necessary to restore nutrition to the affected area as quickly as possible. To do this, the patient is prescribed drugs that resolve blood clots. It is possible to remove them mechanically. When thrombolysis fails, the patient is prescribed Acetylsalicylic acid and vasoactive drugs.
In case of a stroke, it is extremely important to provide timely treatment to the damaged areas of the brain. A course of use of the drug accelerates the process of recovery of brain cells after a stroke, even in cases of impaired blood circulation or hypoxia. This allows for rapid restoration of memory, thinking, speech, swallowing reflex and restoration of other functions of daily activities. Gliatilin has a positive effect on the transmission of nerve impulses, protects brain cells from repeated damage, which prevents the risk of recurrent stroke.
The drug is well tolerated by patients; it is contraindicated for use by pregnant, lactating women and people with hypersensitivity to choline alfoscerate.
Courses will need to be taken regularly. You definitely need to do physical therapy, undergo physical therapy, and visit a massage therapist. After a stroke, many patients have to restore motor skills over a long period of time and learn to care for themselves independently.
Relatives and friends should provide support to the patient and not leave him alone with the problem. Psychologists are involved in the work. Sessions with a speech therapist are often required.
Stroke test
There is a test called BE FAST, which is used in medicine to instantly diagnose a stroke attack. The abbreviation has its own meaning:
- B - balance. You need to watch how a person makes movements. Poor balance indicates an impending blow.
- E - eyes. Check the level of visual acuity - have the patient alternately close/open his eyes and tell what he sees in front of him.
- F - face. Ask to smile and stick out your tongue. During an attack, curvature occurs in one direction.
- A - arms. Have the victim raise both arms or shake their palms - one of the limbs will be weaker or will not rise.
- S - speech. Talk to the victim - if there is a lack of cerebral blood supply, speech is impaired.
- T - time. The patient denies the disorder.
If you discover at least one type of deviation, immediately contact the Yusupov Clinic, where experienced doctors will provide primary medical care, establish an accurate diagnosis, and prescribe therapeutic measures. For this purpose, innovative medical technologies of the European level, powerful equipment, and an individual approach are used. You can ask questions and get tested by calling the numbers provided.
Possible consequences, complications
The main danger of a stroke is death. If a person survives, the disease will still make itself felt with certain complications.
Early consequences include:
- Brain swelling.
- Coma.
- Pneumonia.
- Paralysis. It can be partial or complete. Most often, one half of the body is affected.
- Repeated stroke.
- Bedsores.
- Mental disorders. They can manifest themselves in moodiness, irritability, aggression, and anxiety. Sometimes dementia develops.
- Sleep disorders.
- Myocardial infarction, gastric ulcer. These disorders develop against the background of increased levels of stress hormones.
After an ischemic stroke, death occurs in 15-25% of cases. Hemorrhagic damage to the blood vessels of the brain leads to the death of 50-60% of patients. The cause of death is precisely severe complications, for example, pneumonia or acute heart failure. The first 3 months after a stroke are considered the most dangerous.
Arms recover worse in patients than legs. A person's future health is determined by the severity of brain damage, the speed of medical care, his age and the presence of chronic diseases.
Long-term consequences include:
- Formation of blood clots in various parts of the body.
- Depression.
- Speech problems.
- Memory loss.
- Deterioration of intellectual abilities.
After a stroke, you have to deal with the consequences for many months. Sometimes a person never manages to fully recover. For rehabilitation to be as successful as possible, you must strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions.
Stroke is a serious pathology because it affects the brain. Therefore, even the slightest suspicion of a developing vascular accident is a reason to urgently seek medical help.
Types of stroke
Stroke is classified into three types:
1. Hemorrhagic. Its cause is a rupture of a brain vessel, which causes blood to accumulate in the surrounding tissues. Neurons are deformed and their functionality is impaired. Hemorrhagic stroke occurs due to bleeding in the brain into the white matter area. The disease is provoked by sudden surges in pressure that the vascular walls are unable to withstand. The vessels rupture, and hematomas form at the site of the ruptures. The resulting tumor puts pressure on the diseased area of the brain, causing its functioning to be disrupted. 2. Ischemic. It develops due to poor blood supply to tissues, since arterial blood is difficult to reach certain parts of the brain. This is facilitated by thrombosis of the vessel. Blood circulation stops, the diseased area of the brain loses oxygen and nutrients, and cells begin to die. This type of stroke is common in old age. Vessel rupture can also occur due to a detached plaque or after a myocardial infarction. 3. Subarachnoid hemorrhage. Occurs due to a rupture of an aneurysm or injury to a vessel, resulting in an accumulation of blood mass in the brain cavity.
What types of stroke do older people suffer from? In elderly patients, all three types can occur, but they are most susceptible to the ischemic type.
A stroke can be:
1. acute (symptoms appear sharply and increase); 2. subacute (slower development - up to a week with a gradual increase in symptoms); 3. chronic (the disease develops gradually - from a week or longer, it is rare).
Diagnostic methods
It is important to quickly distinguish a stroke from other diseases that can lead to the development of similar symptoms. It is almost impossible to do this on your own, as well as to determine the type of vascular accident.
The main difference between an ischemic stroke is a gradual increase in symptoms that do not lead to loss of consciousness. With hemorrhagic hemorrhage, the patient passes out quickly. However, stroke does not always have a classic course. The disease may begin and progress atypically.
Diagnosis begins with examination of the patient. The doctor collects anamnesis and determines the presence of chronic diseases. Most often, you can get information not from the victim himself, but from his relatives. The doctor performs an ECG, determines the heart rate, takes a blood test, and measures blood pressure.
It is possible to make the correct diagnosis and obtain maximum information about the patient’s condition thanks to instrumental diagnostic methods. The best option is a CT scan of the brain. Performing an MRI is difficult because the procedure takes a long time. It takes about an hour. It is impossible to spend this amount of time diagnosing an acute stroke.
Computed tomography allows you to clarify the type of pathology, where it is concentrated, to understand how badly the brain is damaged, whether the ventricles are affected, etc. The main problem is that it is not always possible to perform a CT scan in the shortest possible time. In this case, doctors have to focus on the symptoms of the disease.
To determine the source of the stroke, the method of diffusion-weighted tomography (DWI) is used. The information will be received within a few minutes.
Other examination methods include:
- Lumbar puncture.
- Cerebral angiography.
- Magnetic resonance angiography. It is performed without the introduction of a contrast agent.
- Doppler ultrasound.
Once the diagnosis is made, the doctor will immediately begin treatment.
Who is at risk
There are people who need to be especially wary of developing a stroke, as they are at risk.
Among them:
- Persons with hypertension.
- Patients with diabetes.
- Men and women over 65 years of age.
- People with abdominal obesity.
- Persons with a hereditary predisposition to vascular pathologies.
- Patients who have previously had a stroke or heart attack.
- Patients with diagnosed atherosclerosis.
- Women over 35 years of age taking oral contraceptives.
- Smokers.
- People suffering from heart rhythm disturbances.
- People with high cholesterol levels.
Most often, patients with the listed diagnoses are registered at the dispensary. Special mention should be made of people living in a state of chronic stress. Emotional stress negatively affects all systems of the body and can cause a stroke.
Features of stroke in older people
WHO reports that 5-6 million people suffer from strokes every year. It is one of the 10 most common causes of death. In Russia, the incidence rate is 450 thousand people annually. The disease occurs in people of all ages, but the highest risk of morbidity is in people over 60 years of age (75% of morbidity cases from general statistics). The risk of getting sick doubles every ten years.
Stroke occurs more often in men. In women, more cases are observed over the age of 70-80 years. There is a genetic predisposition to strokes in children whose parents suffered from cerebrovascular accidents.
Vascular pathologies are typical for older people. Due to age-related changes in the body, blood circulation deteriorates, blood vessels become brittle, blood pressure increases, atherosclerosis develops, and heart function is disrupted.
Vascular problems are associated with age-related changes in the nervous system: a decrease in the mass and volume of the brain, degenerative changes in the white matter, deterioration in the activity and atrophy of neurons, pathology of the cerebral ventricles and other reasons. All this creates the basis for the development of a stroke.
In old age, stroke is difficult to bear. It is difficult to select an effective treatment and make a prognosis for the patient’s future condition. There is little chance of full recovery; many people remain disabled for life. There is a high risk of re-bleeding.
Stroke is a serious health problem for retirees. More than 50% of cases of morbidity lead to coma. Recovery after a stroke is difficult and lengthy; there is no guarantee of a full return of body functions.
If you notice the first signs, you should immediately call an ambulance. This is very important: most deaths are due to the fact that a person did not receive medical assistance on time. It is important to recognize an attack as early as possible, provide medical assistance and then carry out long and thorough rehabilitation. In this case, the chances of a good recovery are high.
How to provide first aid for a stroke
There is a clear algorithm for providing first aid to a person suffering from a stroke :
- Call a medical team . To do this, you need to dial 103 from a landline phone. If you happen to have a smartphone at hand, then the call is made to the single number 112. The doctor must immediately be informed that the person is unwell and there is a suspicion of a stroke.
- The victim must be laid on a flat surface so that his head is higher than his body. They take off his glasses and remove his lenses. If possible, you need to help him get removable dentures.
- If there is no consciousness, then you need to open the patient’s mouth slightly and turn his head to the side . This is done to prevent aspiration of vomit. It is imperative to listen to the patient’s breathing.
- For better access to fresh air, it is recommended to open a window or vent..
- Before the arrival of the medical team, it is necessary to prepare documents, if any..
Doctors need to be informed about the person’s illnesses, as well as what medications he is taking. It is prohibited to give the victim any medications. Medication correction should be carried out by emergency physicians. You should not try to give water or food to a person. This may make the situation worse.
If the patient falls and has an epileptic attack, there is no need to unclench his teeth or try to hold him. It is necessary to protect the victim from injury. To do this, place a soft object, such as a pillow, under his head. If a stroke with an epileptic attack happened on the street, then you can use a jacket or other suitable thing. Foam flowing from the mouth is wiped away with a cloth. The head should be elevated at all times.
There is no need to try to bring a person to his senses with ammonia. Until the end of the attack, it should not be moved from place to place.
If breathing stops, resuscitation measures must be started immediately. To do this, perform a heart massage and breathe mouth to mouth or mouth to nose.
Treatment and rehabilitation
The patient receives treatment in a hospital. All patients with suspected stroke are hospitalized on an emergency basis. The optimal period for providing medical care is the first 3 hours after a brain accident has occurred. The person is placed in the intensive care unit of a neurological hospital. After the acute period has been overcome, he is transferred to the early rehabilitation unit.
Until the diagnosis is established, basic therapy is carried out. The patient’s blood pressure is adjusted, the heart rate is normalized, and the required blood pH level is maintained. To reduce cerebral edema, diuretics and corticosteroids are prescribed. Craniotomy is possible to reduce the degree of compression. If necessary, the patient is connected to an artificial respiration apparatus.
Be sure to direct efforts to eliminate the symptoms of stroke and alleviate the patient’s condition. He is prescribed medications to lower body temperature, anticonvulsants, and antiemetics. Medicines that have a neuroprotective effect are used.
Pathogenetic therapy is based on the type of stroke. In case of ischemic brain damage, it is necessary to restore nutrition to the affected area as quickly as possible. To do this, the patient is prescribed drugs that resolve blood clots. It is possible to remove them mechanically. When thrombolysis fails, the patient is prescribed Acetylsalicylic acid and vasoactive drugs.
If a patient develops a hemorrhagic stroke, it is important to stop the bleeding. To do this, the patient is prescribed drugs that thicken the blood, for example, Vikasol. It is possible to perform an operation to remove the resulting hematoma. It is aspirated using special equipment, or through open access by performing craniotomy.
Relatives and friends should provide support to the patient and not leave him alone with the problem. Psychologists are involved in the work. Sessions with a speech therapist are often required.