Pneumonia is an acute infectious disease in which the inflammatory process is localized in the lung tissue. Inflammation is caused by various microorganisms - bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa. At the Yusupov Hospital, pulmonologists prescribe comprehensive treatment for pneumonia. Individual treatment regimens include antibacterial drugs, agents that thin sputum and improve bronchial drainage function, and immunomodulators.
Patients with mild pneumonia are treated on an outpatient basis. In moderate and severe cases of the disease, patients with pneumonia are hospitalized in a therapy clinic. Particularly severe patients are treated in the intensive care unit.
The mechanism of action of cans and mustard plasters
Medical banks
Cupping treatment involves a vacuum effect on the skin in the respiratory area, which increases blood flow and tissue exchange in these areas. For the procedure, you cannot use ordinary jars; you must purchase special vessels with a semicircular bottom and thickenings at the edges at the pharmacy. The standard volume of medical jars ranges from 30 to 79 ml.
When installing the can, part of the skin seems to be drawn into it under the influence of negative pressure. After the container is torn away from the skin, small hematomas may form on the body, as the pressure breaks the smallest vessels of the subcutaneous tissue. Further, restoration processes are activated in this area, the restoration of nearby tissues and organs is stimulated. Therefore, when placing cups on the skin in the area of the respiratory system, the recovery process from bronchitis, pneumonia and other diseases is accelerated.
As a result of treatment, pain is reduced, inflammatory processes cease, tissue regeneration and recovery are accelerated.
Mustard plasters
Mustard plaster is a bag of porous material filled with mustard powder, which is previously degreased. The mechanism of its action is based on the irritating effect of mustard seed essential oil. At the site where the mustard plaster is installed, the skin warms up and turns red, the superficial vessels dilate, and blood circulation in the subcutaneous tissue increases.
Another effect that is observed as a result of applying mustard plasters is irritation of the nerve endings of the skin and activation of the central nervous system, which leads to the release of adrenaline and the launch of the immune response of phagocytic cells.
As a result of double exposure, not only does trophism and tissue respiration increase, but also the immune system is stimulated. Warming the surrounding tissues helps to increase metabolism and speedy removal of sputum from the bronchi.
Complex of physical therapy exercises
Therapeutic exercises for bronchitis are prescribed by a doctor. There is a special breathing technique that speeds up the removal of mucus and cleansing of the bronchi. The main types of exercise therapy include:
- Yoga, developed by ancient Indian monks.
- Bodyflex is a five-stage breathing process that is combined with physical exercise.
- Strelnikova's technique. It is indicated for bronchitis, as it is a breathing exercise that promotes a speedy recovery.
Massage for bronchitis is not complicated, but children will simply need it, more details in the video:
Contraindications to their use
General contraindications to the use of mustard plasters and cupping apply to people with diseases:
- Spine;
- Oncological formations;
- Cramps;
- Blood clotting disorders;
- Pulmonary tuberculosis.
In addition, these drugs cannot be used during pregnancy and lactation, at elevated body temperature, or when the patient is mentally excited. For purulent rashes and other skin diseases, it is not recommended to install mustard plasters and cups, so as not to provoke inflammatory processes and not aggravate the patient’s condition.
There are also contraindications for each of the methods separately.
Thus, mustard plasters cannot be installed on newborns until the first year of life; until three years of age, they are used only through a pad in the form of cotton material, a bandage or a napkin.
Mustard plasters are contraindicated for:
- Psoriasis;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Allergic reactions.
Medical cups are contraindicated for illnesses
- Blood;
- Hypertension;
- Heart failure and vascular diseases;
- Tendency to thrombosis.
General exhaustion of the body, nervousness and insomnia are also contraindications. Medical cups are used starting from the age of three; they should not be used on small children.
Why does the disease occur in children and adults?
All cases of this disease are usually divided into acute and chronic. The main cause of acute tracheitis is a variety of infections - bacterial, viral, fungal, etc. In addition, acute tracheitis can also develop under the influence of some strong factors in the inhaled air, for example, concentrated acid fumes or excessively hot water vapor.
Chronic tracheitis in children and adults often results from an untreated acute form of the disease. In addition, unexpressed and long-lasting inflammation of the tracheal mucosa can occur under the influence of a number of provoking factors:
- smoking tobacco products (the most common cause);
- frequent hypothermia of the upper respiratory tract;
- constant inhalation of dust, chemically aggressive particles, etc., for example, when living in unfavorable environmental conditions with a polluted atmosphere;
- working in hazardous industries without using respiratory protection;
- congestive disorders caused by pathologies such as emphysema or diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- hypersensitivity to certain substances that cause allergic reactions in humans.
When to expect the effect?
As the only means of treating bronchitis and pneumonia, the effectiveness of mustard plasters and cupping will be low. Moreover, in the acute stage of diseases, improvement can often only be achieved using antibacterial therapy.
When treating diseases of the respiratory system in children under 12 years of age, in addition to drug therapy and auxiliary techniques - cupping and mustard plasters - massage and breathing exercises should be used. Vacuum cupping massage in combination with Strelnikova’s breathing exercises shows good results in the treatment of bronchitis.
Tangible results from the use of mustard plasters and cupping appear after the second or third procedure; if there is no improvement, this technique should be abandoned.
Antibacterial therapy
The basis of treatment for pneumonia is antibacterial therapy. At the Yusupov Hospital, pulmonologists use the latest drugs registered in the Russian Federation. When a sick patient enters a therapy clinic, the choice of antibiotic is made empirically. Doctors take into account the epidemiological and clinical situation, and lung radiography data.
Since the disease is most often caused by pneumococci, initial therapy begins with penicillins and aminopenicillins. Second-line drugs are cephalosporins. If you are allergic to β-lactam antibiotics, all these medications are not used. Alternative agents are macrolides.
In cases of severe pneumonia, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital choose broad-spectrum antibacterial agents for initial treatment. They use combinations of antibiotics to suppress the maximum number of possible infectious agents. The drugs are administered intravenously and intramuscularly.
In the therapy clinic, doctors widely use a new generation of fluoroquinolones to treat pneumonia:
- levofloxacin;
- moxifloxacin;
- sparfloxacin.
They are highly effective, suppressing gram-positive and gram-negative microflora, as well as intracellular microorganisms (mycoplasma, chlamydia, legionella).
In nosocomial pneumonia, the most common pathogens are gram-negative bacilli and staphylococci. In these cases, combinations of metronidazole with third-generation cephalosporins or ciprofloxacin are used to treat pneumonia. Patients after traumatic brain injuries are treated with monotherapy with IV generation cephalosporins or ciprofloxacin; if necessary, a combination of a III generation cephalosporin with ciprofloxacin or aminoglycosides is used.
How to install mustard plasters correctly?
Mustard plasters can be installed only after the patient’s condition has stabilized, when all that remains of all the symptoms of bronchitis and bronchopneumonia is a lingering cough. Mustard plasters improve the condition of adults and children with dry cough and congestion in the lungs. As the skin warms up, blood flows out from the affected areas into the vessels of the subcutaneous tissue. In addition, after the procedure, the immune system is activated and expectoration is facilitated, which reduces intoxication of the body with excess sputum.
Mustard plasters can be done within a day after the temperature for bronchitis subsides. In case of pneumonia, you need to wait two days from the moment the temperature stabilizes.
How to put mustard plasters on your back?
Mustard plasters can be installed under and between the shoulder blades, in the upper area of the sternum, as well as on the calves and feet in the heel area. Mustard plasters should not be installed too close to each other, located in the area of the projection of the kidneys and heart, or on the mammary glands in women.
- A bag of mustard powder is dipped in warm water (40-45 °C) and placed on the selected area depending on the site of inflammation, kept for five to fifteen minutes and removed, after which the skin is wiped with a damp cloth and the patient is left to rest in bed for several hours .
- The procedure for installing mustard plasters should not be painful for the patient; a slight burning sensation is acceptable, but not necessary. If the burning becomes unbearable, you should immediately remove the mustard plaster and wipe the skin with a damp cloth.
- Redness of the skin after installation of mustard plaster may persist for several days, but a bright red or purple color indicates individual intolerance or an allergic reaction in the patient.
- It is forbidden to wipe the skin with alcohol or alcohol-containing products after installing mustard plasters.
Adverse consequences
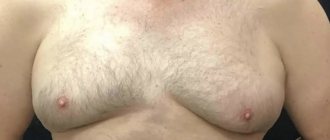
Adverse consequences of using mustard plasters can be skin irritation up to severe burns, skin hyperpigmentation, and the development of allergies, both local (severe hyperemia, urticaria) and systemic (Quincke's edema).
You can see in the photo what an allergic reaction to mustard might look like.
One of the options for an allergic reaction to mustard plasters
If the patient experiences a strong burning sensation and/or pain, further procedures should be abandoned, the mustard plasters should be removed, the mustard should be removed, the skin should be washed with warm water and lubricated with baby cream.
Cupping for the treatment of bronchitis
Before using medical cups as part of complex therapy for bronchitis and pneumonia, you should consult a doctor. The danger of this method lies in the likelihood of rupture of lung tissue located close to the skin tissue, which aggravates the patient’s condition.
Cups can be used only after the patient has passed the acute stage of bronchitis and pneumonia - with their help you can speed up the recovery process. Contraindications for use are symptoms such as fever, signs of intoxication, fever, respiratory failure. Cupping can be placed no earlier than two days after the cessation of these symptoms, when the patient’s condition has stabilized.
How to put cans on your back?
The procedure for installing medical cups:
- The patient is placed on his stomach. Wipe your back with alcohol for disinfection and Vaseline or nourishing cream so that when the can is torn off, the skin is not injured.
- To carry out the procedure, you must have a set of clean and dry medical jars, alcohol, cotton wool, matches, tweezers, and Vaseline.
- Places for installing cups are selected depending on the location of the area of the inflamed organ; the areas under the shoulder blades, collarbones, lower back, and the area between the shoulder blade and spine are suitable for this. In any case, the site where the jar is placed should not have bony protrusions; choose an area with good muscle and fat layer, avoid the heart area to avoid complications.
- The cotton wool is held with tweezers, moistened with alcohol and set on fire. Burning cotton wool is introduced into the jar for a few seconds without touching the walls of the container, after which the jar is placed on the selected area of the skin.
- During the first procedure, the jar is held on the skin for 1-2 minutes; for repeated procedures, which are carried out with a break of at least a day, the duration can be gradually increased to 15 minutes.
- To remove the jar, you need to tilt it slightly to the side and press your finger on the skin from the opposite edge so that a little air enters the container. Then the can comes off the skin more easily without injuring it.
If the procedure is carried out correctly, the patient does not experience severe discomfort or pain; warmth and slight tension may be felt at the site where the jar is placed. The skin color in these areas becomes reddish or purple, but after a few days the hematomas resolve.
Diagnosis when symptoms of tracheitis appear in children and adults
Typically, identifying this disease does not cause any particular problems. SM-Clinic specialists establish a preliminary diagnosis after an initial examination and interview with the patient. In addition, to clarify the form and extent of the disease, the doctor may prescribe additional examinations:
- Laryngo- and tracheobronchoscopy - direct visualization of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract using an endoscope;
- X-ray of the chest organs;
- culture of sputum for bacteriological examination and identification of the infectious agent that caused the inflammation;
- general and biochemical urine and blood tests;
- tests with allergenic substances if the allergic nature of the disease is suspected.
When should you stop using cans and mustard plasters?
These techniques cannot be used if any of the above contraindications are present, as well as if the patient’s subjective sensations worsen – if an unbearable burning sensation, pain, or psychological discomfort occurs.
Author of the article:
Mochalov Pavel Alexandrovich |
Doctor of Medical Sciences therapist Education: Moscow Medical Institute named after. I. M. Sechenov, specialty - “General Medicine” in 1991, in 1993 “Occupational diseases”, in 1996 “Therapy”. Our authors
Prevention of tracheitis
In order to reduce the likelihood of this pathology occurring, you need to:
- completely stop smoking;
- limit alcohol consumption;
- exclude too cold or too hot foods from the diet;
- reduce the consumption of spicy foods and carbonated drinks; maintain a room temperature of 22–230C and air humidity of about 50%;
- periodically ventilate the rooms and carry out wet cleaning in them;
- promptly contact specialists for the treatment of upper respiratory tract diseases.
List of scientific literature used:
- Blot M., Bonniaud-Blot P., Favrolt N., Chavanet P., Piroth L. Update on childhood and adult infectious tracheitis. Médecine et Maladies Infectieuses. 2021 Nov; 47(7):443-452.
- Casazza G., Graham M.E., Nelson D., Chaulk D., Sandweiss D., Meier J. Pediatric Bacterial Tracheitis—A Variable Entity: Case Series with Literature Review. Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. Mar 2021; 160(3):546-549.
- Lauren V. Burton, Michael Silberman. Bacterial Tracheitis. StatPearls Publishing. 2021, Jan.
- Russell CJ, Shiroishi MS, Siantz E., Wu BW, Patino CM The use of inhaled antibiotic therapy in the treatment of ventilator-associated pneumonia and tracheobronchitis: a systematic review. BMC Pulmonary Medicine. 2021, Mar. 08;16:40.
- Orlova N.V., Suranova T.G. Acute respiratory diseases: clinical features, drug therapy. Medical Council, 2018, No. 15, p. 82-88.
- Pechkareva A.V. All about ENT diseases. To help a specialist. Publisher: Phoenix. Series: Medicine, 2013, 219 pp.
- Sakhatarova O.V., Levchenko N.P. Diagnostics in otorhinolaryngology and ophthalmology. MDK.01.01 Propaedeutics of clinical disciplines. Publisher: Phoenix, 2015, 206 pp.